简介
本文给出C++版以及Rust版调用windows API实现QOS的示例,并提出一些注意事项。QOS可以用来区分socket 优先级、实现带宽控制等诸多功能。
UDP版本
该示例的重要部分是客户端应用程序。客户端代码的工作方式如下:
1. 通过套接字连接到目标 IP 地址。
2. 通过调用 QOSCreateHandle 初始化 QOS 子系统。
3. 通过调用 QOSAddSocketToFlow 为套接字创建一个流。
4. 通过调用 QOSQueryFlow 查询源主机和目标主机之间路径的特性。使用的两个估计值是:- 瓶颈带宽:最大理论吞吐量;
- 可用带宽:新流量的当前可用吞吐量。根据网络配置的不同:
A. 可能进行带宽估算。例如,目标可能在另一个子网上。如果是这样,客户端将仅进行流量整形并根据指定的流量类型标记优先级,但永远无法接收可用带宽的通知或估计,而出站流量将根据 DLNA 规范进行标记。
B. QOS 子系统可能没有足够的时间来估计到目的地主机的条件。如果发生这种情况,客户端将在重试之前休眠 1 秒。在生产应用程序中,您可以通过在 A/V 流量开始之前调用 QOSStartTrackingClient API 来最小化发生这种情况的可能性。建议在目标与客户端位于同一子网上时始终使用此 API。5. 如果可用带宽的估计值小于请求的带宽,则客户端将修订请求的带宽。
6. 客户端为我们的流设置了一个固定速率,该速率将限制出站流量到请求的带宽。为此,它考虑了地址族和使用的协议(UDP)的线路开销。
7. 客户端注册了拥塞通知。
8. 使用形状机制作为控制循环以期望速率发送流量。应用程序使用 TransmitPackets API 调用发送数据包。客户端利用形状器仅在所有数据包离开主机时才完成此 Winsock 传输操作的事实,以确定一次发送多少个数据包。
9. 当外部条件将网络推入拥塞状态时,将接收到拥塞通知。作为反应,客户端将将目标比特率降低到初始值的十分之一。此外,客户端将在可用带宽足以返回到先前的比特率时请求通知。
代码如下:
/*++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++
THIS CODE AND INFORMATION IS PROVIDED "AS IS" WITHOUT WARRANTY OF
ANY KIND, EITHER EXPRESSED OR IMPLIED, INCLUDING BUT NOT LIMITED TO
THE IMPLIED WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY AND/OR FITNESS FOR A
PARTICULAR PURPOSE.
Copyright (c) Microsoft Corporation. All rights reserved.
Module Name:
qossample.c
Abstract:
This program implements a simple traffic generator which uses the QOS2
api to not overload the network path between the source and its destination.
Although the application can be run as a receiver to process the traffic
generated, the client side of the application is the important part of this
sample. This code is in the Client function.
The code for the client works as follows:
1) A socket is connected to the destination IP address
2) The QOS subsystem is initialized by a call to QOSCreateHandle
3) A flow is created for the socket by a call to QOSAddSocketToFlow
4) The characteristics of the path between the source host and destination
host are queried through QOSQueryFlow. The two estimates used are:
- the bottleneck bandwidth: the maximum theoretical throughput;
- and the available bandwidth: the currently available throughput for
new traffic
Depending on your network configuration:
A) It may be impossible to run network experiments to the destination.
For example, the destination might be on another subnet. If so, the
client will only shape traffic and mark priority with DSCP based on
the specified traffic type, but will never be able to receive
notifications or estimates of available bandwidth and outgoing traffic
would be marked per the DLNA specification.
B) The QOS subsystem may not have had enough time to estimate conditions
to the destination host. If this happens, the client will sleep for 1s
before retrying. In a production application you could minize the
likelihood of this happening by calling, before the start of your
A/V traffic, the QOSStartTrackingClient API. It is suggested that this
API always be used when the destination is on the same subnet as the
client.
5) If the estimate of available bandwidth is less than the requested
bandwidth, the client revises the requested bandwidth.
6) The client sets a shaping rate for our flow that will limit the outgoing
traffic to the requested bandwidth. To do so, it accounts for the wire
overhead given both the address family as well as the protocol used, UDP.
7) The client registers for notifications of congestion.
8) Traffic is sent at the desired rate using the shaping mechanism as the
control loop. The application uses the API call TransmitPackets to
send the packet bunches. The client uses the fact that the shaper will
only complete this Winsock transmit operation when all packets have left
the host to determine how many packets to send at a time.
9) A congestion notification will be received whenever external conditions
push the network into a congested state. The client, as a reaction, will
lower the targeted bit rate to one-tenth of the initial value. Moreover,
the client will request notification when the bandwidth available is
enough to return to the previous bit rate.
Environment:
User-Mode only
Revision History:
------------------------------------------------------------------------------*/
#include <winsock2.h>
#include <mswsock.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <qos2.h>
#pragma comment(lib, "ws2_32.lib")
#pragma comment(lib, "QWave.lib")
#pragma warning(disable:4127) // condition expression is constant
//******************************************************************************
// Forward declarations
//******************************************************************************
VOID
client(
__in int argc,
__in_ecount(argc) char* argv[]
);
VOID
server();
VOID
help();
//******************************************************************************
// Global defines
//******************************************************************************
// Size of the data part of each datagram that is exchanged between the
// client and the server. This does not count the IP and UDP header.
#define DATAGRAM_SIZE 1400
// Number of bursts we are aiming for per second
#define BURSTS_PER_SECOND 40
// Port to be used for communication,
// 40007 in hex in network byte order
#define PORT 0x479c
//******************************************************************************
// Global variables
//******************************************************************************
// Array used by both the client routine and the server routine to
// send and receive data
CHAR dataBuffer[DATAGRAM_SIZE];
// Version of the QOS subsystem we wish to use
QOS_VERSION QosVersion = { 1 , 0 };
//******************************************************************************
// Routine:
// main
//
// Description:
// Entry point. Verifies that the number of parameters is enough to
// ascertain whether this instance is to be a client or server.
//
//******************************************************************************
int
_cdecl
main(
__in int argc,
__in_ecount(argc) char* argv[]
)
{
// Verify the number of command line arguments
if (argc < 2) {
help();
exit(0);
}
if (strcmp(argv[1], "-s") == 0) {
// If the call was "qossample -s" run as a server
server();
}
else if (strcmp(argv[1], "-c") == 0) {
// If the call was "qossample -c ..." run as a client
client(argc, argv);
}
// Else, run the help routine
help();
return 1;
}
//******************************************************************************
// Routine:
// socketCreate
//
// Description:
// This routine prepares the socket for the client instance. To do so,
// it converts the address parameter from string to IP address. Then
// it creates a UDP socket which it connects to this destination.
//
// Since we will use TransmitPackets for our send operations, the function
// pointer is obtained from Winsock.
//
//******************************************************************************
VOID
socketCreate(
__in PCHAR destination,
__out SOCKET* socket,
__out ADDRESS_FAMILY* addressFamily,
__out LPFN_TRANSMITPACKETS* transmitPackets
) {
// Return value of WSAStartup
WSADATA wsaData;
// Temporarily used to represent the destination IP address
SOCKADDR_STORAGE destAddr;
// Result of the various Winsock API calls
INT returnValue;
// Used by WSAStringToAddressA
INT sockaddrLen;
// Used by WSAIoctl
DWORD bytesReturned;
// GUID of the TransmitPacket Winsock2 function which we will
// use to send the traffic at the client side.
GUID TransmitPacketsGuid = WSAID_TRANSMITPACKETS;
// Start Winsock
returnValue = WSAStartup(MAKEWORD(2, 2), &wsaData);
if (returnValue != 0) {
printf("%s:%d - WSAStartup failed (%d)\n",
__FILE__, __LINE__, returnValue);
exit(1);
}
// First attempt to convert the string to an IPv4 address
sockaddrLen = sizeof(destAddr);
destAddr.ss_family = AF_INET;
returnValue = WSAStringToAddressA(destination,
AF_INET,
NULL,
(LPSOCKADDR)&destAddr,
&sockaddrLen);
if (returnValue != ERROR_SUCCESS) {
// If this fails,
// Attempt to convert the string to an IPv6 address
sockaddrLen = sizeof(destAddr);
destAddr.ss_family = AF_INET6;
returnValue = WSAStringToAddressA(destination,
AF_INET6,
NULL,
(LPSOCKADDR)&destAddr,
&sockaddrLen);
if (returnValue != ERROR_SUCCESS) {
// If this again fails, exit the application
// But print out the help information first.
printf("%s:%d - WSAStringToAddressA failed (%d)\n",
__FILE__, __LINE__, WSAGetLastError());
help();
exit(1);
}
}
// Set the destination port.
SS_PORT((PSOCKADDR)&destAddr) = PORT;
// Copy the address family back to caller
*addressFamily = destAddr.ss_family;
// Create a UDP socket
*socket = WSASocket(destAddr.ss_family,
SOCK_DGRAM,
0,
NULL,
0,
WSA_FLAG_OVERLAPPED);
if (*socket == INVALID_SOCKET) {
printf("%s:%d - WSASocket failed (%d)\n",
__FILE__, __LINE__, WSAGetLastError());
exit(1);
}
// Connect the new socket to the destination
returnValue = WSAConnect(*socket,
(PSOCKADDR)&destAddr,
sizeof(destAddr),
NULL,
NULL,
NULL,
NULL);
if (returnValue != NO_ERROR) {
printf("%s:%d - WSAConnect failed (%d)\n",
__FILE__, __LINE__, WSAGetLastError());
exit(1);
}
// Query the function pointer for the TransmitPacket function
returnValue = WSAIoctl(*socket,
SIO_GET_EXTENSION_FUNCTION_POINTER,
&TransmitPacketsGuid,
sizeof(GUID),
transmitPackets,
sizeof(PVOID),
&bytesReturned,
NULL,
NULL);
if (returnValue == SOCKET_ERROR) {
printf("%s:%d - WSAIoctl failed (%d)\n",
__FILE__, __LINE__, WSAGetLastError());
exit(1);
}
}
//******************************************************************************
// Routine:
// client
//
// Description:
// This routine creates a datagram socket which it connects to the remote
// IP address. This socket is then added to a QOS flow. The application
// uses the flow to rate control its outgoing traffic. Packets on this flow
// will be prioritized if the network path between the client and receiver
// support prioritization. Specifically, if the receiver is:
//
// A) On-link (same subnet), both 802.1Q and DSCP are applied subject to
// available bandwidth and network support.
// B) Off-link (different subnet), only DSCP is applied regardless of
// available bandwidth.
//
// Moreover, the application queries the characteristics of the network
// path for the socket. If estimates are available, the application:
//
// 1) may readjust its throughput so as to not cause congestion on the
// network.
// 2) will be notified when the network enters congestion. As a result,
// it will lower it's throughput to 1/10 the targeted rate.
// 3) will be notified when the network is no longer congested and enough
// bandwidth is available for the application to return to its targeted
// rate.
//
//******************************************************************************
VOID
client(
__in int argc,
__in_ecount(argc) char* argv[]
) {
// Address family of the datagram socket
ADDRESS_FAMILY addressFamily;
// Socket for our traffic experiment
SOCKET socket;
// Function pointer to the TransmitPacket Winsock2 function
LPFN_TRANSMITPACKETS transmitPacketsFn;
// Array of transmit elements
LPTRANSMIT_PACKETS_ELEMENT transmitEl;
// Target packet rate and bit rate this application will aim to send
// If there is no congestion
ULONG targetPacketRate, targetBitRate;
// Current rate at which the application is sending. If the network is
// congested, this will be less than the target rate
ULONG currentPacketRate, currentBitRate;
// Counters for the achieved packet rate and achieved bit rate
ULONG achievedPacketRate, achievedBitRate;
// Timer; used to periodically output to the screen our counters
HANDLE timerEvent;
LARGE_INTEGER timerAwakenTime;
// Handle to the QOS subsystem
// Returned by QOSCreateHandle
HANDLE qosHandle;
// ID of the QOS flow we will create for the socket.
// Returned by QOSAddSocketToFlow
QOS_FLOWID flowID;
// Result of QOSQueryFlow
QOS_FLOW_FUNDAMENTALS flowFund;
// Parameter to QOSSetFlow
QOS_FLOWRATE_OUTGOING flowRate;
// If TRUE, the QOS subsystem is running network experiments on the
// network path to the destination. If false, estimates are not available.
// The flow is still marked and shaped.
BOOL estimatesAvailable;
// Result of the QOS API calls.
BOOL result;
// Overlapped operation used for TransmitPackets
WSAOVERLAPPED sendOverlapped;
// Overlapped operation used for QOSNotifyFlow to be notified
// of network congestions.
OVERLAPPED congestionOverlapped;
// Overlapped operation used for QOSNotifyFlow to be notified when,
// after congestion, there is enough bandwidth for the target rate
OVERLAPPED availableOverlapped;
// TRUE if the network is currently congested
BOOL congestion;
ULONG temp;
// Verify the number of command line arguments
if (argc != 4) {
help();
exit(1);
}
// Identify what destination IP address we're trying to talk to and
// connect a UDP socket to it
socketCreate(argv[2],
&socket,
&addressFamily,
&transmitPacketsFn);
printf("socket resut %d\n", socket);
if (FALSE == QOSCreateHandle(&QosVersion, &qosHandle)) {
printf("%s:%d - QOSCreateHandle failed (%d)\n",
__FILE__, __LINE__, GetLastError());
exit(1);
}
// The Flow ID parameter MUST be set to 0 as input to QOSAddSocketToFlow
flowID = 0;
// Create a flow for our socket
result = QOSAddSocketToFlow(qosHandle,
socket,
NULL,
QOSTrafficTypeVoice,
QOS_NON_ADAPTIVE_FLOW,
&flowID);
if (result == FALSE) {
printf("%s:%d - QOSAddSocketToFlow failed (%d)\n",
__FILE__, __LINE__, GetLastError());
exit(1);
}
// Read the data rate in bits/s passed on the command line
targetBitRate = atol(argv[3]);
if (targetBitRate == 0) {
help();
exit(1);
}
// Convert from bits to bytes
targetBitRate /= 8;
// Calculate how many packets we need; round up.
targetPacketRate = targetBitRate / ARRAYSIZE(dataBuffer);
if (targetBitRate % ARRAYSIZE(dataBuffer) != 0)
targetPacketRate++;
// Calculate the number of packets per bursts; round up
if (targetPacketRate % BURSTS_PER_SECOND != 0) {
targetPacketRate /= BURSTS_PER_SECOND;
targetPacketRate++;
}
else {
targetPacketRate /= BURSTS_PER_SECOND;
}
// Calculate the final bit rate, targetBitRate, in bps that the application
// will send.
targetBitRate = BURSTS_PER_SECOND
* targetPacketRate
* ARRAYSIZE(dataBuffer)
* 8;
//
// Allocate an array of transmit elements big enough to send
// targetPacketRate packets every burst.
transmitEl = static_cast<LPTRANSMIT_PACKETS_ELEMENT>( HeapAlloc(GetProcessHeap(),
HEAP_ZERO_MEMORY,
sizeof(TRANSMIT_PACKETS_ELEMENT)
* targetPacketRate));
if (transmitEl == NULL) {
printf("%s:%d - HeapAlloc failed (%d)\n",
__FILE__, __LINE__, GetLastError());
exit(1);
}
// For the purpose of this application, we only use one data buffer for all
// of our packets.
ZeroMemory(&dataBuffer, sizeof(dataBuffer));
//
// Initialize each of these transmit element to point to the same zeroed out
// data buffer
for (temp = 0; temp < targetPacketRate; temp++) {
transmitEl[temp].dwElFlags = TP_ELEMENT_MEMORY | TP_ELEMENT_EOP;
transmitEl[temp].pBuffer = dataBuffer;
transmitEl[temp].cLength = sizeof(dataBuffer);
}
// Print out what we'll be doing
printf("----------------------------------"
"----------------------------------\n"
"This instance of the QOS sample program is aiming to:\n"
"\t - Send %d bits of UDP traffic per second\n"
"\t - In packets of %d bytes\n"
"\t - In bursts of %d packets every %d milliseconds\n\n"
"----------------------------------"
"----------------------------------\n",
targetBitRate,
ARRAYSIZE(dataBuffer),
targetPacketRate,
1000 / BURSTS_PER_SECOND);
// Assume, by default, that estimates are not available
estimatesAvailable = FALSE;
printf("Querying fundamentals about the network path: ");
do {
temp = sizeof(flowFund);
// Query the flow fundamentals for the path to the destination.
// This will return estimates of the bottleneck bandwidth, available
// bandwidth and average RTT.
result = QOSQueryFlow(qosHandle,
flowID,
QOSQueryFlowFundamentals,
&temp,
&flowFund,
0,
NULL);
if (result == FALSE) {
DWORD lastError;
lastError = GetLastError();
if (lastError == ERROR_NO_DATA) {
// If the call failed, this could be because the QOS subsystem
// has not yet gathered enough data for estimates. If so, the
// QOS2 api returns ERROR_NO_DATA.
printf(".");
Sleep(1000);
}
else if (lastError == ERROR_NOT_SUPPORTED)
{
// If the call failed, this could be because the QOS subsystem
// cannot run network experiments on the network path to the
// destination. If so, the API returns ERROR_NOT_SUPPORTED.
printf("NOT SUPPORTED\n"
"\t Network conditions to this destination could not\n"
"\t be detected as your network configuration is not\n"
"\t supported for network experiments\n");
break;
}
else {
printf("%s:%d - QOSQueryFlow failed (%d)\n",
__FILE__, __LINE__, lastError);
exit(1);
}
}
else if ((flowFund.BottleneckBandwidthSet == FALSE)
|| (flowFund.AvailableBandwidthSet == FALSE)) {
// If the call succeeded but bottleneck bandwidth or
// available bandwidth are not known then estimates are still
// processing; query again in 1 second.
printf(".");
Sleep(1000);
}
else {
// Estimate where available.
double bottleneck;
double available;
estimatesAvailable = TRUE;
// Convert the bottleneck bandwidth from bps to mbps
bottleneck = (double)flowFund.BottleneckBandwidth;
bottleneck /= 1000000.0;
// Convert available bandwidth from bps to mbps
available = (double)flowFund.AvailableBandwidth;
available /= 1000000.0;
printf("DONE\n"
"\t - Bottleneck bandwidth is approximately %4.2f Mbps\n"
"\t - Available bandwidth is approximately %4.2f Mbps\n",
bottleneck,
available);
break;
}
} while (TRUE);
if (estimatesAvailable == TRUE) {
UINT64 targetBitRateWithHeaders;
printf("\nNOTE: the accuracy of the QOS estimates can be impacted by\n"
"any of the following,\n\n"
"\t - Both the network interface at the client\n"
"\t and at the server must be using NDIS 6 drivers.\n"
"\t - If the server is not a Windows Vista host, verify that \n"
"\t it implements the LLD2 networking protocol. You can\n"
"\t find more information at http://www.microsoft.com.\n"
"\t - IPSec, VPNs and enterprise class networking equipment\n"
"\t may interfere with network experiments.\n\n");
// Calculate what our target bit rate, with protocol headers for
// IP(v4/v6) and UDP will be.
targetBitRateWithHeaders = QOS_ADD_OVERHEAD(addressFamily,
IPPROTO_UDP,
ARRAYSIZE(dataBuffer),
targetBitRate);
if (flowFund.AvailableBandwidth < targetBitRateWithHeaders) {
// If the estimate of available bandwidth is not sufficient for the
// target bit rate (with headers), drop to a lesser throughput
UINT64 availableBandwidth;
// The estimate returned does not account for headers
// Remove the estimated overhead for our address family and UDP.
availableBandwidth = QOS_SUBTRACT_OVERHEAD(
addressFamily,
IPPROTO_UDP,
ARRAYSIZE(dataBuffer),
flowFund.AvailableBandwidth);
// Calculate the rate of packets we can realistically send
targetPacketRate = (LONG)availableBandwidth / 8;
targetPacketRate /= ARRAYSIZE(dataBuffer);
targetPacketRate /= BURSTS_PER_SECOND;
// Calculate the real bit rate we'll be using
targetBitRate = BURSTS_PER_SECOND
* targetPacketRate
* ARRAYSIZE(dataBuffer)
* 8;
printf("Not enough available bandwidth for the requested bitrate.\n"
"Downgrading to lesser bitrate - %d.\n", targetBitRate);
}
}
// Our starting rate is this target bit rate
currentBitRate = targetBitRate;
currentPacketRate = targetPacketRate;
// Ask the QOS subsystem to shape our traffic to this bit rate. Note that
// the application needs to account for the size of the IP(v4/v6)
// and UDP headers.
// Calculate the real bandwidth we will need to be shaped to.
flowRate.Bandwidth = QOS_ADD_OVERHEAD(addressFamily,
IPPROTO_UDP,
ARRAYSIZE(dataBuffer),
currentBitRate);
// Set shaping characteristics on our QOS flow to smooth out our bursty
// traffic.
flowRate.ShapingBehavior = QOSShapeAndMark;
// The reason field is not applicable for the initial call.
flowRate.Reason = QOSFlowRateNotApplicable;
result = QOSSetFlow(qosHandle,
flowID,
QOSSetOutgoingRate,
sizeof(flowRate),
&flowRate,
0,
NULL);
if (result == FALSE) {
printf("%s:%d - QOSSetFlow failed (%d)\n",
__FILE__, __LINE__, GetLastError());
exit(1);
}
// Allocate a waitable timer. We will use this timer to periodically
// awaken and output statistics.
timerEvent = CreateWaitableTimer(NULL, FALSE, NULL);
if (timerEvent == NULL) {
printf("%s:%d - CreateWaitableTimer failed (%d)\n",
__FILE__, __LINE__, GetLastError());
exit(1);
}
//
// Set the sampling time to 1 second
timerAwakenTime.QuadPart = -10000000; // 1 second
if (FALSE == SetWaitableTimer(timerEvent,
&timerAwakenTime,
1000,
NULL,
NULL,
FALSE)) {
printf("%s:%d - SetWaitableTimer failed (%d)\n",
__FILE__, __LINE__, GetLastError());
exit(1);
}
// Prepare the support overlapped structures to detect congestion,
// notifications of bandwidth change and the completion of our send
// routines.
ZeroMemory(&congestionOverlapped, sizeof(congestionOverlapped));
congestionOverlapped.hEvent = CreateEvent(NULL, FALSE, FALSE, NULL);
if (congestionOverlapped.hEvent == NULL) {
printf("%s:%d - CreateEvent failed (%d)\n",
__FILE__, __LINE__, GetLastError());
exit(1);
}
ZeroMemory(&availableOverlapped, sizeof(availableOverlapped));
availableOverlapped.hEvent = CreateEvent(NULL, FALSE, FALSE, NULL);
if (availableOverlapped.hEvent == NULL) {
printf("%s:%d - CreateEvent failed (%d)\n",
__FILE__, __LINE__, GetLastError());
exit(1);
}
ZeroMemory(&sendOverlapped, sizeof(sendOverlapped));
sendOverlapped.hEvent = CreateEvent(NULL, FALSE, FALSE, NULL);
if (sendOverlapped.hEvent == NULL) {
printf("%s:%d - CreateEvent failed (%d)\n",
__FILE__, __LINE__, GetLastError());
exit(1);
}
if (estimatesAvailable == TRUE) {
// If estimates are available, we request a notification
// for congestion. This notification will complete whenever network
// congestion is detected.
result = QOSNotifyFlow(qosHandle,
flowID,
QOSNotifyCongested,
NULL,
NULL,
0,
&congestionOverlapped);
if (result == FALSE) {
DWORD lastError;
lastError = GetLastError();
if (lastError != ERROR_IO_PENDING) {
printf("%s:%d - QOSNotifyFlow failed (%d)\n",
__FILE__, __LINE__, lastError);
exit(1);
}
}
}
printf("----------------------------------"
"----------------------------------\n"
" # packets | # of bits | Bottleneck "
"| Available | Congestion \n"
"----------------------------------"
"----------------------------------\n");
// Initialize our counters to 0
achievedBitRate = achievedPacketRate = 0;
congestion = FALSE;
do {
BOOL sendNextGroup;
// Send the first burst of packets
result = (*transmitPacketsFn)(socket,
transmitEl,
currentPacketRate,
0xFFFFFFFF,
&sendOverlapped,
TF_USE_KERNEL_APC);
if (result == FALSE) {
DWORD lastError;
lastError = WSAGetLastError();
if (lastError != ERROR_IO_PENDING) {
printf("%s:%d - TransmitPackets failed (%d)\n",
__FILE__, __LINE__, GetLastError());
exit(1);
}
}
// Increase the counter of sent data
achievedPacketRate += currentPacketRate;
achievedBitRate += currentPacketRate * ARRAYSIZE(dataBuffer) * 8;
sendNextGroup = FALSE;
do {
HANDLE waitEvents[3];
DWORD waitResult;
// Wait for any of the 3 events to complete
// The 1 second periodic timer
waitEvents[0] = timerEvent;
if (congestion)
// Notification of available bandwidth
waitEvents[1] = availableOverlapped.hEvent;
else
// Notification of congestion
waitEvents[1] = congestionOverlapped.hEvent;
// Notification that the send operation has completed
waitEvents[2] = sendOverlapped.hEvent;
waitResult = WaitForMultipleObjects(ARRAYSIZE(waitEvents),
(PHANDLE)waitEvents,
FALSE,
INFINITE);
switch (waitResult) {
case WAIT_OBJECT_0: {
// The event for the periodic timer is set
printf("%10d | ", achievedPacketRate);
printf("%10d | ", achievedBitRate);
if (estimatesAvailable) {
// If estimates are available for the network path
// query for estimates and output to the console along
// with our counters.
// Ascertained through QOSQueryFlow
BOOL estimateIndicatesCongestion;
// Default is unknown
estimateIndicatesCongestion = FALSE;
ZeroMemory(&flowFund, sizeof(flowFund));
temp = sizeof(flowFund);
QOSQueryFlow(qosHandle,
flowID,
QOSQueryFlowFundamentals,
&temp,
&flowFund,
0,
NULL);
if (flowFund.BottleneckBandwidthSet)
printf("%10d | ", flowFund.BottleneckBandwidth);
else
printf(" NO DATA | ");
if (flowFund.AvailableBandwidthSet) {
if (flowFund.AvailableBandwidth == 0)
estimateIndicatesCongestion = TRUE;
printf("%10d | ", flowFund.AvailableBandwidth);
}
else
printf(" NO DATA | ");
if (estimateIndicatesCongestion)
printf(" CONGESTION\n");
else
printf("\n");
}
else {
// Bandwidth estimates are not available
printf(" N/A | N/A |\n");
}
//
// Reset the counters
achievedPacketRate = achievedBitRate = 0;
break;
}
case WAIT_OBJECT_0 + 1: {
// This is either a notification for congestion or
// for bandwidth available
if (congestion == FALSE) {
UINT64 targetBandwidthWithOverhead;
ULONG bufferSize;
//
// Congestion
//
printf("----------------------------------"
"----------------------------------\n"
"CONGESTION\n"
"----------------------------------"
"----------------------------------\n");
//
// Reduce the current rate to one-tenth of the initial rate
// Insure you're always sending at least 1 packet per
// burst.
if (currentPacketRate < 10)
currentPacketRate = 1;
else
currentPacketRate /= 10;
// Calculate the new bit rate we'll be using
currentBitRate = BURSTS_PER_SECOND
* currentPacketRate
* ARRAYSIZE(dataBuffer)
* 8;
// Update the shaping characteristics on our QOS flow
// to smooth out our bursty traffic.
flowRate.Bandwidth = QOS_ADD_OVERHEAD(
addressFamily,
IPPROTO_UDP,
ARRAYSIZE(dataBuffer),
currentBitRate);
flowRate.ShapingBehavior = QOSShapeAndMark;
flowRate.Reason = QOSFlowRateCongestion;
result = QOSSetFlow(qosHandle,
flowID,
QOSSetOutgoingRate,
sizeof(flowRate),
&flowRate,
0,
NULL);
if (result == FALSE) {
printf("%s:%d - QOSSetFlow failed (%d)\n",
__FILE__, __LINE__, GetLastError());
exit(1);
}
// Request a notification for when there is enough bandwidth
// to return to our previous targeted bit rate.
// This will complete only when the network is no longer
// congested and bandwidth is available.
targetBandwidthWithOverhead = QOS_ADD_OVERHEAD(
addressFamily,
IPPROTO_UDP,
ARRAYSIZE(dataBuffer),
targetBitRate);
bufferSize = sizeof(targetBandwidthWithOverhead);
result = QOSNotifyFlow(qosHandle,
flowID,
QOSNotifyAvailable,
&bufferSize,
(PVOID)&targetBandwidthWithOverhead,
0,
&availableOverlapped);
if (result == FALSE) {
DWORD lastError;
lastError = GetLastError();
if (lastError != ERROR_IO_PENDING) {
printf("%s:%d - QOSNotifyFlow failed (%d)\n",
__FILE__, __LINE__, lastError);
exit(1);
}
}
congestion = TRUE;
}
else {
//
// End of congestion
//
printf("----------------------------------"
"----------------------------------\n"
"END OF CONGESTION\n"
"----------------------------------"
"----------------------------------\n");
//
// Reset the current packet rate to the initial target rate
currentPacketRate = targetPacketRate;
// Reset the current bit rate to the initial target rate
currentBitRate = targetBitRate;
// Update the shaping characteristics on our QOS flow
// to smooth out our bursty traffic.
flowRate.Bandwidth = QOS_ADD_OVERHEAD(addressFamily,
IPPROTO_UDP,
ARRAYSIZE(dataBuffer),
targetBitRate);
flowRate.ShapingBehavior = QOSShapeAndMark;
flowRate.Reason = QOSFlowRateCongestion;
result = QOSSetFlow(qosHandle,
flowID,
QOSSetOutgoingRate,
sizeof(flowRate),
&flowRate,
0,
NULL);
if (result == FALSE) {
printf("%s:%d - QOSSetFlow failed (%d)\n",
__FILE__, __LINE__, GetLastError());
exit(1);
}
// Request a notification for the next network congestion
result = QOSNotifyFlow(qosHandle,
flowID,
QOSNotifyCongested,
NULL,
NULL,
0,
&congestionOverlapped);
if (result == FALSE) {
DWORD lastError;
lastError = GetLastError();
if (lastError != ERROR_IO_PENDING) {
printf("%s:%d - QOSNotifyFlow failed (%d)\n",
__FILE__, __LINE__, lastError);
exit(1);
}
}
congestion = FALSE;
}
break;
}
case WAIT_OBJECT_0 + 2: {
// The transmit packet has completed its send,
// If it did so successfully, it's time to send the next
// burst of packets.
BOOL overlappedResult;
DWORD ignoredNumOfBytesSent;
DWORD ignoredFlags;
overlappedResult = WSAGetOverlappedResult(
socket,
&sendOverlapped,
&ignoredNumOfBytesSent,
FALSE,
&ignoredFlags);
if (overlappedResult == FALSE) {
printf("%s:%d - TransmitPackets failed (%d)\n",
__FILE__, __LINE__, WSAGetLastError());
exit(1);
}
// Time to send out the next bunch of packets
sendNextGroup = TRUE;
break;
}
default:
// The wait call failed.
printf("%s:%d - WaitForMultipleObjects failed (%d)\n",
__FILE__, __LINE__, GetLastError());
exit(1);
}
} while (sendNextGroup == FALSE);
} while (TRUE);
}
//******************************************************************************
// Routine:
// server
//
// Description:
// This routine creates a socket through which it will receive
// any datagram sent by the client. It counts the number of packet
// and the number of bytes received. Periodically, it outputs this
// information to the console.
//
//******************************************************************************
VOID
server()
{
HANDLE timerEvent;
LARGE_INTEGER timerAwakenTime;
// Return value of WSAStartup
WSADATA wsaData;
// The socket used to receive data
SOCKET socket;
// IPv6 wildcard address and port number 40007 to listen on at the server
SOCKADDR_IN6 IPv6ListeningAddress = { AF_INET6,
PORT,
0,
IN6ADDR_ANY_INIT,
0 };
// Result value from the various API calls
DWORD result;
// Used to specify an option to setsocktopt
ULONG optionValue;
// Overlapped structure used to post asynchronous receive calls
WSAOVERLAPPED recvOverlapped;
// Counters of the number of bytes and packets received over
// a period of time.
DWORD numPackets, numBytes;
// Initialize Winsock
result = WSAStartup(MAKEWORD(2, 2), &wsaData);
if (result != 0) {
printf("%s:%d - WSAStartup failed (%d)\n",
__FILE__, __LINE__, GetLastError());
exit(1);
}
// Create an IPv6 datagram socket
socket = WSASocket(AF_INET6,
SOCK_DGRAM,
0,
NULL,
0,
WSA_FLAG_OVERLAPPED);
if (socket == INVALID_SOCKET) {
printf("%s:%d - WSASocket failed (%d)\n",
__FILE__, __LINE__, WSAGetLastError());
exit(1);
}
// Set IPV6_V6ONLY to FALSE before the bind operation
// This will permit us to receive both IPv6 and IPv4 traffic on the socket.
optionValue = FALSE;
result = setsockopt(socket,
IPPROTO_IPV6,
IPV6_V6ONLY,
(PCHAR)&optionValue,
sizeof(optionValue));
if (SOCKET_ERROR == result) {
printf("%s:%d - setsockopt failed (%d)\n",
__FILE__, __LINE__, WSAGetLastError());
exit(1);
}
// Bind the socket
result = bind(socket,
(PSOCKADDR)&IPv6ListeningAddress,
sizeof(IPv6ListeningAddress));
if (result != NO_ERROR) {
printf("%s:%d - bind failed (%d)\n",
__FILE__, __LINE__, WSAGetLastError());
exit(1);
}
// Create an event to be used for the overlapped of our
// receive operations. The event is initialized to FALSE and set
// to auto-reset.
recvOverlapped.hEvent = CreateEvent(NULL, FALSE, FALSE, NULL);
if (recvOverlapped.hEvent == NULL) {
printf("%s:%d - CreateEvent failed (%d)\n",
__FILE__, __LINE__, WSAGetLastError());
exit(1);
}
// Create a timer event on which we will be able to wait.
// We wish to be awaken every second to print out the count of packets
// and number of bytes received.
timerEvent = CreateWaitableTimer(NULL, FALSE, NULL);
if (timerEvent == NULL) {
printf("%s:%d - CreateWaitableTimer failed (%d)\n",
__FILE__, __LINE__, WSAGetLastError());
exit(1);
}
// Awaken first in 1 second
timerAwakenTime.QuadPart = -10000000; // 1 second
if (FALSE == SetWaitableTimer(timerEvent,
&timerAwakenTime,
1000, // Awaken every second
NULL,
NULL,
FALSE)) {
printf("%s:%d - SetWaitableTimer failed (%d)\n",
__FILE__, __LINE__, WSAGetLastError());
exit(1);
}
// Initialize the counters to 0
numPackets = 0;
numBytes = 0;
printf("-------------------------\n"
" # packets | # of bits |\n"
"-------------------------\n");
do {
// Array of events for WaitForMultipleObjects
HANDLE waitEvents[2];
// Used for WSARecv
DWORD numberOfBytesReceived;
// Used for WSARecv
DWORD dwFlags;
// Used for WSARecv
WSABUF buf;
// The buffer is always the same global array
buf.len = sizeof(dataBuffer);
buf.buf = (PCHAR)dataBuffer;
// No flags.
dwFlags = 0;
// Post a receive operation
// We only have one receive outstanding at a time.
result = WSARecv(socket,
&buf,
1,
&numberOfBytesReceived,
&dwFlags,
&recvOverlapped,
NULL);
if (result != 0) {
// The receive call failed. This could be because the
// call will be completed asynchronously (WSA_IO_PENDING) or
// it could be a legitimate error
DWORD errorCode;
errorCode = WSAGetLastError();
if (errorCode != WSA_IO_PENDING) {
printf("%s:%d - WSARecv failed (%d)\n",
__FILE__, __LINE__, errorCode);
exit(1);
}
// If the error was WSA_IO_PENDING the call will be completed
// asynchronously.
}
// Prepare our array of events to wait on. We will wait on:
// 1) The event from the receive operation
// 2) The event for the timer
waitEvents[0] = recvOverlapped.hEvent;
waitEvents[1] = timerEvent;
// We wait for either event to complete
result = WaitForMultipleObjects(ARRAYSIZE(waitEvents),
(PHANDLE)waitEvents,
FALSE,
INFINITE);
switch (result) {
case WAIT_OBJECT_0: {
// The receive operation completed.
// Determine the true result of the receive call.
BOOL overlappedResult;
overlappedResult = WSAGetOverlappedResult(socket,
&recvOverlapped,
&numberOfBytesReceived,
FALSE,
&dwFlags);
if (overlappedResult == FALSE) {
// The receive call failed.
printf("%s:%d - WSARecv failed (%d)\n",
__FILE__, __LINE__, WSAGetLastError());
exit(1);
}
// The receive call succeeded
// Increase our counters and post a new receive.
numPackets++;
numBytes += numberOfBytesReceived;
break;
}
case WAIT_OBJECT_0 + 1: {
// The timer event fired: our 1 second period has gone by.
// Print the average to the console
printf("%10d | %10d |\n", numPackets, numBytes * 8);
// Reset the counters
numPackets = numBytes = 0;
break;
}
default:
// The wait call failed.
printf("%s:%d - WaitForMultipleObjects failed (%d)\n",
__FILE__, __LINE__, GetLastError());
exit(1);
}
// We continue this loop until the process is forceably stopped
// through Ctrl-C.
} while (TRUE);
}
//******************************************************************************
// Routine:
// help
//
// Description:
// This routine prints out the usage information for the program
//
//******************************************************************************
VOID
help()
{
printf("USAGE:\n"
"\tSERVER: qossample -s\n"
"\tCLIENT: qossample -c IP-ADDRESS BIT-RATE\n\n"
"\tIn the following example, the application would try to send\n"
"\t20 Mb of traffic to the host at 10.0.0.1:\n"
"\tqossample -c 10.0.0.1 20000000\n");
return;
}
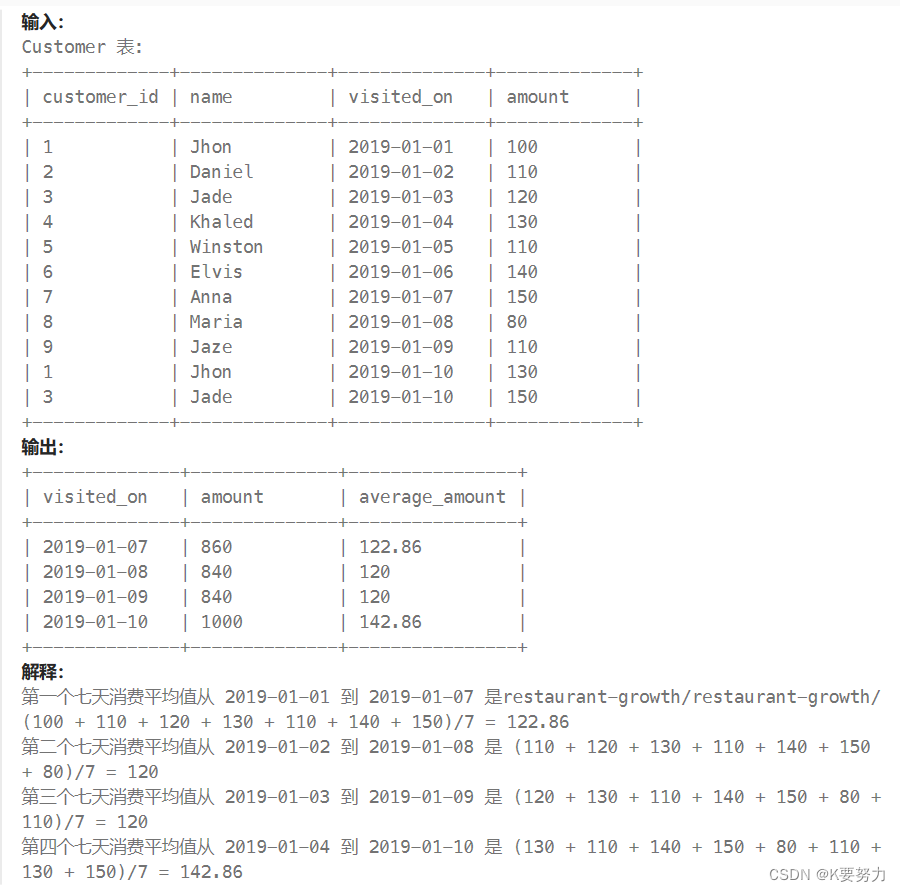
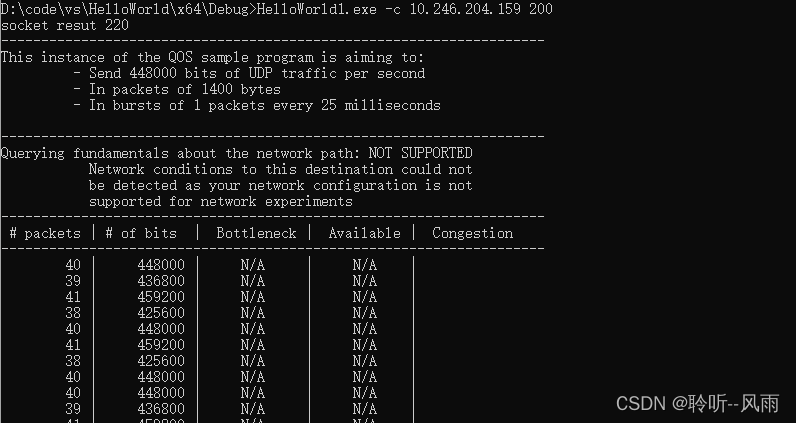
我测试时客户端和服务端是在不同的子网下,所以不支持带宽估计。运行结果如下:
客户端:
注意事项:
- 服务端和客户端运行在同一台机器上好像不行,我这边实测QOSAddSocketToFlow方法会报Element Not Found错误。参考:winapi - QOSAddSocketToFlow returns error - ELEMENT NOT FOUND - Stack Overflow
- QOSAddSocketToFlow方法第5个参数传0会报50 Not support错误。怀疑可能是因为客户端和服务端未在同一个子网所致,实际未验证。
TCP版本
TCP代码:
流程和UDP一样,代码中的注释可以忽略。
/*++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++
THIS CODE AND INFORMATION IS PROVIDED "AS IS" WITHOUT WARRANTY OF
ANY KIND, EITHER EXPRESSED OR IMPLIED, INCLUDING BUT NOT LIMITED TO
THE IMPLIED WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY AND/OR FITNESS FOR A
PARTICULAR PURPOSE.
Copyright (c) Microsoft Corporation. All rights reserved.
Module Name:
qossample.c
Abstract:
This program implements a simple traffic generator which uses the QOS2
api to not overload the network path between the source and its destination.
Although the application can be run as a receiver to process the traffic
generated, the client side of the application is the important part of this
sample. This code is in the Client function.
The code for the client works as follows:
1) A socket is connected to the destination IP address
2) The QOS subsystem is initialized by a call to QOSCreateHandle
3) A flow is created for the socket by a call to QOSAddSocketToFlow
4) The characteristics of the path between the source host and destination
host are queried through QOSQueryFlow. The two estimates used are:
- the bottleneck bandwidth: the maximum theoretical throughput;
- and the available bandwidth: the currently available throughput for
new traffic
Depending on your network configuration:
A) It may be impossible to run network experiments to the destination.
For example, the destination might be on another subnet. If so, the
client will only shape traffic and mark priority with DSCP based on
the specified traffic type, but will never be able to receive
notifications or estimates of available bandwidth and outgoing traffic
would be marked per the DLNA specification.
B) The QOS subsystem may not have had enough time to estimate conditions
to the destination host. If this happens, the client will sleep for 1s
before retrying. In a production application you could minize the
likelihood of this happening by calling, before the start of your
A/V traffic, the QOSStartTrackingClient API. It is suggested that this
API always be used when the destination is on the same subnet as the
client.
5) If the estimate of available bandwidth is less than the requested
bandwidth, the client revises the requested bandwidth.
6) The client sets a shaping rate for our flow that will limit the outgoing
traffic to the requested bandwidth. To do so, it accounts for the wire
overhead given both the address family as well as the protocol used, UDP.
7) The client registers for notifications of congestion.
8) Traffic is sent at the desired rate using the shaping mechanism as the
control loop. The application uses the API call TransmitPackets to
send the packet bunches. The client uses the fact that the shaper will
only complete this Winsock transmit operation when all packets have left
the host to determine how many packets to send at a time.
9) A congestion notification will be received whenever external conditions
push the network into a congested state. The client, as a reaction, will
lower the targeted bit rate to one-tenth of the initial value. Moreover,
the client will request notification when the bandwidth available is
enough to return to the previous bit rate.
Environment:
User-Mode only
Revision History:
------------------------------------------------------------------------------*/
#include <winsock2.h>
#include <mswsock.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <qos2.h>
#pragma comment(lib, "ws2_32.lib")
#pragma comment(lib, "QWave.lib")
#pragma warning(disable:4127) // condition expression is constant
//******************************************************************************
// Forward declarations
//******************************************************************************
VOID
client(
__in int argc,
__in_ecount(argc) char* argv[]
);
VOID
server();
VOID
help();
//******************************************************************************
// Global defines
//******************************************************************************
// Size of the data part of each datagram that is exchanged between the
// client and the server. This does not count the IP and UDP header.
#define DATAGRAM_SIZE 1400
// Number of bursts we are aiming for per second
#define BURSTS_PER_SECOND 40
// Port to be used for communication,
// 40007 in hex in network byte order
#define PORT 0x479c
//******************************************************************************
// Global variables
//******************************************************************************
// Array used by both the client routine and the server routine to
// send and receive data
CHAR dataBuffer[DATAGRAM_SIZE];
// Version of the QOS subsystem we wish to use
QOS_VERSION QosVersion = { 1 , 0 };
//******************************************************************************
// Routine:
// main
//
// Description:
// Entry point. Verifies that the number of parameters is enough to
// ascertain whether this instance is to be a client or server.
//
//******************************************************************************
int
_cdecl
main(
__in int argc,
__in_ecount(argc) char* argv[]
)
{
// Verify the number of command line arguments
if (argc < 2) {
help();
exit(0);
}
if (strcmp(argv[1], "-s") == 0) {
// If the call was "qossample -s" run as a server
server();
}
else if (strcmp(argv[1], "-c") == 0) {
// If the call was "qossample -c ..." run as a client
client(argc, argv);
}
// Else, run the help routine
help();
return 1;
}
//******************************************************************************
// Routine:
// socketCreate
//
// Description:
// This routine prepares the socket for the client instance. To do so,
// it converts the address parameter from string to IP address. Then
// it creates a UDP socket which it connects to this destination.
//
// Since we will use TransmitPackets for our send operations, the function
// pointer is obtained from Winsock.
//
//******************************************************************************
VOID
socketCreate(
__in PCHAR destination,
__out SOCKET* socket,
__out ADDRESS_FAMILY* addressFamily,
__out LPFN_TRANSMITPACKETS* transmitPackets
) {
// Return value of WSAStartup
WSADATA wsaData;
// Temporarily used to represent the destination IP address
SOCKADDR_STORAGE destAddr;
// Result of the various Winsock API calls
INT returnValue;
// Used by WSAStringToAddressA
INT sockaddrLen;
// Used by WSAIoctl
DWORD bytesReturned;
// GUID of the TransmitPacket Winsock2 function which we will
// use to send the traffic at the client side.
GUID TransmitPacketsGuid = WSAID_TRANSMITPACKETS;
// Start Winsock
returnValue = WSAStartup(MAKEWORD(2, 2), &wsaData);
if (returnValue != 0) {
printf("%s:%d - WSAStartup failed (%d)\n",
__FILE__, __LINE__, returnValue);
exit(1);
}
// First attempt to convert the string to an IPv4 address
sockaddrLen = sizeof(destAddr);
destAddr.ss_family = AF_INET;
returnValue = WSAStringToAddressA(destination,
AF_INET,
NULL,
(LPSOCKADDR)&destAddr,
&sockaddrLen);
if (returnValue != ERROR_SUCCESS) {
// If this fails,
// Attempt to convert the string to an IPv6 address
sockaddrLen = sizeof(destAddr);
destAddr.ss_family = AF_INET6;
returnValue = WSAStringToAddressA(destination,
AF_INET6,
NULL,
(LPSOCKADDR)&destAddr,
&sockaddrLen);
if (returnValue != ERROR_SUCCESS) {
// If this again fails, exit the application
// But print out the help information first.
printf("%s:%d - WSAStringToAddressA failed (%d)\n",
__FILE__, __LINE__, WSAGetLastError());
help();
exit(1);
}
}
// Set the destination port.
SS_PORT((PSOCKADDR)&destAddr) = PORT;
// Copy the address family back to caller
*addressFamily = destAddr.ss_family;
// Create a UDP socket
*socket = WSASocket(destAddr.ss_family,
SOCK_STREAM,
0,
NULL,
0,
WSA_FLAG_OVERLAPPED);
if (*socket == INVALID_SOCKET) {
printf("%s:%d - WSASocket failed (%d)\n",
__FILE__, __LINE__, WSAGetLastError());
exit(1);
}
// Connect the new socket to the destination
returnValue = WSAConnect(*socket,
(PSOCKADDR)&destAddr,
sizeof(destAddr),
NULL,
NULL,
NULL,
NULL);
if (returnValue != NO_ERROR) {
printf("%s:%d - WSAConnect failed (%d)\n",
__FILE__, __LINE__, WSAGetLastError());
exit(1);
}
// Query the function pointer for the TransmitPacket function
returnValue = WSAIoctl(*socket,
SIO_GET_EXTENSION_FUNCTION_POINTER,
&TransmitPacketsGuid,
sizeof(GUID),
transmitPackets,
sizeof(PVOID),
&bytesReturned,
NULL,
NULL);
if (returnValue == SOCKET_ERROR) {
printf("%s:%d - WSAIoctl failed (%d)\n",
__FILE__, __LINE__, WSAGetLastError());
exit(1);
}
}
//******************************************************************************
// Routine:
// client
//
// Description:
// This routine creates a datagram socket which it connects to the remote
// IP address. This socket is then added to a QOS flow. The application
// uses the flow to rate control its outgoing traffic. Packets on this flow
// will be prioritized if the network path between the client and receiver
// support prioritization. Specifically, if the receiver is:
//
// A) On-link (same subnet), both 802.1Q and DSCP are applied subject to
// available bandwidth and network support.
// B) Off-link (different subnet), only DSCP is applied regardless of
// available bandwidth.
//
// Moreover, the application queries the characteristics of the network
// path for the socket. If estimates are available, the application:
//
// 1) may readjust its throughput so as to not cause congestion on the
// network.
// 2) will be notified when the network enters congestion. As a result,
// it will lower it's throughput to 1/10 the targeted rate.
// 3) will be notified when the network is no longer congested and enough
// bandwidth is available for the application to return to its targeted
// rate.
//
//******************************************************************************
VOID
client(
__in int argc,
__in_ecount(argc) char* argv[]
) {
// Address family of the datagram socket
ADDRESS_FAMILY addressFamily;
// Socket for our traffic experiment
SOCKET socket;
// Function pointer to the TransmitPacket Winsock2 function
LPFN_TRANSMITPACKETS transmitPacketsFn;
// Array of transmit elements
LPTRANSMIT_PACKETS_ELEMENT transmitEl;
// Target packet rate and bit rate this application will aim to send
// If there is no congestion
ULONG targetPacketRate, targetBitRate;
// Current rate at which the application is sending. If the network is
// congested, this will be less than the target rate
ULONG currentPacketRate, currentBitRate;
// Counters for the achieved packet rate and achieved bit rate
ULONG achievedPacketRate, achievedBitRate;
// Timer; used to periodically output to the screen our counters
HANDLE timerEvent;
LARGE_INTEGER timerAwakenTime;
// Handle to the QOS subsystem
// Returned by QOSCreateHandle
HANDLE qosHandle;
// ID of the QOS flow we will create for the socket.
// Returned by QOSAddSocketToFlow
QOS_FLOWID flowID;
// Result of QOSQueryFlow
QOS_FLOW_FUNDAMENTALS flowFund;
// Parameter to QOSSetFlow
QOS_FLOWRATE_OUTGOING flowRate;
// If TRUE, the QOS subsystem is running network experiments on the
// network path to the destination. If false, estimates are not available.
// The flow is still marked and shaped.
BOOL estimatesAvailable;
// Result of the QOS API calls.
BOOL result;
// Overlapped operation used for TransmitPackets
WSAOVERLAPPED sendOverlapped;
// Overlapped operation used for QOSNotifyFlow to be notified
// of network congestions.
OVERLAPPED congestionOverlapped;
// Overlapped operation used for QOSNotifyFlow to be notified when,
// after congestion, there is enough bandwidth for the target rate
OVERLAPPED availableOverlapped;
// TRUE if the network is currently congested
BOOL congestion;
ULONG temp;
// Verify the number of command line arguments
if (argc != 4) {
help();
exit(1);
}
// Identify what destination IP address we're trying to talk to and
// connect a UDP socket to it
socketCreate(argv[2],
&socket,
&addressFamily,
&transmitPacketsFn);
printf("socket resut %d\n", socket);
if (FALSE == QOSCreateHandle(&QosVersion, &qosHandle)) {
printf("%s:%d - QOSCreateHandle failed (%d)\n",
__FILE__, __LINE__, GetLastError());
exit(1);
}
// The Flow ID parameter MUST be set to 0 as input to QOSAddSocketToFlow
flowID = 0;
// Create a flow for our socket
result = QOSAddSocketToFlow(qosHandle,
socket,
NULL,
QOSTrafficTypeExcellentEffort,
QOS_NON_ADAPTIVE_FLOW,
&flowID);
if (result == FALSE) {
printf("%s:%d - QOSAddSocketToFlow failed (%d)\n",
__FILE__, __LINE__, GetLastError());
exit(1);
}
// Read the data rate in bits/s passed on the command line
targetBitRate = atol(argv[3]);
if (targetBitRate == 0) {
help();
exit(1);
}
// Convert from bits to bytes
targetBitRate /= 8;
// Calculate how many packets we need; round up.
targetPacketRate = targetBitRate / ARRAYSIZE(dataBuffer);
if (targetBitRate % ARRAYSIZE(dataBuffer) != 0)
targetPacketRate++;
// Calculate the number of packets per bursts; round up
if (targetPacketRate % BURSTS_PER_SECOND != 0) {
targetPacketRate /= BURSTS_PER_SECOND;
targetPacketRate++;
}
else {
targetPacketRate /= BURSTS_PER_SECOND;
}
// Calculate the final bit rate, targetBitRate, in bps that the application
// will send.
targetBitRate = BURSTS_PER_SECOND
* targetPacketRate
* ARRAYSIZE(dataBuffer)
* 8;
//
// Allocate an array of transmit elements big enough to send
// targetPacketRate packets every burst.
transmitEl = static_cast<LPTRANSMIT_PACKETS_ELEMENT>(HeapAlloc(GetProcessHeap(),
HEAP_ZERO_MEMORY,
sizeof(TRANSMIT_PACKETS_ELEMENT)
* targetPacketRate));
if (transmitEl == NULL) {
printf("%s:%d - HeapAlloc failed (%d)\n",
__FILE__, __LINE__, GetLastError());
exit(1);
}
// For the purpose of this application, we only use one data buffer for all
// of our packets.
ZeroMemory(&dataBuffer, sizeof(dataBuffer));
//
// Initialize each of these transmit element to point to the same zeroed out
// data buffer
for (temp = 0; temp < targetPacketRate; temp++) {
transmitEl[temp].dwElFlags = TP_ELEMENT_MEMORY | TP_ELEMENT_EOP;
transmitEl[temp].pBuffer = dataBuffer;
transmitEl[temp].cLength = sizeof(dataBuffer);
}
// Print out what we'll be doing
printf("----------------------------------"
"----------------------------------\n"
"This instance of the QOS sample program is aiming to:\n"
"\t - Send %d bits of UDP traffic per second\n"
"\t - In packets of %d bytes\n"
"\t - In bursts of %d packets every %d milliseconds\n\n"
"----------------------------------"
"----------------------------------\n",
targetBitRate,
ARRAYSIZE(dataBuffer),
targetPacketRate,
1000 / BURSTS_PER_SECOND);
// Assume, by default, that estimates are not available
estimatesAvailable = FALSE;
printf("Querying fundamentals about the network path: ");
do {
temp = sizeof(flowFund);
// Query the flow fundamentals for the path to the destination.
// This will return estimates of the bottleneck bandwidth, available
// bandwidth and average RTT.
result = QOSQueryFlow(qosHandle,
flowID,
QOSQueryFlowFundamentals,
&temp,
&flowFund,
0,
NULL);
if (result == FALSE) {
DWORD lastError;
lastError = GetLastError();
if (lastError == ERROR_NO_DATA) {
// If the call failed, this could be because the QOS subsystem
// has not yet gathered enough data for estimates. If so, the
// QOS2 api returns ERROR_NO_DATA.
printf(".");
Sleep(1000);
}
else if (lastError == ERROR_NOT_SUPPORTED)
{
// If the call failed, this could be because the QOS subsystem
// cannot run network experiments on the network path to the
// destination. If so, the API returns ERROR_NOT_SUPPORTED.
printf("NOT SUPPORTED\n"
"\t Network conditions to this destination could not\n"
"\t be detected as your network configuration is not\n"
"\t supported for network experiments\n");
break;
}
else {
printf("%s:%d - QOSQueryFlow failed (%d)\n",
__FILE__, __LINE__, lastError);
exit(1);
}
}
else if ((flowFund.BottleneckBandwidthSet == FALSE)
|| (flowFund.AvailableBandwidthSet == FALSE)) {
// If the call succeeded but bottleneck bandwidth or
// available bandwidth are not known then estimates are still
// processing; query again in 1 second.
printf(".");
Sleep(1000);
}
else {
// Estimate where available.
double bottleneck;
double available;
estimatesAvailable = TRUE;
// Convert the bottleneck bandwidth from bps to mbps
bottleneck = (double)flowFund.BottleneckBandwidth;
bottleneck /= 1000000.0;
// Convert available bandwidth from bps to mbps
available = (double)flowFund.AvailableBandwidth;
available /= 1000000.0;
printf("DONE\n"
"\t - Bottleneck bandwidth is approximately %4.2f Mbps\n"
"\t - Available bandwidth is approximately %4.2f Mbps\n",
bottleneck,
available);
break;
}
} while (TRUE);
if (estimatesAvailable == TRUE) {
UINT64 targetBitRateWithHeaders;
printf("\nNOTE: the accuracy of the QOS estimates can be impacted by\n"
"any of the following,\n\n"
"\t - Both the network interface at the client\n"
"\t and at the server must be using NDIS 6 drivers.\n"
"\t - If the server is not a Windows Vista host, verify that \n"
"\t it implements the LLD2 networking protocol. You can\n"
"\t find more information at http://www.microsoft.com.\n"
"\t - IPSec, VPNs and enterprise class networking equipment\n"
"\t may interfere with network experiments.\n\n");
// Calculate what our target bit rate, with protocol headers for
// IP(v4/v6) and UDP will be.
targetBitRateWithHeaders = QOS_ADD_OVERHEAD(addressFamily,
IPPROTO_UDP,
ARRAYSIZE(dataBuffer),
targetBitRate);
if (flowFund.AvailableBandwidth < targetBitRateWithHeaders) {
// If the estimate of available bandwidth is not sufficient for the
// target bit rate (with headers), drop to a lesser throughput
UINT64 availableBandwidth;
// The estimate returned does not account for headers
// Remove the estimated overhead for our address family and UDP.
availableBandwidth = QOS_SUBTRACT_OVERHEAD(
addressFamily,
IPPROTO_UDP,
ARRAYSIZE(dataBuffer),
flowFund.AvailableBandwidth);
// Calculate the rate of packets we can realistically send
targetPacketRate = (LONG)availableBandwidth / 8;
targetPacketRate /= ARRAYSIZE(dataBuffer);
targetPacketRate /= BURSTS_PER_SECOND;
// Calculate the real bit rate we'll be using
targetBitRate = BURSTS_PER_SECOND
* targetPacketRate
* ARRAYSIZE(dataBuffer)
* 8;
printf("Not enough available bandwidth for the requested bitrate.\n"
"Downgrading to lesser bitrate - %d.\n", targetBitRate);
}
}
// Our starting rate is this target bit rate
currentBitRate = targetBitRate;
currentPacketRate = targetPacketRate;
// Ask the QOS subsystem to shape our traffic to this bit rate. Note that
// the application needs to account for the size of the IP(v4/v6)
// and UDP headers.
// Calculate the real bandwidth we will need to be shaped to.
flowRate.Bandwidth = QOS_ADD_OVERHEAD(addressFamily,
IPPROTO_UDP,
ARRAYSIZE(dataBuffer),
currentBitRate);
// Set shaping characteristics on our QOS flow to smooth out our bursty
// traffic.
flowRate.ShapingBehavior = QOSShapeAndMark;
// The reason field is not applicable for the initial call.
flowRate.Reason = QOSFlowRateNotApplicable;
result = QOSSetFlow(qosHandle,
flowID,
QOSSetOutgoingRate,
sizeof(flowRate),
&flowRate,
0,
NULL);
if (result == FALSE) {
printf("%s:%d - QOSSetFlow failed (%d)\n",
__FILE__, __LINE__, GetLastError());
exit(1);
}
// Allocate a waitable timer. We will use this timer to periodically
// awaken and output statistics.
timerEvent = CreateWaitableTimer(NULL, FALSE, NULL);
if (timerEvent == NULL) {
printf("%s:%d - CreateWaitableTimer failed (%d)\n",
__FILE__, __LINE__, GetLastError());
exit(1);
}
//
// Set the sampling time to 1 second
timerAwakenTime.QuadPart = -10000000; // 1 second
if (FALSE == SetWaitableTimer(timerEvent,
&timerAwakenTime,
1000,
NULL,
NULL,
FALSE)) {
printf("%s:%d - SetWaitableTimer failed (%d)\n",
__FILE__, __LINE__, GetLastError());
exit(1);
}
// Prepare the support overlapped structures to detect congestion,
// notifications of bandwidth change and the completion of our send
// routines.
ZeroMemory(&congestionOverlapped, sizeof(congestionOverlapped));
congestionOverlapped.hEvent = CreateEvent(NULL, FALSE, FALSE, NULL);
if (congestionOverlapped.hEvent == NULL) {
printf("%s:%d - CreateEvent failed (%d)\n",
__FILE__, __LINE__, GetLastError());
exit(1);
}
ZeroMemory(&availableOverlapped, sizeof(availableOverlapped));
availableOverlapped.hEvent = CreateEvent(NULL, FALSE, FALSE, NULL);
if (availableOverlapped.hEvent == NULL) {
printf("%s:%d - CreateEvent failed (%d)\n",
__FILE__, __LINE__, GetLastError());
exit(1);
}
ZeroMemory(&sendOverlapped, sizeof(sendOverlapped));
sendOverlapped.hEvent = CreateEvent(NULL, FALSE, FALSE, NULL);
if (sendOverlapped.hEvent == NULL) {
printf("%s:%d - CreateEvent failed (%d)\n",
__FILE__, __LINE__, GetLastError());
exit(1);
}
if (estimatesAvailable == TRUE) {
// If estimates are available, we request a notification
// for congestion. This notification will complete whenever network
// congestion is detected.
result = QOSNotifyFlow(qosHandle,
flowID,
QOSNotifyCongested,
NULL,
NULL,
0,
&congestionOverlapped);
if (result == FALSE) {
DWORD lastError;
lastError = GetLastError();
if (lastError != ERROR_IO_PENDING) {
printf("%s:%d - QOSNotifyFlow failed (%d)\n",
__FILE__, __LINE__, lastError);
exit(1);
}
}
}
printf("----------------------------------"
"----------------------------------\n"
" # packets | # of bits | Bottleneck "
"| Available | Congestion \n"
"----------------------------------"
"----------------------------------\n");
// Initialize our counters to 0
achievedBitRate = achievedPacketRate = 0;
congestion = FALSE;
do {
BOOL sendNextGroup;
// Send the first burst of packets
result = (*transmitPacketsFn)(socket,
transmitEl,
currentPacketRate,
0xFFFFFFFF,
&sendOverlapped,
TF_USE_KERNEL_APC);
if (result == FALSE) {
DWORD lastError;
lastError = WSAGetLastError();
if (lastError != ERROR_IO_PENDING) {
printf("%s:%d - TransmitPackets failed (%d)\n",
__FILE__, __LINE__, GetLastError());
exit(1);
}
}
// Increase the counter of sent data
achievedPacketRate += currentPacketRate;
achievedBitRate += currentPacketRate * ARRAYSIZE(dataBuffer) * 8;
sendNextGroup = FALSE;
do {
HANDLE waitEvents[3];
DWORD waitResult;
// Wait for any of the 3 events to complete
// The 1 second periodic timer
waitEvents[0] = timerEvent;
if (congestion)
// Notification of available bandwidth
waitEvents[1] = availableOverlapped.hEvent;
else
// Notification of congestion
waitEvents[1] = congestionOverlapped.hEvent;
// Notification that the send operation has completed
waitEvents[2] = sendOverlapped.hEvent;
waitResult = WaitForMultipleObjects(ARRAYSIZE(waitEvents),
(PHANDLE)waitEvents,
FALSE,
INFINITE);
switch (waitResult) {
case WAIT_OBJECT_0: {
// The event for the periodic timer is set
printf("%10d | ", achievedPacketRate);
printf("%10d | ", achievedBitRate);
if (estimatesAvailable) {
// If estimates are available for the network path
// query for estimates and output to the console along
// with our counters.
// Ascertained through QOSQueryFlow
BOOL estimateIndicatesCongestion;
// Default is unknown
estimateIndicatesCongestion = FALSE;
ZeroMemory(&flowFund, sizeof(flowFund));
temp = sizeof(flowFund);
QOSQueryFlow(qosHandle,
flowID,
QOSQueryFlowFundamentals,
&temp,
&flowFund,
0,
NULL);
if (flowFund.BottleneckBandwidthSet)
printf("%10d | ", flowFund.BottleneckBandwidth);
else
printf(" NO DATA | ");
if (flowFund.AvailableBandwidthSet) {
if (flowFund.AvailableBandwidth == 0)
estimateIndicatesCongestion = TRUE;
printf("%10d | ", flowFund.AvailableBandwidth);
}
else
printf(" NO DATA | ");
if (estimateIndicatesCongestion)
printf(" CONGESTION\n");
else
printf("\n");
}
else {
// Bandwidth estimates are not available
printf(" N/A | N/A |\n");
}
//
// Reset the counters
achievedPacketRate = achievedBitRate = 0;
break;
}
case WAIT_OBJECT_0 + 1: {
// This is either a notification for congestion or
// for bandwidth available
if (congestion == FALSE) {
UINT64 targetBandwidthWithOverhead;
ULONG bufferSize;
//
// Congestion
//
printf("----------------------------------"
"----------------------------------\n"
"CONGESTION\n"
"----------------------------------"
"----------------------------------\n");
//
// Reduce the current rate to one-tenth of the initial rate
// Insure you're always sending at least 1 packet per
// burst.
if (currentPacketRate < 10)
currentPacketRate = 1;
else
currentPacketRate /= 10;
// Calculate the new bit rate we'll be using
currentBitRate = BURSTS_PER_SECOND
* currentPacketRate
* ARRAYSIZE(dataBuffer)
* 8;
// Update the shaping characteristics on our QOS flow
// to smooth out our bursty traffic.
flowRate.Bandwidth = QOS_ADD_OVERHEAD(
addressFamily,
IPPROTO_UDP,
ARRAYSIZE(dataBuffer),
currentBitRate);
flowRate.ShapingBehavior = QOSShapeAndMark;
flowRate.Reason = QOSFlowRateCongestion;
result = QOSSetFlow(qosHandle,
flowID,
QOSSetOutgoingRate,
sizeof(flowRate),
&flowRate,
0,
NULL);
if (result == FALSE) {
printf("%s:%d - QOSSetFlow failed (%d)\n",
__FILE__, __LINE__, GetLastError());
exit(1);
}
// Request a notification for when there is enough bandwidth
// to return to our previous targeted bit rate.
// This will complete only when the network is no longer
// congested and bandwidth is available.
targetBandwidthWithOverhead = QOS_ADD_OVERHEAD(
addressFamily,
IPPROTO_UDP,
ARRAYSIZE(dataBuffer),
targetBitRate);
bufferSize = sizeof(targetBandwidthWithOverhead);
result = QOSNotifyFlow(qosHandle,
flowID,
QOSNotifyAvailable,
&bufferSize,
(PVOID)&targetBandwidthWithOverhead,
0,
&availableOverlapped);
if (result == FALSE) {
DWORD lastError;
lastError = GetLastError();
if (lastError != ERROR_IO_PENDING) {
printf("%s:%d - QOSNotifyFlow failed (%d)\n",
__FILE__, __LINE__, lastError);
exit(1);
}
}
congestion = TRUE;
}
else {
//
// End of congestion
//
printf("----------------------------------"
"----------------------------------\n"
"END OF CONGESTION\n"
"----------------------------------"
"----------------------------------\n");
//
// Reset the current packet rate to the initial target rate
currentPacketRate = targetPacketRate;
// Reset the current bit rate to the initial target rate
currentBitRate = targetBitRate;
// Update the shaping characteristics on our QOS flow
// to smooth out our bursty traffic.
flowRate.Bandwidth = QOS_ADD_OVERHEAD(addressFamily,
IPPROTO_UDP,
ARRAYSIZE(dataBuffer),
targetBitRate);
flowRate.ShapingBehavior = QOSShapeAndMark;
flowRate.Reason = QOSFlowRateCongestion;
result = QOSSetFlow(qosHandle,
flowID,
QOSSetOutgoingRate,
sizeof(flowRate),
&flowRate,
0,
NULL);
if (result == FALSE) {
printf("%s:%d - QOSSetFlow failed (%d)\n",
__FILE__, __LINE__, GetLastError());
exit(1);
}
// Request a notification for the next network congestion
result = QOSNotifyFlow(qosHandle,
flowID,
QOSNotifyCongested,
NULL,
NULL,
0,
&congestionOverlapped);
if (result == FALSE) {
DWORD lastError;
lastError = GetLastError();
if (lastError != ERROR_IO_PENDING) {
printf("%s:%d - QOSNotifyFlow failed (%d)\n",
__FILE__, __LINE__, lastError);
exit(1);
}
}
congestion = FALSE;
}
break;
}
case WAIT_OBJECT_0 + 2: {
// The transmit packet has completed its send,
// If it did so successfully, it's time to send the next
// burst of packets.
BOOL overlappedResult;
DWORD ignoredNumOfBytesSent;
DWORD ignoredFlags;
overlappedResult = WSAGetOverlappedResult(
socket,
&sendOverlapped,
&ignoredNumOfBytesSent,
FALSE,
&ignoredFlags);
if (overlappedResult == FALSE) {
printf("%s:%d - TransmitPackets failed (%d)\n",
__FILE__, __LINE__, WSAGetLastError());
exit(1);
}
// Time to send out the next bunch of packets
sendNextGroup = TRUE;
break;
}
default:
// The wait call failed.
printf("%s:%d - WaitForMultipleObjects failed (%d)\n",
__FILE__, __LINE__, GetLastError());
exit(1);
}
} while (sendNextGroup == FALSE);
} while (TRUE);
}
//******************************************************************************
// Routine:
// server
//
// Description:
// This routine creates a socket through which it will receive
// any datagram sent by the client. It counts the number of packet
// and the number of bytes received. Periodically, it outputs this
// information to the console.
//
//******************************************************************************
VOID
server()
{
HANDLE timerEvent;
LARGE_INTEGER timerAwakenTime;
// Return value of WSAStartup
WSADATA wsaData;
// IPv6 wildcard address and port number 40007 to listen on at the server
SOCKADDR_IN6 IPv6ListeningAddress = { AF_INET6,
PORT,
0,
IN6ADDR_ANY_INIT,
0 };
// Result value from the various API calls
DWORD result;
// Used to specify an option to setsocktopt
ULONG optionValue;
// Overlapped structure used to post asynchronous receive calls
WSAOVERLAPPED recvOverlapped;
// Counters of the number of bytes and packets received over
// a period of time.
DWORD numPackets, numBytes;
// Initialize Winsock
result = WSAStartup(MAKEWORD(2, 2), &wsaData);
if (result != 0) {
printf("%s:%d - WSAStartup failed (%d)\n",
__FILE__, __LINE__, GetLastError());
exit(1);
}
// 创建 TCP 监听套接字
SOCKET listener = socket(AF_INET, SOCK_STREAM, IPPROTO_TCP);
if (listener == INVALID_SOCKET) {
printf("Error creating socket: %ld\n", WSAGetLastError());
WSACleanup();
exit(1);
}
// 绑定到本地地址和端口
struct sockaddr_in addr;
addr.sin_family = AF_INET;
addr.sin_addr.s_addr = htonl(INADDR_ANY);
addr.sin_port = PORT;
int res = bind(listener, (struct sockaddr*)&addr, sizeof(addr));
if (res == SOCKET_ERROR) {
printf("Error binding socket: %ld\n", WSAGetLastError());
closesocket(listener);
WSACleanup();
exit(1);
}
else {
printf("begin listen on %d", PORT);
}
// 开始监听传入的连接
res = listen(listener, SOMAXCONN);
if (res == SOCKET_ERROR) {
printf("Error listening on socket: %ld\n", WSAGetLastError());
closesocket(listener);
WSACleanup();
exit(1);
}
// 接受连接并处理请求
while (1) {
struct sockaddr_in client_addr;
int client_addr_len = sizeof(client_addr);
SOCKET client = accept(listener, (struct sockaddr*)&client_addr, &client_addr_len);
if (client == INVALID_SOCKET) {
printf("Error accepting client: %ld\n", WSAGetLastError());
closesocket(listener);
WSACleanup();
exit(1);
}
while (true) {
// 读取请求数据
char buf[1024];
int bytes_read = recv(client, buf, sizeof(buf), 0);
if (bytes_read == SOCKET_ERROR)
{
printf("Error read: %ld\n", WSAGetLastError());
break;
}
// 打印请求数据
printf("Received request:%d \n", bytes_read);
}
printf("client closed!\n");
// 关闭连接
closesocket(client);
}
// 关闭监听套接字和清理 Winsock
closesocket(listener);
WSACleanup();
}
//******************************************************************************
// Routine:
// help
//
// Description:
// This routine prints out the usage information for the program
//
//******************************************************************************
VOID
help()
{
printf("USAGE:\n"
"\tSERVER: qossample -s\n"
"\tCLIENT: qossample -c IP-ADDRESS BIT-RATE\n\n"
"\tIn the following example, the application would try to send\n"
"\t20 Mb of traffic to the host at 10.0.0.1:\n"
"\tqossample -c 10.0.0.1 20000000\n");
return;
}
Rust写的TCP版本
这段代码是一个 Rust 程序,它使用 Windows 系统的 QoS API 来实现一个简单的客户端,连接到指定的服务器并发送一条消息。
程序的主要步骤如下:
1. 连接到服务器,创建一个 TCP 流。
2. 获取流的原始套接字句柄。
3. 使用 QOSCreateHandle 函数创建一个 QoS 句柄。
4. 使用 QOSAddSocketToFlow 函数将套接字添加到 QoS 流中,指定流量类型为音视频流量。
5. 发送一条消息到服务器。
6. 从服务器接收一条消息。
7. 使用 QOSCloseHandle 函数关闭 QoS 句柄。
在程序中,使用了 Rust 的标准库中的 io、net 和 os 模块,以及第三方库 windows-sys,该库提供了对 Windows 系统 API 的 Rust 绑定。
程序使用了 unsafe 关键字,这是因为它调用了 Windows 系统的 API,这些 API 不是 Rust 的安全代码。程序还使用了 panic! 宏来处理错误情况,这将导致程序崩溃并打印错误消息。
总的来说,这段代码演示了如何使用 Rust 和 Windows 系统的 QoS API 来实现一个简单的客户端,连接到服务器并发送一条消息。这条消息的DSCP值是被设置过的。
// 导入必要的库
use std::io::{Read, Write};
use std::net::TcpStream;
use std::os::windows::io::AsRawSocket;
// 导入 Windows API
use windows_sys::Win32::Foundation::{GetLastError, FALSE, HANDLE};
use windows_sys::Win32::NetworkManagement::QoS::{
QOSAddSocketToFlow, QOSCloseHandle, QOSCreateHandle, QOSTrafficTypeAudioVideo,
QOS_NON_ADAPTIVE_FLOW, QOS_VERSION,
};
use windows_sys::Win32::Networking::WinSock::SOCKET;
fn main() -> std::io::Result<()> {
// 连接到服务器
let mut stream = TcpStream::connect("118.24.148.75:8080")?; // 连接到服务器
let socket = stream.as_raw_socket(); // 获取 socket
// 创建 QoS 句柄
let version = QOS_VERSION {
MajorVersion: 1,
MinorVersion: 0,
};
let mut qos_handle: HANDLE = 0;
let res = unsafe { QOSCreateHandle(&version, &mut qos_handle) }; // 创建 QoS 句柄
if res == FALSE {
let error = unsafe { GetLastError() };
panic!("Error creating QoS handle: {}, {}", res, error);
}
let mut flowid = 0;
//会将dscp值设置为0x28
let res = unsafe {
QOSAddSocketToFlow(
qos_handle,
socket as SOCKET,
std::ptr::null_mut(),
QOSTrafficTypeAudioVideo,
QOS_NON_ADAPTIVE_FLOW,
&mut flowid,
)
};
if res == FALSE {
panic!("Error adding socket to flow: {}", res);
}
// 发送数据
stream.write_all(b"Hello, server!")?;
// 接收数据
let mut buf = [0; 512];
let size = stream.read(&mut buf)?;
let response = String::from_utf8_lossy(&buf[..size]);
println!("Received: {}", response);
let ret = unsafe { QOSCloseHandle(qos_handle) };
if ret == FALSE {
panic!("Error closing QoS handle: {}", ret);
}
Ok(())
}
Cargo.toml如下
[package]
name = "hello"
version = "0.1.0"
edition = "2021"
# See more keys and their definitions at https://doc.rust-lang.org/cargo/reference/manifest.html
[dependencies]
#rand = "0.7"
#bytes = "1"
#tokio = { version = "1.0", features = ["full"] }
#socket2 = {}
#once_cell = "1.8"
#signal-hook = {}
#nix = {features = ["net"]}
windows-sys = {version = "*",features = ["Win32_Foundation","Win32_Networking_WinSock","Win32_NetworkManagement","Win32_NetworkManagement_QoS"]}