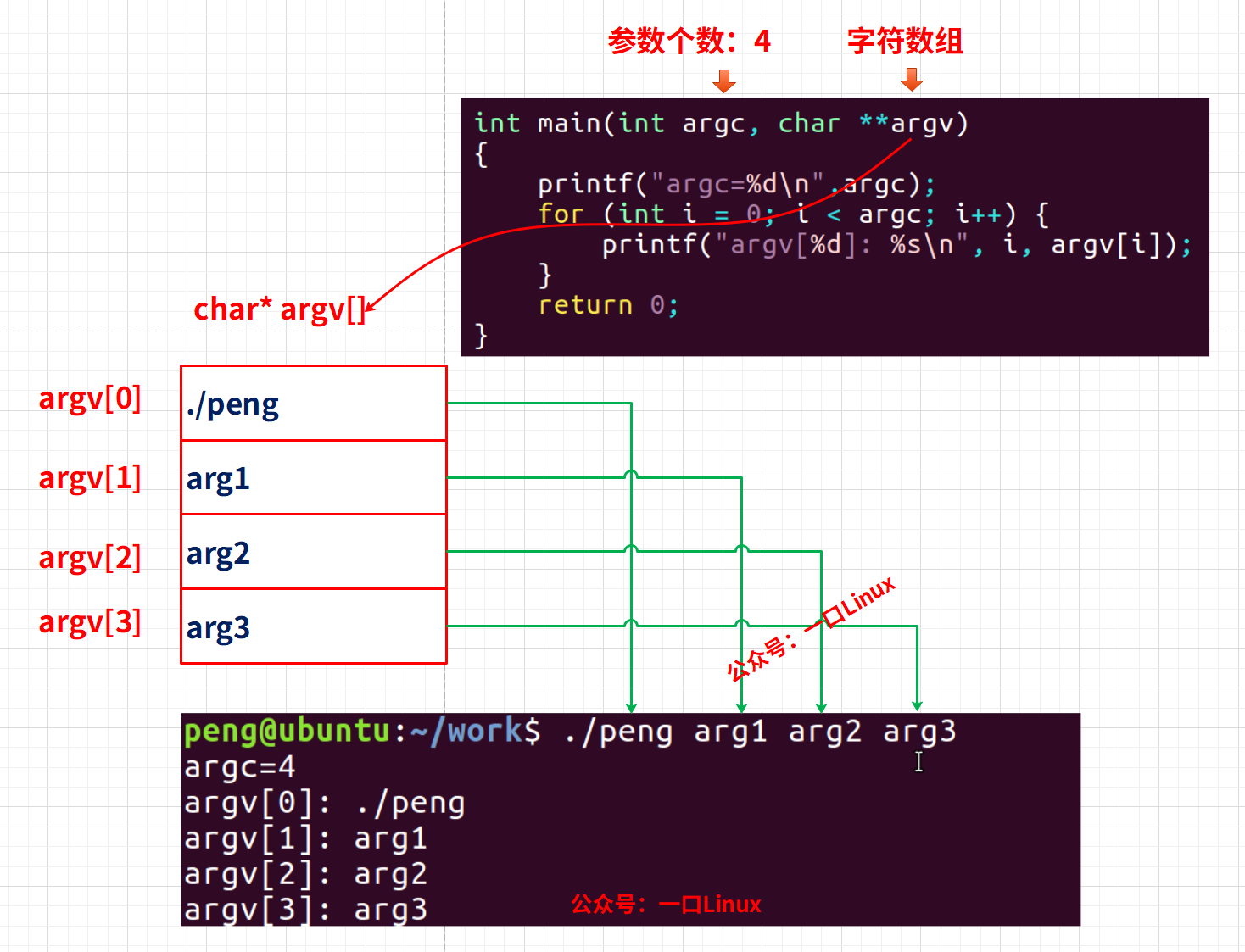
this指针
概念
谁调用
this
所在的函数
,this
就存储谁的地址
特点
1,
在当前类的非静态成员函数中调用本类非静态成员时
,
默认有
this
关键字
2,
静态成员函数
,
没有
this
指针。
示例
#include <iostream>
#include <cstring>
using namespace std;
class Stu{
private:
char name[50];
char sex[10];
int age;
public:
Stu(){}
Stu(char *n,char *s,int a):age(a)
{
strcpy(name,n);
strcpy(sex,s);
}
void test01()
{
//以下两句代码效果相同
//证明本类函数中调用本类成员默认使用this关键字
cout << this->name << endl;
cout << name << endl;
}
static void test02()
{
//报错,因为静态函数中没有this
//cout << name << endl;
}
};
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
Stu s("张三","男",18);
s.test01();
s.test02();
return 0;
}使用场景
1,
局部变量与成员变量重名时
,
使用
this
区分
2,
调用本类其他成员
,
此时
this
可以省略不写
示例
#include <iostream>
#include <cstring>
using namespace std;
class Stu{
private:
char name[50];
char sex[10];
int age;
public:
Stu(){}
Stu(char *name,char *sex,int age)
{
//当局部变量与成员变量重名,使用this区分
strcpy(this->name,name);
strcpy(this->sex,sex);
this->age = age;
}
void print_info()
{
//调用本类成员变量
cout << this->name << endl;
cout << this->sex << endl;
cout << this->age << endl;
}
void test()
{
//调用本类成员函数
this->print_info();
}
};
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
Stu s("张三","男",18);
s.print_info();
s.test();
return 0;
}实例
使用
:*this
完成链式编程
#include <iostream>
#include <cstring>
using namespace std;
class Stu{
private:
char name[50];
char sex[10];
int age;
public:
Stu(){}
Stu(char *name,char *sex,int age)
{
strcpy(this->name,name);
strcpy(this->sex,sex);
this->age = age;
}
void print_info()
{
cout << this->name << endl;
cout << this->sex << endl;
cout << this->age << endl;
}
Stu& eat(char *foodName)
{
cout << name << "吃" << foodName << endl;
return *this;
}
};
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
Stu s("张三","男",18);
s.eat("凉皮").eat("肉夹馍").eat("甑糕");
return 0;
}const修饰成员函数(了解)
特点
const修饰的成员函数内部不能对成员数据写操作,
mutable
修饰的成员数据 除外。
实例
class Stu{
private:
char name[50];
char sex[10];
int age;
mutable int score;
public:
Stu(){}
Stu(char *name,char *sex,int age)
{
strcpy(this->name,name);
strcpy(this->sex,sex);
this->age = age;
}
void print_info()
{
cout << this->name << endl;
cout << this->sex << endl;
cout << this->age << endl;
}
Stu& eat(char *foodName)
{
cout << name << "吃" << foodName << endl;
return *this;
}
void test() const
{
//age = 10;//错误
score = 99;//正确
}
};友元函数(重要)
概述
关键字
:friend
可以声明
:
1,全局函数
2,成员函数
3,类
注意
:
友元打破c++
的封装性。一般用于运算符重载
全局友元函数
特点
可以访问其友元类的任意成员
,
包括私有成员
步骤
1,
在定义并实例全局函数
2,
在类中声明步骤
1
中的函数为友元函数
3,
步骤
1
中定义的函数
,
可以访问步骤
2
中定义的类中的所有成员
示例
#include <iostream>
#include <cstring>
using namespace std;
class Stu{
friend void test(Stu &stu);
private:
char name[50];
char sex[10];
int age;
public:
Stu(){}
Stu(char *name,char *sex,int age)
{
strcpy(this->name,name);
strcpy(this->sex,sex);
this->age = age;
}
void print_info()
{
cout << this->name << endl;
cout << this->sex << endl;
cout << this->age << endl;
}
private:
void eat(char *foodName)
{
cout << name << "吃" << foodName << endl;
}
};
void test(Stu& stu)
{
//调用友元类的私有属性
cout << stu.name << endl;
cout << stu.sex << endl;
cout << stu.age << endl;
//调用友元类的私有函数
stu.eat("大嘴巴子");
}
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
Stu s("张三","男",18);
test(s);
return 0;
}成员友元函数
特点
可以访问其友元类的任意成员,
包括私有成员
注意
1,
成员函数作为友元 那么成员函数所在的类 必须定义到最上方
2,
成员函数所在的类的所有成员函数 必须在两个类的下方实现
步骤
1,定义
B
类
,
但不现实
2,定义成员函数
A1
所在的类
A,
但其中只定义该成员函数
A1
3,实现
B
类
,
并在其中声明成员函数
A1
为友元函数
4,实现成员函数
示例
#include <iostream>
#include <cstring>
using namespace std;
//定义B类,但是没有实现
class B;
class A{
public:
void test(B& b);
};
class B{
friend void A::test(B& b);
private:
int a;
public:
B(int a)
{
this->a = a;
}
private:
void print_B()
{
cout << "a = " << a << endl;
}
};
void A::test(B& b)
{
cout << b.a << endl;
b.print_B();
}
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
A a;
B b(10);
a.test(b);
return 0;
}整个类作为友元函数
特点
在B
中声明
A
为
B
的友元类
,
此时
A
中任意成员函数中皆可直接访问
B
中的成员
步骤
1,
定义
B
类
2,
定义并实现
A
类
,
其中函数只定义不实现
3,
实现
B
类
,
在其中声明
A
类为友元类
4,
实现
A
类中的成员函数
示例
#include <iostream>
#include <cstring>
using namespace std;
//定义B类,但是没有实现
class B;
class A{
public:
void test01(B& b);
void test02(B& b);
};
class B{
friend class A;
private:
int a;
public:
B(int a)
{
this->a = a;
}
private:
void print_B()
{
cout << "a = " << a << endl;
}
};
void A::test01(B& b)
{
cout << "test01" << endl;
cout << b.a << endl;
b.print_B();
}
void A::test02(B& b)
{
cout << "test02" << endl;
cout << b.a << endl;
b.print_B();
}
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
A a;
B b(10);
a.test01(b);
cout << "--------------------" << endl;
a.test02(b);
return 0;
}注意
1,
友元关系不能被继承。
2,
友元关系是单向的,类
A
是类
B
的朋友,但类
B
不一定是类
A
的朋友。
3,
友元关系不具有传递性。类
B
是类
A
的朋友,类
C
是类
B
的朋友,但类
C
不一
定是类
A
的朋友
实例
说明
遥控器类的对象可以操作电视机类对象的成员
所以遥控器类是电视机类的友元类
代码
#include <iostream>
#include <cstring>
using namespace std;
class TV;
class YK{
public:
void up(TV& tv);
void down(TV& tv);
};
class TV{
friend class YK;
private:
int yl;
public:
TV(){}
TV(int yl)
{
this->yl = yl;
}
};
void YK::up(TV &tv)
{
tv.yl++;
cout << "当前音量:" << tv.yl << endl;
}
void YK::down(TV &tv)
{
tv.yl--;
cout << "当前音量:" << tv.yl << endl;
}
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
TV tv(10);
YK yk;
yk.up(tv);
yk.up(tv);
yk.up(tv);
yk.down(tv);
yk.down(tv);
yk.down(tv);
return 0;
}string
c++
字符串类
,
使其字符串操作方便
示例
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
string str01 = "hello";
string str02 = str01;//字符串赋值
cout << str01 << endl;//字符串输出
cout << str02 << endl;
str02 = "world";
cout << str01 << endl;
cout << str02 << endl;
string str03 = str01 + str02;//字符串拼接
cout << str03 << endl;
string str04;
cin >> str04;//字符串输入
cout << str04 << endl;
string str05 = "Hi C++";
string str06 = "Hi C++";
string str07 = "Hi C";
cout << (str05 == str06) << endl;//判断字符串内容是否相同
cout << (str05 == str07) << endl;
cout << &str05 << endl;//打印str05地址
cout << &str06 << endl;//打印str06地址
return 0;
}重载
引入
经源码查看
string
发现其也是一个类
那么为什么
string
的类对象可以使用
>>,<<,+,==
等运算符
,
我们自定义的类不行呢
?
因为
string
类对运算符进行了重载
那我们如何实现运算符的重载
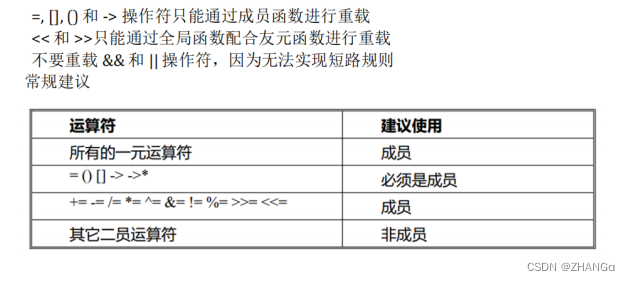
概述
作用
是对已有的运算符重新进行定义,赋予其另一种功能,以适应不同的数据类型。
关键字
operator
语法
返回值类型 operator+
运算符
(
形参列表
)
{
函数体
}
如:
>>
void operator>>(形参列表
)
{
}
思路
1
、分析运算符的运算对象的个数
2
、分析运算符左边的运算对象是 自定对象 还是其他
左边:是其他 只能全局函数实现 (必须使用友元)
左边:自定义对象
可以用使用全局函数重载运算符(参数个数 和 运算符对象的个数一致)
也可以使用成员函数重载运算符(参数可以少一个) (推荐)
示例1:重载<<,>>运算符
效果
使其可以通过<<
输出自定义类型的变量或通过
>>
输入自定义类型变量
分析
<<
或
>>
符号左边为
cout
或
cin
不是自定义对象
,
只能使用全局函数对其进行重载
示例
#include <iostream>
#include <cstring>
using namespace std;
class Data{
public:
int x,y,z;
Data(){}
Data(int a,int b,int c):x(a),y(b),z(c){}
};
//第一个参数为运算符左边的变量
//第二个参数为运算符右边的变量
istream& operator >>(istream& in,Data& d)
{
in >> d.x >> d.y >> d.z;
return in;
}
ostream& operator <<(ostream& out,Data& d)
{
out << "x = " << d.x << "\ty = " << d.y << "\tz = " << d.z << endl;
return out;
}
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
Data d;
cin >> d;
cout << d << endl;
return 0;
}示例2:重载+运算符
效果
使用+
运算符将自定义类型对象的属性一一相加
分析
+符号左边为自定义类型
,
可以使用全局函数重载也可以使用成员函数中
示例:全局函数重载
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
class Data{
public:
int x,y,z;
Data(){}
Data(int a,int b,int c):x(a),y(b),z(c){}
};
//第一个参数为运算符左边的变量
//第二个参数为运算符右边的变量
Data* operator +(Data& d1,Data& d2)
{
Data *d = new Data();
d->x = d1.x + d2.x;
d->y = d1.y + d2.y;
d->z = d1.z + d2.z;
return d;
}
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
Data d1(1,2,3);
Data d2(1,2,3);
Data* d3 = d1 + d2;
cout << d3->x << d3->y << d3->z << endl;
return 0;
}
示例
2:
成员函数重载
+
运算符
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
class Data{
public:
int x,y,z;
Data(){}
Data(int a,int b,int c):x(a),y(b),z(c){}
//调用该函数的对象为运算符左边的变量
//参数为运算符右边的变量
Data* operator +(Data& d2)
{
Data *d = new Data();
d->x = this->x + d2.x;
d->y = this->y + d2.y;
d->z = this->z + d2.z;
return d;
}
};
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
Data d1(1,2,3);
Data d2(1,2,3);
Data* d3 = d1 + d2;
cout << d3->x << d3->y << d3->z << endl;
return 0;
}示例3:重载==运算符
效果
比较类中成员变量值是否相同
分析
符号左边为自定义类型,
可以使用全局函数重载也可以使用成员函数中
示例
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
class Data{
public:
int x,y,z;
Data(){}
Data(int a,int b,int c):x(a),y(b),z(c){}
//调用该函数的对象为运算符左边的变量
//参数为运算符右边的变量
bool operator ==(Data& d2)
{
if(this->x == d2.x && this->y == d2.y && this->z == d2.z)
{
return true;
}
else
{
return false;
}
}
};
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
Data d1(1,2,3);
Data d2(1,2,3);
Data d3(2,2,3);
cout << (d1 == d2) << endl;
cout << (d1 == d3) << endl;
return 0;
}示例4:重载++运算符
注意
++
运算符分为
++
在前与
++
在后两种所以需要重载两种
当编译器看到
++a(
前置
++),
它就调用
operator++(Type& a)(
全局函数
),operator++
()(
成员函数
)
当编译器看到
a++(
后置
++),
它就会去调用
operator++(Type& a,int)(
全局函
数
),operator++(int)(
成员函数
)
示例
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
class Data{
public:
int x,y,z;
Data(){}
Data(int a,int b,int c):x(a),y(b),z(c){}
Data& operator ++()//++前置
{
++x;
++y;
++z;
return *this;
}
Data operator ++(int)//++后置
{
Data old = *this;//记录旧值
++x;
++y;
++z;
return old;//返回旧值
}
};
ostream& operator <<(ostream& out,Data& d)
{
out << d.x << d.y << d.z << endl;
return out;
}
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
Data d1(1,2,3);
++d1;
cout << d1;
Data d2(1,2,3);
Data d3 = d2++;
cout << d3;
cout << d2;
return 0;
}示例5:重载*与->
要求
重载指针运算符实现智能指针
推演
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
class Data{
private:
int x,y,z;
public:
Data(){
cout << "无参构造函数" << endl;
}
Data(int a,int b,int c):x(a),y(b),z(c){
cout << "有参构造函数" << endl;
}
~Data()
{
cout << "析构函数" << endl;
}
};
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
Data *p = new Data();
return 0;
}
观察以上代码
,
我们发现创建的对象没有被销毁
,
但是我们在编写代码时经常会忘记销
毁
,
那该怎么办呢
?
解决方案如下
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
class Data{
private:
int x,y,z;
public:
Data(){
cout << "无参构造函数" << endl;
}
Data(int a,int b,int c):x(a),y(b),z(c){
cout << "有参构造函数" << endl;
}
~Data()
{
cout << "析构函数" << endl;
}
};
class FreeData{
private:
Data* p;
public:
FreeData(){
p = NULL;
}
FreeData(Data* data){
p = data;
}
~FreeData(){
if(p != NULL)
{
delete p;
p = NULL;
}
}
};
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
FreeData fd(new Data(1,2,3));
return 0;
}
现在我们发现
Data
对象可以销毁
,
但是如何调用其对象中的属性呢
?
方案如下
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
class Data{
private:
int x,y,z;
public:
Data(){
cout << "无参构造函数" << endl;
}
Data(int a,int b,int c):x(a),y(b),z(c){
cout << "有参构造函数" << endl;
}
~Data()
{
cout << "析构函数" << endl;
}
int getX()
{
return x;
}
};
class FreeData{
private:
Data* p;
public:
FreeData(){
p = NULL;
}
FreeData(Data* data){
p = data;
}
~FreeData(){
if(p != NULL)
{
delete p;
p = NULL;
}
}
Data& operator *()
{
return *p;
}
Data* operator ->()
{
return p;
}
};
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
FreeData fd(new Data(1,2,3));
cout << (*fd).getX() << endl;
cout << fd->getX() << endl;
return 0;
}示例6:重载()
作用
当类对象作为函数调用时,会执行
operator()(
参数列表
)
函数。
对象作为函数调用
对象名
(
实参列表
);
一种仿函数
示例
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
class Data{
friend ostream& operator <<(ostream& out,Data& d);
private:
int x,y,z;
public:
Data(){
cout << "无参构造函数" << endl;
}
Data(int a,int b,int c):x(a),y(b),z(c){
cout << "有参构造函数" << endl;
}
~Data()
{
cout << "析构函数" << endl;
}
void operator ()(int a,int b,int c){
this->x += a;
this->y += b;
this->z += c;
}
};
ostream& operator <<(ostream& out,Data& d)
{
out << d.x << "\t" << d.y << "\t" << d.z << endl;
return out;
}
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
Data d(1,2,3);
d(2,5,8);
cout << d;
return 0;
}示例7:重载=
注意
=
重载时,可能会调用类本身的拷贝构造函数。
如果左值是没有创建的对象时
,
会调用拷贝构造函数
.
如果左值是已创建的类对象
,
会执行
=
重载函数
,
实现数据的拷贝
示例
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
class Data{
friend ostream& operator <<(ostream& out,Data& d);
private:
int x,y,z;
public:
Data(){
cout << "无参构造函数" << endl;
}
Data(int a,int b,int c):x(a),y(b),z(c){
cout << "有参构造函数" << endl;
}
Data(const Data& d)
{
cout << "执行拷贝构造" << endl;
this->x = d.x;
this->y = d.y;
this->z = d.z;
}
~Data()
{
cout << "析构函数" << endl;
}
void operator =(Data& d){
cout << "执行重载=运算符的函数" << endl;
this->x = d.x;
this->y = d.y;
this->z = d.z;
}
};
ostream& operator <<(ostream& out,Data& d)
{
out << d.x << "\t" << d.y << "\t" << d.z << endl;
return out;
}
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
Data d1(1,2,3);
Data d2(3,6,9);
d1 = d2;//d1已完成初始化,执行重载的=号运算符
Data d3 = d2;//d3未完成初始化,执行拷贝构造
return 0;
}注意: