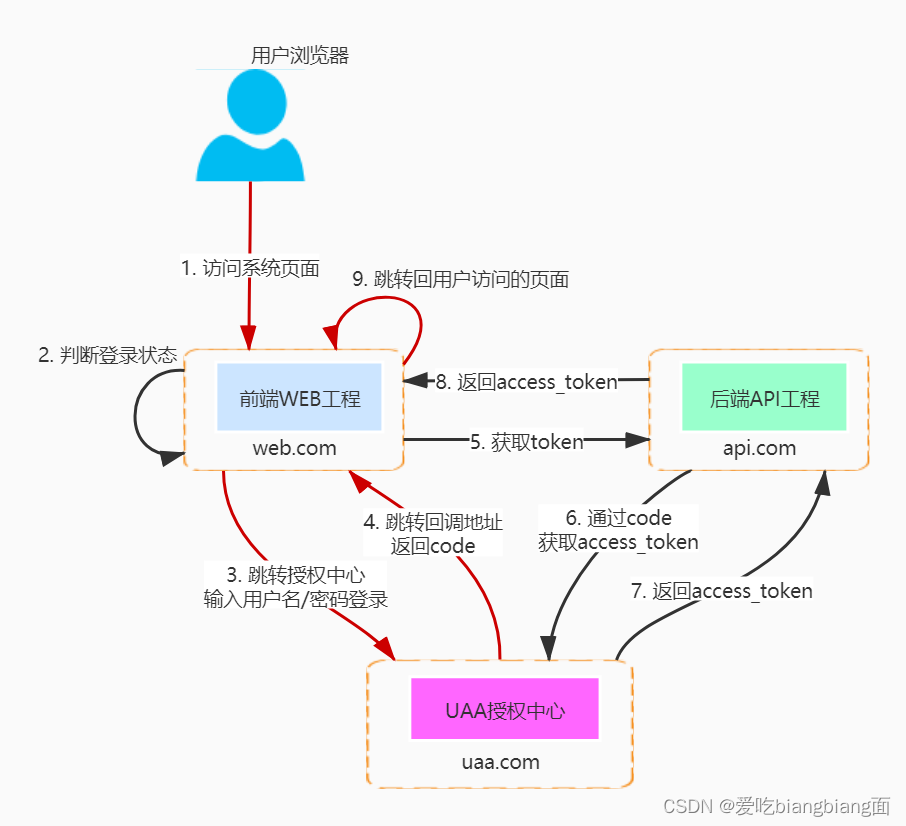
继续【Gradio的重要函数以及一些代码示例学习(一)】
1 fastapi+gradio的联合使用:mount_gradio_app
1.1 mount_gradio_app一个页面两个模块
分页的效果实现,主要依靠mount_gradio_app,启发于:Support multiple pages in a gradio app
from fastapi import FastAPI
from fastapi.responses import HTMLResponse
import gradio as gr
app = FastAPI()
HELLO_ROUTE = "/hello"
GOODBYE_ROUTE = "/goodbye"
iframe_dimensions = "height=300px width=1000px"
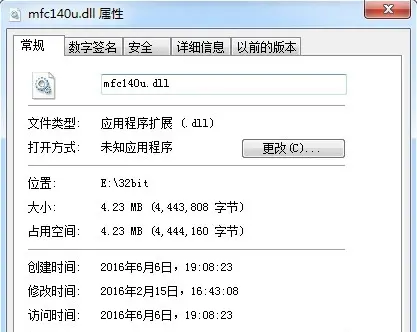
index_html = f'''
<h1>Put header here</h1>
<h3>
You can mount multiple gradio apps on a single FastAPI object for a multi-page app.
However if you mount a gradio app downstream of another gradio app, the downstream
apps will be stuck loading.
</h3>
<h3>
So in particular if you mount a gradio app at the index route "/", then all your
other mounted gradio apps will be stuck loading. But don't worry, you can still embed
your downstream gradio apps into the index route using iframes like I do here. In fact,
you probably want to do this anyway since its your index page, which you want to detail
more fully with a jinja template.
For a full example, you can see my <a href=https://yfu.one/>generative avatar webapp</a>
</h3>
<div>
<iframe src={HELLO_ROUTE} {iframe_dimensions}></iframe>
</div>
<div>
<iframe src={GOODBYE_ROUTE} {iframe_dimensions}></iframe>
</div>
'''
@app.get("/", response_class=HTMLResponse)
def index():
return index_html
hello_app = gr.Interface(lambda x: "Hello, " + x + "!", "textbox", "textbox")
goodbye_app = gr.Interface(lambda x: "Goodbye, " + x + "!", "textbox", "textbox")
app = gr.mount_gradio_app(app, hello_app, path=HELLO_ROUTE)
app = gr.mount_gradio_app(app, goodbye_app, path=GOODBYE_ROUTE)
if __name__ == "__main__":
import uvicorn
uvicorn.run(app)
此时通过mount_gradio_app在fastapi同时部署两个模块,来看一下例子:
1.2 mount_gradio_app两个页面两个模块
启发于:230902-部署Gradio到已有FastAPI及服务器中
import gradio as gr
def greet(text: str) -> str:
return text
demo1 = gr.Interface(
fn=greet,
inputs=gr.components.Textbox(label='Input-1'),
outputs=gr.components.Textbox(label='Output-1'),
allow_flagging='never'
)
demo2 = gr.Interface(
fn=greet,
inputs=gr.components.Textbox(label='Input-2'),
outputs=gr.components.Textbox(label='Output-2'),
allow_flagging='never'
)
from fastapi import FastAPI
import gradio as gr
app = FastAPI()
@app.get('/')
async def root():
return 'Gradio app is running at /gradio', 200
app = gr.mount_gradio_app(app, demo1, path='/gradio1')
app = gr.mount_gradio_app(app, demo2, path='/gradio2')
import uvicorn
uvicorn.run(app)
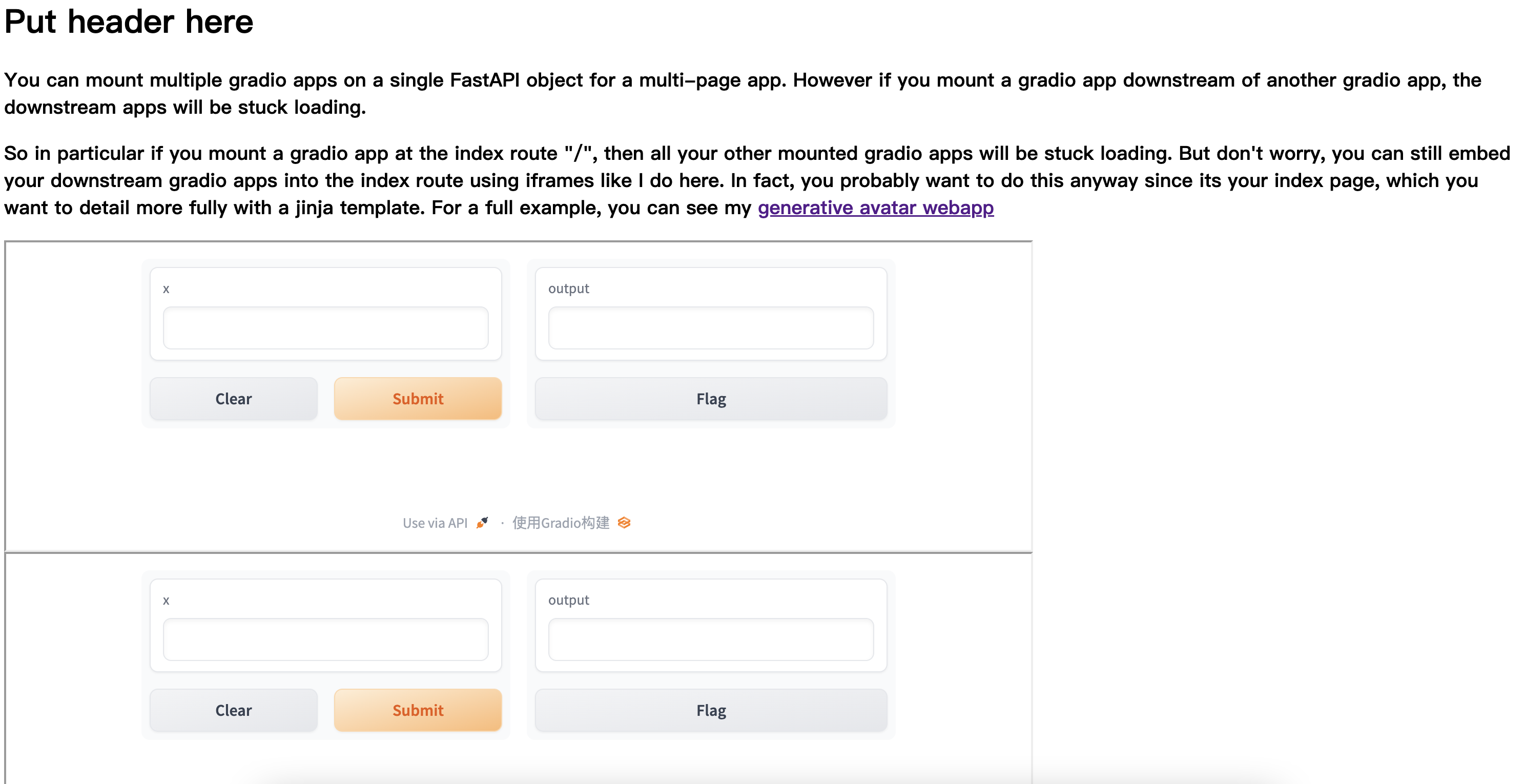
这里定义了两个gradio模块,demo1和demo2,通过mount_gradio_app,映射到两个子路径,gradio1和gradio2
所以这里,需要通过http://127.0.0.1:8000/gradio2/和http://127.0.0.1:8000/gradio1/ 到达两个页面:
2 TabbedInterface组件进行选项卡布局
官方教程:tabbedinterface
启发于:Gradio使用介绍 和 优雅组合,高效交互:Gradio Combining Interfaces模块解析
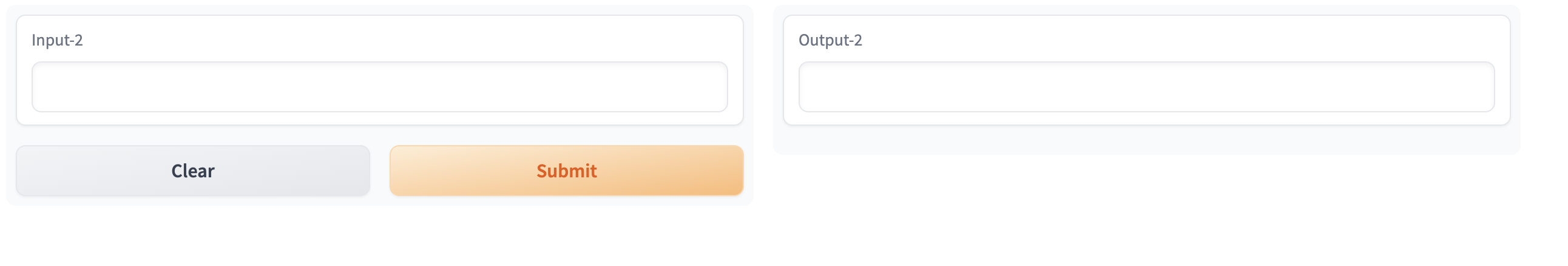
TabbedInterface可以通过提供一个Interface列表来创建,每个Interface都会在一个单独的选项卡中显示。您可以根据需要为每个选项卡指定名称,也可以使用默认的"Tab 1"、"Tab 2"等名称。
几个参数的构成:
2.1 Parallel:并行比较案例
Parallel可以将多个接口并行比较它们的输出。要将接口放在Parallel中,它们必须共享相同的输入组件,但可以有不同的输出组件。
import gradio as gr
greeter_1 = gr.Interface(lambda name: f"Hello {name}!", inputs="textbox", outputs=gr.Textbox(label="Greeter 1"))
greeter_2 = gr.Interface(lambda name: f"Greetings {name}!", inputs="textbox", outputs=gr.Textbox(label="Greeter 2"))
demo = gr.Parallel(greeter_1, greeter_2)
if __name__ == "__main__":
demo.launch()
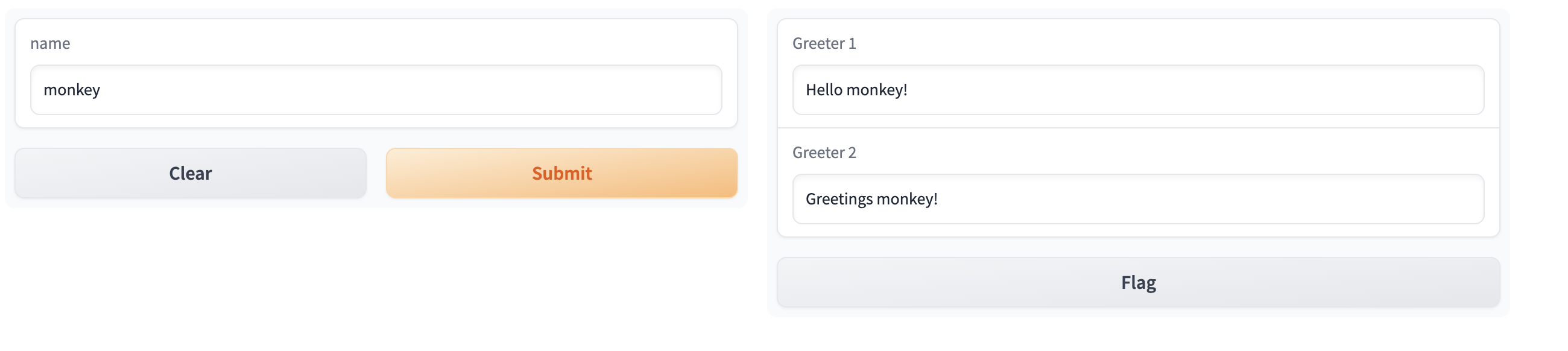
可以看到一个输入,两个输出
2.2 Series:串行连接
Series可以将多个接口串行连接在一起,将一个接口的输出作为下一个接口的输入。要使用Series,接口之间的输入和输出组件必须匹配。
示例用法:
import gradio as gr
get_name = gr.Interface(lambda name: name, inputs="textbox", outputs="textbox")
prepend_hello = gr.Interface(lambda name: f"Hello {name}!", inputs="textbox", outputs="textbox")
append_nice = gr.Interface(lambda greeting: f"{greeting} Nice to meet you!",
inputs="textbox", outputs=gr.Textbox(label="Greeting"))
demo = gr.Series(get_name, prepend_hello, append_nice)
if __name__ == "__main__":
demo.launch()
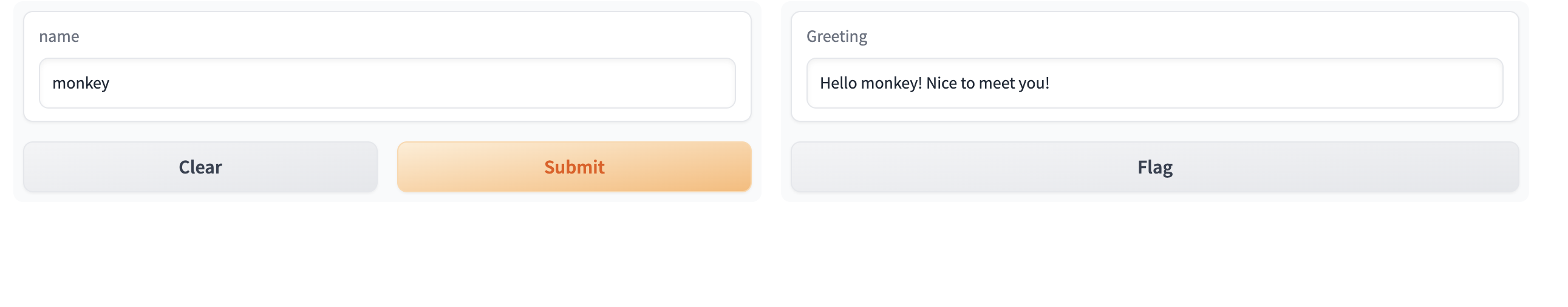
两个组件可以联动
2.3 第三个TabbedInterface的案例:
import gradio as gr
css = """
#warning {background-color: #FFCCCB}
.feedback textarea {font-size: 24px !important}
"""
with gr.Blocks(css=css) as demo1:
with gr.Row():
with gr.Column(scale=1):
gr.Textbox(label="name", elem_id="warning")
gr.Textbox(label="age", elem_classes="feedback")
with gr.Column(scale=2):
gr.Dropdown(["one", "two", "tree"], label="class")
gr.CheckboxGroup(["male", "female"], label="sex")
with gr.Column(scale=1):
gr.Radio(["is_girl"], label="is_girl")
gr.Slider(1, 100, 20)
with gr.Row():
gr.Button(value="Submit")
gr.Button(value="Clear")
with gr.Blocks(css=css) as demo2:
with gr.Row():
with gr.Column(scale=1):
gr.Textbox(label="name", elem_id="warning")
gr.Textbox(label="age", elem_classes="feedback")
with gr.Column(scale=2):
gr.Dropdown(["one", "two", "tree"], label="class")
gr.CheckboxGroup(["male", "female"], label="sex")
with gr.Column(scale=1):
gr.Radio(["is_girl"], label="is_girl")
gr.Slider(1, 100, 20)
with gr.Row():
gr.Button(value="Submit")
gr.Button(value="Clear")
app = gr.TabbedInterface([demo1, demo2], ["First", "Second"])
app.launch()
如果应用的并发流量很大,gradio还提供排队处理机制,在demo.queue()中可以指定并发处理数量,例如
with gr.Blocks() as demo:
#...
demo.queue(concurrency_count=3)
demo.launch()
最终的效果为:
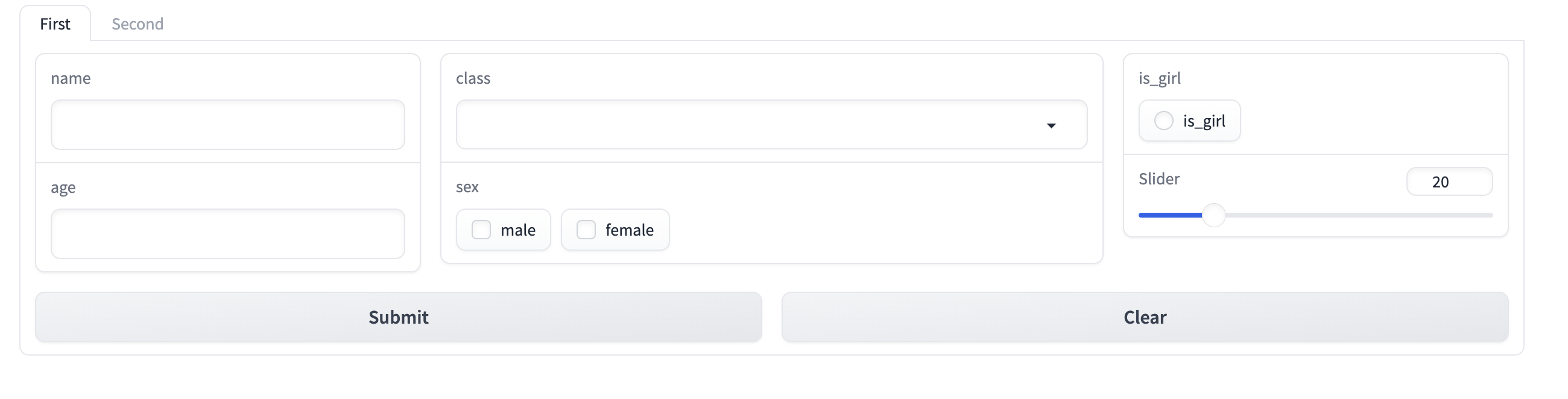
可以看到最上面有两个选项可以选择不同的控件组成
3 未测试
分页的效果实现,主要依靠mount_gradio_app,启发于:Support multiple pages in a gradio app
import gradio as gr
gr.Blocks():
gr.Page("My amazing page", route="/"):
gr.Markdown("# My amazing page")
gr.Textbox("Page one")
gr.Page("My second amazing page", route="/page-two"):
gr.Markdown("# My second amazing page")
gr.Textbox("Page two")



![13.求面积[有问题]](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/8761d080cb1e4fc1aac3be9ff8ae27c3.png)