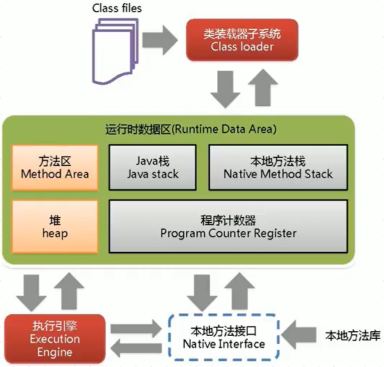
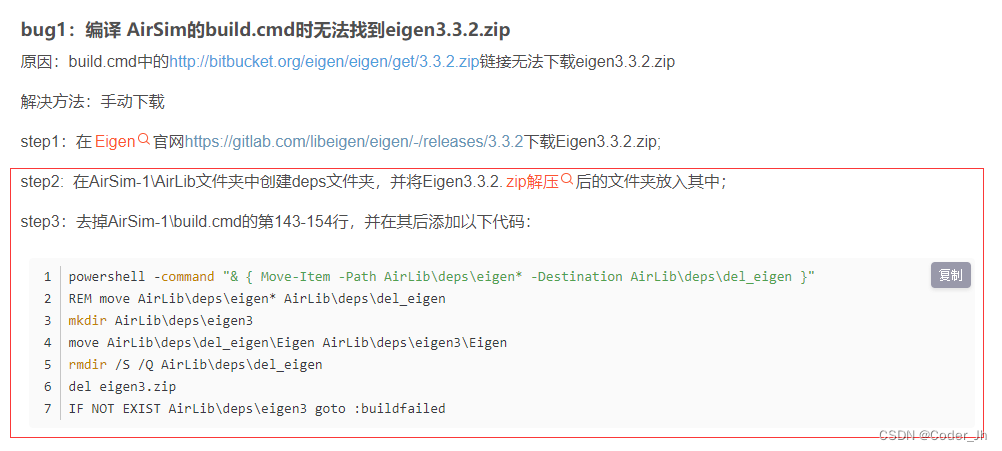
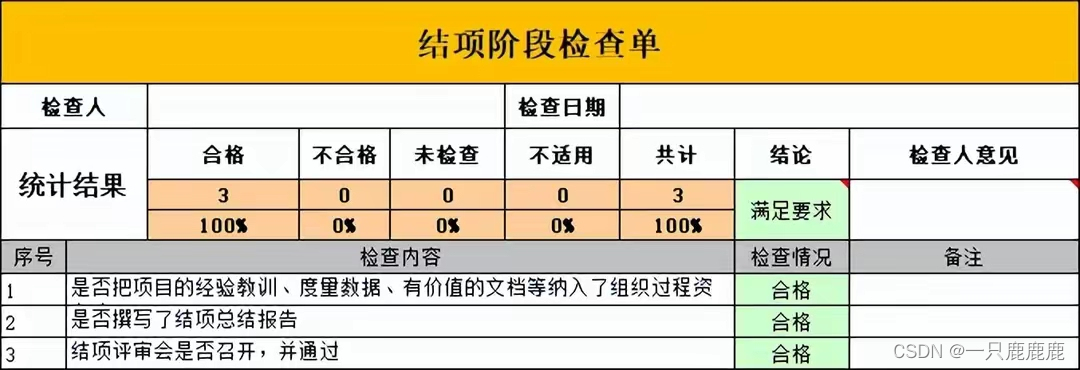
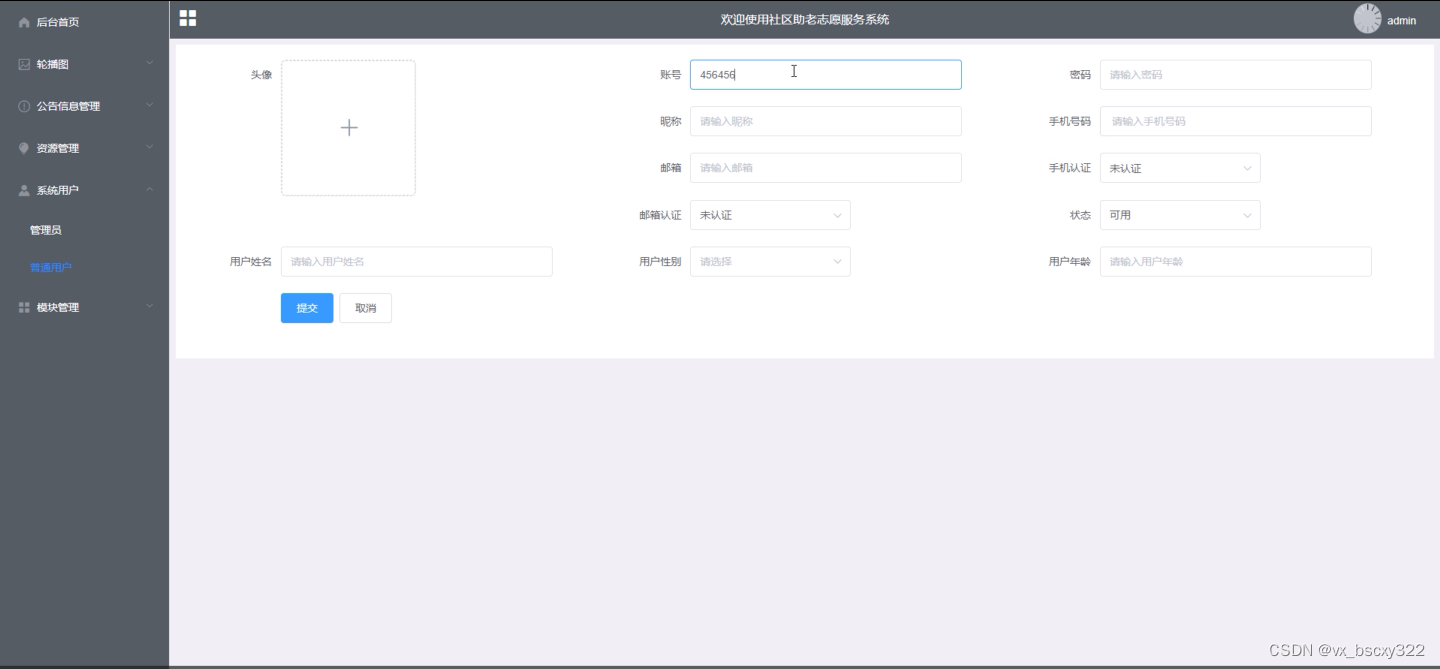
1.GlobalTransactionalInterceptor 对事务方法对增强
我们已经知道 GlobalTransactionScanner 会给bean的类或方法上面标注有@GlobalTransactional 注解 和 @GlobalLock的 添加一个 advisor (DefaultPointcutAdvisor ,advisor = 绑定了PointCut 的 advise)
而此处的 DefaultPointcutAdvisor 的 advice 为 GlobalTransactionalInterceptor,PointCut 为 Pointcut.TRUE(匹配所有方法)
然后由 DynamicAdvisedInterceptor 回调函数 获取当前 bean对应的 AdvisedSupport , 从中遍历所有的 advisor,然后再获取 此 advisor 绑定的 PointCut 对目标方法进行匹配 ,如果满足,则添加到 拦截器链路中,后续递归调用
接下来我们看下 GlobalTransactionalInterceptor 对目标方法做了哪些增强
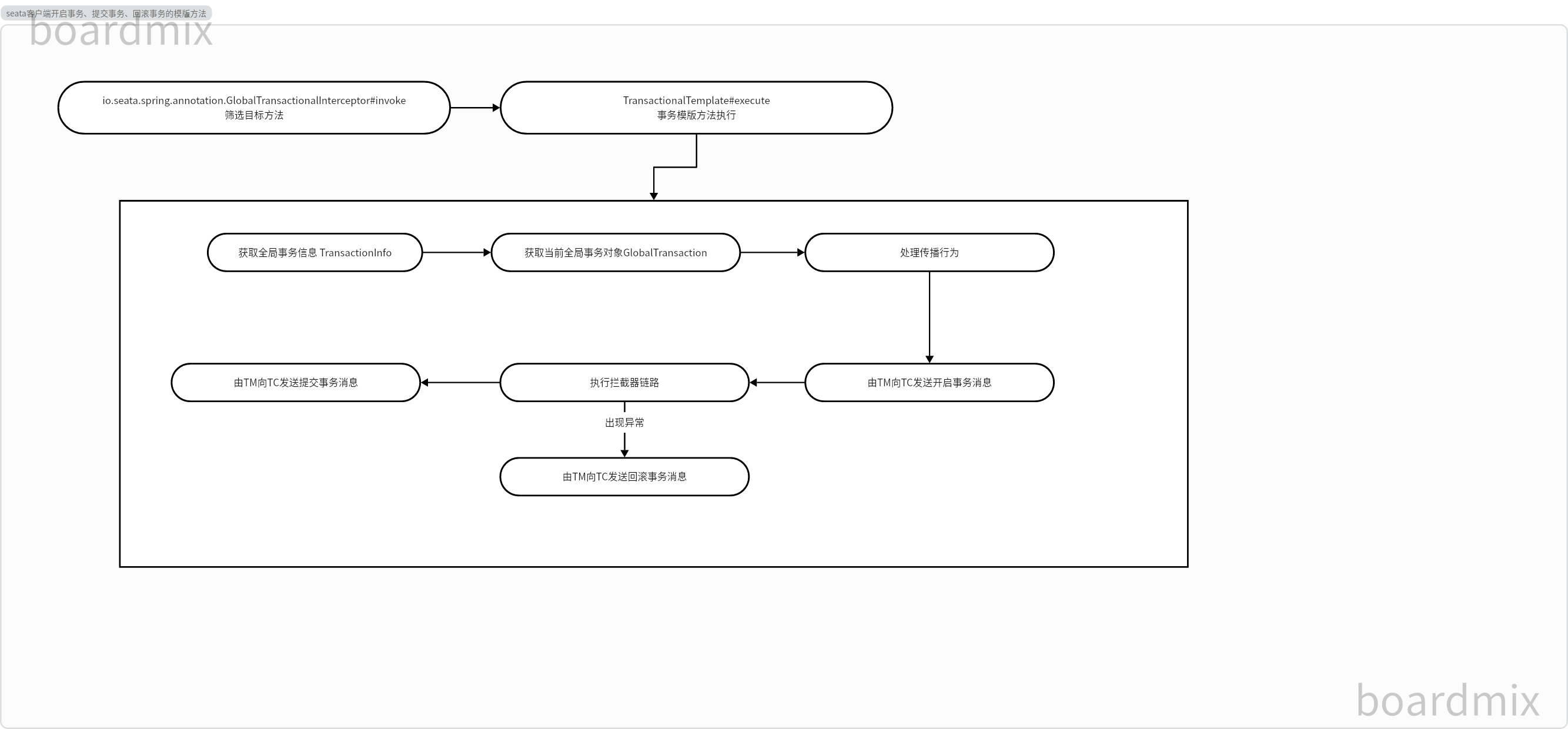
io.seata.spring.annotation.GlobalTransactionalInterceptor#invoke
public Object invoke(final MethodInvocation methodInvocation) throws Throwable {
Class<?> targetClass =
methodInvocation.getThis() != null ? AopUtils.getTargetClass(methodInvocation.getThis()) : null;
Method specificMethod = ClassUtils.getMostSpecificMethod(methodInvocation.getMethod(), targetClass);
// Method.getDeclaringClass 获取方法声明的类 如果是静态方法,则返回方法所在类;如果是实例方法,则返回方法所在类的超类
//!specificMethod.getDeclaringClass().equals(Object.class) 排除Object方法
if (specificMethod != null && !specificMethod.getDeclaringClass().equals(Object.class)) {
final Method method = BridgeMethodResolver.findBridgedMethod(specificMethod);
//默认包装生成的DefaultPointcutAdvisor 拦截所有的方法
// public DefaultPointcutAdvisor(Advice advice) {
// this(Pointcut.TRUE, advice);
// }
//因此在此处对方法进行过滤 只处理标注了@GlobalTransactional 和 @GlobalLock 注解的方法
final GlobalTransactional globalTransactionalAnnotation =
getAnnotation(method, targetClass, GlobalTransactional.class);
final GlobalLock globalLockAnnotation = getAnnotation(method, targetClass, GlobalLock.class);
boolean localDisable = disable || (degradeCheck && degradeNum >= degradeCheckAllowTimes);
if (!localDisable) {
if (globalTransactionalAnnotation != null || this.aspectTransactional != null) {
//根据@GlobalTransactional 注解的属性封装事务切面信息
AspectTransactional transactional;
if (globalTransactionalAnnotation != null) {
transactional = new AspectTransactional(globalTransactionalAnnotation.timeoutMills(),
globalTransactionalAnnotation.name(), globalTransactionalAnnotation.rollbackFor(),
globalTransactionalAnnotation.rollbackForClassName(),
globalTransactionalAnnotation.noRollbackFor(),
globalTransactionalAnnotation.noRollbackForClassName(),
globalTransactionalAnnotation.propagation(),
globalTransactionalAnnotation.lockRetryInterval(),
globalTransactionalAnnotation.lockRetryTimes());
} else {
transactional = this.aspectTransactional;
}
//处理全局事务
return handleGlobalTransaction(methodInvocation, transactional);
} else if (globalLockAnnotation != null) {
//处理全局锁
return handleGlobalLock(methodInvocation, globalLockAnnotation);
}
}
}
return methodInvocation.proceed();
}
2.全局事务执行器 TransactionalExecutor 的匿名实现
io.seata.spring.annotation.GlobalTransactionalInterceptor#handleGlobalTransaction
Object handleGlobalTransaction(final MethodInvocation methodInvocation,
final AspectTransactional aspectTransactional) throws Throwable {
boolean succeed = true;
try {
return transactionalTemplate.execute(new TransactionalExecutor() {
@Override
public Object execute() throws Throwable {
// 责任链模式 继续执行链路上的其他拦截器方法,如果已经执行到最后一个
// 则直接执行目标方法
return methodInvocation.proceed();
}
public String name() {
String name = aspectTransactional.getName();
if (!StringUtils.isNullOrEmpty(name)) {
return name;
}
return formatMethod(methodInvocation.getMethod());
}
@Override
public TransactionInfo getTransactionInfo() {
//注解解析
// reset the value of timeout
int timeout = aspectTransactional.getTimeoutMills();
if (timeout <= 0 || timeout == DEFAULT_GLOBAL_TRANSACTION_TIMEOUT) {
timeout = defaultGlobalTransactionTimeout;
}
TransactionInfo transactionInfo = new TransactionInfo();
transactionInfo.setTimeOut(timeout);
transactionInfo.setName(name());
transactionInfo.setPropagation(aspectTransactional.getPropagation());
transactionInfo.setLockRetryInterval(aspectTransactional.getLockRetryInterval());
transactionInfo.setLockRetryTimes(aspectTransactional.getLockRetryTimes());
Set<RollbackRule> rollbackRules = new LinkedHashSet<>();
for (Class<?> rbRule : aspectTransactional.getRollbackFor()) {
rollbackRules.add(new RollbackRule(rbRule));
}
for (String rbRule : aspectTransactional.getRollbackForClassName()) {
rollbackRules.add(new RollbackRule(rbRule));
}
for (Class<?> rbRule : aspectTransactional.getNoRollbackFor()) {
rollbackRules.add(new NoRollbackRule(rbRule));
}
for (String rbRule : aspectTransactional.getNoRollbackForClassName()) {
rollbackRules.add(new NoRollbackRule(rbRule));
}
transactionInfo.setRollbackRules(rollbackRules);
return transactionInfo;
}
});
} catch (TransactionalExecutor.ExecutionException e) {
TransactionalExecutor.Code code = e.getCode();
//根据异常类型执行不同的钩子方法
switch (code) {
case RollbackDone:
throw e.getOriginalException();
case BeginFailure:
succeed = false;
failureHandler.onBeginFailure(e.getTransaction(), e.getCause());
throw e.getCause();
case CommitFailure:
succeed = false;
failureHandler.onCommitFailure(e.getTransaction(), e.getCause());
throw e.getCause();
case RollbackFailure:
failureHandler.onRollbackFailure(e.getTransaction(), e.getOriginalException());
throw e.getOriginalException();
case RollbackRetrying:
failureHandler.onRollbackRetrying(e.getTransaction(), e.getOriginalException());
throw e.getOriginalException();
default:
throw new ShouldNeverHappenException(String.format("Unknown TransactionalExecutor.Code: %s", code));
}
} finally {
if (degradeCheck) {
EVENT_BUS.post(new DegradeCheckEvent(succeed));
}
}
}
将事务参数信息封装到TransactionInfo对象中,如事务传播行为,超时时间,超时重试次数,异常回滚类型等等,
如果出现异常,则根据异常类型分别执行不同的钩子方法
并且会继续回调拦截器链路上的其他拦截器方法
3.TransactionalTemplate 全局事务执行过程的模版方法
io.seata.tm.api.TransactionalTemplate#execute
public Object execute(TransactionalExecutor business) throws Throwable {
// 1. Get transactionInfo
//获取@GlobalTransation注解的属性封装的TransactionInfo
TransactionInfo txInfo = business.getTransactionInfo();
if (txInfo == null) {
throw new ShouldNeverHappenException("transactionInfo does not exist");
}
// 1.1 Get current transaction, if not null, the tx role is 'GlobalTransactionRole.Participant'.
// GlobalTransactionContext 全局事务上下文对象 用于创建一个新事务,或者获取当前事务
// GlobalTransactionContext.getCurrent - > RootContext.getXID -> ContextCore.get
// ContextCore 是一个接口 seata有两个实现 FastThreadLocalContextCore ThreadLocalContextCore 都是基于ThreadLocal存储XID
GlobalTransaction tx = GlobalTransactionContext.getCurrent();
// 1.2 Handle the transaction propagation.
// 获取当前事务的传播行为
Propagation propagation = txInfo.getPropagation();
// 用于存储被挂起的事务XID
SuspendedResourcesHolder suspendedResourcesHolder = null;
try {
//处理事务的传播行为
switch (propagation) {
//如果当前事务的传播行为是 NOT_SUPPORTED 则以非事务的方式执行调用methodInvocation.proceed()
// 如果当前拦截器不为拦截链的最后一个,则将获取下一个拦截器执行invoke方法,如果是最后一个,则直接执行目标方法
case NOT_SUPPORTED:
// If transaction is existing, suspend it.
//如果当前存在全局事务,则挂起当前事务
if (existingTransaction(tx)) {
suspendedResourcesHolder = tx.suspend();
}
// Execute without transaction and return.
// 继续执行拦截器链
return business.execute();
case REQUIRES_NEW:
// If transaction is existing, suspend it, and then begin new transaction.
// 如果当前存在事务 则挂起当前事务 并创建一个新的事务
if (existingTransaction(tx)) {
suspendedResourcesHolder = tx.suspend();
tx = GlobalTransactionContext.createNew();
}
// Continue and execute with new transaction
break;
case SUPPORTS:
// If transaction is not existing, execute without transaction.
// 如果不存在事务 则跳过当前事务拦截器 执行拦截器链并返回
if (notExistingTransaction(tx)) {
return business.execute();
}
// Continue and execute with new transaction
break;
case REQUIRED:
// If current transaction is existing, execute with current transaction,
// else continue and execute with new transaction.
break;
case NEVER:
// If transaction is existing, throw exception.
// 有事务抛出异常
if (existingTransaction(tx)) {
throw new TransactionException(
String.format("Existing transaction found for transaction marked with propagation 'never', xid = %s"
, tx.getXid()));
} else {
// Execute without transaction and return.
return business.execute();
}
case MANDATORY:
// If transaction is not existing, throw exception.
// 要求必须有事务,没事务抛出异常
if (notExistingTransaction(tx)) {
throw new TransactionException("No existing transaction found for transaction marked with propagation 'mandatory'");
}
// Continue and execute with current transaction.
break;
default:
throw new TransactionException("Not Supported Propagation:" + propagation);
}
// 1.3 If null, create new transaction with role 'GlobalTransactionRole.Launcher'.
// 如果当前的事务上下文中不存在事务,实例化默认全局事务对象 且此次事务发起为 TM 角色为 Launcher
if (tx == null) {
tx = GlobalTransactionContext.createNew();
}
// set current tx config to holder
// 记录当前的全局锁配置,存放到 ThreadLocal
GlobalLockConfig previousConfig = replaceGlobalLockConfig(txInfo);
try {
// 2. If the tx role is 'GlobalTransactionRole.Launcher', send the request of beginTransaction to TC,
// else do nothing. Of course, the hooks will still be triggered.
// 执行全局事务开启的前后置钩子方法
// 如果当前事务的角色是 Participant 也就是 RM ,判断当前事务上下文RootContext是否存在XID,如果不存在,抛出异常
// 如果当前事务的角色是 launcher 也就是 TM ,判断当前事务上下文RootContext是否存在XID,如果存在,抛出异常
// 如果不存在,则通过TmNettyRemotingClient 向TC发送一个 GlobalReportRequest 同步消息,并获取TC返回的XID,绑定到RootContext
beginTransaction(txInfo, tx);
Object rs;
try {
// Do Your Business
// 执行执行拦截器链路
rs = business.execute();
} catch (Throwable ex) {
// 3. The needed business exception to rollback.
// 如果抛出异常,判断异常是否在指定的范围中(默认为Throwable类及其子类)
// 执行异常回滚的前后钩子方法
// 如果当前事务的角色是 launcher 也就是 TM ,通过TmNettyRemotingClient 向TC发送一个 GlobalRollbackRequest 同步消息
// 并记录TC返回的当前事务状态Status
completeTransactionAfterThrowing(txInfo, tx, ex);
throw ex;
}
// 4. everything is fine, commit.
// 如果方法执行过程中没有出现异常
// 执行事务提交的前后置方法
// 如果当前事务的角色是 launcher 也就是 TM ,通过TmNettyRemotingClient 向TC发送一个 GlobalCommitRequest 同步消息
// 并记录TC返回的当前事务状态Status
commitTransaction(tx);
return rs;
} finally {
//5. clear
// 恢复以前的全局锁配置
resumeGlobalLockConfig(previousConfig);
// 执行整个事务完成的前后置方法
triggerAfterCompletion();
// 移除当前绑定的事务钩子对象
cleanUp();
}
} finally {
// If the transaction is suspended, resume it.
// 当前事务执行完毕后,恢复挂起的事务,
// 获取suspendedResourcesHolder关联的xid,由RootContext重新绑定
if (suspendedResourcesHolder != null) {
tx.resume(suspendedResourcesHolder);
}
}
}
判断RootContext中是否绑定了XID,如果没有绑定,说明当前不存在事务返回null,如果有绑定XID,则返回默认的GlobalTransaction实现,记录当前全局事务的状态为beging,且为事务的参与者participate。接下来根据全局事务不同的传播行为,进一步判断需不需要挂起当前的全局事务,或者跳过事务处理,如果当前的传播行为要求有一个事务,而当前不存在全局事务(GlobalTransaction对象为null),则无参实例化GlobalTransaction,默认为事务的发起者luancher,事务状态未知
接着执行不同的钩子方法,且都是由事务发起者luancher使用 TmNettyRemotingClient 与 TC 通信,发送GlobalReportRequest消息,如果链路执行顺利,则发送GlobalCommitRequest消息,如果出现异常,发送GlobalRollbackRequest
4.总结与流程图