list容器概念
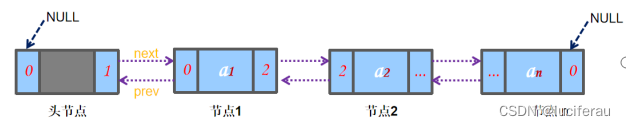
list是一个双向链表容器,可高效地进行插入删除元素。
List 特点:
- list不可以随机存取元素,所以不支持at.(position)函数与[]操作符。可以对其迭代器执行++,但是不能这样操作迭代器:it+3
- 使用时包含 #include <list>
list对象的构造函数
list同样采用模板类实现,对象的默认构造形式:list<T> listT; 如:
- list<int> lstInt; //定义一个存放int的list容器。
- list<float> lstFloat; //定义一个存放float的list容器。
- list<string> lstString; //定义一个存放string的list容器。
注意:尖括号内还可以设置指针类型或自定义类型
list对象的带参构造函数
方式一:list(beg,end); //将[beg, end)区间中的元素拷贝给本身。
方式二:list(n,elem); //构造函数将n个elem拷贝给本身。
方式三:list(const list &lst); //拷贝构造函数。
list<int> lstInt1;
lstInt1.push_back(1);
lstInt1.push_back(2);
lstInt1.push_back(3);
list<int> lstInt2(lstInt1.begin(),lstInt1.end()); //1 2 3
list<int> lstInt3(5,8); //8 8 8 8 8
list<int> lstInt4(lstIntA); //1 2 3
list头尾的添加移除操作

list<int> lstInt;
lstInt.push_back(1);
lstInt.push_back(2);
lstInt.push_back(3);
lstInt.push_back(4);
lstInt.push_back(5);
lstInt.pop_front();
lstInt.pop_front();
lstInt.push_front(11);
lstInt.push_front(12);
lstInt.pop_back();
lstInt.pop_back();
// lstInt {12, 11, 3}list数据的读取
- list.front(); //返回第一个元素。
- list.back(); //返回最后一个元素。
list<int> lstInt;
lstInt.push_back(1);
lstInt.push_back(2);
lstInt.push_back(3);
lstInt.push_back(4);
lstInt.push_back(5);
int iFront = lstInt.front(); //1
int iBack = lstInt.back(); //5
lstInt.front() = 11; //11
lstInt.back() = 19; //19list与迭代器

list<int> lstInt;
lstInt.push_back(1);
lstInt.push_back(3);
lstInt.push_back(5);
lstInt.push_back(7);
lstInt.push_back(9);
for (list<int>::iterator it=lstInt.begin(); it!=lstInt.end(); ++it)
{
cout << *it;
cout << " ";
}
for (list<int>::reverse_iterator rit=lstInt.rbegin(); rit!=lstInt.rend(); ++rit)
{
cout << *rit;
cout << " ";
}list的赋值

llist<int> lstIntA,lstIntB,lstIntC,lstIntD;
lstIntA.push_back(1);
lstIntA.push_back(3);
lstIntA.push_back(5);
lstIntA.push_back(7);
lstIntA.push_back(9);
lstIntB.assign(lstIntA.begin(),lstIntA.end()); //1 3 5 7 9
lstIntB.assign(++lstIntA.begin(),--lstIntA.end()); //3 5 7
lstIntC.assign(5,8); //8 8 8 8 8
lstIntD = lstIntA; //1 3 5 7 9
lstIntC.swap(lstIntD); //互换list的大小

list<int> lstIntA;
lstIntA.push_back(1);
lstIntA.push_back(2);
lstIntA.push_back(3);
if (!lstIntA.empty())
{
int iSize = lstIntA.size(); //3
lstIntA.resize(5); //1 2 3 0 0
lstIntA.resize(7,1); //1 2 3 0 0 1 1
lstIntA.resize(5); //1 2 3 0 0
}
list的插入

list<int> listA;
list<int> listB;
listA.push_back(1);
listA.push_back(2);
listA.push_back(3);
listA.push_back(4);
listA.push_back(5);
listB.push_back(11);
listB.push_back(12);
listB.push_back(13);
listB.push_back(14);
listA.insert(listA.begin(), -1); //{-1, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5}
listA.insert( ++listA.begin(), 2, -2); //{-1, -2, -2, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5}
listA.insert(listA.begin() , listB.begin() , listB.end()); //{11, 12, 13, 14, -1, -2, -2, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5}
for(list<int>::iterator it = listA.begin(); it!=listA.end(); it++){
cout<< *it<<endl;
}list的删除

// demo 15-32
#include <list>
#include <vector>
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main(void){
//list 删除元素
list<int> listA;
listA.push_back(1);
listA.push_back(2);
listA.push_back(3);
listA.push_back(4);
listA.push_back(5);
//erase 的用法
list<int>::iterator itBegin=listA.begin();
++ itBegin;
list<int>::iterator itEnd=listA.begin();
++ itEnd;
++ itEnd;
++ itEnd;
listA.erase(itBegin,itEnd);//此时容器lstInt包含按顺序的1, 4, 5三个元素。
listA.erase(listA.begin());//此时容器lstInt包含按顺序的4, 5三个元素。
listA.push_back(4); // 4, 5, 4
listA.insert(listA.end(), 5, 4); //4, 5, 4, 4, 4, 4, 4, 4
/*remove 删除元素*/
//方式一 直接调用remove 方法
//listA.remove(4);
//方式二 遍历然后逐个删除
for(list<int>::iterator it=listA.begin(); it!=listA.end(); ){
if(*it == 4){
it =listA.erase(it); //相当于执行了++
}else {
it++;
}
}
for (list<int>::iterator it=listA.begin(); it!=listA.end(); ++it)
{
cout << *it;
cout << " ";
}
system("pause");
return 0;
}list的反向排列
- list.reverse(); //反转链表,比如list包含1, 2, 3, 4, 5五个元素,运行此方
法后,list就包含5, 4, 3, 2, 1元素。
list<int> listA;
listA.push_back(1);
listA.push_back(2);
listA.push_back(3);
listA.push_back(4);
listA.push_back(5);
listA.reverse(); //5, 4, 3, 2, 1