前言
大家好,在今天的讨论中,我们将深入研究如何将ActiveMQ迁移到云端,以便更好地利用Kubernetes的容器调度和资源管理能力,确保ActiveMQ的高可用性和可扩展性。
ActiveMQ是Apache开源组织推出的一款开源的、完全支持JMS1.1和J2EE1.4规范的JMS Provider实现的消息中间件(MOM)。它是所有开源项目中最流行也最强大的开源消息中间件,主要用于分布式系统架构中,可以实现高可用、高性能、可伸缩、易用和安全的企业级面向消息服务的系统。
ActiveMQ的核心概念主要包括以下几个方面:
- 消息:消息是ActiveMQ中最基本的单位,它包含了实际需要传输的数据。
- 主题(Topic):主题是一种广播类型的消息模式,一个生产者向一个主题发送消息,而所有的消费者都可以接收到这个消息。这种方式非常适合于需要将一条消息分发到多个消费者的场景。
- 队列(Queue):队列是一种点对点的消息模式,一个生产者向一个队列发送消息,只有一个消费者能接收到这个消息。这种方式非常适合于需要将一条消息发送给一个特定的消费者的场景。
- 消费者(Consumer):消费者是从队列或主题中获取并处理消息的应用程序。
- 生产者(Producer):生产者是创建并向队列或主题发送消息的应用程序。
- 消息代理(Broker):消息代理是ActiveMQ的核心组件,它负责接收、存储和转发消息。在ActiveMQ中,每一个运行的实例都是一个消息代理。
- JMS(Java Message Service):Java消息服务是关于面向消息中间件的API,用于在两个应用程序之间或者分布式系统中发送消息,进行异步通信。JMS与具体的平台无关,绝大多数MOM(Message Oriented Middleware)提供商都对JMS提供了支持,例如ActiveMQ就是其中一个实现。
一、部署单机ActiveMQ
步骤一:创建ConfigMap
首先,我们需要创建ConfigMap,用来存储和管理ActiveMQ的相关配置。
apiVersion: v1
kind: ConfigMap
metadata:
name: activemq-config-single
namespace: 你实际的namespace
data:
activemq.xml: |
<beans
xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
http://activemq.apache.org/schema/core http://activemq.apache.org/schema/core/activemq-core.xsd">
<!-- Allows us to use system properties as variables in this configuration file -->
<bean class="org.springframework.beans.factory.config.PropertyPlaceholderConfigurer">
<property name="locations">
<value>file:${activemq.conf}/credentials.properties</value>
</property>
</bean>
<!-- Allows accessing the server log -->
<bean id="logQuery" class="io.fabric8.insight.log.log4j.Log4jLogQuery"
lazy-init="false" scope="singleton"
init-method="start" destroy-method="stop">
</bean>
<!--
The <broker> element is used to configure the ActiveMQ broker.
-->
<broker xmlns="http://activemq.apache.org/schema/core" brokerName="activemq-single" dataDirectory="${activemq.data}">
<plugins>
<simpleAuthenticationPlugin>
<users>
<authenticationUser username="my_mq_test" password="my_mq_test" groups="users,admins"/>
</users>
</simpleAuthenticationPlugin>
</plugins>
<destinationPolicy>
<policyMap>
<policyEntries>
<policyEntry topic=">" >
<!-- The constantPendingMessageLimitStrategy is used to prevent
slow topic consumers to block producers and affect other consumers
by limiting the number of messages that are retained
For more information, see:
http://activemq.apache.org/slow-consumer-handling.html
-->
<pendingMessageLimitStrategy>
<constantPendingMessageLimitStrategy limit="1000"/>
</pendingMessageLimitStrategy>
</policyEntry>
</policyEntries>
</policyMap>
</destinationPolicy>
<!--
The managementContext is used to configure how ActiveMQ is exposed in
JMX. By default, ActiveMQ uses the MBean server that is started by
the JVM. For more information, see:
http://activemq.apache.org/jmx.html
-->
<managementContext>
<managementContext createConnector="false"/>
</managementContext>
<!--
Configure message persistence for the broker. The default persistence
mechanism is the KahaDB store (identified by the kahaDB tag).
For more information, see:
http://activemq.apache.org/persistence.html
-->
<persistenceAdapter>
<kahaDB directory="${activemq.data}/kahadb"/>
</persistenceAdapter>
<!--
The systemUsage controls the maximum amount of space the broker will
use before disabling caching and/or slowing down producers. For more information, see:
http://activemq.apache.org/producer-flow-control.html
-->
<systemUsage>
<systemUsage>
<memoryUsage>
<memoryUsage percentOfJvmHeap="70" />
</memoryUsage>
<storeUsage>
<storeUsage limit="100 gb"/>
</storeUsage>
<tempUsage>
<tempUsage limit="50 gb"/>
</tempUsage>
</systemUsage>
</systemUsage>
<!--
The transport connectors expose ActiveMQ over a given protocol to
clients and other brokers. For more information, see:
http://activemq.apache.org/configuring-transports.html
-->
<transportConnectors>
<!-- DOS protection, limit concurrent connections to 1000 and frame size to 100MB -->
<transportConnector name="openwire" uri="tcp://0.0.0.0:30226?maximumConnections=1000&wireFormat.maxFrameSize=104857600"/>
<transportConnector name="amqp" uri="amqp://0.0.0.0:30227?maximumConnections=1000&wireFormat.maxFrameSize=104857600"/>
<transportConnector name="stomp" uri="stomp://0.0.0.0:30228?maximumConnections=1000&wireFormat.maxFrameSize=104857600"/>
<transportConnector name="mqtt" uri="mqtt://0.0.0.0:30229?maximumConnections=1000&wireFormat.maxFrameSize=104857600"/>
<transportConnector name="ws" uri="ws://0.0.0.0:30230?maximumConnections=1000&wireFormat.maxFrameSize=104857600"/>
</transportConnectors>
<!-- destroy the spring context on shutdown to stop jetty -->
<shutdownHooks>
<bean xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" class="org.apache.activemq.hooks.SpringContextHook" />
</shutdownHooks>
</broker>
<!--
Enable web consoles, REST and Ajax APIs and demos
The web consoles requires by default login, you can disable this in the jetty.xml file
Take a look at ${ACTIVEMQ_HOME}/conf/jetty.xml for more details
-->
<import resource="jetty.xml"/>
</beans>
---
apiVersion: v1
kind: ConfigMap
metadata:
name: activemq-config-jetty-realm
namespace: 你实际的namespace
data:
jetty-realm.properties: |
admin: my_mq_test, admin
user: user, user
在上面的配置中,我们在activemq.xml中使用简单授权配置以及修改了默认的端口号以提高服务的安全性;在jetty-realm.properties中配置了web端控制台的登录用户名和密码,格式为:
用户名 : 密码 ,角色名
步骤二:创建Deployment
接下来,我们需要创建一个Deployment,用来定义ActiveMQ的副本数量、镜像版本等相关信息。
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
name: activemq-single
namespace: 你实际的namespace
spec:
progressDeadlineSeconds: 600
replicas: 1
selector:
matchLabels:
app: activemq-single
strategy:
rollingUpdate:
maxSurge: 50%
maxUnavailable: 50%
type: RollingUpdate
template:
metadata:
labels:
app: activemq-single
spec:
affinity:
nodeAffinity:
requiredDuringSchedulingIgnoredDuringExecution:
nodeSelectorTerms:
- matchExpressions:
- key: project.node
operator: In
values:
- 你实际的节点名称
volumes:
- name: timezone
hostPath:
path: /usr/share/zoneinfo/Asia/Shanghai
- name: config-activemq
configMap:
name: activemq-config-single
- name: jetty-realm
configMap:
name: activemq-config-jetty-realm
containers:
- name: activemq
image: webcenter/activemq:5.14.3
imagePullPolicy: IfNotPresent
terminationMessagePath: /dev/termination-log
terminationMessagePolicy: File
volumeMounts:
- name: config-activemq
mountPath: /opt/activemq/conf/activemq.xml
subPath: activemq.xml
- name: jetty-realm
mountPath: /opt/activemq/conf/jetty-realm.properties
subPath: jetty-realm.properties
env:
- name: HOST_IP
valueFrom:
fieldRef:
fieldPath: status.hostIP
- name: POD_IP
valueFrom:
fieldRef:
fieldPath: status.podIP
- name: POD_NAME
valueFrom:
fieldRef:
fieldPath: metadata.name
- name: TZ
value: "Asia/Shanghai"
在上述配置中,我们定义了一个名为activemq-single的Deployment。在这里,我们使用的镜像已经版本为webcenter/activemq:5.14.3,并且使用了之前创建的ConfigMap中的配置文件。
步骤三:创建Service
然后,我们还需要创建一个Service,用来将K8S集群中运行的ActiveMQ实例暴露为可访问的服务。
apiVersion: v1
kind: Service
metadata:
name: service-activemq-single
namespace: 你实际的namespace
spec:
selector:
app: activemq-single
type: NodePort
sessionAffinity: None
ports:
- name: activemq-admin
port: 8161
targetPort: 8161
nodePort: 30225
- name: activemq-tcp
port: 30226
targetPort: 30226
nodePort: 30226
- name: activemq-amqp
port: 30227
targetPort: 30227
nodePort: 30227
- name: activemq-stomp
port: 30228
targetPort: 30228
nodePort: 30228
- name: activemq-mqtt
port: 30229
targetPort: 30229
nodePort: 30229
- name: activemq-ws
port: 30230
targetPort: 30230
nodePort: 30230
步骤四:验证单机ActiveMQ
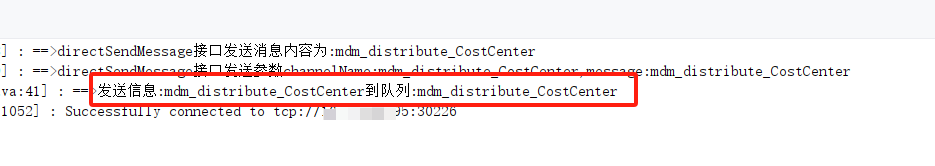
- 首先,我们启动一个
生产者链接到刚部署的单机ActiveMQ上,并且向名称为mdm_distribute_CostCenter的队列中发送了一条消息,消息内容为mdm_distribute_CostCenter。
- 接下来,我们再启动一个
消息者同样链接到刚部署的单机ActiveMQ上,并且监听名为mdm_distribute_CostCenter的队列。

- 最后,我们可以在web端的admin页面查看相应队列中的记录

小结
以上就是在K8S中部署单机ActiveMQ的相关步骤。通过这些步骤,我们成功地使用无状态的Deployment部署了一个可用的单机ActiveMQ。
二、部署ActiveMQ集群(networks of brokers)
步骤一:创建ConfigMap
与单机版类似,我们同样需要创建一个ConfigMap来存储和管理ActiveMQ的相关配置。
apiVersion: v1
kind: ConfigMap
metadata:
name: activemq-config-node-0
namespace: 你实际的namespace
data:
activemq.xml: |
<beans
xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
http://activemq.apache.org/schema/core http://activemq.apache.org/schema/core/activemq-core.xsd">
<!-- Allows us to use system properties as variables in this configuration file -->
<bean class="org.springframework.beans.factory.config.PropertyPlaceholderConfigurer">
<property name="locations">
<value>file:${activemq.conf}/credentials.properties</value>
</property>
</bean>
<!-- Allows accessing the server log -->
<bean id="logQuery" class="io.fabric8.insight.log.log4j.Log4jLogQuery"
lazy-init="false" scope="singleton"
init-method="start" destroy-method="stop">
</bean>
<!--
The <broker> element is used to configure the ActiveMQ broker.
-->
<broker xmlns="http://activemq.apache.org/schema/core" brokerName="activemq-node-0" dataDirectory="${activemq.data}">
<networkConnectors>
<networkConnector userName="my_mq_test" password="my_mq_test" uri="static:(tcp://你的实际ip:30220)" duplex="true"/>
</networkConnectors>
<plugins>
<simpleAuthenticationPlugin>
<users>
<authenticationUser username="my_mq_test" password="my_mq_test" groups="users,admins"/>
</users>
</simpleAuthenticationPlugin>
</plugins>
<destinationPolicy>
<policyMap>
<policyEntries>
<policyEntry topic=">" >
<!-- The constantPendingMessageLimitStrategy is used to prevent
slow topic consumers to block producers and affect other consumers
by limiting the number of messages that are retained
For more information, see:
http://activemq.apache.org/slow-consumer-handling.html
-->
<pendingMessageLimitStrategy>
<constantPendingMessageLimitStrategy limit="1000"/>
</pendingMessageLimitStrategy>
</policyEntry>
</policyEntries>
</policyMap>
</destinationPolicy>
<!--
The managementContext is used to configure how ActiveMQ is exposed in
JMX. By default, ActiveMQ uses the MBean server that is started by
the JVM. For more information, see:
http://activemq.apache.org/jmx.html
-->
<managementContext>
<managementContext createConnector="false"/>
</managementContext>
<!--
Configure message persistence for the broker. The default persistence
mechanism is the KahaDB store (identified by the kahaDB tag).
For more information, see:
http://activemq.apache.org/persistence.html
-->
<persistenceAdapter>
<kahaDB directory="${activemq.data}/kahadb"/>
</persistenceAdapter>
<!--
The systemUsage controls the maximum amount of space the broker will
use before disabling caching and/or slowing down producers. For more information, see:
http://activemq.apache.org/producer-flow-control.html
-->
<systemUsage>
<systemUsage>
<memoryUsage>
<memoryUsage percentOfJvmHeap="70" />
</memoryUsage>
<storeUsage>
<storeUsage limit="100 gb"/>
</storeUsage>
<tempUsage>
<tempUsage limit="50 gb"/>
</tempUsage>
</systemUsage>
</systemUsage>
<!--
The transport connectors expose ActiveMQ over a given protocol to
clients and other brokers. For more information, see:
http://activemq.apache.org/configuring-transports.html
-->
<transportConnectors>
<!-- DOS protection, limit concurrent connections to 1000 and frame size to 100MB -->
<transportConnector name="openwire" uri="tcp://0.0.0.0:30218?maximumConnections=1000&wireFormat.maxFrameSize=104857600"/>
<transportConnector name="amqp" uri="amqp://0.0.0.0:30221?maximumConnections=1000&wireFormat.maxFrameSize=104857600"/>
<transportConnector name="stomp" uri="stomp://0.0.0.0:30222?maximumConnections=1000&wireFormat.maxFrameSize=104857600"/>
<transportConnector name="mqtt" uri="mqtt://0.0.0.0:30223?maximumConnections=1000&wireFormat.maxFrameSize=104857600"/>
<transportConnector name="ws" uri="ws://0.0.0.0:30224?maximumConnections=1000&wireFormat.maxFrameSize=104857600"/>
</transportConnectors>
<!-- destroy the spring context on shutdown to stop jetty -->
<shutdownHooks>
<bean xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" class="org.apache.activemq.hooks.SpringContextHook" />
</shutdownHooks>
</broker>
<!--
Enable web consoles, REST and Ajax APIs and demos
The web consoles requires by default login, you can disable this in the jetty.xml file
Take a look at ${ACTIVEMQ_HOME}/conf/jetty.xml for more details
-->
<import resource="jetty.xml"/>
</beans>
---
apiVersion: v1
kind: ConfigMap
metadata:
name: activemq-config-node-1
namespace: 你实际的namespace
data:
activemq.xml: |
<beans
xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
http://activemq.apache.org/schema/core http://activemq.apache.org/schema/core/activemq-core.xsd">
<!-- Allows us to use system properties as variables in this configuration file -->
<bean class="org.springframework.beans.factory.config.PropertyPlaceholderConfigurer">
<property name="locations">
<value>file:${activemq.conf}/credentials.properties</value>
</property>
</bean>
<!-- Allows accessing the server log -->
<bean id="logQuery" class="io.fabric8.insight.log.log4j.Log4jLogQuery"
lazy-init="false" scope="singleton"
init-method="start" destroy-method="stop">
</bean>
<!--
The <broker> element is used to configure the ActiveMQ broker.
-->
<broker xmlns="http://activemq.apache.org/schema/core" brokerName="activemq-node-0" dataDirectory="${activemq.data}">
<networkConnectors>
<networkConnector userName="my_mq_test" password="my_mq_test" uri="static:(tcp://你的实际ip:30218)" duplex="true"/>
</networkConnectors>
<plugins>
<simpleAuthenticationPlugin>
<users>
<authenticationUser username="my_mq_test" password="my_mq_test" groups="users,admins"/>
</users>
</simpleAuthenticationPlugin>
</plugins>
<destinationPolicy>
<policyMap>
<policyEntries>
<policyEntry topic=">" >
<!-- The constantPendingMessageLimitStrategy is used to prevent
slow topic consumers to block producers and affect other consumers
by limiting the number of messages that are retained
For more information, see:
http://activemq.apache.org/slow-consumer-handling.html
-->
<pendingMessageLimitStrategy>
<constantPendingMessageLimitStrategy limit="1000"/>
</pendingMessageLimitStrategy>
</policyEntry>
</policyEntries>
</policyMap>
</destinationPolicy>
<!--
The managementContext is used to configure how ActiveMQ is exposed in
JMX. By default, ActiveMQ uses the MBean server that is started by
the JVM. For more information, see:
http://activemq.apache.org/jmx.html
-->
<managementContext>
<managementContext createConnector="false"/>
</managementContext>
<!--
Configure message persistence for the broker. The default persistence
mechanism is the KahaDB store (identified by the kahaDB tag).
For more information, see:
http://activemq.apache.org/persistence.html
-->
<persistenceAdapter>
<kahaDB directory="${activemq.data}/kahadb"/>
</persistenceAdapter>
<!--
The systemUsage controls the maximum amount of space the broker will
use before disabling caching and/or slowing down producers. For more information, see:
http://activemq.apache.org/producer-flow-control.html
-->
<systemUsage>
<systemUsage>
<memoryUsage>
<memoryUsage percentOfJvmHeap="70" />
</memoryUsage>
<storeUsage>
<storeUsage limit="100 gb"/>
</storeUsage>
<tempUsage>
<tempUsage limit="50 gb"/>
</tempUsage>
</systemUsage>
</systemUsage>
<!--
The transport connectors expose ActiveMQ over a given protocol to
clients and other brokers. For more information, see:
http://activemq.apache.org/configuring-transports.html
-->
<transportConnectors>
<!-- DOS protection, limit concurrent connections to 1000 and frame size to 100MB -->
<transportConnector name="openwire" uri="tcp://0.0.0.0:30220?maximumConnections=1000&wireFormat.maxFrameSize=104857600"/>
<transportConnector name="amqp" uri="amqp://0.0.0.0:30221?maximumConnections=1000&wireFormat.maxFrameSize=104857600"/>
<transportConnector name="stomp" uri="stomp://0.0.0.0:30222?maximumConnections=1000&wireFormat.maxFrameSize=104857600"/>
<transportConnector name="mqtt" uri="mqtt://0.0.0.0:30223?maximumConnections=1000&wireFormat.maxFrameSize=104857600"/>
<transportConnector name="ws" uri="ws://0.0.0.0:30224?maximumConnections=1000&wireFormat.maxFrameSize=104857600"/>
</transportConnectors>
<!-- destroy the spring context on shutdown to stop jetty -->
<shutdownHooks>
<bean xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" class="org.apache.activemq.hooks.SpringContextHook" />
</shutdownHooks>
</broker>
<!--
Enable web consoles, REST and Ajax APIs and demos
The web consoles requires by default login, you can disable this in the jetty.xml file
Take a look at ${ACTIVEMQ_HOME}/conf/jetty.xml for more details
-->
<import resource="jetty.xml"/>
</beans>
---
apiVersion: v1
kind: ConfigMap
metadata:
name: activemq-config-jetty-realm
namespace: 你实际的namespace
data:
jetty-realm.properties: |
admin: my_mq_test, admin
user: user, user
步骤二:创建Deployment
接下来,我们需要创建2个Deployment,分别对应ActiveMQ集群中的2个节点。主要区别在于使用ConfigMap中的配置文件的不同和containers中暴露的端口不同。
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
name: activemq-node-0
namespace: 你实际的namespace
spec:
progressDeadlineSeconds: 600
replicas: 1
selector:
matchLabels:
app: activemq-node-0
strategy:
rollingUpdate:
maxSurge: 50%
maxUnavailable: 50%
type: RollingUpdate
template:
metadata:
labels:
app: activemq-node-0
name: activemq-node
spec:
affinity:
nodeAffinity:
requiredDuringSchedulingIgnoredDuringExecution:
nodeSelectorTerms:
- matchExpressions:
- key: project.node
operator: In
values:
- 你实际的节点名称
volumes:
- name: timezone
hostPath:
path: /usr/share/zoneinfo/Asia/Shanghai
- name: config-activemq
configMap:
name: activemq-config-node-0
- name: jetty-realm
configMap:
name: activemq-config-jetty-realm
containers:
- name: activemq
image: webcenter/activemq:5.14.3
imagePullPolicy: IfNotPresent
terminationMessagePath: /dev/termination-log
terminationMessagePolicy: File
volumeMounts:
- name: config-activemq
mountPath: /opt/activemq/conf/activemq.xml
subPath: activemq.xml
- name: jetty-realm
mountPath: /opt/activemq/conf/jetty-realm.properties
subPath: jetty-realm.properties
env:
- name: HOST_IP
valueFrom:
fieldRef:
fieldPath: status.hostIP
- name: POD_IP
valueFrom:
fieldRef:
fieldPath: status.podIP
- name: POD_NAME
valueFrom:
fieldRef:
fieldPath: metadata.name
- name: TZ
value: "Asia/Shanghai"
---
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
name: activemq-node-1
namespace: 你实际的namespace
spec:
progressDeadlineSeconds: 600
replicas: 1
selector:
matchLabels:
app: activemq-node-1
strategy:
rollingUpdate:
maxSurge: 50%
maxUnavailable: 50%
type: RollingUpdate
template:
metadata:
labels:
app: activemq-node-1
name: activemq-node
spec:
affinity:
nodeAffinity:
requiredDuringSchedulingIgnoredDuringExecution:
nodeSelectorTerms:
- matchExpressions:
- key: project.node
operator: In
values:
- 你实际的节点名称
volumes:
- name: timezone
hostPath:
path: /usr/share/zoneinfo/Asia/Shanghai
- name: config-activemq
configMap:
name: activemq-config-node-1
- name: jetty-realm
configMap:
name: activemq-config-jetty-realm
containers:
- name: activemq
image: webcenter/activemq:5.14.3
imagePullPolicy: IfNotPresent
terminationMessagePath: /dev/termination-log
terminationMessagePolicy: File
volumeMounts:
- name: config-activemq
mountPath: /opt/activemq/conf/activemq.xml
subPath: activemq.xml
- name: jetty-realm
mountPath: /opt/activemq/conf/jetty-realm.properties
subPath: jetty-realm.properties
env:
- name: HOST_IP
valueFrom:
fieldRef:
fieldPath: status.hostIP
- name: POD_IP
valueFrom:
fieldRef:
fieldPath: status.podIP
- name: POD_NAME
valueFrom:
fieldRef:
fieldPath: metadata.name
- name: TZ
value: "Asia/Shanghai"
步骤三:创建Service
然后,我们还需要来创建Service,用来将K8S集群中运行的ActiveMQ实例暴露为可访问的服务。这里同样需要创建2个Service,分别对应步骤二中的2个Deployment,还需要1个Service来暴露公共的端口。
apiVersion: v1
kind: Service
metadata:
name: service-activemq-common
namespace: 你实际的namespace
spec:
selector:
name: activemq-node
type: NodePort
sessionAffinity: None
ports:
- name: activemq-amqp
port: 30221
targetPort: 30221
nodePort: 30221
- name: activemq-stomp
port: 30222
targetPort: 30222
nodePort: 30222
- name: activemq-mqtt
port: 30223
targetPort: 30223
nodePort: 30223
- name: activemq-ws
port: 30224
targetPort: 30224
nodePort: 30224
---
apiVersion: v1
kind: Service
metadata:
name: service-activemq-node-0
namespace: 你实际的namespace
spec:
selector:
app: activemq-node-0
type: NodePort
sessionAffinity: None
ports:
- name: activemq-admin
port: 8161
targetPort: 8161
nodePort: 30217
- name: activemq-tcp
port: 30218
targetPort: 30218
nodePort: 30218
---
apiVersion: v1
kind: Service
metadata:
name: service-activemq-node-1
namespace: 你实际的namespace
spec:
selector:
app: activemq-node-1
type: NodePort
sessionAffinity: None
ports:
- name: activemq-admin
port: 8161
targetPort: 8161
nodePort: 30219
- name: activemq-tcp
port: 30220
targetPort: 30220
nodePort: 30220
步骤五:验证ActiveMQ集群
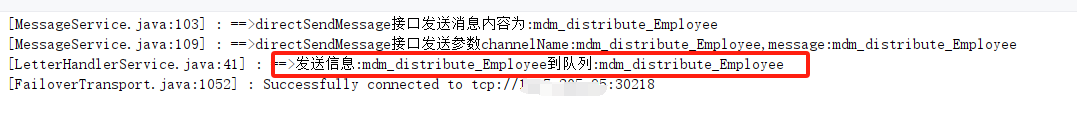
- 首先,我们启动一个
生产者链接到刚部署的集群ActiveMQ上,并且向名称为mdm_distribute_Employee的队列中发送了一条消息,消息内容为mdm_distribute_Employee。
- 接下来,我们再启动一个
消息者同样链接到刚部署的集群ActiveMQ上,并且监听名为mdm_distribute_Employee的队列。
- 最后,我们可以在web端的admin页面查看相应队列中的记录

小结
在K8S中部署ActiveMQ集群的相关步骤已经介绍完毕。通过这些步骤,我们成功地使用无状态的Deployment部署了一个可用的ActiveMQ集群。
结论
本文详尽地探讨了在K8S环境中部署ActiveMQ单机与集群的详细步骤。细读全文,我们可以发现,ActiveMQ的数据存储仍在POD中,这是由于业务需求所决定的。当发送MQ消息时,数据需要先被写入数据库,然后再进行发送,因此ActiveMQ的数据存储变得无关紧要。当然,我们还可以选择使用pvc或者直接挂载到宿主机等方式来保存数据。相较于传统的手动部署方式,利用K8S进行部署能够带来更高的便捷性和效率,从而更快速地完成ActiveMQ集群的部署和管理任务。