纯追踪算法
纯追踪基础
The core idea is to find a point on the path in front of the robot and find the linear and angular velocity to help drive towards it.
核心思想是在机器人前方的路径上找到一个点,并找到一个合适的线速度和角速度,以驱动机器人朝向该点运动。
Once it moves forward, a new point is selected, and the process repeats until the end of the path.
一旦它向前移动,就会选择一个新的前视点,这个过程会一直重复,直到到达路径终点。
In order to simply book-keeping, the global path is continuously pruned to the closest point to the robot (see the figure below) so that we only have to process useful path points. Then, the section of the path within the local costmap bounds is transformed to the robot frame and a lookahead point is determined using a predefined distance
为了简化簿记,全局路径被持续修剪到离机器人最近的点(见下图),这样我们只需要处理有用的路径点。然后,在局部代价地图内的路径被转换到机器人坐标系下,并使用预定义前视距离确定一个前瞻点。
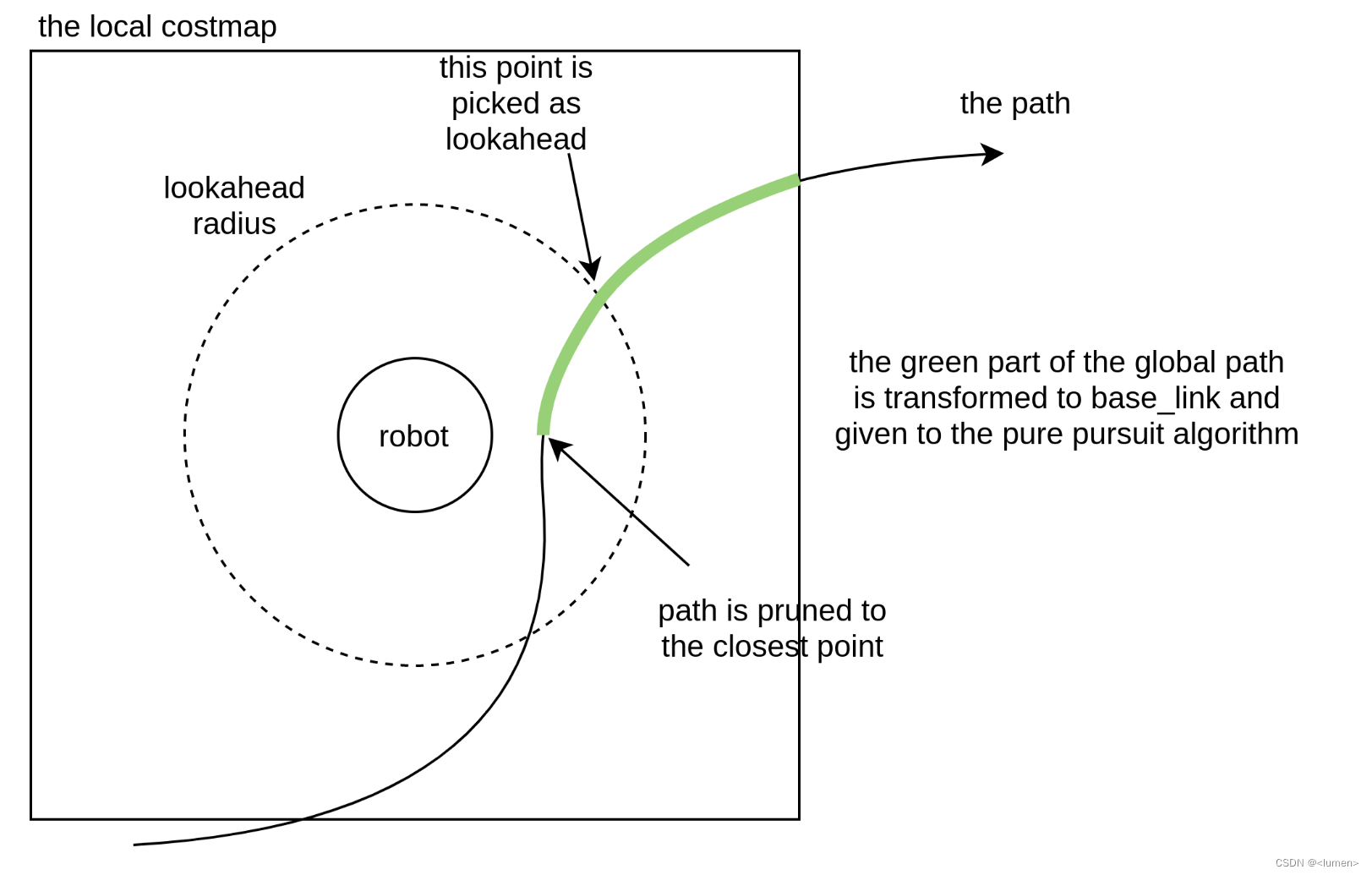
Finally, the lookahead point will be given to the pure pursuit algorithm which finds the curvature of the path required to drive the robot to the lookahead point. This curvature is then applied to the velocity commands to allow the robot to drive
最后,前瞻点将被传递给纯追踪算法,该算法找到驱动机器人到达前瞻点所需的路径曲率。然后,将该曲率应用于速度指令,以使机器人能够行驶。
Note that a pure pursuit controller is that, it “purely” pursues the path without interest or concern about dynamic obstacles. Therefore, this controller should only be used when paired with a path planner that can generate a path the robot can follow. For a circular (or can be treated as circular) robot, this can really be any planner since you can leverage the particle / inflation relationship in planning. For a “large” robot for the environment or general non-circular robots, this must be something kinematically feasible, like the Smac Planner, such that the path is followable
需要注意的是,纯追踪控制器“纯粹”追踪路径而不关心动态障碍物。因此,该控制器应该只在与能够生成机器人可遵循路径的路径规划器配对时使用。对于圆形(或可被视为圆形)的机器人来说,这可以是任何规划器,因为你可以利用规划中的粒子/膨胀关系。对于“大型”环境或一般非圆形机器人,必须使用一些在运动学上可行的东西,比如Smac Planner,这样路径才能被跟随。
Regulated Pure Pursuit Features
We have created a new variation on the pure pursuit algorithm that we dubb the Regulated Pure Pursuit algorithm. We combine the features of the Adaptive Pure Pursuit algorithm with rules around linear velocity with a focus on consumer, industrial, and service robot’s needs. We also implement several common-sense safety mechanisms like collision detection
我们创建了一种新的纯追踪算法变体,称之为调节纯追踪(Regulated Pure Pursuit)算法。我们将自适应纯追踪(Adaptive Pure Pursuit)算法的特性与围绕线性速度的规则相结合,重点关注消费类、工业和服务型机器人的需求。我们还实现了几种常识性的安全机制,如碰撞检测。
The Regulated Pure Pursuit controller implements active collision detection. We use a parameter to set the maximum allowable time before a potential collision on the current velocity command. Using the current linear and angular velocity, we project forward in time that duration and check for collisions. Intuitively, you may think that collision checking between the robot and the lookahead point seems logical. However, if you’re maneuvering in tight spaces, it makes alot of sense to only search forward a given amount of time to give the system a little leeway to get itself out. In confined spaces especially, we want to make sure that we’re collision checking a reasonable amount of space for the current action being taken (e.g. if moving at 0.1 m/s, it makes no sense to look 10 meters ahead to the carrot, or 100 seconds into the future). This helps look further at higher speeds / angular rotations and closer with fine, slow motions in constrained environments so it doesn’t over report collisions from valid motions near obstacles. If you set the maximum allowable to a large number, it will collision check all the way, but not exceeding, the lookahead point. We visualize the collision checking arc on the lookahead_arc topic
这个Regulated Pure Pursuit控制器实现了主动碰撞检测。我们使用一个参数来设置在当前速度命令上可能发生潜在碰撞之前的最大允许时间。利用当前的线性和角速度,我们在将来的这段时间内进行投影,并检查是否存在碰撞。直观地看,你可能会认为在机器人和预瞄点之间进行碰撞检查是合理的。然而,如果你在狭窄空间中操纵,只搜索一定时间范围内是有意义的,这样可以给系统一些余地来解决问题。特别是在狭窄空间中,我们希望确保为当前正在执行的动作进行合理范围的碰撞检查(例如,以0.1米/秒移动时,向前查找到预瞄点10米甚至100秒的未来是没有意义的)。这有助于在高速度/角速度下进一步查看,以及在受限环境中进行细微、缓慢运动时更加接近,这样就不会因为靠近障碍物的有效运动而过度报告碰撞。如果将最大允许时间设置为一个较大的数字,它将在预瞄点之前进行碰撞检查,但不会超过该点。我们将这种碰撞检测弧线可视化在预瞄弧线话题上。
The regulated pure pursuit algorithm also makes use of the common variations on the pure pursuit algorithm. We implement the adaptive pure pursuit’s main contribution of having velocity-scaled lookahead point distances. This helps make the controller more stable over a larger range of potential linear velocities. There are parameters for setting the lookahead gain (or lookahead time) and thresholded values for minimum and maximum.
调节纯追踪算法还利用了纯追踪算法的常见变体。我们实现了自适应纯追踪算法的主要特点,即基于速度缩放的前瞻点距离。这有助于使控制器在更大范围的潜在线性速度下更加稳定。我们设置了前瞻增益(或前瞻时间)的参数,并对最小和最大值进行了阈值化。
The final minor improvement we make is slowing on approach to the goal. Knowing that the optimal lookahead distance is X, we can take the difference in X and the actual distance of the lookahead point found to find the lookahead point error. During operations, the variation in this error should be exceptionally small and won’t be triggered. However, at the end of the path, there are no more points at a lookahead distance away from the robot, so it uses the last point on the path. So as the robot approaches a target, its error will grow and the robot’s velocity will be reduced proportional to this error until a minimum threshold. This is also tracked by the kinematic speed limits to ensure drivability.
我们所做的最后一项小改进是在接近目标时减速。知道最佳前瞻距离为X,我们可以计算实际前瞻点距离与X之间的差值,从而得到前瞻点误差。在操作过程中,这种误差的变化应该异常地小,并且不会被触发。然而,在路径结束时,没有点距离机器人有一个前瞻距离,因此它会使用路径上的最后一个点。因此,随着机器人接近目标,其误差会增大,并且机器人的速度会按比例减小,直到达到最小阈值。这也受到运动学速度限制的跟踪,以确保可驾驶性。
The major improvements that this work implements is the regulations on the linear velocity based on some cost functions. They were selected to remove long-standing bad behavior within the pure pursuit algorithm. Normal Pure Pursuit has an issue with overshoot and poor handling in particularly high curvature (or extremely rapidly changing curvature) environments. It is commonly known that this will cause the robot to overshoot from the path and potentially collide with the environment. These cost functions in the Regulated Pure Pursuit algorithm were also chosen based on common requirements and needs of mobile robots uses in service, commercial, and industrial use-cases; scaling by curvature creates intuitive behavior of slowing the robot when making sharp turns and slowing when its near a potential collision so that small variations don’t clip obstacles. This is also really useful when working in partially observable environments (like turning in and out of aisles / hallways often) so that you slow before a sharp turn into an unknown dynamic environment to be more conservative in case something is in the way immediately requiring a stop.
这项工作实施的主要改进是基于一些成本函数对线性速度进行调节。这些函数的选择旨在消除Pure Pursuit算法中长期存在的不良行为。普通的Pure Pursuit算法在特别高曲率(或曲率极快变化)的环境中存在超调和较差的处理能力的问题。众所周知,这会导致机器人超出路径,并有可能与环境发生碰撞。Regulated Pure Pursuit算法中的这些成本函数也是基于服务、商业和工业用例中移动机器人的常见需求和需求而选择的;通过曲率缩放可以形成直观的行为,使机器人在进行急转弯时减速,并在靠近潜在碰撞物时减速,以防止小的变化导致碰撞障碍物。这在部分可观测的环境中非常有用(比如经常在过道/走廊间转弯),可以在进入未知动态环境之前减速,更保守地假设有可能立即需要停车的障碍物。
The cost functions penalize the robot’s speed based on its proximity to obstacles and the curvature of the path. This is helpful to slow the robot when moving close to things in narrow spaces and scaling down the linear velocity by curvature helps to stabilize the controller over a larger range of lookahead point distances. This also has the added benefit of removing the sensitive tuning of the lookahead point / range, as the robot will track paths far better. Tuning is still required, but it is substantially easier to get reasonable behavior with minor adjustments
成本函数根据机器人与障碍物的接近程度和路径的曲率对其速度进行惩罚。这有助于在狭窄空间中接近物体时减缓机器人的速度,并通过曲率缩减线性速度有助于稳定控制器在更大范围的预瞄点距离上。这还有一个额外的好处,即消除了对预瞄点/范围的敏感调整,因为机器人将更好地跟踪路径。仍然需要进行调整,但通过微小调整可以更容易地获得合理的行为。
An unintended tertiary benefit of scaling the linear velocities by curvature is that a robot will natively rotate to rough path heading when using holonomic planners that don’t start aligned with the robot pose orientation. As the curvature will be very high, the linear velocity drops and the angular velocity takes over to rotate to heading. While not perfect, it does dramatically reduce the need to rotate to a close path heading before following and opens up a broader range of planning techniques. Pure Pursuit controllers otherwise would be completely unable to recover from this in even modestly confined spaces
通过曲率缩减线性速度的一个意外的第三个好处是,当使用不与机器人姿势方向对齐的全向规划器时,机器人将自然旋转到粗糙的路径航向。由于曲率会非常高,线性速度下降,角速度接管旋转到航向的任务。虽然不完美,但确实大大减少了在跟随路径之前需要旋转到接近路径航向的需求,并扩大了规划技术的广泛范围。否则,纯追踪控制器甚至在相对狭窄的空间中都无法从中恢复。
Mixing the proximity and curvature regulated linear velocities with the time-scaled collision checker, we see a near-perfect combination allowing the regulated pure pursuit algorithm to handle high starting deviations from the path and navigate collision-free in tight spaces without overshoot
通过将距离和曲率调节的线性速度与时间缩放的碰撞检测器结合起来,我们可以看到几乎完美的组合,使得调节后的Pure Pursuit算法能够处理路径上的高起始偏差,并且在狭窄空间中无需超调即可避开碰撞。
Note: The maximum allowed time to collision is thresholded by the lookahead point, starting in Humble. This is such that collision checking isn’t significantly overshooting the path, which can cause issues in constrained environments. For example, if there were a straight-line path going towards a wall that then turned left, if this parameter was set to high, then it would detect a collision past the point of actual robot intended motion. Thusly, if a robot is moving fast, selecting further out lookahead points is not only a matter of behavioral stability for Pure Pursuit, but also gives a robot further predictive collision detection capabilities. The max allowable time parameter is still in place for slow commands, as described in detail above
注意:允许的最大碰撞时间由观测点作为阈值进行限制,从Humble开始。这样做是为了确保碰撞检测不会明显超出路径,这可能会在受限环境中引发问题。举例来说,如果有一条直线路径指向一堵墙,然后向左转,若该参数设置过高,那么它将在实际机器人意图运动点之后检测到碰撞。因此,如果机器人移动速度较快,选择更远的观测点不仅是Pure Pursuit算法行为稳定性的问题,同时也赋予机器人更强大的预测性碰撞检测能力。最大允许时间参数仍然适用于慢速指令,就像上面详细描述的那样。
| 参数名 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| desired_linear_vel | 所需的最大线性速度 |
| lookahead_dist | 用于查找前瞻点的前瞻距离 |
| min_lookahead_dist | 当使用速度缩放的前瞻距离时的最小前瞻距离阈值 |
| max_lookahead_dist | 当使用速度缩放的前瞻距离时的最大前瞻距离阈值 |
| lookahead_time | 用于通过投影速度找到速度缩放的前瞻距离的时间。也称为前瞻增益 |
| rotate_to_heading_angular_vel | 如果使用旋转到航向,则使用的角速度 |
| transform_tolerance | TF变换容差 |
| use_velocity_scaled_lookahead_dist | 是否使用速度缩放的前瞻距离或常量前瞻距离 |
| min_approach_linear_velocity | 靠近目标时应用的最小速度阈值 |
| approach_velocity_scaling_dist | 从变换路径末端开始应用速度缩放的累积距离。默认为代价地图正向范围减去一个代价地图单元长度 |
| use_collision_detection | 是否启用碰撞检测 |
| max_allowed_time_to_collision_up_to_carrot | 在启用碰撞检测时,检查碰撞的最大时间。限制为所选前瞻距离的最大距离 |
| use_regulated_linear_velocity_scaling | 是否使用曲率的调节功能 |
| use_cost_regulated_linear_velocity_scaling | 是否使用障碍物接近的调节功能 |
| cost_scaling_dist | 触发线性速度缩放的障碍物最小距离。如果启用了use_cost_regulated_linear_velocity_scaling,则设置的值应小于或等于代价地图膨胀层中设置的膨胀半径,因为膨胀用于计算距离障碍物的距离 |
| cost_scaling_gain | 乘法增益,应<= 1.0,用于在障碍物处于cost_scaling_dist内时进一步缩放速度。较低的值会更快地降低速度。 |
| inflation_cost_scaling_factor | 本地代价地图膨胀层中设置的cost_scaling_factor的值。为了使用膨胀单元值准确计算距离障碍物,该值应完全相同 |
| regulated_linear_scaling_min_radius | 触发调节功能的转弯半径。请记住,转弯越急,半径越小 |
| regulated_linear_scaling_min_speed | 调节功能可以发送的最小速度,以确保即使在成本高且曲率高的空间中仍然可以实现进程 |
| use_fixed_curvature_lookahead | 启用曲率检测的固定前瞻。对于具有长前瞻的系统非常有用 |
| curvature_lookahead_dist | 用于确定速度调节目的的曲率的前瞻距离。仅当启用use_fixed_curvature_lookahead时使用 |
| use_rotate_to_heading | 是否在使用全向规划器时启用旋转到粗略航向和目标方向。建议对除了阿克曼类型之外的所有机器人类型都启用 |
| rotate_to_heading_min_angle | 路径方向与起始机器人方向之间的差异,触发原地旋转的最小角度,如果启用use_rotate_to_heading |
| max_angular_accel | 在旋转到航向时允许的最大角加速度 |
| max_robot_pose_search_dist | 沿路径绑定机器人最近姿态的最大集成距离。默认情况下,它设置为最大代价地图范围,因此除非本地代价地图中有循环,否则不应手动设置 |
Example fully-described XML with default parameter values:
controller_server:
ros__parameters:
controller_frequency: 20.0
min_x_velocity_threshold: 0.001
min_y_velocity_threshold: 0.5
min_theta_velocity_threshold: 0.001
progress_checker_plugins: ["progress_checker"]
goal_checker_plugins: "goal_checker"
controller_plugins: ["FollowPath"]
progress_checker:
plugin: "nav2_controller::SimpleProgressChecker"
required_movement_radius: 0.5
movement_time_allowance: 10.0
goal_checker:
plugin: "nav2_controller::SimpleGoalChecker"
xy_goal_tolerance: 0.25
yaw_goal_tolerance: 0.25
stateful: True
FollowPath:
plugin: "nav2_regulated_pure_pursuit_controller::RegulatedPurePursuitController"
desired_linear_vel: 0.5
lookahead_dist: 0.6
min_lookahead_dist: 0.3
max_lookahead_dist: 0.9
lookahead_time: 1.5
rotate_to_heading_angular_vel: 1.8
transform_tolerance: 0.1
use_velocity_scaled_lookahead_dist: false
min_approach_linear_velocity: 0.05
approach_velocity_scaling_dist: 1.0
use_collision_detection: true
max_allowed_time_to_collision_up_to_carrot: 1.0
use_regulated_linear_velocity_scaling: true
use_cost_regulated_linear_velocity_scaling: false
regulated_linear_scaling_min_radius: 0.9
regulated_linear_scaling_min_speed: 0.25
use_fixed_curvature_lookahead: false
curvature_lookahead_dist: 1.0
use_rotate_to_heading: true
rotate_to_heading_min_angle: 0.785
max_angular_accel: 3.2
max_robot_pose_search_dist: 10.0
cost_scaling_dist: 0.3
cost_scaling_gain: 1.0
inflation_cost_scaling_factor: 3.0
Topics
| 主题 | 类型 | 描述 |
|---|---|---|
| lookahead_point | geometry_msgs/PointStamped | 路径上的当前前瞻点 |
| lookahead_arc | nav_msgs/Path | 机器人和"胡萝卜"之间的可行驶弧线。弧长取决于max_allowed_time_to_collision_up_to_carrot,在给定时间内从机器人姿态处向前模拟。在碰撞状态下,最后发布的弧线将是导致碰撞的点,包括第一个碰撞点及之前的点。 |
注意:lookahead_arc也是一个很好的速度指示器,当到达“full”或最大时间时,您就知道机器人以最大速度行驶。如果少了20%,那么您就可以知道机器人的速度大约低于最大速度的20%。可以将其视为碰撞检测边界,同时也是速度表。
用户须知:
默认情况下,use_cost_regulated_linear_velocity_scaling设置为false,因为我们设置的通用沙盒环境是TB3世界。这是一个高度受限制的环境,所以它会过度触发,使机器人减速,因为每个地方的代价都很高。建议在不在成本持续高的空间工作时将其设置为true。
要调整以获得自适应Pure Pursuit行为,请将所有布尔参数设置为false,除了use_velocity_scaled_lookahead_dist,并确保调整lookahead_time、min_lookahead_dist和max_lookahead_dist。
要调整以获得Pure Pursuit行为,请将所有布尔参数设置为false,并确保调整lookahead_dist。
目前,没有旋转到目标方向的行为,因此预期路径的朝向是目标的朝向,或者目标检查器已设置了一个大致的min_theta_velocity_threshold。旋转到目标航向的实现正在进行中。
前瞻距离的选择高度依赖于机器人的大小、响应性、控制器更新频率和速度。请确保为您的平台调整此值,尽管规则特性主要减少了对该值的大量调整的必要性。如果看到摆动,增加距离或比例。如果收敛到路径的速度不如预期的快,减小它。