目录
232.用栈实现队列
225.用队列模拟实现栈
注:本文是基于C语言实现的代码,所以栈和队列是在力扣上制造实现的,如果你使用C++等语言,可以忽略前面相当大部分的代码。
在栈模拟实现栈和队列之前,我们先来复习一下栈和队列的定义,你必须对栈和队列有详细的了解,并模拟实现过,否则,一下实现对你的理解可能较为困难。
栈:只允许一端(栈顶)进行插入和删除操作。
队列:只允许一端进行插入,令一端进行删除操作。
数据结构入门————栈和队列(C语言/零基础/小白/新手+模拟实现+例题讲解)-CSDN博客
232.用栈实现队列
232. 用栈实现队列 - 力扣(LeetCode)


对于队列,我们使用链式结构,进行尾插和头插,如果我们只使用一个栈来说,这是非常困难的,那我们就转变一下思路,使用两个栈来实现。这里我们叫一个为emptys(空栈),另一个叫nonemptys(非空栈)。
当我们想要插入时直接尾插到nonemptys(如果是第一次插入,无所谓emptys,nonemptys)。
想要删除时,就将nonemptys栈的第二个及以后的数据插入到emptys中,然后将nonemptys中第一个数据删除,最后再将emptysz栈数据导入nonemptys中。
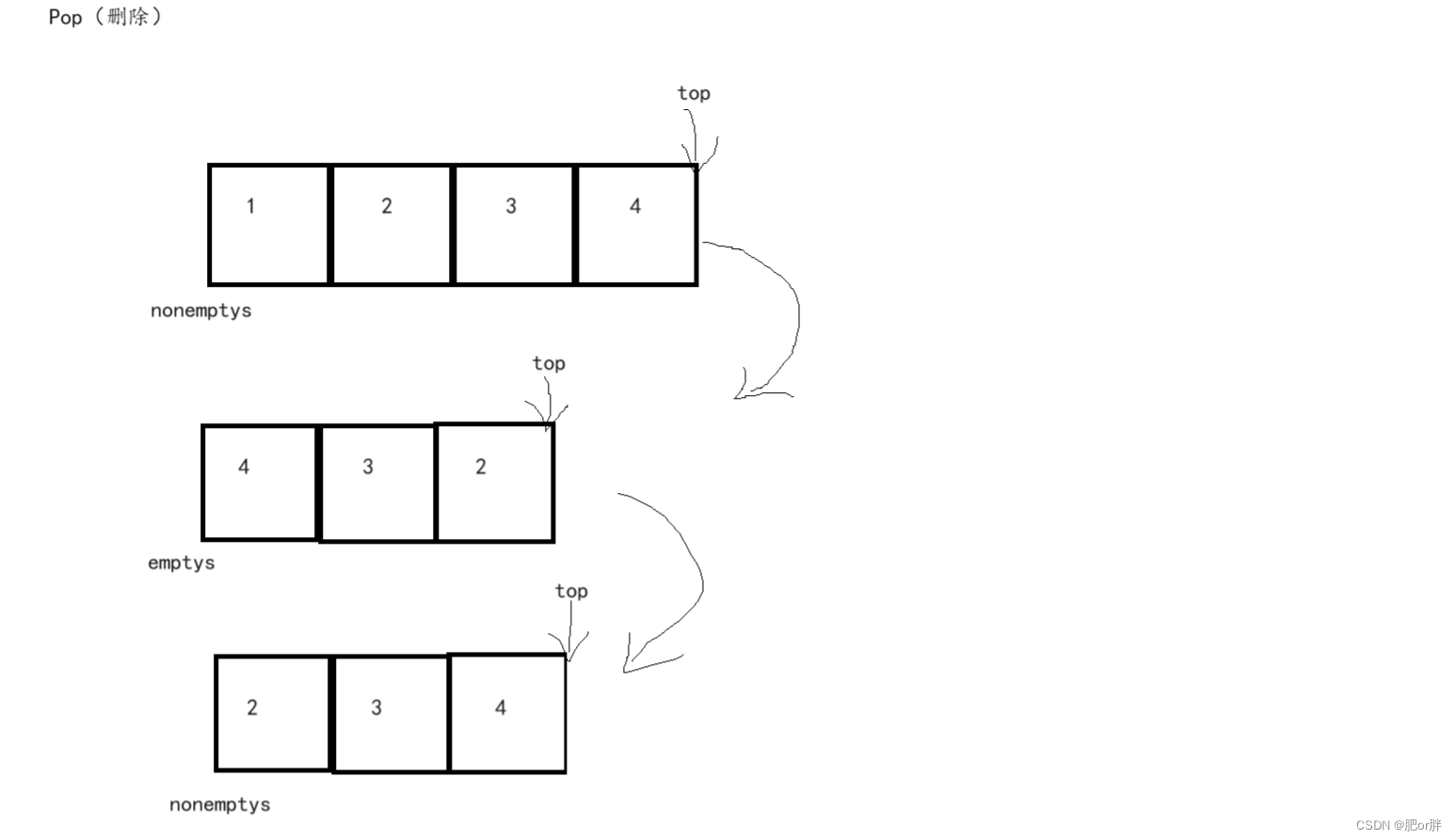
注:因为C语言,并没有对顺序栈的实现,所以我们要自己定义一个顺序栈结构。
typedef int STDataType;
typedef struct Stack
{
STDataType* a;
int top;
int capacity;
}ST;
//初始化
void StackInit(ST* pst)
{
assert(pst);
pst->a = NULL;
pst->top = 0;
pst->capacity = 0;
}
//销毁
void StackDestroy(ST* pst)
{
assert(pst);
free(pst->a);
pst->a = NULL;
pst->top = 0;
pst->capacity = 0;
}
//插入
void StackPush(ST* pst, STDataType x)
{
assert(pst);
if (pst->top == pst->capacity)
{
int newcapacity = (pst->capacity == 0) ? 4 : pst->capacity * 2;
STDataType* temp = (STDataType*)realloc(pst->a, sizeof(STDataType) * newcapacity);
if (temp == NULL)
{
perror("realloc");
return;
}
pst->a = temp;
pst->capacity = newcapacity;
}
pst->a[pst->top] = x;
pst->top++;
}
//删除
void StackPop(ST* pst)
{
assert(pst);
assert(pst->top > 0);
pst->top--;
}
//返回top值
STDataType StackTop(ST* pst)
{
assert(pst);
assert(pst->top > 0);
return pst->a[pst->top - 1];
}
//判断是否为空
bool StackEmpty(ST* pst)
{
assert(pst);
return pst->top == 0;
}
//元素个数
int StackSize(ST* pst)
{
assert(pst);
return pst->top;
}
typedef struct {
ST st1;
ST st2;
} MyQueue;
MyQueue* myQueueCreate() {
MyQueue* pq = (MyQueue*)malloc(sizeof(MyQueue));
if (pq == NULL)
{
perror("malloc");
return NULL;
}
StackInit(&pq->st1);
StackInit(&pq->st2);
return pq;
}
void myQueuePush(MyQueue* obj, int x) {
if (!StackEmpty(&obj->st1))
{
StackPush(&obj->st1, x);
}
else
{
StackPush(&obj->st2, x);
}
}
int myQueuePop(MyQueue* obj) {
ST* emptys = &obj->st1;
ST* nonemptys = &obj->st2;
if (!StackEmpty(&obj->st1))
{
emptys = &obj->st2;
nonemptys = &obj->st1;
}
while (StackSize(nonemptys) > 1)
{
StackPush(emptys, StackTop(nonemptys));
StackPop(nonemptys);
}
int first = StackTop(nonemptys);
StackPop(nonemptys);
while (StackSize(emptys) > 0)
{
StackPush(nonemptys, StackTop(emptys));
StackPop(emptys);
}
return first;
}
int myQueuePeek(MyQueue* obj) {
ST* emptys = &obj->st1;
ST* nonemptys = &obj->st2;
if (!StackEmpty(&obj->st1))
{
emptys = &obj->st2;
nonemptys = &obj->st1;
}
while (StackSize(nonemptys) > 1)
{
StackPush(emptys, StackTop(nonemptys));
StackPop(nonemptys);
}
int first = StackTop(nonemptys);
StackPush(emptys, StackTop(nonemptys));
StackPop(nonemptys);
while (StackSize(emptys) > 0)
{
StackPush(nonemptys, StackTop(emptys));
StackPop(emptys);
}
return first;
}
bool myQueueEmpty(MyQueue* obj) {
return StackEmpty(&obj->st1) && StackEmpty(&obj->st2);
}
void myQueueFree(MyQueue* obj) {
StackDestroy(&obj->st1);
StackDestroy(&obj->st2);
free(obj);
}
225.用队列模拟实现栈
225. 用队列实现栈 - 力扣(LeetCode)

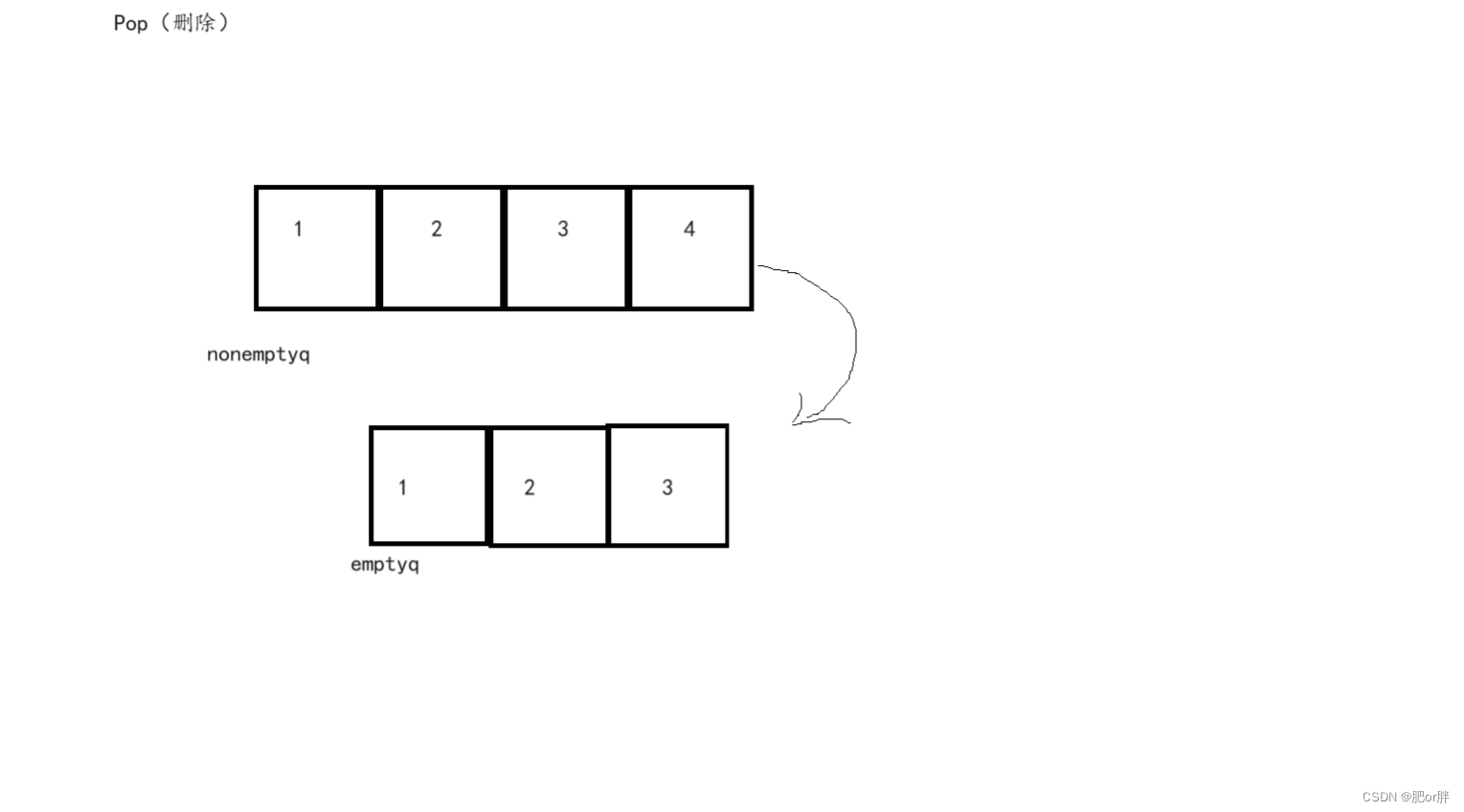
对于队列,我们也可以使用同样的思路,使用两个栈将数据来回导入导出,来实现队列的一端进行插入,另一端进行删除操作的定义。这里我们叫一个为emptyq(空队列),另一个叫nonemptys(非空队列)。
当我们想要插入时直接尾插到nonemptyq(如果是第一次插入,无所谓emptyq,nonemptyq)。
当我们想要删除时,将nonemptyq中第二个及以上的数据导入emptyq中,再将nonemptyq中的第一个数据删除。
注:因为C语言,并没有对链式队列的实现,所以我们要自己定义一个链式队列。
typedef int QNDataType;
typedef struct QueueNode
{
QNDataType data;
struct QueueNode* next;
}QNode;
typedef struct Queue
{
QNode* phead;
QNode* ptail;
int size;
}Queue;
//初始化
void QueueInit(Queue* pq)
{
assert(pq);
pq->phead = NULL;
pq->ptail = NULL;
pq->size = 0;
}
//插入
void QueuePush(Queue* pq, QNDataType x)
{
assert(pq);
QNode* newnode = (QNode*)malloc(sizeof(QNode));
if (newnode == NULL)
{
perror("mallloc");
return;
}
newnode->data = x;
newnode->next = NULL;
if (pq->ptail == NULL)
{
pq->ptail = pq->phead = newnode;
}
else
{
pq->ptail->next = newnode;
pq->ptail = newnode;
}
pq->size++;
}
//删除
void QueuePop(Queue* pq)
{
assert(pq);
assert(pq->phead);
if (pq->phead->next == NULL)
{
pq->phead = pq->phead->next;
pq->ptail = NULL;
}
else
{
QNode* del = pq->phead;
pq->phead = pq->phead->next;
free(del);
del = NULL;
}
pq->size--;
}
//获取头部元素
QNDataType QueueFront(Queue* pq)
{
assert(pq);
assert(pq->phead);
return pq->phead->data;
}
//获取尾部元素
QNDataType QueueBack(Queue* pq)
{
assert(pq);
assert(pq->phead);
return pq->ptail->data;
}
//元素个数
int QueueSize(Queue* pq)
{
assert(pq);
QNode* cur = pq->phead;
int size = 0;
while (cur != NULL)
{
size++;
cur = cur->next;
}
return size;
}
//判断是否为空
bool QueueEmpty(Queue* pq)
{
assert(pq);
return pq->phead == NULL;
}
//销毁
void QueueDestroy(Queue* pq)
{
assert(pq);
while(!QueueEmpty(pq))
{
QueuePop(pq);
}
pq->size = 0;
}
typedef struct {
Queue q1;
Queue q2;
} MyStack;
MyStack* myStackCreate() {
MyStack* pst = (MyStack*)malloc(sizeof(MyStack));
QueueInit(&pst->q1);
QueueInit(&pst->q2);
return pst;
}
void myStackPush(MyStack* obj, int x) {
if(!QueueEmpty(&obj->q1))
{
QueuePush(&obj->q1,x);
}
else
{
QueuePush(&obj->q2,x);
}
}
int myStackPop(MyStack* obj) {
Queue* empty = &obj->q1;
Queue* nonempty = &obj->q2;
if(!QueueEmpty(&obj->q1))
{
empty = &obj->q2;
nonempty = &obj->q1;
}
while(QueueSize(nonempty) > 1)
{
QueuePush(empty,QueueFront(nonempty));
QueuePop(nonempty);
}
int top = QueueFront(nonempty);
QueuePop(nonempty);
return top;
}
int myStackTop(MyStack* obj) {
if(!QueueEmpty(&obj->q1))
{
return obj->q1.ptail->data;
}
else{
return obj->q2.ptail->data;
}
}
bool myStackEmpty(MyStack* obj) {
return QueueEmpty(&obj->q1) && QueueEmpty(&obj->q2);
}
void myStackFree(MyStack* obj) {
QueueDestroy(&obj->q1);
QueueDestroy(&obj->q2);
free(obj);
}如果你看到这里,如果对其中代码有疑问,或者有更好的实现,欢迎大家在评论区讨论交流,方便大家更好的学习。