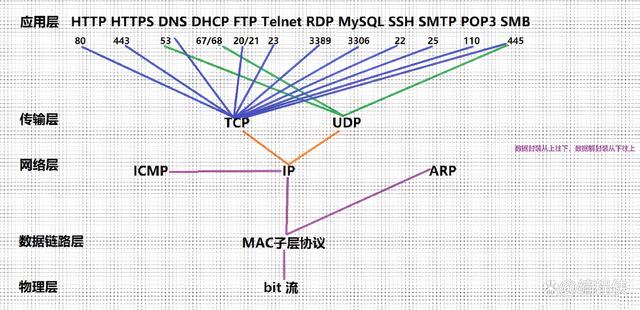
dbCAN(碳水化合物酶基因数据库)是一个专门用于在基因组中预测碳水化合物酶基因的在线工具。它基于隐马尔可夫模型(HMM)和BLAST搜索,能够在蛋白质序列中识别和注释不同类型的碳水化合物酶基因,包括纤维素酶、木质素酶、半纤维素酶、淀粉酶、果糖酶等等。 dbCAN是一个非常有用的生物信息学工具,对于研究纤维素生物转化、生物能源、生产生物基化学品等领域的研究具有重要意义。
Run_dbCAN是一个用于预测生物信息学中的碳水化合物活性酶的工具。它用于分析基因组或转录组数据,以识别编码碳水化合物活性酶的基因。
相关文章:
dbCAN2: a meta server for automated carbohydrate-active enzyme annotation | Nucleic Acids Research | Oxford Academic
dbCAN3: automated carbohydrate-active enzyme and substrate annotation | Nucleic Acids Research | Oxford Academic
dbCAN-seq: a database of carbohydrate-active enzyme (CAZyme) sequence and annotation | Nucleic Acids Research | Oxford Academic
github最新版代码源
GitHub - linnabrown/run_dbcan: Run_dbcan V4, using genomes/metagenomes/proteomes of any assembled organisms (prokaryotes, fungi, plants, animals, viruses) to search for CAZymes.
其他相关链接(有些链接暂时打不开,大家可以等一段时间后再试,或者站内找本人发布的相关资源下载):
CAZy - Home
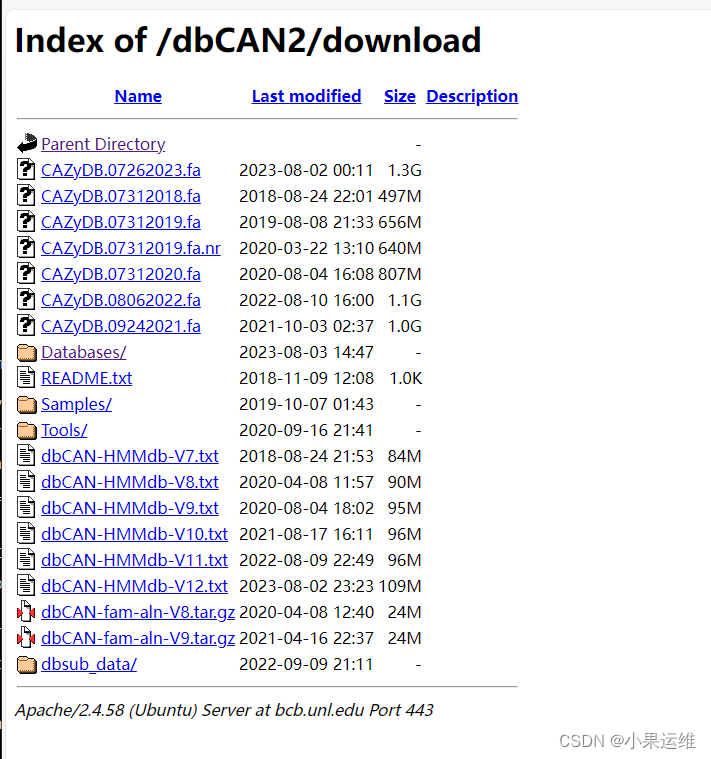
Index of /dbCAN2/download (unl.edu)
https://github.com/linnabrown/run_dbcan/issues
dbCAN-sub
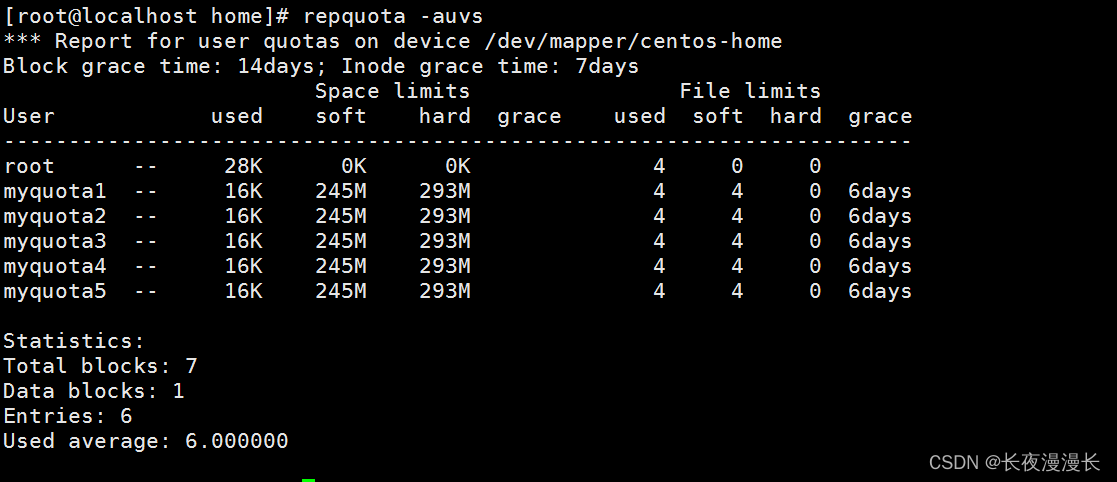
1、安装dbcan
conda环境安装
conda create -n run_dbcan python=3.8 dbcan -c conda-forge -c bioconda
conda activate run_dbcandocker 拉取
docker pull haidyi/run_dbcan:latest
docker run --name <preferred_name> -v <host-path>:<container-path> -it haidyi/run_dbcan:latest run_dbcan <input_file> [params] --out_dir <output_dir>2、数据库配置
可以在指定位置建立db或dbcan的目录,然后下载相关文件包并用对应的软件处理,这里面有些文件不是最新的,大家可以修改后下载最新版然后再执行,下面的脚本是官方的,首先看是否有db文件夹,如果没有就创建db,然后进入db文件夹开始下载和处理数据库文件,这个可以分开来做,大家应该都理解。
test -d db || mkdir db
cd db \
&& wget http://bcb.unl.edu/dbCAN2/download/Databases/fam-substrate-mapping-08252022.tsv \
&& wget http://bcb.unl.edu/dbCAN2/download/Databases/PUL.faa && makeblastdb -in PUL.faa -dbtype prot \
&& wget http://bcb.unl.edu/dbCAN2/download/Databases/dbCAN-PUL_07-01-2022.xlsx \
&& wget http://bcb.unl.edu/dbCAN2/download/Databases/dbCAN-PUL_07-01-2022.txt \
&& wget http://bcb.unl.edu/dbCAN2/download/Databases/dbCAN-PUL.tar.gz && tar xvf dbCAN-PUL.tar.gz \
&& wget http://bcb.unl.edu/dbCAN2/download/Databases/dbCAN_sub.hmm && hmmpress dbCAN_sub.hmm \
&& wget http://bcb.unl.edu/dbCAN2/download/Databases/V11/CAZyDB.08062022.fa && diamond makedb --in CAZyDB.08062022.fa -d CAZy \
&& wget https://bcb.unl.edu/dbCAN2/download/Databases/V11/dbCAN-HMMdb-V11.txt && mv dbCAN-HMMdb-V11.txt dbCAN.txt && hmmpress dbCAN.txt \
&& wget https://bcb.unl.edu/dbCAN2/download/Databases/V11/tcdb.fa && diamond makedb --in tcdb.fa -d tcdb \
&& wget http://bcb.unl.edu/dbCAN2/download/Databases/V11/tf-1.hmm && hmmpress tf-1.hmm \
&& wget http://bcb.unl.edu/dbCAN2/download/Databases/V11/tf-2.hmm && hmmpress tf-2.hmm \
&& wget https://bcb.unl.edu/dbCAN2/download/Databases/V11/stp.hmm && hmmpress stp.hmm \
&& cd ../ && wget http://bcb.unl.edu/dbCAN2/download/Samples/EscheriaColiK12MG1655.fna \
&& wget http://bcb.unl.edu/dbCAN2/download/Samples/EscheriaColiK12MG1655.faa \
&& wget http://bcb.unl.edu/dbCAN2/download/Samples/EscheriaColiK12MG1655.gff
手动下载位置:Index of /dbCAN2/download (unl.edu)
SignalP数据库下载和配置
文章:Predicting Secretory Proteins with SignalP | SpringerLink
SignalP 4.1 - DTU Health Tech - Bioinformatic Services
需要填写邮箱信息同意后才会发送限时链接(4小时内有效)到对应邮箱
当然大家可以直接在网上丢个fasta文件,选择参数后提交在线的注释任务。
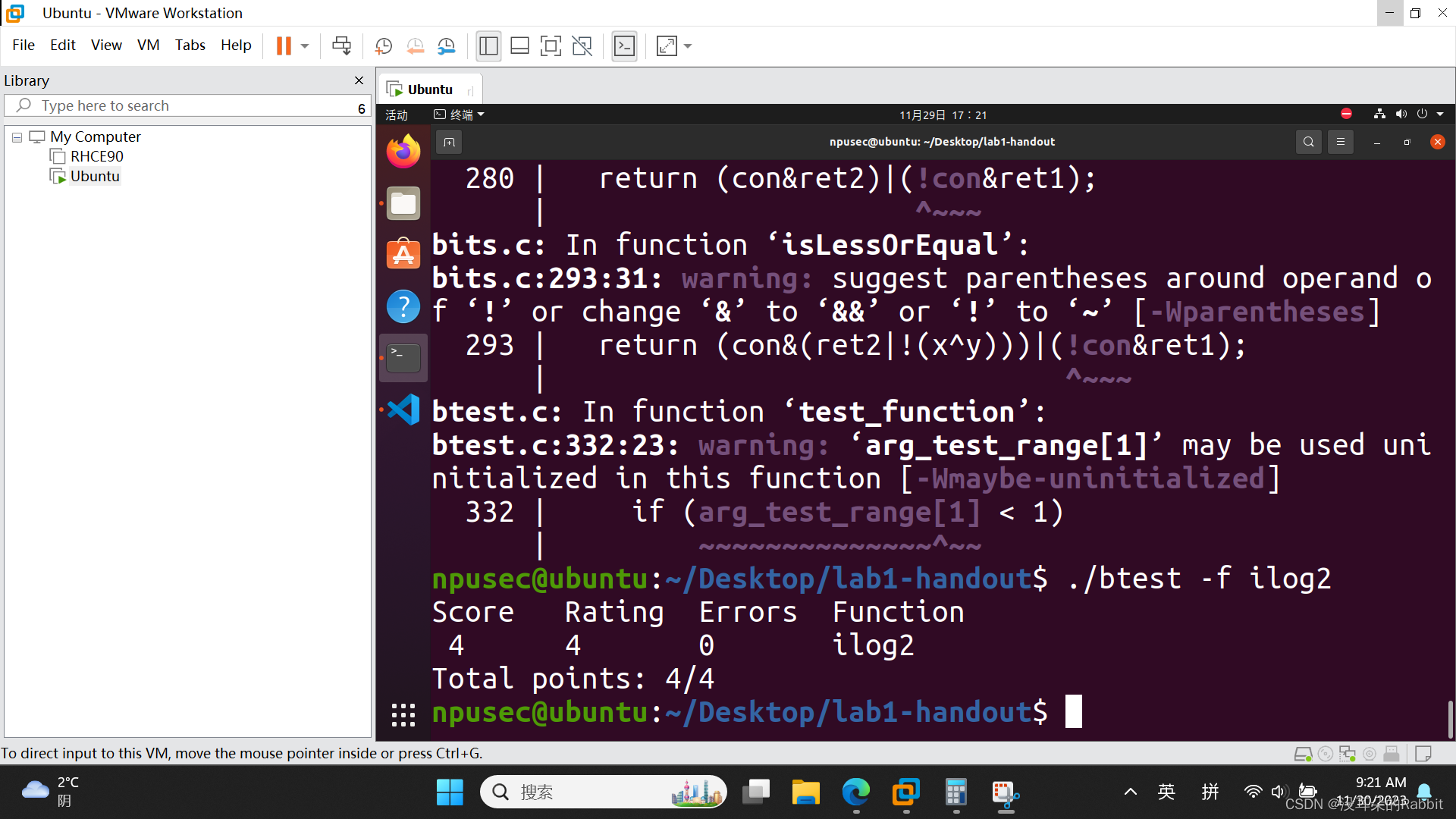
3、使用run_dbcan
帮助信息:
Required arguments:
inputFile User input file. Must be in FASTA format.
{protein,prok,meta} Type of sequence input. protein=proteome; prok=prokaryote; meta=metagenome
optional arguments:
-h, --help show this help message and exit
--dbCANFile DBCANFILE
Indicate the file name of HMM database such as dbCAN.txt, please use the newest one from dbCAN2 website.
--dia_eval DIA_EVAL DIAMOND E Value
--dia_cpu DIA_CPU Number of CPU cores that DIAMOND is allowed to use
--hmm_eval HMM_EVAL HMMER E Value
--hmm_cov HMM_COV HMMER Coverage val
--hmm_cpu HMM_CPU Number of CPU cores that HMMER is allowed to use
--out_pre OUT_PRE Output files prefix
--out_dir OUT_DIR Output directory
--db_dir DB_DIR Database directory
--tools {hmmer,diamond,dbcansub,all} [{hmmer,diamond,dbcansub,all} ...], -t {hmmer,diamond,dbcansub,all} [{hmmer,diamond,dbcansub,all} ...]
Choose a combination of tools to run
--use_signalP USE_SIGNALP
Use signalP or not, remember, you need to setup signalP tool first. Because of signalP license, Docker version does not have signalP.
--signalP_path SIGNALP_PATH, -sp SIGNALP_PATH
The path for signalp. Default location is signalp
--gram {p,n,all}, -g {p,n,all}
Choose gram+(p) or gram-(n) for proteome/prokaryote nucleotide, which are params of SingalP, only if user use singalP
-v VERSION, --version VERSION
dbCAN-sub parameters:
--dbcan_thread DBCAN_THREAD, -dt DBCAN_THREAD
--tf_eval TF_EVAL tf.hmm HMMER E Value
--tf_cov TF_COV tf.hmm HMMER Coverage val
--tf_cpu TF_CPU tf.hmm Number of CPU cores that HMMER is allowed to use
--stp_eval STP_EVAL stp.hmm HMMER E Value
--stp_cov STP_COV stp.hmm HMMER Coverage val
--stp_cpu STP_CPU stp.hmm Number of CPU cores that HMMER is allowed to use
CGC_Finder parameters:
--cluster CLUSTER, -c CLUSTER
Predict CGCs via CGCFinder. This argument requires an auxillary locations file if a protein input is being used
--cgc_dis CGC_DIS CGCFinder Distance value
--cgc_sig_genes {tf,tp,stp,tp+tf,tp+stp,tf+stp,all}
CGCFinder Signature Genes value
CGC_Substrate parameters:
--cgc_substrate run cgc substrate prediction?
--pul PUL dbCAN-PUL PUL.faa
-o OUT, --out OUT
-w WORKDIR, --workdir WORKDIR
-env ENV, --env ENV
-oecami, --oecami out eCAMI prediction intermediate result?
-odbcanpul, --odbcanpul
output dbCAN-PUL prediction intermediate result?
dbCAN-PUL homologous searching parameters:
how to define homologous gene hits and PUL hits
-upghn UNIQ_PUL_GENE_HIT_NUM, --uniq_pul_gene_hit_num UNIQ_PUL_GENE_HIT_NUM
-uqcgn UNIQ_QUERY_CGC_GENE_NUM, --uniq_query_cgc_gene_num UNIQ_QUERY_CGC_GENE_NUM
-cpn CAZYME_PAIR_NUM, --CAZyme_pair_num CAZYME_PAIR_NUM
-tpn TOTAL_PAIR_NUM, --total_pair_num TOTAL_PAIR_NUM
-ept EXTRA_PAIR_TYPE, --extra_pair_type EXTRA_PAIR_TYPE
None[TC-TC,STP-STP]. Some like sigunature hits
-eptn EXTRA_PAIR_TYPE_NUM, --extra_pair_type_num EXTRA_PAIR_TYPE_NUM
specify signature pair cutoff.1,2
-iden IDENTITY_CUTOFF, --identity_cutoff IDENTITY_CUTOFF
identity to identify a homologous hit
-cov COVERAGE_CUTOFF, --coverage_cutoff COVERAGE_CUTOFF
query coverage cutoff to identify a homologous hit
-bsc BITSCORE_CUTOFF, --bitscore_cutoff BITSCORE_CUTOFF
bitscore cutoff to identify a homologous hit
-evalue EVALUE_CUTOFF, --evalue_cutoff EVALUE_CUTOFF
evalue cutoff to identify a homologous hit
dbCAN-sub major voting parameters:
how to define dbsub hits and dbCAN-sub subfamily substrate
-hmmcov HMMCOV, --hmmcov HMMCOV
-hmmevalue HMMEVALUE, --hmmevalue HMMEVALUE
-ndsc NUM_OF_DOMAINS_SUBSTRATE_CUTOFF, --num_of_domains_substrate_cutoff NUM_OF_DOMAINS_SUBSTRATE_CUTOFF
define how many domains share substrates in a CGC, one protein may include several subfamily domains.
-npsc NUM_OF_PROTEIN_SUBSTRATE_CUTOFF, --num_of_protein_substrate_cutoff NUM_OF_PROTEIN_SUBSTRATE_CUTOFF
define how many sequences share substrates in a CGC, one protein may include several subfamily domains.
-subs SUBSTRATE_SCORS, --substrate_scors SUBSTRATE_SCORS
each cgc contains with substrate must more than this value命令及结果参考
#参考格式
run_dbcan [inputFile] [inputType] [-c AuxillaryFile] [-t Tools]
#结果说明
uniInput - The unified input file for the rest of the tools
(created by prodigal if a nucleotide sequence was used)
dbsub.out - the output from the dbCAN_sub run
diamond.out - the output from the diamond blast
hmmer.out - the output from the hmmer run
tf.out - the output from the diamond blast predicting TF's for CGCFinder
tc.out - the output from the diamond blast predicting TC's for CGCFinder
cgc.gff - GFF input file for CGCFinder
cgc.out - ouput from the CGCFinder run
overview.txt - Details the CAZyme predictions across the three tools with signalp results
###说的都很清楚了,就不重复了,英文可以chatgpt或者百度吧示例:
run_dbcan EscheriaColiK12MG1655.fna prok --out_dir output_EscheriaColiK12MG1655
run_dbcan EscheriaColiK12MG1655.faa protein --out_dir output_EscheriaColiK12MG1655
run_dbcan EscheriaColiK12MG1655.fna prok -c cluster --out_dir output_EscheriaColiK12MG1655
run_dbcan EscheriaColiK12MG1655.faa protein -c EscheriaColiK12MG1655.gff --out_dir output_EscheriaColiK12MG1655手动注释CAZyDB
1、下载指定文件的数据库文件,注意下载最新版本:
###中间07312020表示2020年7月31日的版本,大家可以浏览download目录查看确认最新版
wget -c http://bcb.unl.edu/dbCAN2/download/CAZyDB.07312020.fa
wget -c http://bcb.unl.edu/dbCAN2/download/Databases/CAZyDB.07302020.fam-activities.txt
2、使用diamond工具进行快速比对
#基于fasta文件生成diamond比对参考数据库
diamond makedb --in CAZyDB.07312020.fa --db CAZyDB.07312020
# 提取fam对应注释
grep -v '#' CAZyDB.07302020.fam-activities.txt |sed 's/ //'| sed '1 i CAZy\tDescription' > CAZy_description.txt
###位置 /database/CAZyDB
diamond blastp --db /database/CAZyDB/CAZyDB.07312020 --query out_pro.fa --threads 10 -e 1e-5 --outfmt 6 --max-target-seqs 1 --quiet --out ./gene_diamond.f6
# 提取基因与dbcan分类对应表
perl ./format_dbcan2list.pl -i gene_diamond.f6 -o gene.list
#按对应表累计丰度
python ./summarizeAbundance.py -i gene.count -m gene.list -c 2 -s ',' -n raw -o ./TPM这里面format_dbcan2list.pl和summarizeAbundance.py的来源是来自刘永鑫文章和github代码仓库,后面有时间再给大家做详细介绍,或者大家看相关文章自己研究:
https://doi.org/10.1002/imt2.83
YongxinLiu/EasyMicrobiome (github.com)