2023.11.8
Spring为Bean提供了多种实例化方式,通常包括4种方式。
- 第一种:通过构造方法实例化
- 第二种:通过简单工厂模式实例化
- 第三种:通过factory-bean实例化
- 第四种:通过FactoryBean接口实例化
通过构造方法实例化
创建一个bean:
package spring6.beans;
public class User {
public User() {
System.out.println("User类的无参构造方法执行");
}
}
配置xml文件:
<bean id="UserBean" class="spring6.beans.User"/>测试代码:
@Test
public void testConstructor(){
ApplicationContext applicationContext = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("spring.xml");
User user = applicationContext.getBean("UserBean", User.class);
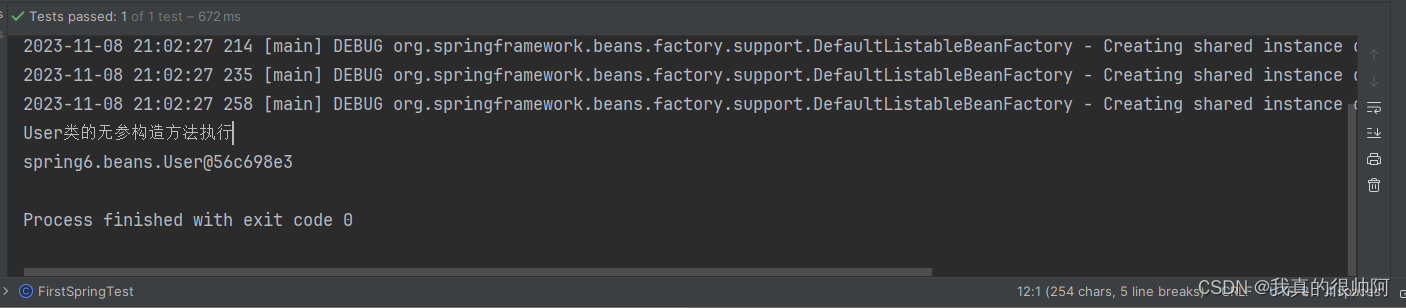
System.out.println(user);
}运行结果:
通过简单工厂模式实例化
先介绍一下简单工厂模式和工厂方法模式:
简单工厂模式:
客户端程序不需要关心对象的创建细节,需要哪个对象时,只需要向工厂索要即可,初步实现了责任的分离。客户端只负责“消费”,工厂负责“生产”。生产和消费分离。
缺点:
-
工厂类集中了所有产品的创造逻辑,形成一个无所不知的全能类,有人把它叫做上帝类。显然工厂类非常关键,不能出问题,一旦出问题,整个系统瘫痪。
-
不符合OCP开闭原则,在进行系统扩展时,需要修改工厂类。
Spring中的BeanFactory就使用了简单工厂模式。
工厂方法模式:
工厂方法模式为每一个对象都创建一个工厂,既保留了简单工厂模式的优点,同时又解决了简单工厂模式的缺点。
优点:
- 一个调用者想创建一个对象,只要知道其名称就可以了。
- 扩展性高,如果想增加一个产品,只要扩展一个工厂类就可以。
- 屏蔽产品的具体实现,调用者只关心产品的接口。
缺点:
- 每次增加一个产品时,都需要增加一个具体类和对象实现工厂,使得系统中类的个数成倍增加,在一定程度上增加了系统的复杂度,同时也增加了系统具体类的依赖。
第一步:定义一个Bean
package spring6.beans;
public class student {
}
第二步:编写简单工厂模式当中的工厂类
package spring6.beans;
public class personFactory {
public static student get(){
return new student();
}
}
第三步:在Spring配置文件中指定创建该Bean的方法(使用factory-method属性指定)
<bean id="student" class="spring6.beans.personFactory" factory-method="get"/>第四步:编写测试程序
@Test
public void testSimpleFactory(){
ApplicationContext applicationContext = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("spring.xml");
student student = applicationContext.getBean("student", student.class);
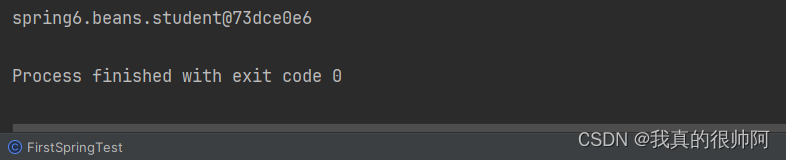
System.out.println(student);
}运行结果:
通过factory-bean实例化
这种方式本质上是:通过工厂方法模式进行实例化。
第一步:定义一个Bean
package spring6.beans;
public class dog {
}
第二步:定义具体工厂类,工厂类中定义实例方法
package spring6.beans;
public class dogFactory {
public dog get(){
return new dog();
}
}
第三步:在Spring配置文件中指定factory-bean以及factory-method
<bean id="dogFactory" class="spring6.beans.dogFactory"/>
<bean id="dog" factory-bean="dogFactory" factory-method="get"/>第四步:编写测试程序
@Test
public void testSelfFactoryBean(){
ApplicationContext applicationContext = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("spring.xml");
dog dog = applicationContext.getBean("dog", dog.class);
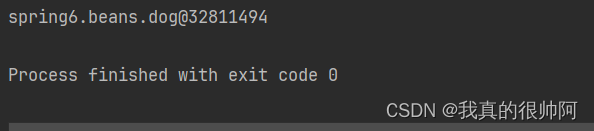
System.out.println(dog);
}运行结果:
通过FactoryBean接口实例化
在上面那种方式中,factory-bean是我们自定义的,factory-method也是我们自己定义的。
在Spring中,当你编写的类直接实现FactoryBean接口之后,factory-bean不需要指定了,factory-method也不需要指定了。
FactoryBean在Spring中是一个接口。被称为“工厂Bean”。“工厂Bean”是一种特殊的Bean。所有的“工厂Bean”都是用来协助Spring框架来创建其他Bean对象的。
factory-bean会自动指向实现FactoryBean接口的类,factory-method会自动指向getObject()方法。
第一步:定义一个Bean
package spring6.beans;
public class cat {
}
第二步:编写一个类实现FactoryBean接口
package spring6.beans;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.FactoryBean;
public class catFactory implements FactoryBean<cat> {
@Override
public cat getObject() throws Exception {
return new cat();
}
@Override
public Class<?> getObjectType() {
return null;
}
}
第三步:在Spring配置文件中配置FactoryBean
<bean id="cat" class="spring6.beans.catFactory"/>测试程序:
@Test
public void testFactoryBean(){
ApplicationContext applicationContext = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("spring.xml");
cat cat = applicationContext.getBean("cat", cat.class);
System.out.println(cat);
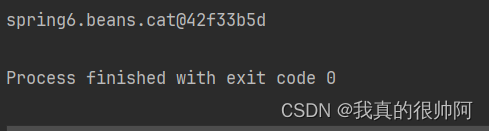
}运行结果:
BeanFactory和FactoryBean的区别
BeanFactory:
BeanFactory是工厂,是Spring IoC容器的顶级对象,被翻译为“Bean工厂”,在Spring的IoC容器中,“Bean工厂”负责创建Bean对象。
FactoryBean:
在Spring中,Bean可以分为两类:
- 第一类:普通Bean
- 第二类:工厂Bean(工厂Bean也是一种Bean,只不过这种Bean比较特殊,它可以辅助Spring实例化其它Bean对象。)
FactoryBean是一个Bean,是一个能够辅助Spring实例化其它Bean对象的一个Bean。








![[动态规划] (十四) 简单多状态 LeetCode LCR 091.粉刷房子](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/img_convert/f67a4ae3724bf6776b5fe0243422260e.png)