算法笔记-第五章-大整数运算
- 大整数运算
- 大整数比较
- 大整数加法
- 大整数减法
- 大整数乘法
- 大整数乘法2
- 大整数除法
大整数运算
一:使用数组存储整数的时候,整数的高位存储在数组的高位,整数的低位存储
在数组的低位
二:把整数按照字符串读入的时候,实际是逆序存储的,就是在读入数组的首需要翻转一下
比如说12345存储在数组当中应该是54321
#include<stdio.h>
#include<string.h>
struct bign
{
int d[100];//这里需要获取大整数的长度,设置一个结构通
int len;
bign()
{
memset(d, 0, sizeof(d));//在定义结构体之后,就需要初始化结构体
int len = 0;
}
};
bign change(char str[])//将字符串转化成bign
{
bign a;
a.len = strlen(str);
for (int i = 0; i < a.len; i++)
{
a.d[i] = str[a.len - i - 1] - '0';
}
return a;
}
bign add(bign a, bign b)
{
bign c;
int carry = 0;//这个是进位
for (int i = 0; i < a.len || i < b.len; i++)
{
int t = a.d[i] + b.d[i] + carry;
a.d[c.len++] = t % 10;
carry = t / 10;
}
if (carry != 0)
{
c.d[c.len++] = carry;
}
return c;
}
void print(bign a)
{
for (int i = a.len - 1; i > +0; i--)
{
printf("%d", a.d[i]);
}
}
int main()
{
char str1[1000], str2[1000];
scanf_s("%s%s", str1, str2);
bign a = change(str1);
bign b = change(str2);
print(add(a, b));
return 0;
}
大整数比较
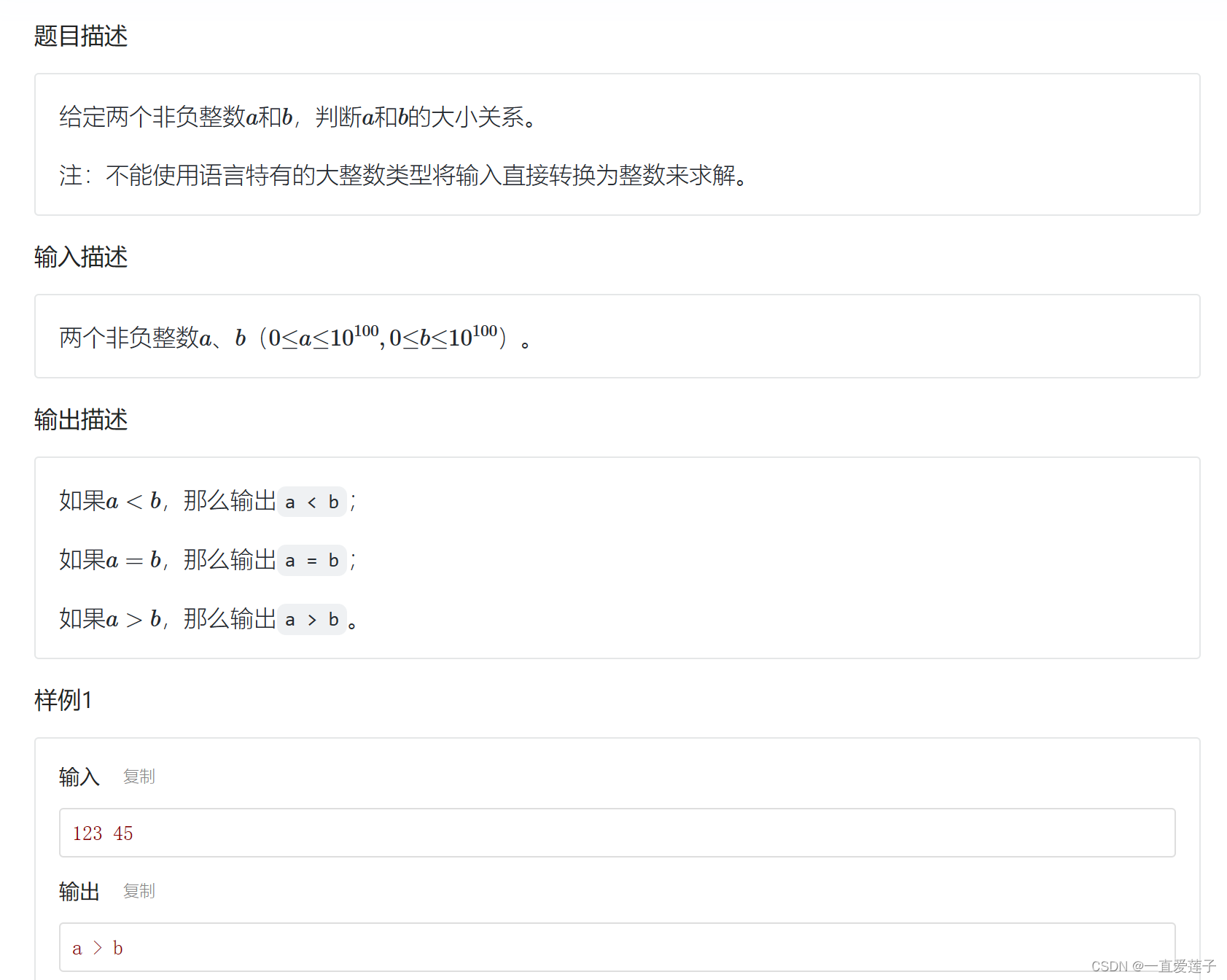
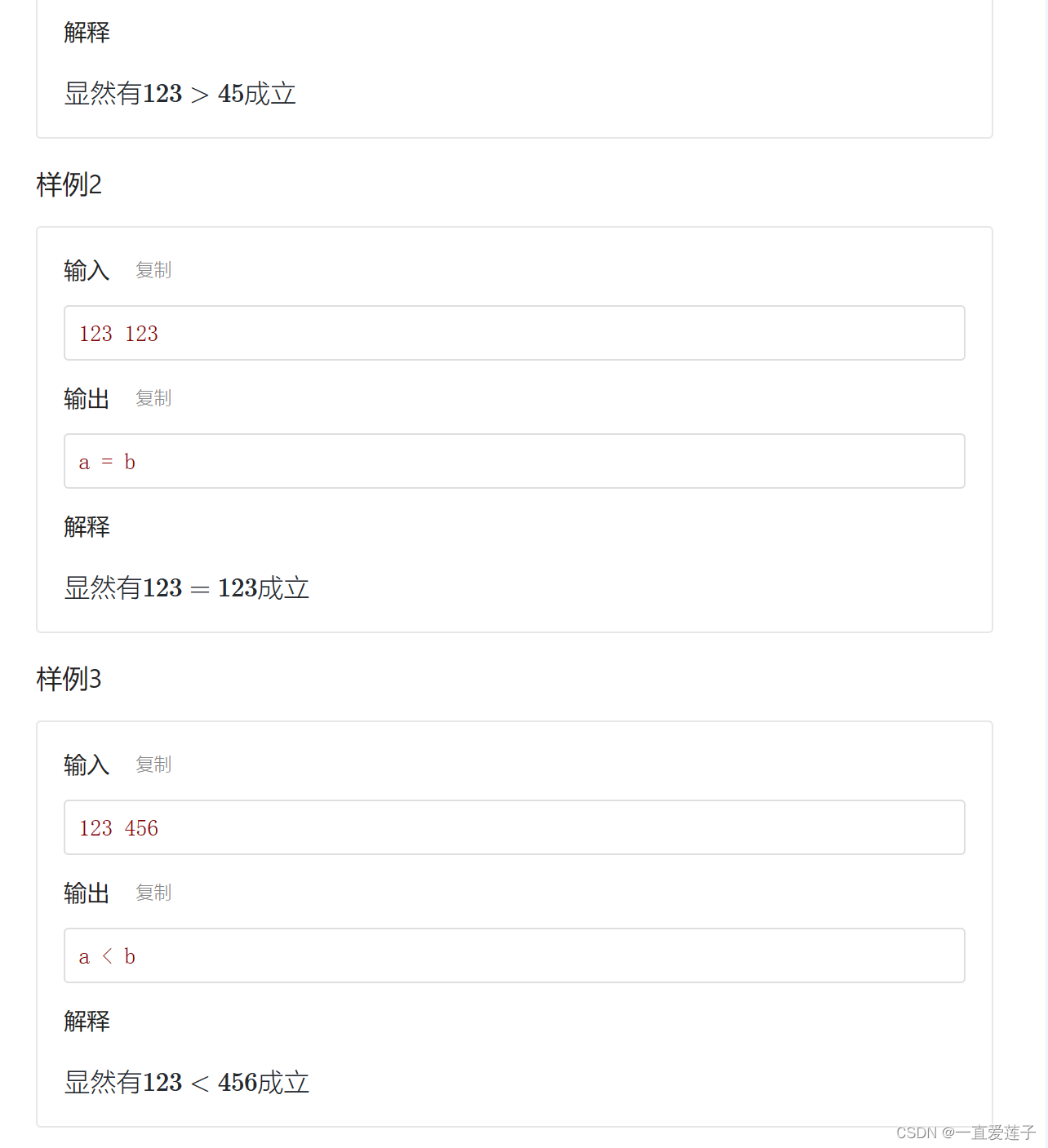
vector简单模拟大整数
typedef vector Bigint;
使用容器来存储
一个vector便可以模拟一个大整数,每位数字倒序储存在vector中
把大整数当作string输入
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <string>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
typedef vector<int> BigInt;
BigInt toBigInt(string nums) {
BigInt result;
for (int i = (int)nums.length() - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
result.push_back(nums[i] - '0');
}
return result;
}
int compare(BigInt a, BigInt b) {
if (a.size() > b.size()) {
return 1;
}
else if (a.size() < b.size()) {
return -1;
}
else {
for (int i = (int)a.size() - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
if (a[i] > b[i]) {
return 1;
}
else if (a[i] < b[i]) {
return -1;
}
}
return 0;
}
}
int main() {
string nums1, nums2;
cin >> nums1 >> nums2;
BigInt a = toBigInt(nums1);
BigInt b = toBigInt(nums2);
int compareResult = compare(a, b);
if (compareResult < 0) {
printf("a < b");
}
else if (compareResult > 0) {
printf("a > b");
}
else {
printf("a = b");
}
}
大整数加法
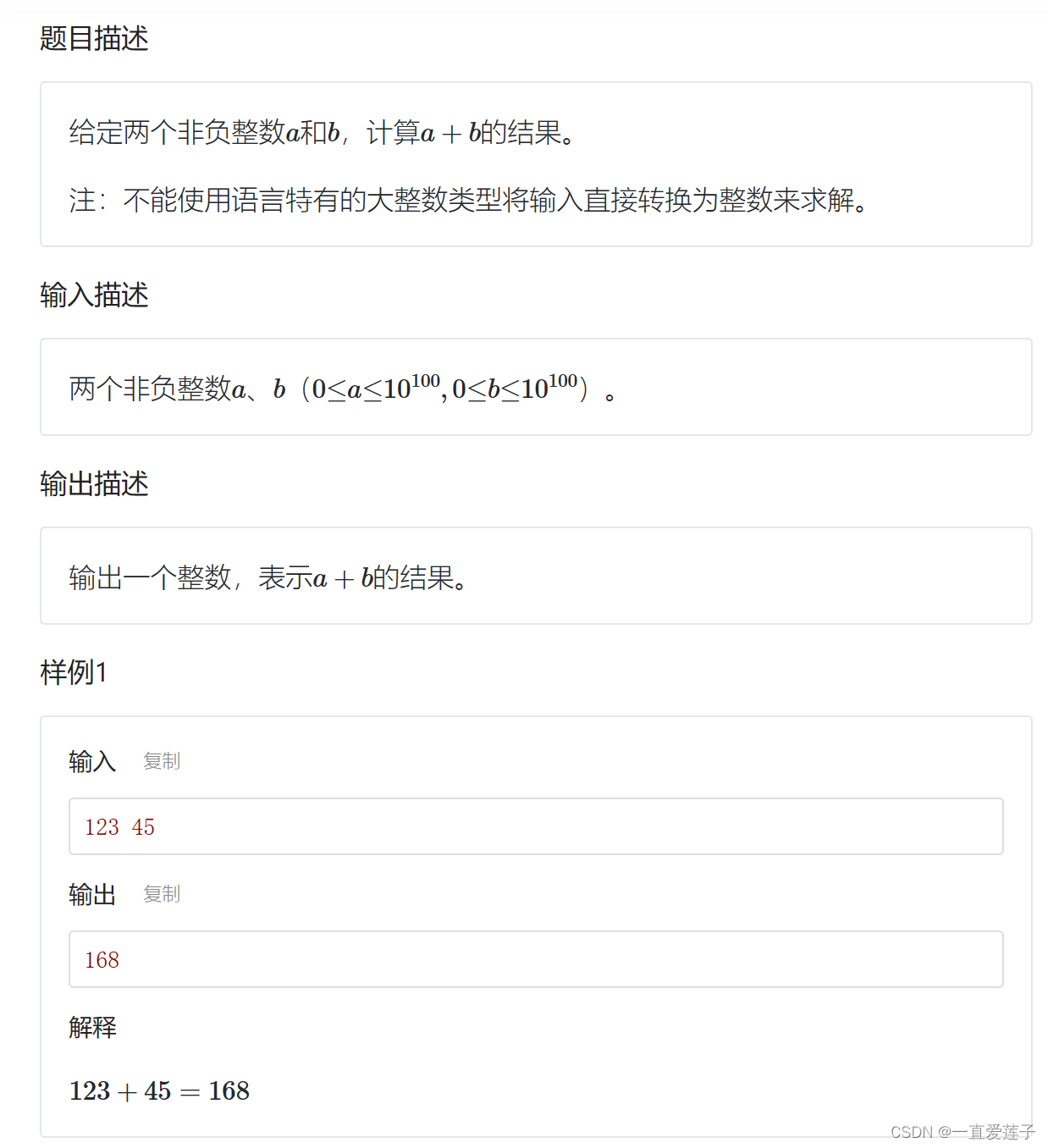
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <string>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
typedef vector<int> BigInt;
BigInt toBigInt(string nums) {//将输入数据转换成整数形式
BigInt result;
for (int i = (int)nums.length() - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
result.push_back(nums[i] - '0');
}
return result;
}
BigInt add(BigInt a, BigInt b) {//将两个大整数进行相加
BigInt c;
int carry = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < a.size() || i < b.size(); i++) {
int aDigit = i < a.size() ? a[i] : 0;
int bDigit = i < b.size() ? b[i] : 0;
int sum = aDigit + bDigit + carry;
c.push_back(sum % 10);
carry = sum / 10;
}
if (carry) {
c.push_back(carry);
}
return c;
}
void print(BigInt a) {
for (int i = (int)a.size() - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
cout << a[i];
}
}
int main() {
string nums1, nums2;
cin >> nums1 >> nums2;
BigInt a = toBigInt(nums1);
BigInt b = toBigInt(nums2);
print(add(a, b));
return 0;
}
大整数减法
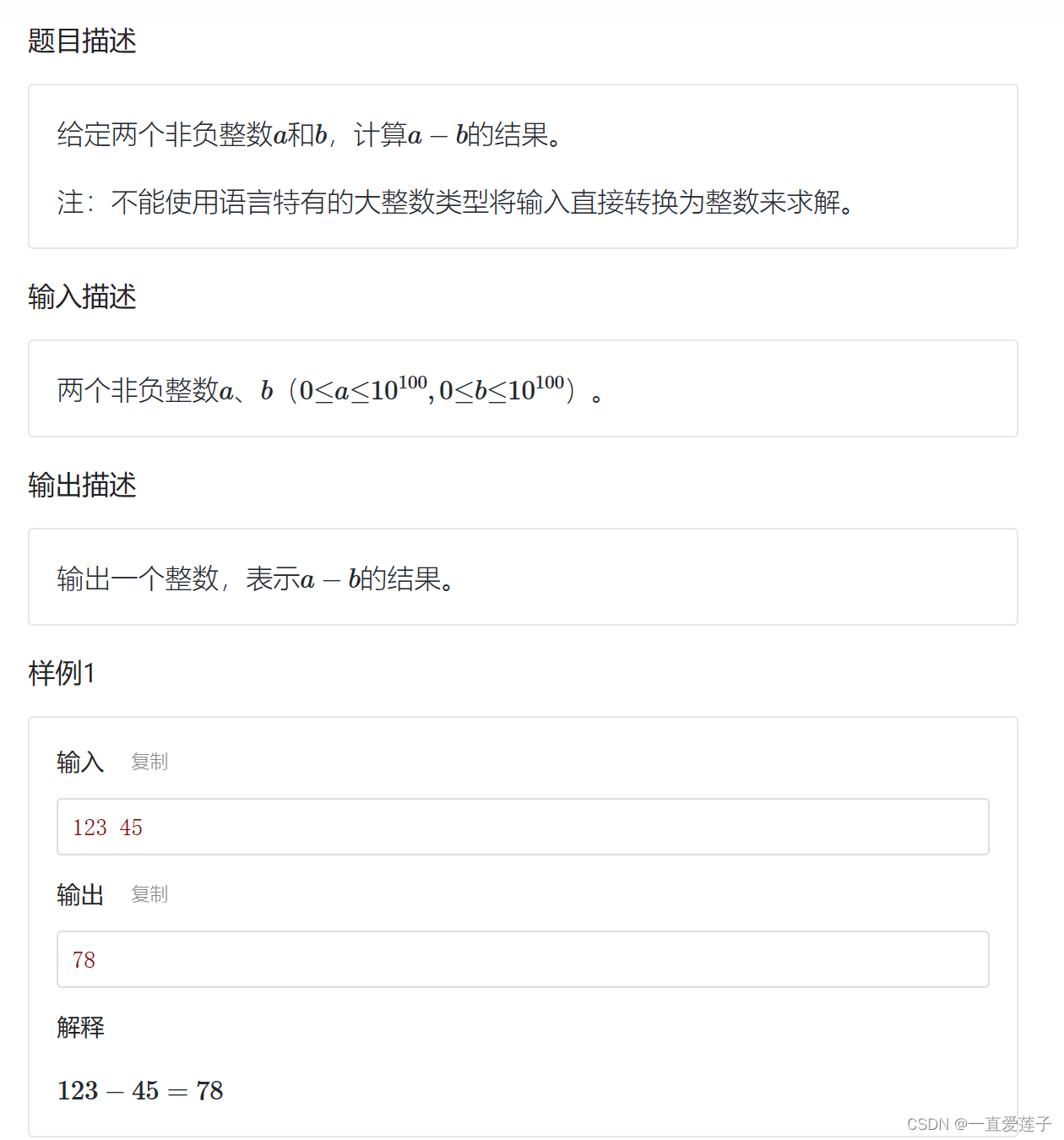
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <string>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
typedef vector<int> BigInt;
BigInt toBigInt(string nums) {
BigInt result;
for (int i = (int)nums.length() - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
result.push_back(nums[i] - '0');
}
return result;
}
int compare(BigInt a, BigInt b) {//将两个进行比较大小
if (a.size() > b.size()) {
return 1;
}
else if (a.size() < b.size()) {
return -1;
}
else {
for (int i = (int)a.size() - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
if (a[i] > b[i]) {
return 1;
}
else if (a[i] < b[i]) {
return -1;
}
}
return 0;
}
}
BigInt sub(BigInt a, BigInt b) {
BigInt c;
int carry = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < a.size(); i++) {
int bDigit = i < b.size() ? b[i] : 0;//通过三位符判断b数组是否已经不能被减了
if (a[i] < bDigit) {//a这个位置小于b(条件)
a[i + 1]--;
a[i] += 10;
}//进位然后进行加值
c.push_back(a[i] - bDigit);
}
while (c.size() > 1 && c.back() == 0) {
c.pop_back();
}
return c;
}
void print(BigInt a) {
for (int i = (int)a.size() - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
cout << a[i];
}
}
int main() {
string nums1, nums2;//以字符串形式输入,后面会进行转换
cin >> nums1 >> nums2;
BigInt a = toBigInt(nums1);
BigInt b = toBigInt(nums2);
if (compare(a, b) >= 0) {
print(sub(a, b));
}
else {
cout << "-";
print(sub(b, a));
}
return 0;
}
大整数乘法
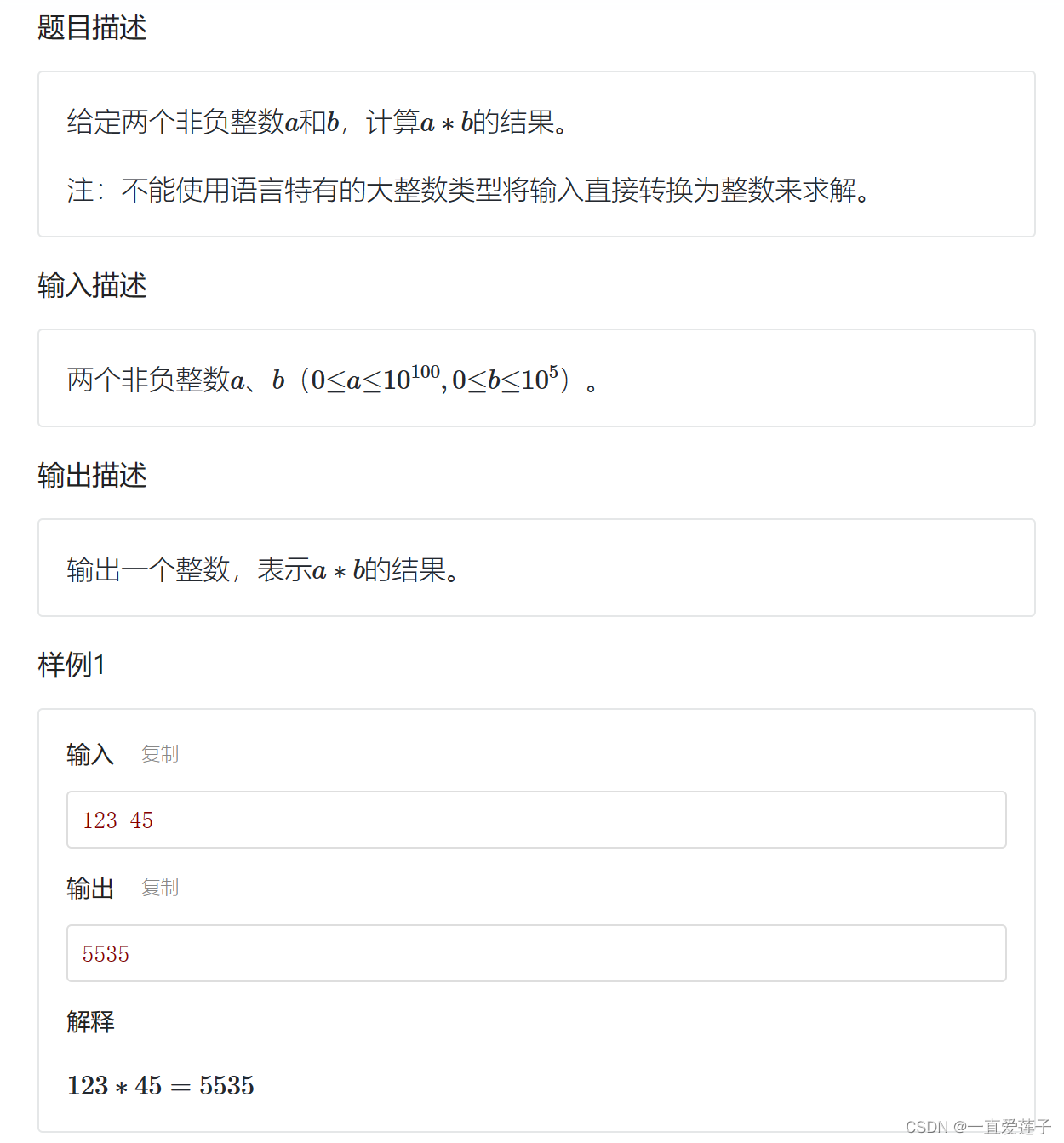
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <string>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
typedef vector<int> BigInt;
BigInt toBigInt(string nums) {
BigInt result;
for (int i = (int)nums.length() - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
result.push_back(nums[i] - '0');
}
return result;
}
BigInt mul(BigInt a, int b) {
BigInt c;
int carry = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < a.size(); i++) {
int temp = a[i] * b + carry;
c.push_back(temp % 10);
carry = temp / 10;
}
while (carry) {
c.push_back(carry % 10);
carry /= 10;
}
while (c.size() > 1 && c.back() == 0) {
c.pop_back();
}
return c;
}
void print(BigInt a) {
for (int i = (int)a.size() - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
cout << a[i];
}
}
int main() {
string nums;
int b;
cin >> nums >> b;
BigInt a = toBigInt(nums);
print(mul(a, b));
return 0;
}
大整数乘法2
注意点:
c.push_back(X) 将元素X加入到c容器的最后一位。
c.back() 返回c容器的最后一个元素的值,并不是该元素的地址。
push_back() 在Vector最后添加一个元素(参数为要插入的值);
删除Vector容器中的最后一个元素;
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <string>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
typedef vector<int> BigInt;
BigInt toBigInt(string nums) {
BigInt result;
for (int i = (int)nums.length() - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
result.push_back(nums[i] - '0');
}
return result;
}
//主要的函数:
//
BigInt mul(BigInt a, BigInt b) {
BigInt c = BigInt(a.size() + b.size() + 1, 0);
for (int i = 0; i < a.size(); i++) {//第一个函数主要是将两个整数进行相乘之后的数据存储在数组当中依次的位置
for (int j = 0; j < b.size(); j++) {
c[i + j] += a[i] * b[j];
}
}
for (int i = 0; i < a.size() + b.size(); i++) {//将数组当中的数据进行进位操作,整理
if (c[i] >= 10) {
c[i + 1] += c[i] / 10;
c[i] = c[i] % 10;
}
}
while (c.size() > 1 && c.back() == 0) {//将数组中的最后一位0进行删除操作
c.pop_back();
}
return c;
}
void print(BigInt a) {
for (int i = (int)a.size() - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
cout << a[i];
}
}
int main() {
string nums1, nums2;
cin >> nums1 >> nums2;
BigInt a = toBigInt(nums1);
BigInt b = toBigInt(nums2);
print(mul(a, b));
return 0;
}
大整数除法
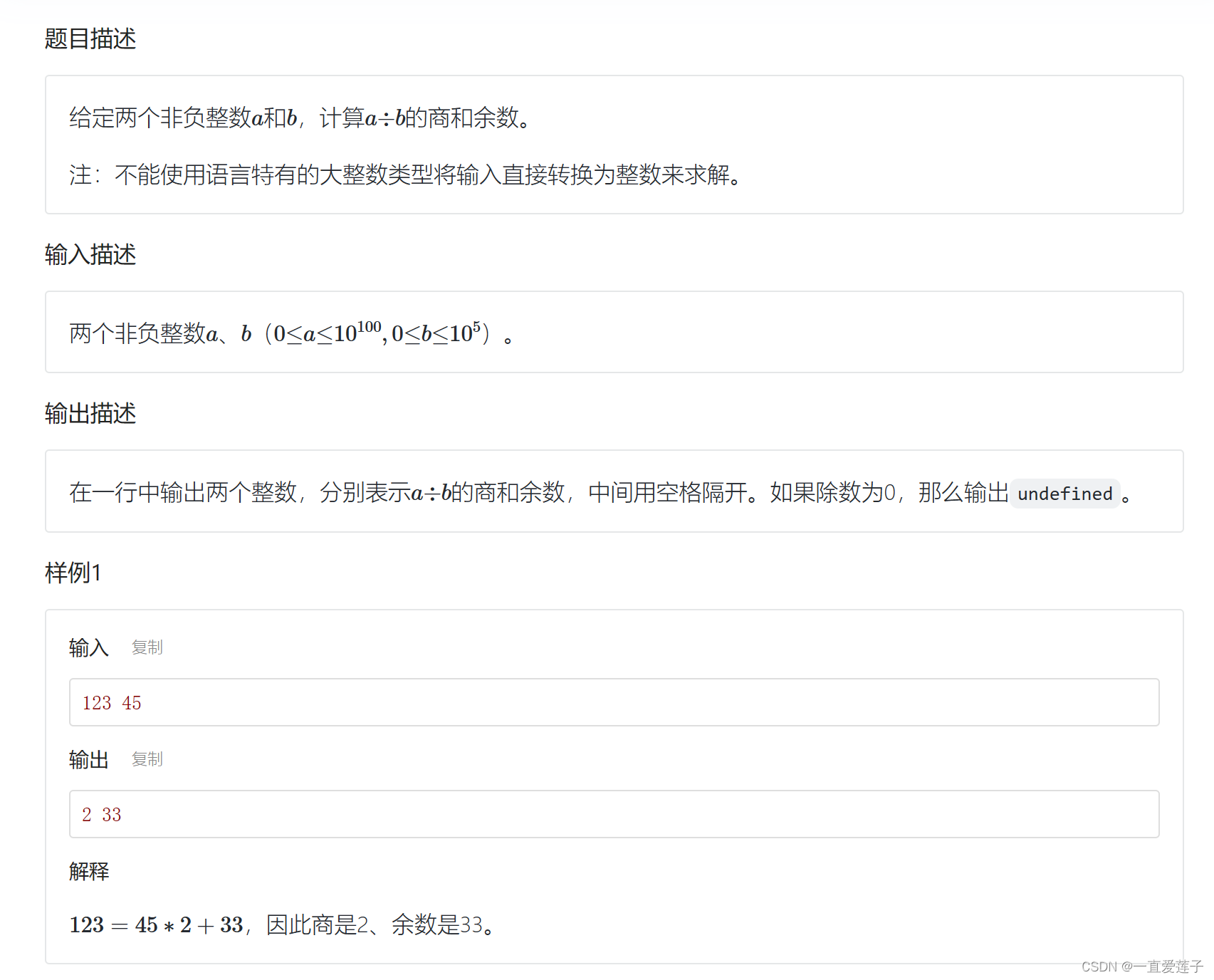
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <string>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
typedef vector<int> BigInt;
BigInt toBigInt(string nums) {
BigInt result;
for (int i = (int)nums.length() - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
result.push_back(nums[i] - '0');
}
return result;
}
BigInt div(BigInt a, int b, int& r) {
BigInt c;
for (int i = (int)a.size() - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
r = r * 10 + a[i];
c.push_back(r / b);
r = r % b;
}
reverse(c.begin(), c.end());
while (c.size() > 1 && c.back() == 0) {
c.pop_back();
}
return c;
}
void print(BigInt a) {
for (int i = (int)a.size() - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
cout << a[i];
}
}
int main() {
string nums;
int b, r = 0;
cin >> nums >> b;
if (b == 0) {
cout << "undefined";
return 0;
}
BigInt a = toBigInt(nums);
BigInt q = div(a, b, r);
print(q);
cout << " " << r;
return 0;
}




![C++初阶 | [三] 类和对象(中)](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/c5aa20b18d404aba8882d21a4dab04b4.png)