功能实现:
- //1:先计算每个字符的权重
- //2:构建哈夫曼树
- //3:得出每个字符的哈夫曼编码。
- //4:根据哈夫曼编码转化为字符
代码实现:
// 哈夫曼编码.cpp : 此文件包含 "main" 函数。程序执行将在此处开始并结束。
//1:先计算每个字符的权重
//2:构建哈夫曼树
//3:得出每个字符的哈夫曼编码。
#include<iostream>
#include<string>
using namespace std;
class node {
public:
char value;
int weight;//权重
node* left;
node* right;
string code;//编码
int zhi;
node() {
left = NULL;
right = NULL;
zhi = 0;
weight = 0;
}
node( int a) {
this->weight = a;
}
void showa() {
cout << value<<" "<< weight<<" "<<code<<endl;
}
};
void note(int notes[][26], string target) { //进行接受整理
for (int i = 0; i < 26; i++) {//记录每个字母出现次数
notes[0][i] = 97 + i;//将本中第一行都分别记录一个小写字母的编码,
}
for (char a : target) {//auto是一个占位符(auto a:target),根据后面的变量,自己推断自己是什么类型,用于变量类型很长
for (int i = 0; i < 26; i++) {
if (notes[0][i] == a) {
notes[1][i]++;
break;
}
}
}
}
void chang_shuzu(node target1[],int& j,int notes[][26]) {//创建所需数组
cout << "电文中出现的字符及其出现的次数如下" << endl;
for (int i = 0; i < 26; i++) {
if (notes[1][i] != 0) {
cout << (char)notes[0][i] << ":" << notes[1][i] << endl;
target1[j].value = (char)notes[0][i];//构建存储字符和权重的数组
target1[j].zhi = 1;
target1[j++].weight = notes[1][i];
}
}
}
void maopao(node target1[],int last,int farst) {//运用冒泡排序,将数组根据权重变成递增数组
for (int i = farst; i < last-1; i++) {
for (int j = farst; j < last- 1; j++) {
if (target1[j].weight > target1[j + 1].weight) {
node temp;
temp = target1[j];
target1[j] = target1[j + 1];
target1[j + 1] = temp;
}
}
}
}
void change_hafuma(node target1[],int &farst,node target2[],int &s) {//取出数组的前两个,将其投入到创建链表中,后来再将数组前两个删除,存入新结合的树
target2[s].weight = target1[farst].weight + target1[farst + 1].weight;
target2[s+1]= target1[farst];
target2[s+2] = target1[farst + 1];
target2[s].left = &target2[s+1];
target2[s].right = &target2[s+2];
farst++;
target1[farst] = target2[s];
s = s + 3;
}
void show(node* x,string h,node target3[],int &e) {//h为编码
if (x->zhi==1) {//则此时指向的是叶子节点
x->code = h;
cout << x->value << ':' << h<<endl;
target3[e].value = x->value;
target3[e++].code = x->code;
return;
}
show(x->left, h + "0", target3,e);
show(x->right, h +"1", target3,e);
}
void show2(string target,node target3[],int last) {//展示电文对应编码
cout << "电文对应编码为:" << endl;
for (char a : target) {
for (int i = 0; i < 100; i++) {
if (a == target3[i].value) {
cout << target3[i].code << " ";
break;
}
}
}
cout << endl;
}
void decode(node target3[],int last){
string target;
string p="";
cout << "输入0-1二进制串(‘e’退出)";
cin >> target;
while (target!="e") {
string he = "";
for (char a : target) {
he += a;
for (int i = 0; i < last; i++) {
if (he == target3[i].code) {
p += target3[i].value;
p += " ";
he = "";
break;
}
}
}
if (he != "") {
cout << "编码错误,无法转换!"<<endl<<endl;
}
else
{
cout <<"编译转换的电文为:" << p<<endl << endl;
}
p = "";
cout << "输入0-1二进制串(‘e’退出)";
cin >> target;
}
}
int main() {
//接收端
int notes[2][26] = { 0 };//令其初始都为0.
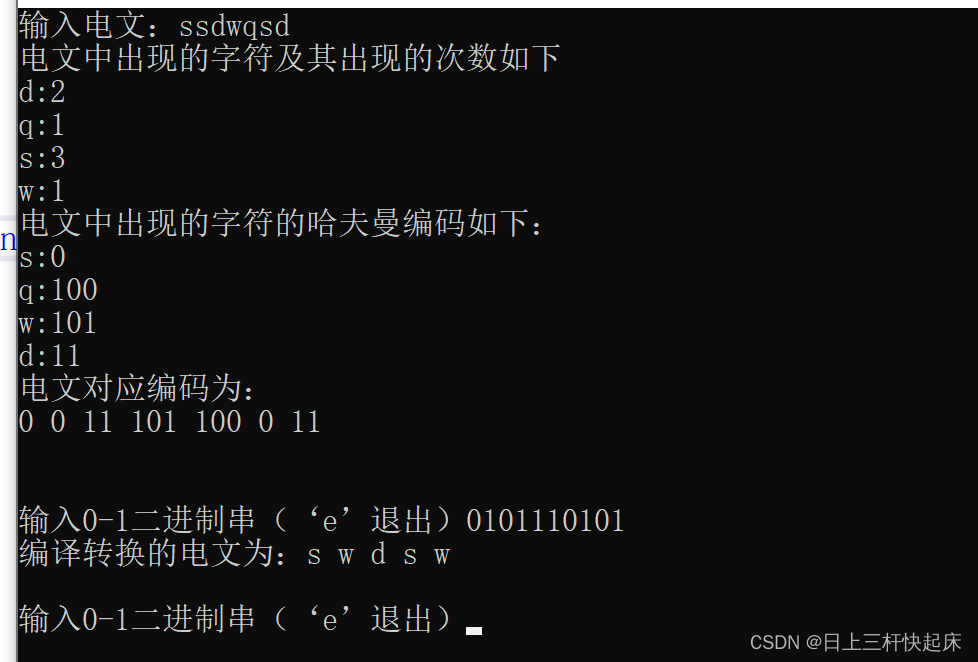
cout << "输入电文:";
string target;
cin >> target;//用了for—each循环遍历
note(notes,target);
node target1[26];//初始记录有效节点
node target2[100];//存储哈夫曼树所有节点
node target3[26];//记录有效节点,此时其内节点中有每个节点的code值
int last = 0;//指向最后一个有效数组元素的后一个
int farst = 0;
int s = 0;//存哈夫曼节点的数组
chang_shuzu(target1, last, notes);//创建数组
//构建哈夫曼树
int z = 0;
int e = 0;
while (last - farst != 1) {
maopao(target1,last,farst);
change_hafuma(target1, farst,target2,s);
}
node x;
x = target1[farst];
cout << "电文中出现的字符的哈夫曼编码如下:"<<endl;
show(&x, "",target3,e);
show2(target,target3, last);
cout << endl << endl;;
decode(target3,last);
}
效果展示: