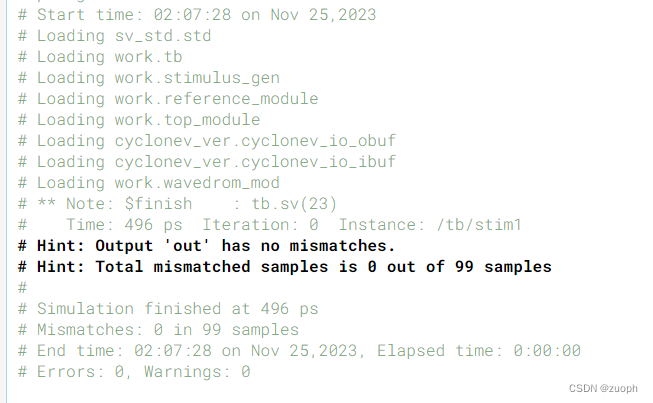
基于WIN10的64位系统演示
一、写在前面
本期,我们继续学习深度学习图像目标检测系列,SSD(Single Shot MultiBox Detector)模型的后续版本,SSDlite模型。
二、SSDlite简介
SSDLite 是 SSD 模型的一个变种,旨在为移动设备和边缘计算设备提供更高效的目标检测。SSDLite 的主要特点是使用了轻量级的骨干网络和特定的卷积操作来减少计算复杂性,从而提高检测速度,同时在大多数情况下仍保持了较高的准确性。
以下是 SSDLite 的主要特性和组件:
(1)轻量级骨干:
SSDLite 不使用 VGG 或 ResNet 这样的重量级骨干。相反,它使用 MobileNet 作为骨干,特别是 MobileNetV2 或 MobileNetV3。这些网络使用深度可分离的卷积和其他轻量级操作来减少计算成本。
(2)深度可分离的卷积:
这是 MobileNet 的核心组件,也被用于 SSDLite。深度可分离的卷积将传统的卷积操作分解为两个较小的操作:一个深度卷积和一个点卷积,这大大减少了计算和参数数量。
(3)多尺度特征映射:
与原始的 SSD 相似,SSDLite 也从不同的层级提取特征图以检测不同大小的物体。
(4)默认框:
SSDLite 也使用默认框(或称为锚框)来进行边界框预测。
(5)单阶段检测:
与 SSD 相同,SSDLite 也是一个单阶段检测器,同时进行边界框回归和分类。
(6)损失函数:
SSDLite 使用与 SSD 相同的组合损失,包括平滑 L1 损失和交叉熵损失。
综上,SSDLite 是为了速度和效率而设计的,特别是针对计算和内存资源有限的设备。通过使用轻量级的骨干和深度可分离的卷积,它能够在减少计算负担的同时,仍然保持合理的检测准确性。
三、数据源
来源于公共数据,文件设置如下:

大概的任务就是:用一个框框标记出MTB的位置。
四、SSDlite实战
直接上代码:
import os
import random
import torch
import torchvision
from torchvision.models.detection import ssdlite320_mobilenet_v3_large
from torchvision.transforms import functional as F
from PIL import Image
from torch.utils.data import DataLoader
import xml.etree.ElementTree as ET
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from torchvision import transforms
import albumentations as A
from albumentations.pytorch import ToTensorV2
import numpy as np
# Function to parse XML annotations
def parse_xml(xml_path):
tree = ET.parse(xml_path)
root = tree.getroot()
boxes = []
for obj in root.findall("object"):
bndbox = obj.find("bndbox")
xmin = int(bndbox.find("xmin").text)
ymin = int(bndbox.find("ymin").text)
xmax = int(bndbox.find("xmax").text)
ymax = int(bndbox.find("ymax").text)
# Check if the bounding box is valid
if xmin < xmax and ymin < ymax:
boxes.append((xmin, ymin, xmax, ymax))
else:
print(f"Warning: Ignored invalid box in {xml_path} - ({xmin}, {ymin}, {xmax}, {ymax})")
return boxes
# Function to split data into training and validation sets
def split_data(image_dir, split_ratio=0.8):
all_images = [f for f in os.listdir(image_dir) if f.endswith(".jpg")]
random.shuffle(all_images)
split_idx = int(len(all_images) * split_ratio)
train_images = all_images[:split_idx]
val_images = all_images[split_idx:]
return train_images, val_images
# Dataset class for the Tuberculosis dataset
class TuberculosisDataset(torch.utils.data.Dataset):
def __init__(self, image_dir, annotation_dir, image_list, transform=None):
self.image_dir = image_dir
self.annotation_dir = annotation_dir
self.image_list = image_list
self.transform = transform
def __len__(self):
return len(self.image_list)
def __getitem__(self, idx):
image_path = os.path.join(self.image_dir, self.image_list[idx])
image = Image.open(image_path).convert("RGB")
xml_path = os.path.join(self.annotation_dir, self.image_list[idx].replace(".jpg", ".xml"))
boxes = parse_xml(xml_path)
# Check for empty bounding boxes and return None
if len(boxes) == 0:
return None
boxes = torch.as_tensor(boxes, dtype=torch.float32)
labels = torch.ones((len(boxes),), dtype=torch.int64)
iscrowd = torch.zeros((len(boxes),), dtype=torch.int64)
target = {}
target["boxes"] = boxes
target["labels"] = labels
target["image_id"] = torch.tensor([idx])
target["iscrowd"] = iscrowd
# Apply transformations
if self.transform:
image = self.transform(image)
return image, target
# Define the transformations using torchvision
data_transform = torchvision.transforms.Compose([
torchvision.transforms.ToTensor(), # Convert PIL image to tensor
torchvision.transforms.Normalize(mean=[0.485, 0.456, 0.406], std=[0.229, 0.224, 0.225]) # Normalize the images
])
# Adjusting the DataLoader collate function to handle None values
def collate_fn(batch):
batch = list(filter(lambda x: x is not None, batch))
return tuple(zip(*batch))
def get_ssdlite_model_for_finetuning(num_classes):
# Load an SSDlite model with a MobileNetV3 Large backbone without pre-trained weights
model = ssdlite320_mobilenet_v3_large(pretrained=False, num_classes=num_classes)
return model
# Function to save the model
def save_model(model, path="SSDlite_mtb.pth", save_full_model=False):
if save_full_model:
torch.save(model, path)
else:
torch.save(model.state_dict(), path)
print(f"Model saved to {path}")
# Function to compute Intersection over Union
def compute_iou(boxA, boxB):
xA = max(boxA[0], boxB[0])
yA = max(boxA[1], boxB[1])
xB = min(boxA[2], boxB[2])
yB = min(boxA[3], boxB[3])
interArea = max(0, xB - xA + 1) * max(0, yB - yA + 1)
boxAArea = (boxA[2] - boxA[0] + 1) * (boxA[3] - boxA[1] + 1)
boxBArea = (boxB[2] - boxB[0] + 1) * (boxB[3] - boxB[1] + 1)
iou = interArea / float(boxAArea + boxBArea - interArea)
return iou
# Adjusting the DataLoader collate function to handle None values and entirely empty batches
def collate_fn(batch):
batch = list(filter(lambda x: x is not None, batch))
if len(batch) == 0:
# Return placeholder batch if entirely empty
return [torch.zeros(1, 3, 224, 224)], [{}]
return tuple(zip(*batch))
#Training function with modifications for collecting IoU and loss
def train_model(model, train_loader, optimizer, device, num_epochs=10):
model.train()
model.to(device)
loss_values = []
iou_values = []
for epoch in range(num_epochs):
epoch_loss = 0.0
total_ious = 0
num_boxes = 0
for images, targets in train_loader:
# Skip batches with placeholder data
if len(targets) == 1 and not targets[0]:
continue
# Skip batches with empty targets
if any(len(target["boxes"]) == 0 for target in targets):
continue
images = [image.to(device) for image in images]
targets = [{k: v.to(device) for k, v in t.items()} for t in targets]
loss_dict = model(images, targets)
losses = sum(loss for loss in loss_dict.values())
optimizer.zero_grad()
losses.backward()
optimizer.step()
epoch_loss += losses.item()
# Compute IoU for evaluation
with torch.no_grad():
model.eval()
predictions = model(images)
for i, prediction in enumerate(predictions):
pred_boxes = prediction["boxes"].cpu().numpy()
true_boxes = targets[i]["boxes"].cpu().numpy()
for pred_box in pred_boxes:
for true_box in true_boxes:
iou = compute_iou(pred_box, true_box)
total_ious += iou
num_boxes += 1
model.train()
avg_loss = epoch_loss / len(train_loader)
avg_iou = total_ious / num_boxes if num_boxes != 0 else 0
loss_values.append(avg_loss)
iou_values.append(avg_iou)
print(f"Epoch {epoch+1}/{num_epochs} Loss: {avg_loss} Avg IoU: {avg_iou}")
# Plotting loss and IoU values
plt.figure(figsize=(12, 5))
plt.subplot(1, 2, 1)
plt.plot(loss_values, label="Training Loss")
plt.title("Training Loss across Epochs")
plt.xlabel("Epochs")
plt.ylabel("Loss")
plt.subplot(1, 2, 2)
plt.plot(iou_values, label="IoU")
plt.title("IoU across Epochs")
plt.xlabel("Epochs")
plt.ylabel("IoU")
plt.show()
# Save model after training
save_model(model)
# Validation function
def validate_model(model, val_loader, device):
model.eval()
model.to(device)
with torch.no_grad():
for images, targets in val_loader:
images = [image.to(device) for image in images]
targets = [{k: v.to(device) for k, v in t.items()} for t in targets]
model(images)
# Paths to your data
image_dir = "tuberculosis-phonecamera"
annotation_dir = "tuberculosis-phonecamera"
# Split data
train_images, val_images = split_data(image_dir)
# Create datasets and dataloaders
train_dataset = TuberculosisDataset(image_dir, annotation_dir, train_images, transform=data_transform)
val_dataset = TuberculosisDataset(image_dir, annotation_dir, val_images, transform=data_transform)
# Updated DataLoader with new collate function
train_loader = DataLoader(train_dataset, batch_size=4, shuffle=True, collate_fn=collate_fn)
val_loader = DataLoader(val_dataset, batch_size=4, shuffle=False, collate_fn=collate_fn)
# Model and optimizer
model = get_ssdlite_model_for_finetuning(2)
optimizer = torch.optim.Adam(model.parameters(), lr=0.001)
# Train and validate
train_model(model, train_loader, optimizer, device="cuda", num_epochs=10)
validate_model(model, val_loader, device="cuda")需要从头训练的,就不跑了,摆烂了。
五、写在后面
目标检测模型门槛更高了,运行起来对硬件要求也很高,时间也很久,都是小时起步的。因此只是简单介绍,算是入个门了。