import geopandas as gpd
import rasterio
from rasterio.mask import mask
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
# 载入shp文件 - 它只包含几何对象
shapefile_path = r'D:\Desktop\新建文件夹 (3)\01.shp'
shapes = gpd.read_file(shapefile_path)
# 打开图像
image_path = r'D:\Desktop\新建文件夹 (3)\nir.tif'
with rasterio.open(image_path) as src:
# 对于shp文件中的每个几何对象
for geometry in shapes.geometry:
# 利用geometry来裁剪图像
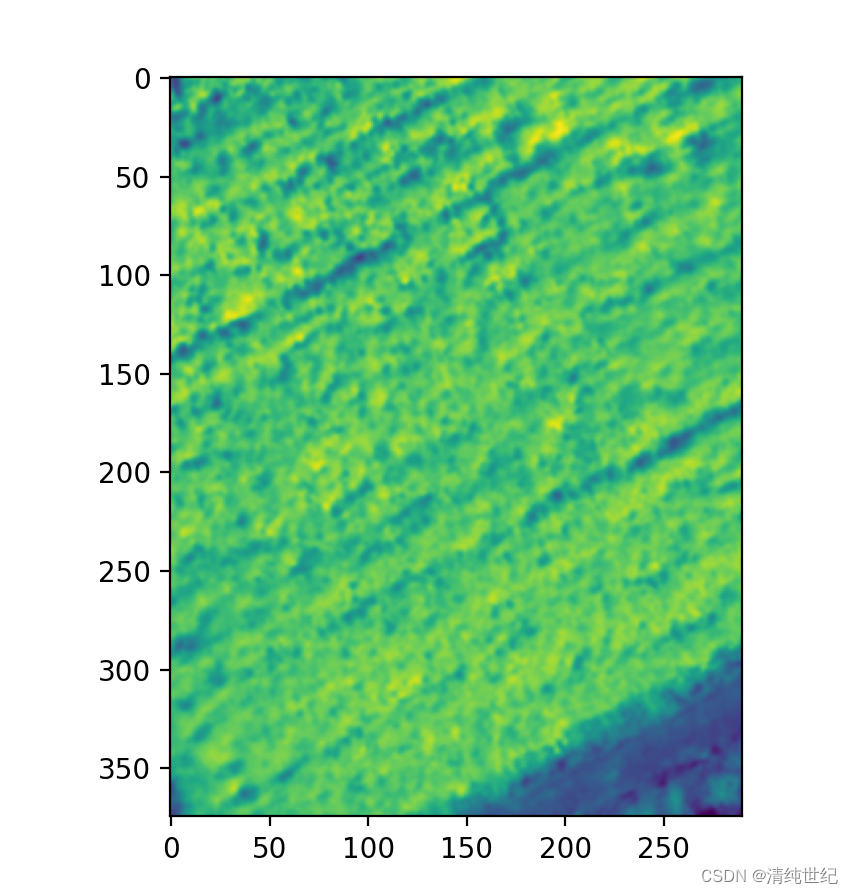
out_image, out_transform = mask(src, [geometry], crop=True) # out_image的维度(c,w,h)
# plt.imshow(out_image[0])
# plt.show()
# 计算裁剪区域的光谱特征(这里是计算平均值)
# 注意检查和处理无数据值或其他特殊值
out_image = out_image.astype('float64')
no_data_value = src.nodatavals[0] # 提取原始图像数据源(src)中定义的第一个无数据值
out_image[out_image == no_data_value] = np.nan # 像素赋值为NaN
mean_values = np.nanmean(out_image, axis=(1, 2)) # 沿着给定轴(在这里是轴1和轴2,分别代表图像的高和宽)上的均值
# 记下或分析这些特征
print(mean_values)