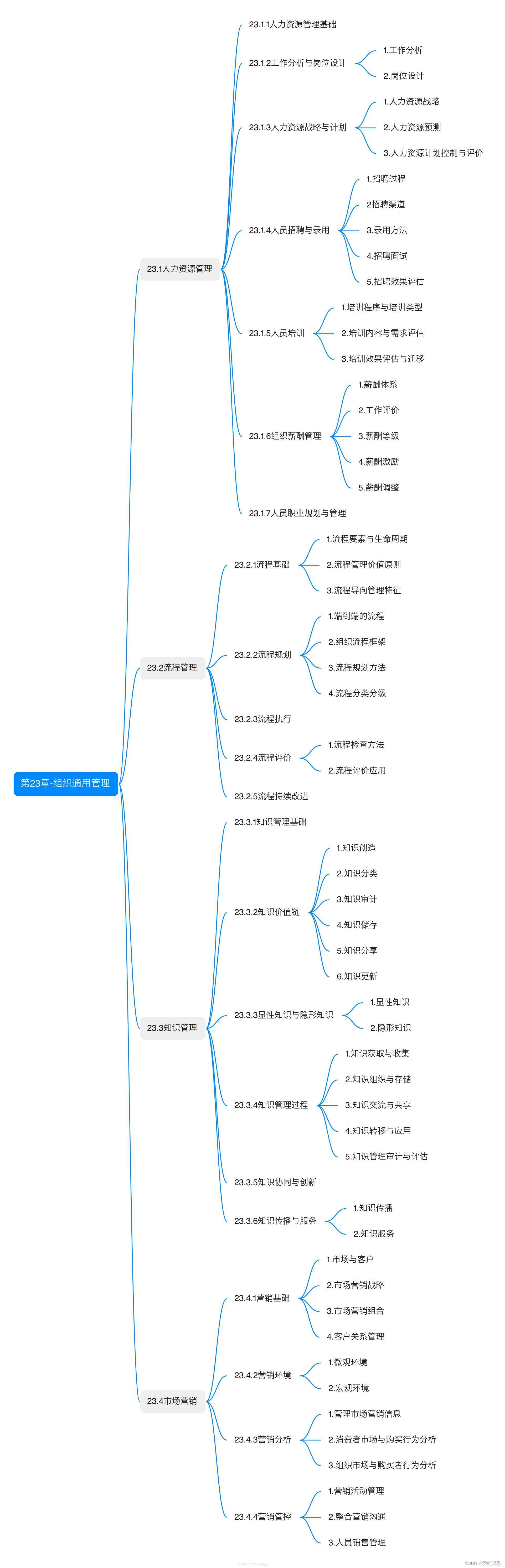
文章目录
- 一、概述
- 二、Jedis 开发示例
- 2.1 导入 maven 依赖
- 2.2 使用连接池读写
- 2.3 使用集群读写
- 2.4 完整示例代码
- 2.5 测试集群的搭建
- 三、Lettuce 开发示例
- 3.1 导入 maven 依赖
- 3.2 读写数据
- 四、Spring Boot Redis 开发示例
- 4.1 导入 maven 依赖
- 4.2 配置Redis服务地址
- 4.3 基于 RedisTemplate 的读写全类型数据
- 4.4 基于 StringRedisTemplate 的读写字符串类型数据
- 4.5 基于 RedisConnection 的读写字节数据
- 4.6 读写 Hash 数据类型
- 4.7 订阅发布
- 4.8 基于SpringBoot的完整测试代码
- 4.9 注意问题
如果您对Redis的了解不够深入请关注本栏目,本栏目包括Redis安装,Redis配置文件说明,Redis命令和数据类型说明,Redis持久化配置,Redis主从复制和哨兵机制,Redis Cluster(集群)配置,Redis Predixy 集群,Redis Twemproxy 集群,Redis Codis 集群,Redis 集群对比,RedisBloom 布隆过滤器。
一、概述
-
Redis(Remote Dictionary Server)是一种高性能的开源内存数据库,它具有多种用途和功能,可以充当缓存、消息队列、数据库、实时分析和数据处理平台等多种角色。具体功能如下:
- 数据缓存: Redis 可以用作应用程序的缓存层,帮助减少对后端数据库的频繁访问。通过将经常使用的数据存储在内存中,可以显著提高读取速度,降低数据库负担,从而提高应用程序性能。
- 会话存储: Redis 可以用于存储用户会话数据,特别是在分布式环境中。这使得用户会话可以跨多个服务器实例进行共享,提高了应用程序的伸缩性和可用性。
- 消息队列: Redis 支持发布/订阅(Pub/Sub)模式,使其成为一个优秀的消息队列平台。应用程序可以使用 Redis 来发送和接收消息,实现异步通信、事件驱动和消息分发。
- 计数器和统计信息: Redis 提供了递增和递减操作,因此它非常适合存储计数器数据。这对于跟踪应用程序中的用户行为、实时统计信息和监视任务非常有用。
- 地理空间数据: Redis 支持地理空间数据(Geospatial Data),因此它可以用于存储位置信息、地图数据和地理位置查询。
- 分布式锁: Redis 可以用于实现分布式锁,确保在分布式系统中的互斥操作。这对于避免竞态条件和数据一致性非常重要。
- 缓存击穿保护: Redis 可以用于缓存击穿保护,通过设置适当的过期时间或使用布隆过滤器来避免某个数据的同时大量请求导致的数据库请求。
- 实时数据传输: Redis 可以用于构建实时数据传输和协作应用程序,如聊天应用、协同编辑和游戏。
- 数据持久性: Redis 提供不同级别的数据持久性选项,以确保数据在服务器重启后不会丢失。
-
下面分别使用 Jedis 、Lettuce 访问Redis 和 在 Spring Boot 使用访问 Redis 的简单示例。
二、Jedis 开发示例
- 开源地址:jedis
2.1 导入 maven 依赖
-
在 pom.xml 添加 jedis
<dependency> <groupId>redis.clients</groupId> <artifactId>jedis</artifactId> <version>3.9.0</version> </dependency>
2.2 使用连接池读写
-
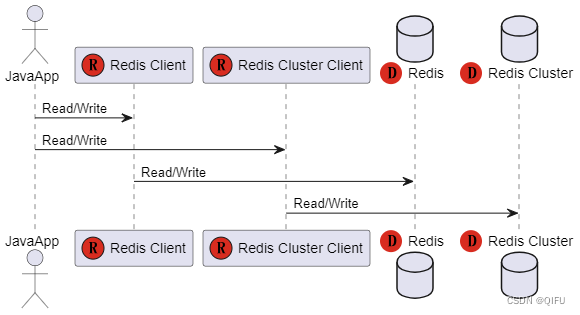
使用连接池对单个Redis实例进行读写
JedisPool pool = new JedisPool("192.168.8.60", 6379); Jedis resource = pool.getResource(); resource.set("aaa", "111"); System.out.println("read redis 1="+resource.get("aaa"));
2.3 使用集群读写
-
使用集群对Redis集群进行读写
Set<HostAndPort> jedisClusterNodes = new HashSet<HostAndPort>(); jedisClusterNodes.add(new HostAndPort("192.168.8.60", 30001)); jedisClusterNodes.add(new HostAndPort("192.168.8.60", 30002)); jedisClusterNodes.add(new HostAndPort("192.168.8.60", 30003)); // jedisClusterNodes.add(new HostAndPort("192.168.8.60", 30004)); // jedisClusterNodes.add(new HostAndPort("192.168.8.60", 30005)); // jedisClusterNodes.add(new HostAndPort("192.168.8.60", 30006)); JedisCluster jedis = new JedisCluster(jedisClusterNodes); jedis.set("ddd", "1111"); System.out.println("read redis 2="+ jedis.get("aaa"));
2.4 完整示例代码
-
以下是完整的测试代码
package top.yiqifu.study.p121; import redis.clients.jedis.HostAndPort; import redis.clients.jedis.Jedis; import redis.clients.jedis.JedisCluster; import redis.clients.jedis.JedisPool; import java.util.HashSet; import java.util.Set; public class Test01_Redis { public static void main(String[] args) { // 通过连接池直接读写数据 testResource(); //通过Redis集群(Cluster)读写数据 testCluster(); } private static void testResource(){ JedisPool pool = new JedisPool("192.168.8.60", 6379); Jedis resource = pool.getResource(); resource.set("aaa", "111"); System.out.println("read redis 1="+resource.get("aaa")); } private static void testCluster(){ Set<HostAndPort> jedisClusterNodes = new HashSet<HostAndPort>(); jedisClusterNodes.add(new HostAndPort("192.168.8.60", 30001)); jedisClusterNodes.add(new HostAndPort("192.168.8.60", 30002)); jedisClusterNodes.add(new HostAndPort("192.168.8.60", 30003)); // jedisClusterNodes.add(new HostAndPort("192.168.8.60", 30004)); // jedisClusterNodes.add(new HostAndPort("192.168.8.60", 30005)); // jedisClusterNodes.add(new HostAndPort("192.168.8.60", 30006)); JedisCluster jedis = new JedisCluster(jedisClusterNodes); jedis.set("ddd", "1111"); System.out.println("read redis 2="+ jedis.get("aaa")); } }
2.5 测试集群的搭建
-
以下给出测试集群搭建的核心命令,具体请参考Redis Cluster(集群)配置。
cd /redis-6.0.6/utils/create-cluster vi create-cluster CLUSTER_HOST=192.168.8.60 PROTECTED_MODE=no ./create-cluster start ./create-cluster create firewall-cmd --permanent --add-port=30001/tcp firewall-cmd --permanent --add-port=30002/tcp firewall-cmd --permanent --add-port=30003/tcp firewall-cmd --permanent --add-port=30004/tcp firewall-cmd --permanent --add-port=30005/tcp firewall-cmd --permanent --add-port=30006/tcp firewall-cmd --reload
三、Lettuce 开发示例
3.1 导入 maven 依赖
-
开源地址:lettuce-core
-
在 pom.xml 添加 lettuce-core
<dependency> <groupId>io.lettuce</groupId> <artifactId>lettuce-core</artifactId> <version>6.1.10.RELEASE</version> </dependency>
3.2 读写数据
-
以下使用 lettuce 来读写Redis,lettuce 最大的特点是支持响应式编程(Reactive API)。
package top.yiqifu.study.p121; import io.lettuce.core.RedisClient; import io.lettuce.core.api.StatefulRedisConnection; import io.lettuce.core.api.async.RedisAsyncCommands; import io.lettuce.core.api.sync.RedisStringCommands; public class Test02_LettuceRedis { public static void main(String[] args) { // 同步/异步方式读写数据 testSync(); } private static void testSync(){ RedisClient client = RedisClient.create("redis://192.168.8.60:6379"); StatefulRedisConnection<String, String> connection = client.connect(); RedisStringCommands sync = connection.sync(); sync.set("aaa", "111"); System.out.println("read redis 1="+sync.get("aaa")); RedisAsyncCommands<String, String> async = connection.async(); async.set("bbb", "222"); System.out.println("read redis 2="+async.get("bbb")); } }
四、Spring Boot Redis 开发示例
4.1 导入 maven 依赖
- 这里 spring-boot-starter-data-redis 是 Redis 的依赖,而 spring-boot-starter-json 是用于数据序列化的 json 依赖。
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-data-redis</artifactId>
<version>2.7.15</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-json</artifactId>
<version>2.7.15</version>
</dependency>
4.2 配置Redis服务地址
- 在 application.yaml 文件中添加配置
spring:
redis:
host: 192.168.8.60
port: 6379
4.3 基于 RedisTemplate 的读写全类型数据
@Autowired
RedisTemplate redisTemplate;
private void testObject(){
redisTemplate.opsForValue().set("aaa", "111");
System.out.println("reda redis 1 = "+redisTemplate.opsForValue().get("aaa"));
}
4.4 基于 StringRedisTemplate 的读写字符串类型数据
@Autowired
StringRedisTemplate stringRedisTemplate;
private void testString(){
stringRedisTemplate.opsForValue().set("bbb", "222");
System.out.println("read redis 2 = "+stringRedisTemplate.opsForValue().get("bbb"));
}
4.5 基于 RedisConnection 的读写字节数据
@Autowired
RedisTemplate redisTemplate;
private void testObject(){
redisTemplate.opsForValue().set("aaa", "111");
System.out.println("reda redis 1 = "+redisTemplate.opsForValue().get("aaa"));
}
4.6 读写 Hash 数据类型
@Autowired
RedisTemplate redisTemplate;
@Autowired
StringRedisTemplate stringRedisTemplate;
@Autowired
@Qualifier("serializerRedisTemplate")
StringRedisTemplate serializerRedisTemplate;
private void testHash(){
// 方法一:使用 StringRedisTemplate 直接读写hash
HashOperations<String, Object, Object> hash = stringRedisTemplate.opsForHash();
hash.put("someInfo", "name" , "qifu");
hash.put("someInfo", "age" , "30");
System.out.println("read redis 4 = "+hash.entries("someInfo"));//hincrby someInfo age 1
// 创建对象
Person person = new Person();
person.setName("zhang san");
person.setAge(20);
Jackson2HashMapper hashMapper = new Jackson2HashMapper(objectMapper, false);
// 方法二:使用 RedisTemplate 读写 hash 对象
redisTemplate.opsForHash().putAll("person1", hashMapper.toHash(person));
Map personMap1 = redisTemplate.opsForHash().entries("person1");
Person value6 = objectMapper.convertValue(personMap1, Person.class);
System.out.println("read redis 6 = "+value6.getName());
// 方法三:使用 StringRedisTemplate 读写 hash 对象
// stringRedisTemplate 需设置 ValueSerializer ,因为age是Integer类型
stringRedisTemplate.setHashValueSerializer(new Jackson2JsonRedisSerializer<Object>(Object.class));
stringRedisTemplate.opsForHash().putAll("person2", hashMapper.toHash(person));
Map personMap2 = stringRedisTemplate.opsForHash().entries("person2");
Person value7 = objectMapper.convertValue(personMap2, Person.class);
System.out.println("read redis 7 = "+value7.getName());
// 方法四:使用自定义 serializerRedisTemplate 读写 hash 对象
serializerRedisTemplate.opsForHash().putAll("person3", hashMapper.toHash(person));
Map personMap3 = serializerRedisTemplate.opsForHash().entries("person3");
Person value8 = objectMapper.convertValue(personMap3, Person.class);
System.out.println("read redis 8 = "+value8.getName());
}
4.7 订阅发布
@Autowired
StringRedisTemplate stringRedisTemplate;
private void testPubsub(){
//pub/sub
stringRedisTemplate.getConnectionFactory().getConnection().subscribe(new MessageListener() {
@Override
public void onMessage(Message message, byte[] pattern) {
System.out.println("sub redis = "+new String(message.getBody()));
}
}, "xxx".getBytes());
stringRedisTemplate.convertAndSend("xxx","yyy");
}
4.8 基于SpringBoot的完整测试代码
-
TestRedis.java
package top.yiqifu.study.p211_redis; import com.fasterxml.jackson.databind.ObjectMapper; import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired; import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Qualifier; import org.springframework.data.redis.connection.Message; import org.springframework.data.redis.connection.MessageListener; import org.springframework.data.redis.connection.RedisConnection; import org.springframework.data.redis.core.HashOperations; import org.springframework.data.redis.core.RedisTemplate; import org.springframework.data.redis.core.StringRedisTemplate; import org.springframework.data.redis.hash.Jackson2HashMapper; import org.springframework.data.redis.serializer.Jackson2JsonRedisSerializer; import org.springframework.stereotype.Component; import java.util.Map; @Component public class TestRedis { @Autowired RedisTemplate redisTemplate; @Autowired StringRedisTemplate stringRedisTemplate; @Autowired @Qualifier("serializerRedisTemplate") StringRedisTemplate serializerRedisTemplate; @Autowired ObjectMapper objectMapper; public void test(){ // 基于 RedisTemplate 测试Redis全类型的读写,如 object this.testObject(); // 基于 StringRedisTemplate 测试Redis字符串类型的读写,如 string this.testString(); // 基于 RedisConnection 测试Redis更底层的字节类型的读写,如 byte[] this.testBytes(); // 基于 StringRedisTemplate 测试Redis的Hash类型的读写,如 hash this.testHash(); // 基于 StringRedisTemplate 测试Redis的发布、订阅 this.testPubsub(); } private void testObject(){ redisTemplate.opsForValue().set("aaa", "111"); System.out.println("reda redis 1 = "+redisTemplate.opsForValue().get("aaa")); } private void testString(){ stringRedisTemplate.opsForValue().set("bbb", "222"); System.out.println("read redis 2 = "+stringRedisTemplate.opsForValue().get("bbb")); } private void testBytes(){ RedisConnection connection = redisTemplate.getConnectionFactory().getConnection(); connection.set("ccc".getBytes(), "333".getBytes()); System.out.println("read redis 3 = "+new String(connection.get("ccc".getBytes()))); } private void testHash(){ // 方法一:使用 StringRedisTemplate 直接读写hash HashOperations<String, Object, Object> hash = stringRedisTemplate.opsForHash(); hash.put("someInfo", "name" , "qifu"); hash.put("someInfo", "age" , "30"); System.out.println("read redis 4 = "+hash.entries("someInfo"));//hincrby someInfo age 1 // 创建对象 Person person = new Person(); person.setName("zhang san"); person.setAge(20); Jackson2HashMapper hashMapper = new Jackson2HashMapper(objectMapper, false); // 方法二:使用 RedisTemplate 读写 hash 对象 redisTemplate.opsForHash().putAll("person1", hashMapper.toHash(person)); Map personMap1 = redisTemplate.opsForHash().entries("person1"); Person value6 = objectMapper.convertValue(personMap1, Person.class); System.out.println("read redis 6 = "+value6.getName()); // 方法三:使用 StringRedisTemplate 读写 hash 对象 // stringRedisTemplate 需设置 ValueSerializer ,因为age是Integer类型 stringRedisTemplate.setHashValueSerializer(new Jackson2JsonRedisSerializer<Object>(Object.class)); stringRedisTemplate.opsForHash().putAll("person2", hashMapper.toHash(person)); Map personMap2 = stringRedisTemplate.opsForHash().entries("person2"); Person value7 = objectMapper.convertValue(personMap2, Person.class); System.out.println("read redis 7 = "+value7.getName()); // 方法四:使用自定义 serializerRedisTemplate 读写 hash 对象 serializerRedisTemplate.opsForHash().putAll("person3", hashMapper.toHash(person)); Map personMap3 = serializerRedisTemplate.opsForHash().entries("person3"); Person value8 = objectMapper.convertValue(personMap3, Person.class); System.out.println("read redis 8 = "+value8.getName()); } private void testPubsub(){ //pub/sub stringRedisTemplate.getConnectionFactory().getConnection().subscribe(new MessageListener() { @Override public void onMessage(Message message, byte[] pattern) { System.out.println("sub redis = "+new String(message.getBody())); } }, "xxx".getBytes()); stringRedisTemplate.convertAndSend("xxx","yyy"); } } -
Config.java
package top.yiqifu.study.p211_redis; import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired; import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean; import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration; import org.springframework.data.redis.connection.RedisConnectionFactory; import org.springframework.data.redis.core.StringRedisTemplate; import org.springframework.data.redis.serializer.Jackson2JsonRedisSerializer; import javax.annotation.Resource; @Configuration public class Config { @Resource RedisConnectionFactory factory; @Bean("serializerRedisTemplate") public StringRedisTemplate getRedisTemplate(){ StringRedisTemplate template = new StringRedisTemplate(factory); template.setHashValueSerializer(new Jackson2JsonRedisSerializer<Object>(Object.class)); return template; } } -
RedisSpringBootApplication.java
package top.yiqifu.study.p211_redis; import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication; import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication; import org.springframework.context.ConfigurableApplicationContext; @SpringBootApplication public class RedisSpringBootApplication { public static void main(String[] args){ ConfigurableApplicationContext context = SpringApplication.run(RedisSpringBootApplication.class, args); TestRedis bean = context.getBean(TestRedis.class); bean.test(); } }
4.9 注意问题
-
在新版本(版本大于2.7)的SpringBoot中,以下写法会报错“Could not autowire. No beans of ‘RedisConnectionFactory’ type found”,如下写法:
@Configuration public class Config { @Bean("serializerRedisTemplate") public StringRedisTemplate getRedisTemplate(RedisConnectionFactory factory){ StringRedisTemplate template = new StringRedisTemplate(factory); template.setHashValueSerializer(new Jackson2JsonRedisSerializer<Object>(Object.class)); return template; } } -
要使用@Resource注解的属性注入,修改后的代码为
@Configuration public class Config { @Resource RedisConnectionFactory factory; @Bean("serializerRedisTemplate") public StringRedisTemplate getRedisTemplate(){ StringRedisTemplate template = new StringRedisTemplate(factory); template.setHashValueSerializer(new Jackson2JsonRedisSerializer<Object>(Object.class)); return template; } }