目录
- 1.概述
- 2.代码实现
- 2.1.节点类
- 2.2.邻接矩阵存储图
- 2.3.邻接表存储图
- 2.4.测试
- 3.扩展
- 3.1.只计算一对顶点之间的最短路径
- 3.2.获取起点到其它节点具体经过的节点
- 4.应用
本文参考:
LABULADONG 的算法网站
1.概述
(1)在图论中,最短路径是指在加权图中两个顶点之间长度最短的路径,这个路径的长度是每条边的权重之和。在现实生活中,可以将图中的顶点表示为地点,将边表示为这些地点之间的道路或交通线路,把每条边的权重定义为行程时间、行驶距离、经济成本、能源消耗等相应的度量单位。在这种情况下,最短路径问题就是为了找到从一个地点到另一个地点的最快、最短、最便宜、最节能的路径。最短路径问题在计算机科学和运筹学方面非常重要,它可以解决很多现实问题,如网页排名算法、路由算法、航班调度、电信网络建设等。Dijkstra 算法是解决最短路径问题的经典算法之一。
(2)迪杰斯特拉算法 (Dijkstra) 是由荷兰计算机科学家狄克斯特拉于1959年提出的,因此又叫狄克斯特拉算法。是从一个顶点到其余各顶点的最短路径算法,解决的是有权图中最短路径问题。迪杰斯特拉算法主要特点是从起始点开始,采用贪心算法的策略,每次遍历到始点距离最近且未访问过的顶点的邻接节点,直到扩展到终点为止。
(3)实现 Dijkstra 算法的一种基本思路如下:
- 维护一个待确定最短路径的节点的集合,初始时只有起点。之后,每次从这个集合中取出一个节点,更新它所有邻居的距离,将它们加入这个集合中。具体实现中,使用一个优先队列来存储待访问的节点,并按照最短距离从小到大的顺序进行访问。
- 在代码中,使用一个数组 dist 来记录起点到每个节点的最短距离,同时使用一个自定义的 Node 类来表示所有待访问的节点,并存储其与起点的距离。算法主体部分由一个 while 循环实现。每次取出队列中距离最小的节点,并遍历其所有邻居,更新起点到每个邻居的距离,然后将未确定最短路径的点加入队列中。
常数较小的情况下,Dijkstra 算法的时间复杂度为 O(ElogV),其中 E 为边数,V 为顶点数。
2.代码实现
2.1.节点类
class Node {
//图中当前节点的 id
int id;
//从 start 节点到当前节点的距离
int distFromStart;
public Node(int id, int distFromStart) {
this.id = id;
this.distFromStart = distFromStart;
}
}
2.2.邻接矩阵存储图
class Solution {
/*
start: 起点
graph: 用于表示图的邻接矩阵
返回值: 起点到图中每一个点的最短距离
*/
public int[] dijkstra(int start, int[][] graph) {
// dist[i] 表示起点 start 到节点 i 的最短路径长度
int[] dist = new int[graph.length];
// dist[i] = Integer.MAX_VALUE 表示起点到节点 i 之间不可达
Arrays.fill(dist, Integer.MAX_VALUE);
//起点与自己之间的最短路径长度为 0
dist[start] = 0;
//自定义优先级队列规则,distFromStart 值较小的节点排在队首
Queue<Node> queue = new PriorityQueue<>(Comparator.comparingInt(a -> a.distFromStart));
queue.offer(new Node(start, 0));
while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
//取出队首元素
Node node = queue.poll();
int id = node.id;
int curDistFromStart = node.distFromStart;
if (curDistFromStart > dist[id]) {
continue;
}
//将与当前节点相邻的所有节点存入队列
for (int i = 0; i < graph[id].length; i++) {
if (graph[id][i] != Integer.MAX_VALUE) {
int distToNextNode = dist[id] + graph[id][i];
// 更新 dist
if (dist[i] > distToNextNode) {
dist[i] = distToNextNode;
queue.offer(new Node(i, distToNextNode));
}
}
}
}
return dist;
}
}
2.3.邻接表存储图
class Solution {
/*
start: 起点
graph: 用于表示图的邻接表
返回值: 起点到图中每一个点的最短距离
*/
public int[] dijkstra(int start, List<int[]>[] graph) {
// dist[i] 表示起点 start 到节点 i 的最短路径长度
int[] dist = new int[graph.length];
// dist[i] = Integer.MAX_VALUE 表示起点到节点 i 之间不可达
Arrays.fill(dist, Integer.MAX_VALUE);
//起点与自己之间的最短路径长度为 0
dist[start] = 0;
//自定义优先级队列规则,distFromStart 值较小的节点排在队首
Queue<Node> queue = new PriorityQueue<>(Comparator.comparingInt(a -> a.distFromStart));
queue.offer(new Node(start, 0));
while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
//取出队首元素
Node node = queue.poll();
int id = node.id;
int curDistFromStart = node.distFromStart;
if (curDistFromStart > dist[id]) {
continue;
}
//将与当前节点相邻的所有节点存入队列
for (int[] neighbor : graph[id]) {
int nextNodeID = neighbor[0];
int distToNextNode = dist[id] + neighbor[1];
//更新 dist
if (dist[nextNodeID] > distToNextNode) {
dist[nextNodeID] = distToNextNode;
queue.offer(new Node(nextNodeID, distToNextNode));
}
}
}
return dist;
}
}
2.4.测试
(1)本测试中的加权无向图如下所示,并且设置起点为 0。
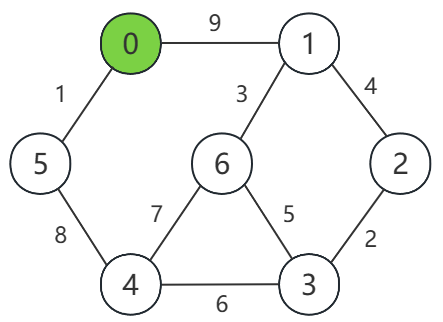
(2)邻接矩阵的测试代码如下:
class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//图的顶点数
int n = 7;
int[][] graph = new int[n][n];
//初始化邻接矩阵,初始化为 Integer.MAX_VALUE 表示不可达
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
Arrays.fill(graph[i], Integer.MAX_VALUE);
}
//添加图的边
graph[0][1] = 9;
graph[0][5] = 1;
graph[1][0] = 9;
graph[1][2] = 4;
graph[1][6] = 3;
graph[2][1] = 4;
graph[2][3] = 2;
graph[3][2] = 2;
graph[3][4] = 6;
graph[3][6] = 5;
graph[4][3] = 6;
graph[4][5] = 8;
graph[4][6] = 7;
graph[5][0] = 1;
graph[5][4] = 8;
graph[6][1] = 3;
graph[6][3] = 5;
graph[6][4] = 7;
Solution solution = new Solution();
int start = 0;
int[] distances = solution.dijkstra(start, graph);
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(distances));
}
}
输出结果如下:
[0, 9, 13, 15, 9, 1, 12]
(3)邻接表的测试代码如下:
class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//图的顶点数
int n = 7;
List<int[]>[] graph = new ArrayList[n];
//初始化邻接表
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
graph[i] = new ArrayList<>();
}
//添加图的边
graph[0].add(new int[]{1, 9});
graph[0].add(new int[]{5, 1});
graph[1].add(new int[]{0, 9});
graph[1].add(new int[]{2, 4});
graph[1].add(new int[]{6, 3});
graph[2].add(new int[]{1, 4});
graph[2].add(new int[]{3, 2});
graph[3].add(new int[]{2, 2});
graph[3].add(new int[]{4, 6});
graph[3].add(new int[]{6, 5});
graph[4].add(new int[]{3, 6});
graph[4].add(new int[]{5, 8});
graph[4].add(new int[]{6, 7});
graph[5].add(new int[]{0, 1});
graph[5].add(new int[]{4, 8});
graph[6].add(new int[]{1, 3});
graph[6].add(new int[]{3, 5});
graph[6].add(new int[]{4, 7});
Solution solution = new Solution();
int start = 0;
int[] distances = solution.dijkstra(start, graph);
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(distances));
}
}
输出结果如下:
[0, 9, 13, 15, 9, 1, 12]
3.扩展
3.1.只计算一对顶点之间的最短路径
如果现在只需计算起点 start 到终点 end 的最短路径,那么只需要简单修改上述代码即可,以用邻接表存储图的代码为例:
class Solution {
/*
start: 起点
graph: 用于表示图的邻接矩阵
返回值: 起点 start 到终点 end 的最短路径
*/
public int dijkstra(int start, int end, int[][] graph) {
//...
while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
//取出队首元素
Node node = queue.poll();
int id = node.id;
int curDistFromStart = node.distFromStart;
//添加如下代码:如果遍历到 end,直接返回 curDistFromStart 即可
if (id == end) {
return curDistFromStart;
}
if (curDistFromStart > dist[id]) {
continue;
}
//...
}
//如果运行到这里,说明 start 到 end 之间不可达
return Integer.MAX_VALUE;
}
}
3.2.获取起点到其它节点具体经过的节点
(1)如果需要找到起点到其余节点的最短路径中依次经过的节点,可以在 Dijkstra 算法中添加一个 prev 数组或 map,记录节点i的前一个访问过的节点 j。在更新 dist[i] 的同时,同时更新 prev[i] = j。最后,通过回溯 prev 数组,可以从目标节点往回遍历,找到最短路径上的所有节点。具体来说,可以按以下步骤实现:
- 初始化 prev 数组,将所有节点的前继节点都设置为起点。
- 在更新 dist[i] 的同时,同时更新 prev[i] = j。
- 当所有节点都处理完毕后,就可以从目标节点往回遍历 prev 数组,找到最短路径上的所有节点。
(2)以用邻接表存储图的代码为例,具体代码如下所示:
class Solution {
/*
start: 起点
graph: 用于表示图的邻接表
返回值: 起点到图中每一个点的最短距离依次所经过的节点
*/
public List<List<Integer>> findShortestPaths(int start, List<int[]>[] graph) {
int n = graph.length;
int[] dist = new int[n];
Arrays.fill(dist, Integer.MAX_VALUE);
dist[start] = 0;
int[] prev = new int[n];
Arrays.fill(prev, start);
Queue<Node> queue = new PriorityQueue<>(Comparator.comparingInt(a -> a.distFromStart));
queue.offer(new Node(start, 0));
while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
Node node = queue.poll();
int id = node.id;
int curDistFromStart = node.distFromStart;
if (curDistFromStart > dist[id]) {
continue;
}
for (int[] neighbor : graph[id]) {
int nextNodeID = neighbor[0];
int distToNextNode = dist[id] + neighbor[1];
if (dist[nextNodeID] > distToNextNode) {
//在更新 dist[nextNodeID] 时,同时更新 prev[nextNodeID]
dist[nextNodeID] = distToNextNode;
prev[nextNodeID] = id;
queue.offer(new Node(nextNodeID, distToNextNode));
}
}
}
//通过 prev 数组回溯路径
List<List<Integer>> paths = new ArrayList<>();
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
List<Integer> path = new ArrayList<>();
int curNode = i;
while (curNode != start) {
path.add(curNode);
curNode = prev[curNode];
}
path.add(start);
Collections.reverse(path);
paths.add(path);
}
return paths;
}
}
(3)测试代码如下:
class Solution {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//图的顶点数
int n = 7;
List<int[]>[] graph = new ArrayList[n];
//初始化邻接表
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
graph[i] = new ArrayList<>();
}
//添加图的边
graph[0].add(new int[]{1, 9});
graph[0].add(new int[]{5, 1});
graph[1].add(new int[]{0, 9});
graph[1].add(new int[]{2, 4});
graph[1].add(new int[]{6, 3});
graph[2].add(new int[]{1, 4});
graph[2].add(new int[]{3, 2});
graph[3].add(new int[]{2, 2});
graph[3].add(new int[]{4, 6});
graph[3].add(new int[]{6, 5});
graph[4].add(new int[]{3, 6});
graph[4].add(new int[]{5, 8});
graph[4].add(new int[]{6, 7});
graph[5].add(new int[]{0, 1});
graph[5].add(new int[]{4, 8});
graph[6].add(new int[]{1, 3});
graph[6].add(new int[]{3, 5});
graph[6].add(new int[]{4, 7});
Solution solution = new Solution();
int start = 4;
List<List<Integer>> paths = solution.findShortestPaths(start, graph);
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
System.out.println("从节点 " + start + " 到节点 " + i +
" 的最短距离经过的节点依次为: " + paths.get(i));
}
}
}
输出结果如下:
从节点 4 到节点 0 的最短距离经过的节点依次为: [4, 5, 0]
从节点 4 到节点 1 的最短距离经过的节点依次为: [4, 6, 1]
从节点 4 到节点 2 的最短距离经过的节点依次为: [4, 3, 2]
从节点 4 到节点 3 的最短距离经过的节点依次为: [4, 3]
从节点 4 到节点 4 的最短距离经过的节点依次为: [4]
从节点 4 到节点 5 的最短距离经过的节点依次为: [4, 5]
从节点 4 到节点 6 的最短距离经过的节点依次为: [4, 6]
4.应用
(1)Dijkstra算法是一种用于解决单源最短路径问题的算法。它可以帮助找到从一个源节点到图中所有其他节点的最短路径。这个算法广泛应用于许多领域,包括以下几个方面:
- 网络路由:Dijkstra 算法在网络路由中被广泛使用,用于计算最短路径来传输数据包。
- 交通规划:Dijkstra 算法可以用于交通网络中的最短路径规划,例如在城市道路网络中找到最短驾驶路线。
- 电信网络:Dijkstra 算法可以用于计算通信网络中的最短路径,例如电话网络或互联网中的数据包传输。
- 地理信息系统 (GIS):Dijkstra 算法可以用于计算地理信息系统中的最短路径,例如导航系统中找到最佳行驶路径。
- 运输和物流:Dijkstra 算法可以用于解决运输和物流问题,例如货物配送中最优路径的规划。
(2)大家可以去 LeetCode 上找相关的 Dijkstra 算法的题目来练习,或者也可以直接查看 LeetCode算法刷题目录 (Java) 这篇文章中的最短路径章节。如果大家发现文章中的错误之处,可在评论区中指出。