示例代码 1,不包含根目录绝对路径:
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <stdio.h>
int main(void)
{
char *fileName = "/Dev/test.txt";
char *abs_path = _fullpath(NULL, fileName, 0);
printf("The absolute path is: %s\n", abs_path);
free(abs_path);
return 0;
}
输出结果:
![]()
示例代码 2,仅输入文件名:
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <stdio.h>
int main(void)
{
char *fileName = "test.txt";
char *abs_path = _fullpath(NULL, fileName, 0);
printf("The absolute path is: %s\n", abs_path);
free(abs_path);
return 0;
}
输出结果:
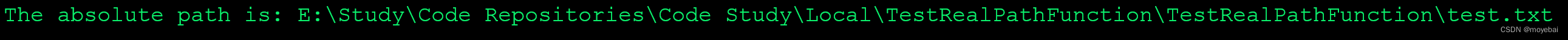
示例代码 3,包含根目录绝对路径:
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <stdio.h>
int main(void)
{
char *fileName = "D:/test.txt";
char *abs_path = _fullpath(NULL, fileName, 0);
printf("The absolute path is: %s\n", abs_path);
free(abs_path);
return 0;
}
输出结果:
![]()
使用命令行输入文件示例代码:
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <stdio.h>
int main(int argc, char **argv)
{
if (argc != 2) {
printf("Usage: myprogram <path>\n");
return 1;
}
char *abs_path = _fullpath(NULL, argv[1], 0);
printf("The absolute path is: %s\n", abs_path);
free(abs_path);
return 0;
}