统计固定时间内两条流数据的匹配情况,需要自定义来实现——可以用窗口(window)来表示。为了更方便地实现基于时间的合流操作,Flink 的 DataStrema API 提供了内置的 join 算子。
窗口联结(Window Join)
一段时间的双流合并
定义时间窗口,并将两条流中共享一个公共键(key)的数据放在窗口中进行配对处理。
stream1.join(stream2)
.where(<KeySelector>) // stream1 的 keyBy
.equalTo(<KeySelector>) // stream2 的 keyBy
.window(<WindowAssigner>)
.apply(<JoinFunction>)
public class WindowJoinDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
StreamExecutionEnvironment env = StreamExecutionEnvironment.getExecutionEnvironment();
env.setParallelism(1);
SingleOutputStreamOperator<Tuple2<String, Integer>> ds1 = env
.fromElements(
Tuple2.of("a", 1),
Tuple2.of("a", 2),
Tuple2.of("b", 3),
Tuple2.of("c", 4)
)
.assignTimestampsAndWatermarks(
WatermarkStrategy
.<Tuple2<String,
Integer>>forMonotonousTimestamps()
.withTimestampAssigner((value, ts) -> value.f1 * 1000L)
);
SingleOutputStreamOperator<Tuple3<String, Integer, Integer>> ds2 = env
.fromElements(
Tuple3.of("a", 1, 1),
Tuple3.of("a", 11, 1),
Tuple3.of("b", 2, 1),
Tuple3.of("b", 12, 1),
Tuple3.of("c", 14, 1),
Tuple3.of("d", 15, 1)
)
.assignTimestampsAndWatermarks(
WatermarkStrategy
.<Tuple3<String,
Integer, Integer>>forMonotonousTimestamps()
.withTimestampAssigner((value, ts) -> value.f1 * 1000L)
);
DataStream<String> join = ds1.join(ds2)
.where(r1 -> r1.f0) // ds1 的keyby
.equalTo(r2 -> r2.f0) // ds2 的keyby
.window(TumblingEventTimeWindows.of(Time.seconds(10)))
.apply(new JoinFunction<Tuple2<String, Integer>, Tuple3<String, Integer, Integer>, String>() {
/**
* 关联上的数据,调用 join 方法
* @param first ds1 的数据
* @param second ds2 的数据
*/
@Override
public String join(Tuple2<String, Integer> first, Tuple3<String, Integer, Integer> second) throws Exception {
return first + "<----->" + second;
}
});
join.print();
env.execute();
}
}
输出:
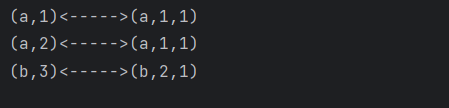
window join:
- 两条流落在同一个时间窗口范围内才能匹配
- 根据 keyBy 的 key,来进行匹配关联
- 只能拿到匹配上的数据,类似有固定时间范围的
inner join
间隔联结(Interval Join)
存在如下场景:两条流匹配的两个数据有可能刚好“卡在”窗口边缘两侧,窗口内就都没有匹配了,可以使用“间隔联结”(interval join)来解决。
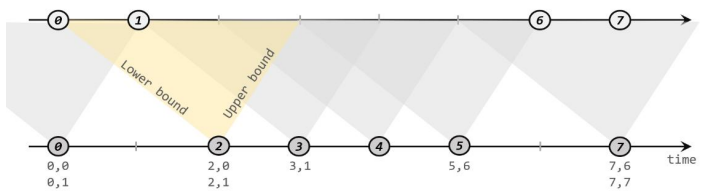
原理
给定两个时间点,分别叫作间隔的“上界”(upperBound)和“下界”(lowerBound);可以开辟一段时间间隔:[a.timestamp + lowerBound, a.timestamp +upperBound], 即以 a 的时间戳为中心,下至下界点、上至上界点的一个闭区间:这段时间作为可以匹配另一条流数据的“窗口”范围。
匹配的条件为:
a.timestamp + lowerBound <= b.timestamp <= a.timestamp + upperBound
stream1
.keyBy(<KeySelector>)
// KeyedStream 调用
.intervalJoin(stream2.keyBy(<KeySelector>))
.between(Time.milliseconds(-2), Time.milliseconds(1)).process (new ProcessJoinFunction<Integer, Integer, String(){
@Override
public void processElement(Integer left, Integer right,Context ctx, Collector<String> out){
out.collect(left + "," + right);
}
});
处理迟到数据,可以使用左右侧输出流
完整代码:
public class IntervalJoinWithLateDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
StreamExecutionEnvironment env = StreamExecutionEnvironment.getExecutionEnvironment();
env.setParallelism(1);
SingleOutputStreamOperator<Tuple2<String, Integer>> ds1 = env
.socketTextStream("hadoop102", 7777)
.map((MapFunction<String, Tuple2<String, Integer>>) value -> {
String[] datas = value.split(",");
return Tuple2.of(datas[0], Integer.valueOf(datas[1]));
})
.assignTimestampsAndWatermarks(
WatermarkStrategy
.<Tuple2<String,
Integer>>forBoundedOutOfOrderness(Duration.ofSeconds(3))
.withTimestampAssigner((value, ts) -> value.f1 * 1000L)
);
SingleOutputStreamOperator<Tuple3<String, Integer, Integer>> ds2 = env
.socketTextStream("hadoop102", 8888)
.map((MapFunction<String, Tuple3<String, Integer, Integer>>) value -> {
String[] datas = value.split(",");
return Tuple3.of(datas[0], Integer.valueOf(datas[1]), Integer.valueOf(datas[2]));
})
.assignTimestampsAndWatermarks(
WatermarkStrategy
.<Tuple3<String, Integer, Integer>>forBoundedOutOfOrderness(Duration.ofSeconds(3))
.withTimestampAssigner((value, ts) -> value.f1 * 1000L)
);
/**
* 【Interval join】
* 1、只支持事件时间
* 2、指定上界、下界的偏移,负号代表时间往前,正号代表时间往后
* 3、process 中,只能处理 join 上的数据
* 4、两条流关联后的 watermark,以两条流中最小的为准
* 5、如果 当前数据的事件时间 < 当前的 watermark,就是迟到数据,主流的 process 不处理
* => between 后,可以指定将 左流 或 右流的迟到数据放入侧输出流
* */
//1. 分别做 keyby,key 其实就是关联条件
KeyedStream<Tuple2<String, Integer>, String> ks1 = ds1.keyBy(r1 -> r1.f0);
KeyedStream<Tuple3<String, Integer, Integer>, String> ks2 = ds2.keyBy(r2 -> r2.f0);
//2. 调用 interval join
// 左右测输出流迟到标签
OutputTag<Tuple2<String, Integer>> ks1LateTag = new OutputTag<>("ks1-late", Types.TUPLE(Types.STRING, Types.INT));
OutputTag<Tuple3<String, Integer, Integer>> ks2LateTag = new OutputTag<>("ks2-late", Types.TUPLE(Types.STRING, Types.INT, Types.INT));
SingleOutputStreamOperator<String> process = ks1
.intervalJoin(ks2)
.between(Time.seconds(-2), Time.seconds(2)) // 指定上下界
.sideOutputLeftLateData(ks1LateTag) // 将ks1的迟到数据,放入侧输出流
.sideOutputRightLateData(ks2LateTag) // 将ks2的迟到数据,放入侧输出流
.process(
new ProcessJoinFunction<Tuple2<String, Integer>, Tuple3<String, Integer, Integer>, String>() {
/**
* 两条流的数据匹配上,才会调用这个方法
* @param left ks1 的数据
* @param right ks2 的数据
* @param ctx 上下文
* @param out 采集器
*/
@Override
public void processElement(Tuple2<String, Integer> left, Tuple3<String, Integer, Integer> right, Context ctx, Collector<String> out) throws Exception {
// 进入这个方法,是关联上的数据
out.collect(left + "<------>" + right);
}
});
process.print("主流");
process.getSideOutput(ks1LateTag).printToErr("ks1迟到数据");
process.getSideOutput(ks2LateTag).printToErr("ks2迟到数据");
env.execute();
}
}