基于WIN10的64位系统演示
一、写在前面
本期,我们继续学习深度学习图像分割系列的最后一个模型,DeepLabv3。
二、DeepLabv3简介
DeepLabv3 是 DeepLab 系列中的第三个版本,以其高准确性和能够在多个尺度上识别物体轮廓而著称。
以下是 DeepLabv3 的一些关键组件和创新:
(1)Atrous 卷积 (扩张卷积):与标准卷积不同,atrous 卷积可以扩大过滤器的视野,以包括更大的上下文,而不增加参数数量或计算量。通过调整 atrous 卷积的速率参数,可以在 DeepLab 中控制计算特征响应的分辨率。
(2)深度可分离卷积:这是一个因子化卷积,可以减少模型计算,并在修改后的 Aligned Xception 和 MobileNet 基础网络中使用。
(3)Atrous 空间金字塔池化(ASPP):为了在多个尺度上稳健地分割物体,ASPP 模块使用多种采样率和有效视场的滤波器探测传入的卷积特征层,从而在多个尺度上捕获物体以及图像上下文。
(4)完全卷积网络:DeepLabv3 是完全卷积的,即它可以接受任何大小的输入图像,并可以产生相应的输出。
(5)结合更先进的 Backbone 架构:虽然原始的 DeepLab 模型基于 VGGNet 和 ResNet 架构,但 DeepLabv3 可以与更先进的 Backbone 架构,如 Xception 和 MobileNet,结合。
(6)改进的 Atrous 空间金字塔池化 (ASPP):DeepLabv3 通过结合图像级特征来改进 ASPP 模块,这些特征捕获了更长范围的信息,有助于物体分割。
总之,DeepLabv3 在其前身 DeepLabv1 和 DeepLabv2 的基础上显著提高了分割性能。结合强大的编码器架构(如 Xception 和 MobileNet),这一模型在 PASCAL VOC 2012 语义图像分割基准测试中取得了最先进的结果。

三、数据源
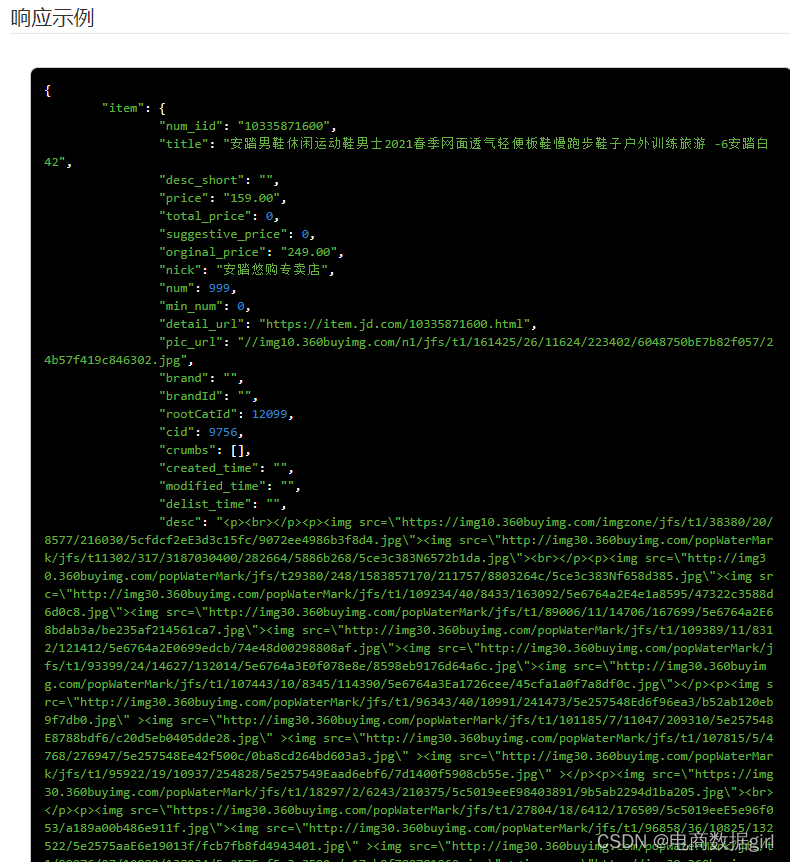
来源于公共数据,主要目的是使用DeepLabv3分割出电子显微镜下的细胞边缘:
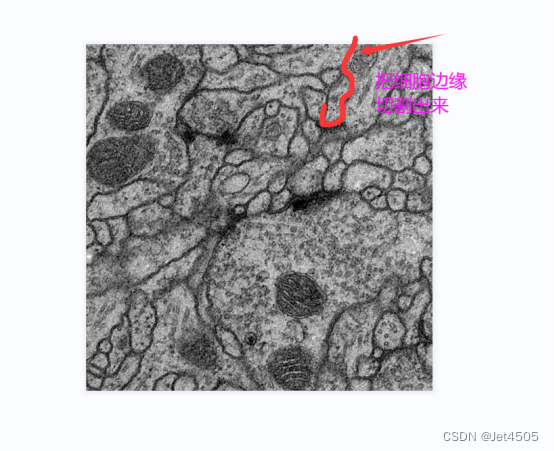
数据分为训练集(train)、训练集的细胞边缘数据(label)以及验证集(test),注意哈,没有提供验证集的细胞边缘数据。因此,后面是算不出验证集的性能参数的。




四、PSPNet实战:
这里,我们使用Pytorch的DeepLabv3预训练模型。
上代码:
(a)数据读取和数据增强
import os
import numpy as np
from skimage.io import imread
from torchvision import transforms, models
from torch.utils.data import DataLoader, Dataset
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
import torch.nn.functional as F
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from sklearn.metrics import roc_curve, auc, accuracy_score, recall_score, precision_score, f1_score
# 设置文件路径
data_folder = 'U-net-master\data_set'
train_images_folder = os.path.join(data_folder, 'train')
label_images_folder = os.path.join(data_folder, 'label')
test_images_folder = os.path.join(data_folder, 'test')
train_images = sorted(os.listdir(train_images_folder))
label_images = sorted(os.listdir(label_images_folder))
test_images = sorted(os.listdir(test_images_folder))
# 定义数据集类
class CustomDataset(Dataset):
def __init__(self, image_paths, mask_paths, transform=None):
self.image_paths = image_paths
self.mask_paths = mask_paths
self.transform = transform
def __len__(self):
return len(self.image_paths)
def __getitem__(self, idx):
image = imread(self.image_paths[idx])
mask = imread(self.mask_paths[idx])
mask[mask == 255] = 1
# Ensure the image has 3 channels
if len(image.shape) == 2:
image = np.stack((image,) * 3, axis=-1)
sample = {'image': image, 'mask': mask}
if self.transform:
sample = self.transform(sample)
return sample
class ToTensorAndNormalize(object):
def __init__(self, mean, std):
self.mean = mean
self.std = std
def __call__(self, sample):
image, mask = sample['image'], sample['mask']
# Swap color axis
# numpy image: H x W x C
# torch image: C x H x W
image = image.transpose((2, 0, 1))
image = torch.from_numpy(image).float()
mask = torch.from_numpy(mask).float()
# Normalize the image
for t, m, s in zip(image, self.mean, self.std):
t.sub_(m).div_(s)
return {'image': image, 'mask': mask}
# Use the new transform for normalization
transform = ToTensorAndNormalize(mean=[0.485, 0.456, 0.406], std=[0.229, 0.224, 0.225])
# 获取数据集
train_dataset = CustomDataset(
image_paths=[os.path.join(train_images_folder, img) for img in train_images],
mask_paths=[os.path.join(label_images_folder, img) for img in label_images],
transform=transform
)
train_loader = DataLoader(train_dataset, batch_size=8, shuffle=True)解读:
其他没什么好说的,就是要注意:上述代码的数据需要人工的安排训练集和测试集。严格按照下面格式放置好各个文件,包括文件夹的命名也不要变动:

(b)DeepLabV3建模
# 获取DeepLabV3模型
device = torch.device('cuda' if torch.cuda.is_available() else 'cpu')
model = models.segmentation.deeplabv3_resnet50(pretrained=False, num_classes=2).to(device)
optimizer = torch.optim.Adam(model.parameters(), lr=1e-4)
criterion = torch.nn.CrossEntropyLoss()
def calc_iou(pred, target):
# Convert prediction to boolean values and flatten
pred = (pred > 0.5).view(-1)
target = target.view(-1)
# Calculate intersection and union
intersection = torch.sum(pred & target)
union = torch.sum(pred | target)
# Avoid division by zero
iou = (intersection + 1e-8) / (union + 1e-8)
return iou.item()
# 初始化损失和IoU的历史记录列表
losses_history = []
ious_history = []
# 训练模型
epochs = 100
for epoch in range(epochs):
model.train()
running_loss = 0.0
total_iou = 0.0
for samples in train_loader:
images = samples['image'].to(device)
masks = samples['mask'].long().to(device)
optimizer.zero_grad()
outputs = model(images)['out']
loss = criterion(outputs, masks)
loss.backward()
optimizer.step()
running_loss += loss.item()
# Calculate IOU
pred_masks = F.softmax(outputs, dim=1)[:, 1]
total_iou += calc_iou(pred_masks, masks)
avg_loss = running_loss / len(train_loader)
avg_iou = total_iou / len(train_loader)
print(f"Epoch {epoch+1}/{epochs}, Loss: {avg_loss}, IOU: {avg_iou}")
# Append to history
losses_history.append(avg_loss)
ious_history.append(avg_iou)迭代的速度也比较慢:
PyTorch 的 torchvision 库为 DeepLabV3 提供了预训练模型。以下是库中可用的预训练模型:
(a)DeepLabV3 with ResNet-101 Backbone:
torchvision.models.segmentation.deeplabv3_resnet101: 这是一个结合了 ResNet-101 结构作为 backbone 的 DeepLabV3 模型。这个模型在 COCO 数据集上进行了预训练,并在 PASCAL VOC 数据集上进行了微调。
(b)DeepLabV3 with ResNet-50 Backbone:
torchvision.models.segmentation.deeplabv3_resnet50: 这是一个结合了 ResNet-50 结构作为 backbone 的 DeepLabV3 模型。这个模型在 COCO 数据集上进行了预训练。
(c)DeepLabV3 with MobileNet Backbone:
尽管 torchvision 的官方版本在发布时没有包含使用 MobileNet 作为 backbone 的 DeepLabV3,但 MobileNet 由于其轻量和适合移动设备的特性,经常被考虑作为分割任务的 backbone。
要使用这些预训练模型,您可以简单地使用以下代码:
import torchvision.models as models
# 使用 ResNet-101 作为 backbone 的 DeepLabV3
model = models.segmentation.deeplabv3_resnet101(pretrained=True)
# 使用 ResNet-50 作为 backbone 的 DeepLabV3
model = models.segmentation.deeplabv3_resnet50(pretrained=True)pretrained=True 表示加载与训练模型相关的权重。如果你只想获取模型结构,可以将其设置为 False。
(c)各种性能指标打印和可视化
###################################误差曲线#######################################
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
# 设置matplotlib支持中文显示
plt.rcParams['font.sans-serif'] = ['SimHei']
plt.rcParams['axes.unicode_minus'] = False
# 绘制训练损失和IoU
plt.figure(figsize=(12, 5))
# 绘制损失
plt.subplot(1, 2, 1)
plt.plot(losses_history, label='训练损失')
plt.title('损失随迭代次数的变化')
plt.xlabel('迭代次数')
plt.ylabel('损失')
plt.legend()
# 绘制IoU
plt.subplot(1, 2, 2)
plt.plot(ious_history, label='训练IoU')
plt.title('IoU随迭代次数的变化')
plt.xlabel('迭代次数')
plt.ylabel('IoU')
plt.legend()
plt.tight_layout()
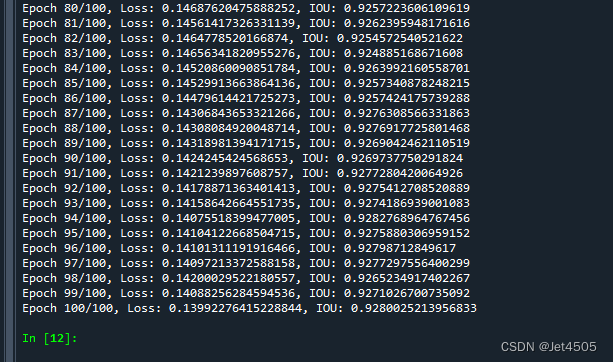
plt.show()直接看结果:

误差和IOU曲线,看起来还可以,100次迭代达到90%。
##############################评价指标,对于某一个样本#######################################
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from sklearn.metrics import roc_curve, auc, accuracy_score, recall_score, precision_score, f1_score
def calc_iou(y_true, y_pred):
intersection = np.logical_and(y_true, y_pred)
union = np.logical_or(y_true, y_pred)
return np.sum(intersection) / np.sum(union)
# 从数据集中获取一个样本
sample = train_dataset[0]
sample_img = sample['image'].unsqueeze(0).to(device)
sample_mask = sample['mask'].cpu().numpy()
# 使用模型进行预测
with torch.no_grad():
model.eval()
prediction = model(sample_img)['out']
# 取前景类并转为CPU
predicted_mask = prediction['out'][0, 1].cpu().numpy()
predicted_mask = (predicted_mask > 0.5).astype(np.uint8)
# 计算ROC曲线
fpr_train, tpr_train, _ = roc_curve(sample_mask.ravel(), predicted_mask.ravel())
# 计算AUC
auc_train = auc(fpr_train, tpr_train)
# 计算其他评估指标
pixel_accuracy_train = accuracy_score(sample_mask.ravel(), predicted_mask.ravel())
iou_train = calc_iou(sample_mask, predicted_mask)
accuracy_train = accuracy_score(sample_mask.ravel(), predicted_mask.ravel())
recall_train = recall_score(sample_mask.ravel(), predicted_mask.ravel())
precision_train = precision_score(sample_mask.ravel(), predicted_mask.ravel())
f1_train = f1_score(sample_mask.ravel(), predicted_mask.ravel())
# 绘制ROC曲线
plt.figure()
plt.plot(fpr_train, tpr_train, color='blue', lw=2, label='Train ROC curve (area = %0.2f)' % auc_train)
plt.xlabel('False Positive Rate')
plt.ylabel('True Positive Rate')
plt.title('ROC Curve')
plt.legend(loc='lower right')
plt.show()
# 定义指标列表
metrics = [
("Pixel Accuracy", pixel_accuracy_train),
("IoU", iou_train),
("Accuracy", accuracy_train),
("Recall", recall_train),
("Precision", precision_train),
("F1 Score", f1_train)
]
# 打印表格的头部
print("+-----------------+------------+")
print("| Metric | Value |")
print("+-----------------+------------+")
# 打印每个指标的值
for metric_name, metric_value in metrics:
print(f"| {metric_name:15} | {metric_value:.6f} |")
print("+-----------------+------------+")注意哈,这个代码只是针对某一个样本的结果:
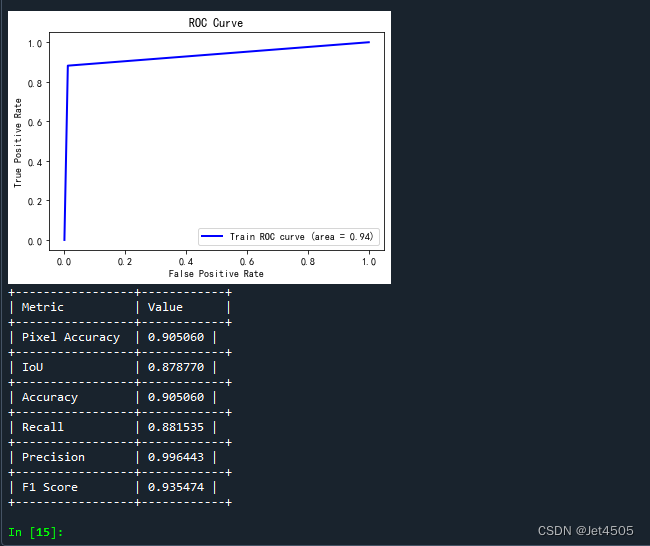
ROC曲线:这里存疑,感觉没啥意义,而且这个曲线看起来有问题,是一个三点折线。
一些性能指标,稍微解释,主要是前两个:
A)Pixel Accuracy:
定义:它是所有正确分类的像素总数与图像中所有像素的总数的比率。
计算:(正确预测的像素数量) / (所有像素数量)。
说明:这个指标评估了模型在每个像素级别上的准确性。但在某些场景中(尤其是当类别非常不平衡时),这个指标可能并不完全反映模型的表现。
B)IoU (Intersection over Union):
定义:对于每个类别,IoU 是该类别的预测结果(预测为该类别的像素)与真实标签之间的交集与并集的比率。
计算:(预测与真实标签的交集) / (预测与真实标签的并集)。
说明:它是一个很好的指标,因为它同时考虑了假阳性和假阴性,尤其在类别不平衡的情况下。
C)Accuracy:
定义:是所有正确分类的像素与所有像素的比例,通常与 Pixel Accuracy 相似。
计算:(正确预测的像素数量) / (所有像素数量)。
D)Recall (or Sensitivity or True Positive Rate):
定义:是真实正样本被正确预测的比例。
计算:(真阳性) / (真阳性 + 假阴性)。
说明:高召回率表示少数阳性样本不容易被漏掉。
E)Precision:
定义:是被预测为正的样本中实际为正的比例。
计算:(真阳性) / (真阳性 + 假阳性)。
说明:高精度表示假阳性的数量很少。
F)F1 Score:
定义:是精度和召回率的调和平均值。它考虑了假阳性和假阴性,并试图找到两者之间的平衡。
计算:2 × (精度 × 召回率) / (精度 + 召回率)。
说明:在不平衡类别的场景中,F1 Score 通常比单一的精度或召回率更有用。
##############################评价指标,对于全部训练集的样本#######################################
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from sklearn.metrics import roc_curve, auc, accuracy_score, recall_score, precision_score, f1_score
# 初始化变量来存储评估指标的累积值和真实标签与预测值
total_pixel_accuracy = 0
total_iou = 0
total_accuracy = 0
total_recall = 0
total_precision = 0
total_f1 = 0
total_auc = 0
all_true_masks = []
all_predicted_masks = []
# 遍历整个训练集
for sample in train_dataset:
sample_img = sample['image'].unsqueeze(0).to(device)
sample_mask = sample['mask'].cpu().numpy()
# 使用模型进行预测
with torch.no_grad():
model.eval()
prediction = model(sample_img)['out']
# 取前景类并转为CPU
predicted_mask = prediction['out'][0, 1].cpu().numpy()
predicted_mask = (predicted_mask > 0.5).astype(np.uint8)
# 收集真实标签和预测值
all_true_masks.extend(sample_mask.ravel())
all_predicted_masks.extend(predicted_mask.ravel())
# 计算ROC曲线和AUC
fpr_train, tpr_train, _ = roc_curve(all_true_masks, all_predicted_masks)
avg_auc = auc(fpr_train, tpr_train)
# 计算其他评估指标
avg_pixel_accuracy = accuracy_score(all_true_masks, all_predicted_masks)
avg_iou = calc_iou(np.array(all_true_masks), np.array(all_predicted_masks))
avg_accuracy = accuracy_score(all_true_masks, all_predicted_masks)
avg_recall = recall_score(all_true_masks, all_predicted_masks)
avg_precision = precision_score(all_true_masks, all_predicted_masks)
avg_f1 = f1_score(all_true_masks, all_predicted_masks)
# 绘制ROC曲线
plt.figure()
plt.plot(fpr_train, tpr_train, color='blue', lw=2, label='Train ROC curve (area = %0.2f)' % avg_auc)
plt.xlabel('False Positive Rate')
plt.ylabel('True Positive Rate')
plt.title('ROC Curve')
plt.legend(loc='lower right')
plt.show()
# 打印评估指标的平均值
metrics = [
("Pixel Accuracy", avg_pixel_accuracy),
("IoU", avg_iou),
("Accuracy", avg_accuracy),
("Recall", avg_recall),
("Precision", avg_precision),
("F1 Score", avg_f1),
("AUC", avg_auc)
]
print("+-----------------+------------+")
print("| Metric | Value |")
print("+-----------------+------------+")
for metric_name, metric_value in metrics:
print(f"| {metric_name:15} | {metric_value:.6f} |")
print("+-----------------+------------+")这个结果是针对有所训练集的:

(d)查看验证集和验证集的具体分割情况
#######################看训练集图片的具体分割效果###########################################
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
# 选择一张训练集图片
img_index = 20
sample = train_dataset[img_index]
train_img = sample['image'].unsqueeze(0).to(device) # 为batch_size添加一个维度
with torch.no_grad():
model.eval()
prediction = model(train_img)
# 使用阈值处理预测掩码
mask_threshold = 0.5
predicted_mask = prediction['out'][0, 1].cpu().numpy() # 选择前景类
predicted_mask = (predicted_mask > mask_threshold).astype(np.uint8)
# 使用matplotlib来展示原始图像、真实掩码和预测的分割图像
plt.figure(figsize=(15, 5))
plt.subplot(1, 3, 1)
plt.title("Original Image")
# Normalize the image to [0,1] range
denorm_img = train_img[0].permute(1, 2, 0).cpu().numpy()
denorm_img = denorm_img - denorm_img.min()
denorm_img = denorm_img / denorm_img.max()
plt.imshow(denorm_img.clip(0, 1))
plt.subplot(1, 3, 2)
plt.title("True Segmentation")
true_mask = sample['mask'].cpu().numpy()
if len(true_mask.shape) == 1: # Ensure mask is 2D
true_mask = true_mask.reshape(int(np.sqrt(true_mask.shape[0])), -1)
plt.imshow(true_mask, cmap='gray')
plt.subplot(1, 3, 3)
plt.title("Predicted Segmentation")
plt.imshow(predicted_mask, cmap='gray')
plt.show()
#######################看测试集图片的具体分割效果###########################################
#看具体分割的效果
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
test_dataset = CustomDataset(
image_paths=[os.path.join(test_images_folder, img) for img in test_images],
mask_paths=[os.path.join(label_images_folder, img) for img in label_images], # 这里我假设您的测试集的标签也在label_images_folder中
transform=transform
)
# 选择一张测试图片
img_index = 20
sample = test_dataset[img_index]
test_img = sample['image'].unsqueeze(0).to(device)
with torch.no_grad():
model.eval()
prediction = model(test_img)
# 使用阈值处理预测掩码
mask_threshold = 0.5
pred_mask = prediction['out'][0, 1].cpu().numpy()
pred_mask = (pred_mask > mask_threshold).astype(np.uint8)
# 使用matplotlib来展示原始图像、真实掩码和预测的分割图像
plt.figure(figsize=(15, 5))
plt.subplot(1, 3, 1)
plt.title("Original Image")
# Normalize the image to [0,1] range
denorm_img = test_img[0].permute(1, 2, 0).cpu().numpy()
denorm_img = denorm_img - denorm_img.min()
denorm_img = denorm_img / denorm_img.max()
plt.imshow(denorm_img.clip(0, 1))
plt.subplot(1, 3, 3)
plt.title("Predicted Segmentation")
plt.imshow(pred_mask, cmap='gray')
plt.show()查看训练集分割效果:

查看验证集分割效果(验证集没有label,所以中间是空的):
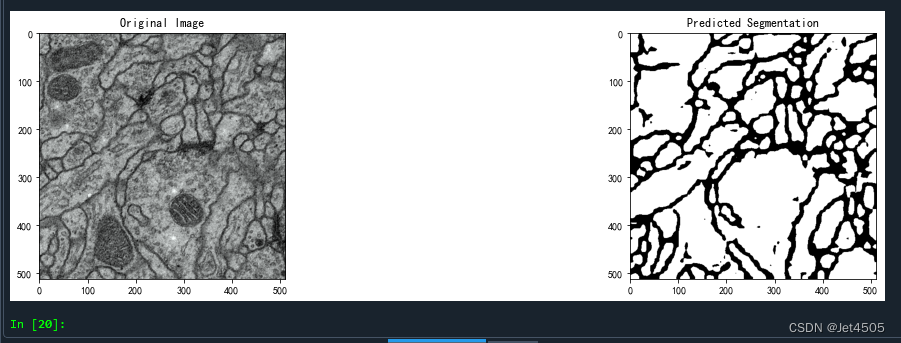
总体来看,达到预期。
五、写在后面
略~
六、数据
链接:https://pan.baidu.com/s/1Cb78MwfSBfLwlpIT0X3q9Q?pwd=u1q1
提取码:u1q1