之前我们探讨了Linux中的tty,tty命令的主要功能是显示当前使用的终端名称。
如果我们想进一步对tty进行设置,就要用到stty。
stty的功能:显示和修改终端特性(Print or change terminal characteristics)。
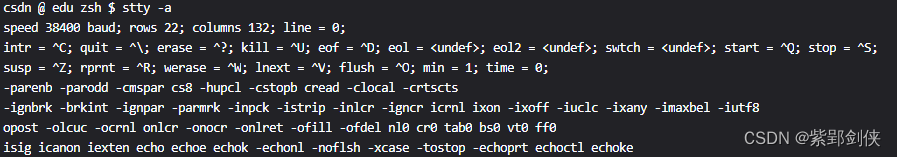
1 stty -a:显示所有当前注册终端的所有设置情况
csdn @ edu zsh $ stty -a
speed 38400 baud; rows 22; columns 132; line = 0;
intr = ^C; quit = ^\; erase = ^?; kill = ^U; eof = ^D; eol = <undef>; eol2 = <undef>; swtch = <undef>; start = ^Q; stop = ^S;
susp = ^Z; rprnt = ^R; werase = ^W; lnext = ^V; flush = ^O; min = 1; time = 0;
-parenb -parodd -cmspar cs8 -hupcl -cstopb cread -clocal -crtscts
-ignbrk -brkint -ignpar -parmrk -inpck -istrip -inlcr -igncr icrnl ixon -ixoff -iuclc -ixany -imaxbel -iutf8
opost -olcuc -ocrnl onlcr -onocr -onlret -ofill -ofdel nl0 cr0 tab0 bs0 vt0 ff0
isig icanon iexten echo echoe echok -echonl -noflsh -xcase -tostop -echoprt echoctl echoke
关于tty的参数和选项很多,我们着重研究一些比较常用的。
2.stty size:打印出终端的行数(rows)和列数(columns)
csdn @ edu zsh $ stty size
22 132
![]()
返回的结果中有两个数字,其中:
- 22:行数(rows)
- 132:列数(columns)
3. stty rows N:设置行数为N;stty columns M:设置列数为M
我们将行数设置为5,列数设置为75。
csdn @ edu bash ~ $ stty rows 5 columns 75
csdn @ edu bash ~ $ stty size
5 75

4 stty eof "string" :改变文件结束符eof
之前在
Linux shell编程学习笔记14:编写和运行第一个shell脚本hello world!
中,我们曾经尝试 使用cp命令 和 /dev/stdin 来创建脚本文件hello.sh,但是在执行脚本文件时会遇到 问题:
user @ host : ~ $ ./hello.sh
bash: ./hello.sh: /bin/bash: 解释器错误: 文本文件忙
![]()
出现这个问题的原因是Linux 中 tty默认的文件结束符eof(end of file)是Ctrl+D,而不是DOS中的Ctrl+Z。
现在我们要创建一个脚本文件a.sh,其内容如下:
echo hello world!
我们先在bash中用Ctrl+D来试试:
csdn @ edu bassh ~ $ cp /dev/stdin a.sh
echo hello world!^D
csdn @ edu bassh ~ $ . a.sh
hello world!
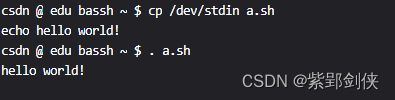
当我们在输入脚本文件a.sh的内容echo hello world!后按Ctrl+D结束,可以顺利执行脚本文件并看到结果。
- 需要注意的是,我们按下Ctrl+D在屏幕上是没有显示的。
如果我们想像DOS一样使用Ctrl+Z做为eof,那们可以使用stty命令来设置:
stty eof "z"
我们在bash中测试看看:
csdn @ edu bassh ~ $ stty eof "z"
csdn @ edu bassh ~ $ cp /dev/stdin a.sh
echo hello world!
^Z
[2]+ Stopped cp /dev/stdin a.sh
csdn @ edu bassh ~ $ . a.sh
hello world!

可以看到,我们先修改eof为Ctrl+Z,然后输入脚本内容并按Ctrl+Z结束,再执行脚本文件,脚本文件可以顺利执行。
5 stty -echo: 禁止回显,stty echo:打开回显
有时我们在输入信息,比如密码时,不希望信息显示出来,那么我们可以使用stty来进行设置。
例如,我们要执行以下命令序列 :
echo -n Enter your password: # 提示用户输入密码,-n选项的作用是显示信息后不换行
stty -echo # 禁止回显
read p # 将用户输入的密码保存到变量p中
stty echo # 打开回显
echo -e "\nyour password is: $p" # 显示用户输入的密码,-e选项的作用是对转义字符(如\n)进行处理其中每行命令后面#的内容为注释,说明命令的功能。
csdn @ edu bassh ~ $ echo -n Enter your password:;stty -echo;read p;stty echo;echo -e "\nyour password is: $p"
Enter your password:
your password is: abc

在上面的例子中,我们输入了密码abc,但在输入的过程中并没有回显出来,而是用最后一条命令显示。
6.stty olcuc:小写字母自动转换为大写字母; stty -olcuc:小写字母不自动转换为大写字母
我们可以通过 执行以下命令序列来测试。
stty olcuc # 小写字母自动转换为大写字母
echo abcABC # 显示字符串abcABC
stty -olcuc # 小写字母不自动转换为大写字母
echo abcABC # 显示字符串abcABC
csdn @ edu bassh \w $ stty olcuc;echo abcABC;stty -olcuc;echo abcABC
ABCABC
abcABC

可以看到,当我们执行命令 stty olcuc 后,命令 echo abcABC 本应输出的abcABC 变成了 ABCABC,当我们执行命令 stty -olcuc 后, 命令 echo abcABC 输出的才是abcABC。
- 需要注意的是,这条命令也会影响到终端命令提示符的显示。
csdn @ edu bassh \w $ stty olcuc
CSDN @ EDU BASSH \W $ STTY -OLCUC
csdn @ edu bassh \w $

在 执行命令 stty olcuc 前,终端命令提示符中的字母是小写的, 执行命令 stty olcuc 后,终端命令提示符中的字母都显示为大写,在执行命令 stty -olcuc 后, 终端命令提示符显示才恢复正常。
7 .stty --help:查看stty命令帮助信息
[csdn @ edu zsh $] stty --help
Usage: stty [-F DEVICE | --file=DEVICE] [SETTING]...
or: stty [-F DEVICE | --file=DEVICE] [-a|--all]
or: stty [-F DEVICE | --file=DEVICE] [-g|--save]
Print or change terminal characteristics.Mandatory arguments to long options are mandatory for short options too.
-a, --all print all current settings in human-readable form
-g, --save print all current settings in a stty-readable form
-F, --file=DEVICE open and use the specified DEVICE instead of stdin
--help display this help and exit
--version output version information and exitOptional - before SETTING indicates negation. An * marks non-POSIX
settings. The underlying system defines which settings are available.Special characters:
* dsusp CHAR CHAR will send a terminal stop signal once input flushed
eof CHAR CHAR will send an end of file (terminate the input)
eol CHAR CHAR will end the line
* eol2 CHAR alternate CHAR for ending the line
erase CHAR CHAR will erase the last character typed
intr CHAR CHAR will send an interrupt signal
kill CHAR CHAR will erase the current line
* lnext CHAR CHAR will enter the next character quoted
quit CHAR CHAR will send a quit signal
* rprnt CHAR CHAR will redraw the current line
start CHAR CHAR will restart the output after stopping it
stop CHAR CHAR will stop the output
susp CHAR CHAR will send a terminal stop signal
* swtch CHAR CHAR will switch to a different shell layer
* werase CHAR CHAR will erase the last word typedSpecial settings:
N set the input and output speeds to N bauds
* cols N tell the kernel that the terminal has N columns
* columns N same as cols N
ispeed N set the input speed to N
* line N use line discipline N
min N with -icanon, set N characters minimum for a completed read
ospeed N set the output speed to N
* rows N tell the kernel that the terminal has N rows
* size print the number of rows and columns according to the kernel
speed print the terminal speed
time N with -icanon, set read timeout of N tenths of a secondControl settings:
[-]clocal disable modem control signals
[-]cread allow input to be received
* [-]crtscts enable RTS/CTS handshaking
* [-]cdtrdsr enable DTR/DSR handshaking
csN set character size to N bits, N in [5..8]
[-]cstopb use two stop bits per character (one with '-')
[-]hup send a hangup signal when the last process closes the tty
[-]hupcl same as [-]hup
[-]parenb generate parity bit in output and expect parity bit in input
[-]parodd set odd parity (or even parity with '-')
* [-]cmspar use "stick" (mark/space) parityInput settings:
[-]brkint breaks cause an interrupt signal
[-]icrnl translate carriage return to newline
[-]ignbrk ignore break characters
[-]igncr ignore carriage return
[-]ignpar ignore characters with parity errors
* [-]imaxbel beep and do not flush a full input buffer on a character
[-]inlcr translate newline to carriage return
[-]inpck enable input parity checking
[-]istrip clear high (8th) bit of input characters
* [-]iutf8 assume input characters are UTF-8 encoded
* [-]iuclc translate uppercase characters to lowercase
* [-]ixany let any character restart output, not only start character
[-]ixoff enable sending of start/stop characters
[-]ixon enable XON/XOFF flow control
[-]parmrk mark parity errors (with a 255-0-character sequence)
[-]tandem same as [-]ixoffOutput settings:
* bsN backspace delay style, N in [0..1]
* crN carriage return delay style, N in [0..3]
* ffN form feed delay style, N in [0..1]
* nlN newline delay style, N in [0..1]
* [-]ocrnl translate carriage return to newline
* [-]ofdel use delete characters for fill instead of null characters
* [-]ofill use fill (padding) characters instead of timing for delays
* [-]olcuc translate lowercase characters to uppercase
* [-]onlcr translate newline to carriage return-newline
* [-]onlret newline performs a carriage return
* [-]onocr do not print carriage returns in the first column
[-]opost postprocess output
* tabN horizontal tab delay style, N in [0..3]
* tabs same as tab0
* -tabs same as tab3
* vtN vertical tab delay style, N in [0..1]Local settings:
[-]crterase echo erase characters as backspace-space-backspace
* crtkill kill all line by obeying the echoprt and echoe settings
* -crtkill kill all line by obeying the echoctl and echok settings
* [-]ctlecho echo control characters in hat notation ('^c')
[-]echo echo input characters
* [-]echoctl same as [-]ctlecho
[-]echoe same as [-]crterase
[-]echok echo a newline after a kill character
* [-]echoke same as [-]crtkill
[-]echonl echo newline even if not echoing other characters
* [-]echoprt echo erased characters backward, between '\' and '/'
[-]icanon enable erase, kill, werase, and rprnt special characters
[-]iexten enable non-POSIX special characters
[-]isig enable interrupt, quit, and suspend special characters
[-]noflsh disable flushing after interrupt and quit special characters
* [-]prterase same as [-]echoprt
* [-]tostop stop background jobs that try to write to the terminal
* [-]xcase with icanon, escape with '\' for uppercase charactersCombination settings:
* [-]LCASE same as [-]lcase
cbreak same as -icanon
-cbreak same as icanon
cooked same as brkint ignpar istrip icrnl ixon opost isig
icanon, eof and eol characters to their default values
-cooked same as raw
crt same as echoe echoctl echoke
dec same as echoe echoctl echoke -ixany intr ^c erase 0177
kill ^u
* [-]decctlq same as [-]ixany
ek erase and kill characters to their default values
evenp same as parenb -parodd cs7
-evenp same as -parenb cs8
* [-]lcase same as xcase iuclc olcuc
litout same as -parenb -istrip -opost cs8
-litout same as parenb istrip opost cs7
nl same as -icrnl -onlcr
-nl same as icrnl -inlcr -igncr onlcr -ocrnl -onlret
oddp same as parenb parodd cs7
-oddp same as -parenb cs8
[-]parity same as [-]evenp
pass8 same as -parenb -istrip cs8
-pass8 same as parenb istrip cs7
raw same as -ignbrk -brkint -ignpar -parmrk -inpck -istrip
-inlcr -igncr -icrnl -ixon -ixoff -iuclc -ixany
-imaxbel -opost -isig -icanon -xcase min 1 time 0
-raw same as cooked
sane same as cread -ignbrk brkint -inlcr -igncr icrnl -iutf8
-ixoff -iuclc -ixany imaxbel opost -olcuc -ocrnl onlcr
-onocr -onlret -ofill -ofdel nl0 cr0 tab0 bs0 vt0 ff0
isig icanon iexten echo echoe echok -echonl -noflsh
-xcase -tostop -echoprt echoctl echoke, all special
characters to their default valuesHandle the tty line connected to standard input. Without arguments,
prints baud rate, line discipline, and deviations from stty sane. In
settings, CHAR is taken literally, or coded as in ^c, 0x37, 0177 or
127; special values ^- or undef used to disable special characters.GNU coreutils online help: <http://www.gnu.org/software/coreutils/>
Report stty translation bugs to <http://translationproject.org/team/>
For complete documentation, run: info coreutils 'stty invocation'
帮助信息的中文译文
stty - 改变并打印终端行设置
用法
stty [-F device] [--file=device] [SETTING]...
stty [-F device] [--file=device] [-a|--all]
stty [-F device] [--file=device] [-g|--save]
描述
打印或改变终端属性.
-a, --all
以可读的格式打印当前的所有设置
-g, --save
以终端可读的格式打印当前的所有设置
-F, --file
打开指定的设备,并用此设备作为输入来代替标准输入
--help
显示帮助并退出
--version
显示版本信息并退出
可选项
SETTING之前的负号'-'表示否定,星号*表明是非POSIX设置. 以下是一些系统定义了的可用设置:
特殊字符
* dsusp CHAR
CHAR表示输入满时,发一个停止信号给终端
eof CHAR
CHAR表示一个文件结束 (结束输入)
eol CHAR
CHAR表示当前行结束
* eol2 CHAR
CHAR是另一个表示结束当前行的字符
erase CHAR
CHAR表示擦除最后一个输入字符
intr CHAR
CHAR表示发一个中断信号
kill CHAR
CHAR表示擦除当前行
* lnext CHAR
CHAR表示输入下一个字符
quit CHAR
CHAR表示发出一个退出信号
* rprnt CHAR
CHAR表示刷新当前行
start CHAR
CHAR表示在停止输出后重新开始输出
stop CHAR
CHAR表示停止输出
susp CHAR
CHAR表示发送一个终端停止信号
* swtch CHAR
CHAR表示切换到不同的外壳层
* werase CHAR
CHAR表示擦除已经输入的最后一个单词
特殊设置
N
把输入和输出的波特率设为N
* cols N
通知内核终端有N列
* columns N
与cols N 相同
ispeed N
设置输入速度为N
* line N
用行约束规则N
min N
和-icanon一起用, 设置一次完整的读操作最小为N个字符
time N
和-icanon一起用, 设置读超时为十分之N秒
ospeed N
设置输出速度为N
* rows N
通知内核终端有N行
* size
根据内核打印出终端的行数和列数
speed
打印出终端的速度
控制设置
[-]clocal
关闭解调器的控制信号
[-]cread
允许接收输入
* [-]crtscts
允许 RTS/CTS 的握手
csN
把字符长度设为N, N 为[5..8]
[-]cstopb
对每字符使用两个停止位 (一个带有 `-')
[-]hup
当最后一个进程关闭终端后,发一个挂起信号
[-]hupcl
同 [-]hup
[-]parenb
在输出中产生奇偶校验位,并要求在输入中也有奇偶校验位
[-]parodd
设置奇校验 (偶校验用 `-')
输入设置:
[-]brkint
暂停并产生中断信号
[-]icrnl
将回车解释为换行
[-]ignbrk
忽略中断信号
[-]igncr
忽略回车符
[-]ignpar
忽略有奇偶校验错的字符
* [-]imaxbel
对一个字符产生嘟叫,但不刷新已满的输入缓冲区
[-]inlcr
将换行解释为回车
[-]inpck
打开输入奇偶校验
[-]istrip
清除输入字符的高位(第8位)
* [-]iuclc
将大写字符转换成小写字符
* [-]ixany
使任何字符都重新开始输出(而 不仅仅是重新输出字符能实现此功能)
[-]ixoff
打开发送开始/停止字符的开关
[-]ixon
打开XON/XOFF的流量控制
[-]parmrk
标记奇偶校验错误 (使用255-0-character 字符序列)
[-]tandem
同 [-]ixoff
输出设置:
* bsN 回退延迟, N 为 [0..1]
* crN 回车延迟, N 为 [0..3]
* ffN 换页延迟, N 为 [0..1]
* nlN 换行延迟, N 为 [0..1]
* [-]ocrnl 将回车解释为换行
* [-]ofdel 使用删除字符来填充,而不是用空字符填充
* [-]ofill 使用填充字符,不使用定时延迟
* [-]olcuc 将小写字符转换成大写
* [-]onlcr 将换行解释为回车-换行
* [-]onlret 换行执行一次回车
* [-]onocr 不在第一列打印回车
[-]opost postprocess 输出
* tabN 水平tab键延迟, N 为 [0..3]
* tabs 同tab0
* -tabs 同tab3
* vtN 垂直方向tab键延迟。。。, N 为 [0..1]
本地设置:
[-]crterase
将擦除字符显示为:退格-空格-退格
* crtkill 根据echoprt和echoe的设置去除所有行
* -crtkill 根据echoctl和echok设置去除所有行
* [-]ctlecho 在头部符号中显示控制字符'^c')
[-]echo
显示输入字符
* [-]echoctl 同 [-]ctlecho
[-]echoe
同[-]crterase
[-]echok
在一个杀死字符后显示一个换行
* [-]echoke 同 [-]crtkill
[-]echonl
即使不显示其它字符也换行
* [-]echoprt 向后显示在 '' 和 '/'之间的擦除字符
[-]icanon
打开 erase, kill, werase, 和 rprnt 这些特殊字符
[-]iexten
打开 非POSIX 特殊字符
[-]isig
打开中断,退出和挂起这些特殊字符
[-]noflsh
在中断和退出这些特殊字符后禁止刷新
* [-]prterase 同 [-]echoprt
* [-]tostop 停止试图写终端的后台作业
* [-]xcase 与icanon同时使用, 表示用`'退出大写状态
综合设置:
* [-]LCASE
同 [-]lcase
cbreak
同 -icanon
-cbreak
同 icanon
cooked
同 brkint ignpar istrip icrnl ixon opost isig icanon, eof 和 eol 字符被设为默认值
-cooked
同 raw
crt
同 echoe echoctl echoke
dec
同 echoe echoctl echoke -ixany intr ^c erase 0177 kill ^u
* [-]decctlq
同 [-]ixany
ek
将擦除,杀死字符设为它们的默认值
evenp
同 parenb -parodd cs7
-evenp
同 -parenb cs8
* [-]lcase 同 xcase iuclc olcuc
litout
同 fB-parenb -istrip -opost cs8
-litout
同 parenb istrip opost cs7
nl
同 -icrnl -onlcr
-nl
同 icrnl -inlcr -igncr onlcr -ocrnl -onlret
oddp
同 parenb parodd cs7
-oddp
同 -parenb cs8
[-]parity
同 [-]evenp
pass8
同 -parenb -istrip cs8
-pass8
同 parenb istrip cs7
raw
同 -ignbrk -brkint -ignpar -parmrk -inpck -istrip -inlcr -igncr -icrnl -ixon -ixoff -iuc lc -ixany -imaxbel -opost -
isig -icanon -xcase min 1 ti me 0
-raw
同 cooked
sane
同 cread -ignbrk brkint -inlcr -igncr icrnl -ixoff -iuclc -ixany imaxbel opost -olcuc -ocrnl onlcr -onocr -onlret -ofill -ofdel nl0 cr0 tab0 bs0 vt0 ff 0 isig icanon iexten echo echoe echok -echonl -noflsh -xcase -tostop -echoprt echoctl echoke, 所有特殊字符 使用缺省值.