package 例题;
import java.lang.reflect.Constructor;
class 例题1Demo {
//变量
String s;
int i, i2, i3;
private 例题1Demo() {//无参构造方法
}
protected 例题1Demo(String s, int i) {//有参构造方法
this.s = s;
this.i = i;
}
public 例题1Demo(String... strings) throws NumberFormatException {//抛出异常
if (0 < strings.length)
i = Integer.valueOf(strings[0]);
if (1 < strings.length)
i2 = Integer.valueOf(strings[1]);
if (2 < strings.length)
i3 = Integer.valueOf(strings[2]);
}
public void print() {//方法
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
System.out.println("s=" + s);
System.out.println("i=" + i);
System.out.println("i2=" + i2);
System.out.println("i3=" + i3);
}
}
public class 例题1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
例题1Demo d1 = new 例题1Demo("10", "20", "30");
Class<? extends 例题1Demo> demoClass = d1.getClass();
// 获得所有构造方法
Constructor[] declaredConstructors = demoClass.getDeclaredConstructors();
for (int i = 0; i < declaredConstructors.length; i++) { // 遍历构造方法
Constructor<?> constructor = declaredConstructors[i];
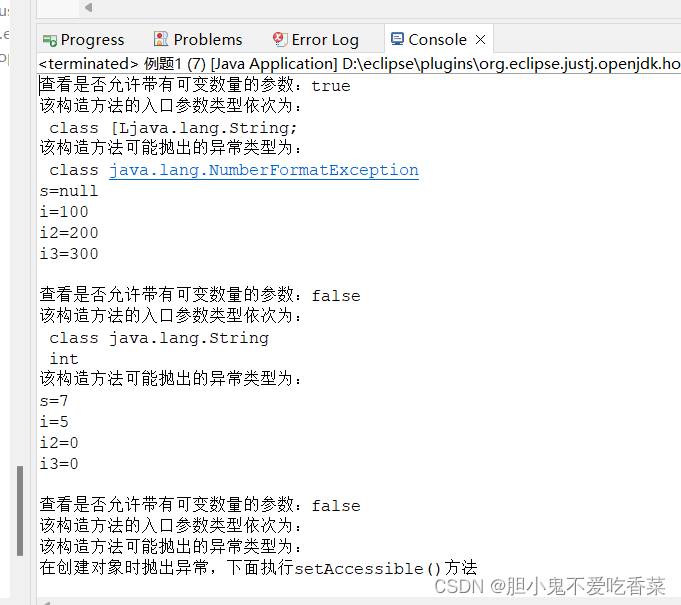
System.out.println("查看是否允许带有可变数量的参数:" + constructor.isVarArgs());
System.out.println("该构造方法的入口参数类型依次为:");
Class[] parameterTypes = constructor.getParameterTypes(); // 获取所有参数类型
for (int j = 0; j < parameterTypes.length; j++) {
System.out.println(" " + parameterTypes[j]);
}
System.out.println("该构造方法可能抛出的异常类型为:");
// 获得所有可能抛出的异常信息类型
Class[] exceptionTypes = constructor.getExceptionTypes();
for (int j = 0; j < exceptionTypes.length; j++) {
System.out.println(" " + exceptionTypes[j]);
}
例题1Demo d2 = null;
try { // 如果该成员变量的访问权限为private,则抛出异常,即不允许访问
if (i == 2) // 通过执行默认没有参数的构造方法创建对象
d2 = (例题1Demo) constructor.newInstance();
else if (i == 1)
// 通过执行具有两个参数的构造方法创建对象
d2 = (例题1Demo) constructor.newInstance("7", 5);
else { // 通过执行具有可变数量参数的构造方法创建对象
Object[] parameters = new Object[] { new String[] { "100", "200", "300" } };
d2 = (例题1Demo) constructor.newInstance(parameters);
}
} catch (Exception e) {
System.out.println("在创建对象时抛出异常,下面执行setAccessible()方法");
constructor.setAccessible(true); // 设置为允许访问
}
if (d2 != null) {
d2.print();
System.out.println();
}
}
}
}
package 例题;
import java.lang.reflect.Field;
class 例题2Demo {
//变量
int i;
public float f;
protected boolean b;
private String s;
}
public class 例题2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
例题2Demo example = new 例题2Demo();
Class exampleC = example.getClass();
// 获得所有成员变量
Field[] declaredFields = exampleC.getDeclaredFields();
for (int i = 0; i < declaredFields.length; i++) { // 遍历成员变量
Field field = declaredFields[i];
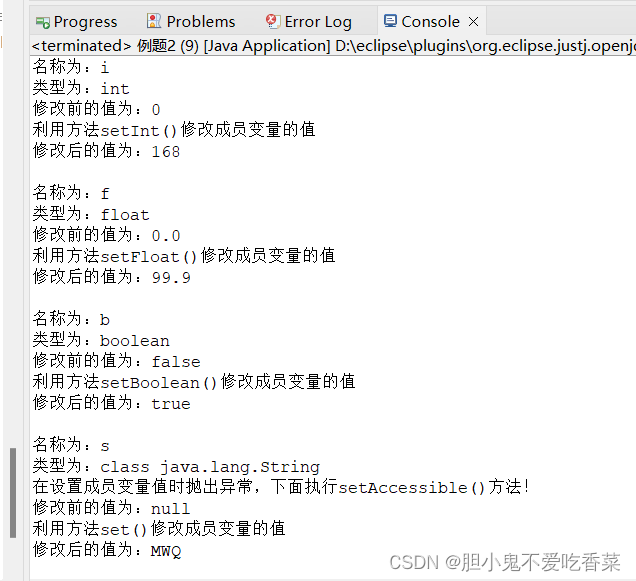
System.out.println("名称为:" + field.getName()); // 获得成员变量名称
Class fieldType = field.getType(); // 获得成员变量类型
System.out.println("类型为:" + fieldType);
boolean isTurn = true;
while (isTurn) {
// 如果该成员变量的访问权限为private,则抛出异常,即不允许访问
try {
isTurn = false;
// 获得成员变量值
System.out.println("修改前的值为:" + field.get(example));
if (fieldType.equals(int.class)) { // 判断成员变量的类型是否为int型
System.out.println("利用方法setInt()修改成员变量的值");
field.setInt(example, 168); // 为int型成员变量赋值
} else if (fieldType.equals(float.class)) { // 判断成员变量的类型是否为float型
System.out.println("利用方法setFloat()修改成员变量的值");
field.setFloat(example, 99.9F); // 为float型成员变量赋值
// 判断成员变量的类型是否为boolean型
} else if (fieldType.equals(boolean.class)) {
System.out.println("利用方法setBoolean()修改成员变量的值");
field.setBoolean(example, true); // 为boolean型成员变量赋值
} else {
System.out.println("利用方法set()修改成员变量的值");
field.set(example, "MWQ"); // 可以为各种类型的成员变量赋值
}
// 获得成员变量值
System.out.println("修改后的值为:" + field.get(example));
} catch (Exception e) {
System.out.println("在设置成员变量值时抛出异常," + "下面执行setAccessible()方法!");
field.setAccessible(true); // 设置为允许访问
isTurn = true;
}
}
System.out.println();
}
}
}
package 例题;
import java.lang.reflect.*;
class 例题3Demo {
//方法
static void staticMethod() {
System.out.println("执行staticMethod()方法");
}
public int publicMethod(int i) {
System.out.println("执行publicMethod()方法");
return i * 100;
}
protected int protectedMethod(String s, int i) throws NumberFormatException {//抛出异常
System.out.println("执行protectedMethod()方法");
return Integer.valueOf(s) + i;
}
private String privateMethod(String... strings) {
System.out.println("执行privateMethod()方法");
StringBuffer stringBuffer = new StringBuffer();
for (int i = 0; i < strings.length; i++) {
stringBuffer.append(strings[i]);
}
return stringBuffer.toString();
}
}
public class 例题3 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
例题3Demo demo = new 例题3Demo();
Class demoClass = demo.getClass();
// 获得所有方法
Method[] declaredMethods = demoClass.getDeclaredMethods();
for (int i = 0; i < declaredMethods.length; i++) {
Method method = declaredMethods[i]; // 遍历方法
System.out.println("名称为:" + method.getName()); // 获得方法名称
System.out.println("是否允许带有可变数量的参数:" + method.isVarArgs());
System.out.println("入口参数类型依次为:");
// 获得所有参数类型
Class[] parameterTypes = method.getParameterTypes();
for (int j = 0; j < parameterTypes.length; j++) {
System.out.println(" " + parameterTypes[j]);
}
// 获得方法返回值类型
System.out.println("返回值类型为:" + method.getReturnType());
System.out.println("可能抛出的异常类型有:");
// 获得方法可能抛出的所有异常类型
Class[] exceptionTypes = method.getExceptionTypes();
for (int j = 0; j < exceptionTypes.length; j++) {
System.out.println(" " + exceptionTypes[j]);
}
boolean isTurn = true;
while (isTurn) {
try {// 如果该方法的访问权限为private,则抛出异常,即不允许访问
isTurn = false;
if ("staticMethod".equals(method.getName()))
method.invoke(demo); // 执行没有入口参数的方法
else if ("publicMethod".equals(method.getName()))
System.out.println("返回值为:" + method.invoke(demo, 168)); // 执行方法
else if ("protectedMethod".equals(method.getName()))
System.out.println("返回值为:" + method.invoke(demo, "7", 5)); // 执行方法
else if ("privateMethod".equals(method.getName())) {
Object[] parameters = new Object[] { new String[] { "M", "W", "Q" } }; // 定义二维数组
System.out.println("返回值为:" + method.invoke(demo, parameters));
}
} catch (Exception e) {
System.out.println("在执行方法时抛出异常," + "下面执行setAccessible()方法!");
method.setAccessible(true); // 设置为允许访问
isTurn = true;
}
}
System.out.println();
}
}
}

//例题4
package 例题;
import java.lang.annotation.ElementType;
import java.lang.annotation.Retention;
import java.lang.annotation.RetentionPolicy;
import java.lang.annotation.Target;
@Target(value = { ElementType.CONSTRUCTOR })//用于构造方法
@Retention(value = RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
public @interface 例题4Constructor_Annotation {
String value() default "默认构造方法";
}
//例题4
package 例题;
import java.lang.annotation.ElementType;
import java.lang.annotation.Retention;
import java.lang.annotation.RetentionPolicy;
import java.lang.annotation.Target;
@Target(value = { ElementType.FIELD,ElementType.METHOD,ElementType.PARAMETER })
@Retention(value = RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
public @interface 例题4Field_Method {
String describe();
Class type() default void.class;
}
package 例题;
public class 例题4 {
//注释字段
@例题4Field_Method(describe = "编号",type = int.class)
int id;
@例题4Field_Method(describe = "姓名",type = String.class)
String name;
//采用默认值注释构造方法
@例题4Constructor_Annotation
public 例题4() {
}
//注释构造方法
@例题4Constructor_Annotation("立即初始化构造方法")
public 例题4(@例题4Field_Method(describe = "编号",type = int.class)
int id,
@例题4Field_Method(describe = "姓名",type = String.class) String name) {
this.id = id;
this.name = name;
}
//注释方法
@例题4Field_Method(describe = "获得编号",type = int.class)
public int getld() {
return id;
}
//成员type采用默认值注释方法
@例题4Field_Method(describe = "设置编号")//注释方法的参数
public void setld(@例题4Field_Method(describe = "编号",type = int.class) int id) {
this.id = id;
}
@例题4Field_Method(describe = "获得姓名",type = String.class)
public String getName() {
return name;
}
@例题4Field_Method(describe = "设置姓名")
public void setName(@例题4Field_Method(describe = "姓名",type = String.class) String name) {
this.name = name;
}
}
package 例题;
import java.lang.annotation.*;
import java.lang.reflect.*;
public class 例题5 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws ClassNotFoundException {
Class recordC = null;
recordC = new 例题4().getClass();
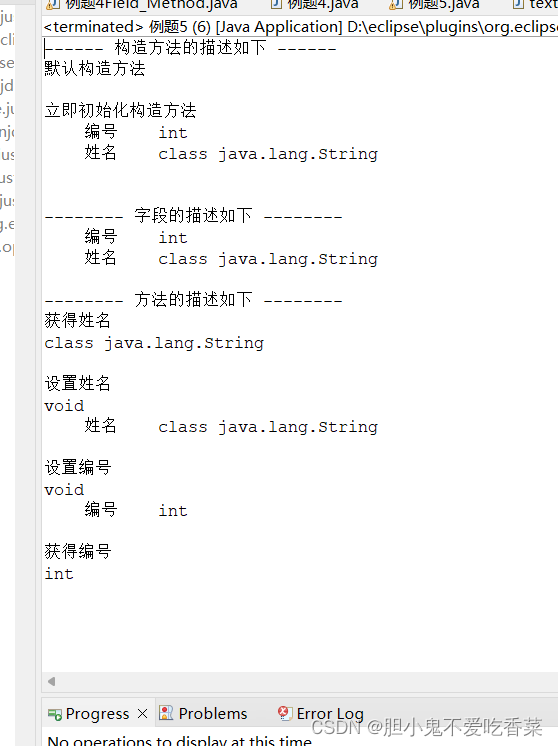
System.out.println("------ 构造方法的描述如下 ------");
Constructor[] declaredConstructors = recordC.getDeclaredConstructors(); // 获得所有构造方法
for (int i = 0; i < declaredConstructors.length; i++) {
Constructor constructor = declaredConstructors[i]; // 遍历构造方法
// 查看是否具有指定类型的注释
if (constructor.isAnnotationPresent(例题4Constructor_Annotation.class)) {
// 获得指定类型的注释
例题4Constructor_Annotation ca = (例题4Constructor_Annotation) constructor
.getAnnotation(例题4Constructor_Annotation.class);
System.out.println(ca.value()); // 获得注释信息
}
Annotation[][] parameterAnnotations = constructor.getParameterAnnotations(); // 获得参数的注释
for (int j = 0; j < parameterAnnotations.length; j++) {
// 获得指定参数注释的长度
int length = parameterAnnotations[j].length;
if (length == 0) // 如果长度为0则表示没有为该参数添加注释
System.out.println(" 未添加Annotation的参数");
else
for (int k = 0; k < length; k++) {
// 获得参数的注释
例题4Field_Method pa = (例题4Field_Method) parameterAnnotations[j][k];
System.out.print(" " + pa.describe()); // 获得参数描述
System.out.println(" " + pa.type()); // 获得参数类型
}
}
System.out.println();
}
System.out.println();
System.out.println("-------- 字段的描述如下 --------");
Field[] declaredFields = recordC.getDeclaredFields(); // 获得所有字段
for (int i = 0; i < declaredFields.length; i++) {
Field field = declaredFields[i]; // 遍历字段
// 查看是否具有指定类型的注释
if (field.isAnnotationPresent(例题4Field_Method.class)) {
// 获得指定类型的注释
例题4Field_Method fa = field.getAnnotation(例题4Field_Method.class);
System.out.print(" " + fa.describe()); // 获得字段的描述
System.out.println(" " + fa.type()); // 获得字段的类型
}
}
System.out.println();
System.out.println("-------- 方法的描述如下 --------");
Method[] methods = recordC.getDeclaredMethods(); // 获得所有方法
for (int i = 0; i < methods.length; i++) {
Method method = methods[i]; // 遍历方法
// 查看是否具有指定类型的注释
if (method.isAnnotationPresent(例题4Field_Method.class)) {
// 获得指定类型的注释
例题4Field_Method ma = method.getAnnotation(例题4Field_Method.class);
System.out.println(ma.describe()); // 获得方法的描述
System.out.println(ma.type()); // 获得方法的返回值类型
}
Annotation[][] parameterAnnotations = method.getParameterAnnotations(); // 获得参数的注释
for (int j = 0; j < parameterAnnotations.length; j++) {
int length = parameterAnnotations[j].length; // 获得指定参数注释的长度
if (length == 0) // 如果长度为0表示没有为该参数添加注释
System.out.println(" 未添加Annotation的参数");
else
for (int k = 0; k < length; k++) {
// 获得指定类型的注释
例题4Field_Method pa = (例题4Field_Method) parameterAnnotations[j][k];
System.out.print(" " + pa.describe()); // 获得参数的描述
System.out.println(" " + pa.type()); // 获得参数的类型
}
}
System.out.println();
}
}
}
//例题16.5