一、AbstractQueuedSynchronized 的三个核心成员变量
阐述一下 AQS 中的三个核心成员变量,后面源码分析流程的时候很多地方有。
state:表示锁的状态,0表示锁未被锁定,大于0的话表示重入锁的次数。state 成员变量被 volatile 修饰,保障了可见性和有序性。head:等待队列的头节点,除了初始化只能通过setHead()方法设置值,如果head存着能保证waitStatus状态不为CANELLED。tail:等待队列尾节点,只能通过equ添加新的等待节点。
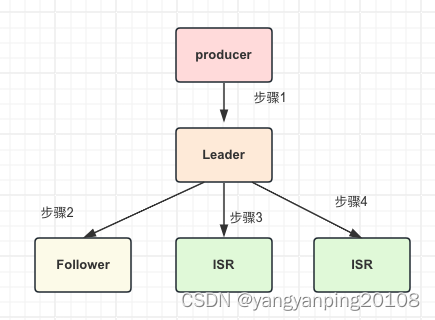
二、可重入锁加锁流程
非公平可重入锁的加锁流程核心部分如下:
- new ReentrantLock().lock()
- NonfairSync.lock()
- AQS.acquire()
- NonfairSync.tryAcquire()
- Sync.nonfairTryAcquire() 加锁成功或者重入锁
- 否则加锁失败,入队等待,AQS.acquireQueued()
-
CAS 获取锁,如果没有线程占用锁(state==0),加锁成功并记录当前线程是有锁线程.(state 的含义是表示已重入锁的数量)
final void lock() { if (compareAndSetState(0, 1)) setExclusiveOwnerThread(Thread.currentThread()); else acquire(1); } -
Sync.nonfairTryAcquire() 又一次尝试去获取锁(state==0),加锁成功并记录当前线程是有锁线程.
-
final Thread current = Thread.currentThread(); int c = getState(); if (c == 0) { if (compareAndSetState(0, acquires)) { setExclusiveOwnerThread(current); return true; } } -
如果没有获取锁成功,则 state 更新为 state+acquires,即state += 1
else if (current == getExclusiveOwnerThread()) { int nextc = c + acquires; if (nextc < 0) // overflow throw new Error("Maximum lock count exceeded"); setState(nextc); return true; } -
其中获取锁成功和更新state值成功都返回为true,否则返回为false。
-
-
入队时仍然会去尝试去加锁,即如果此时队列没有其他节点,node节点的前一个节点是头节点,就会再次尝试加锁。
-
final boolean acquireQueued(final Node node, int arg) { boolean failed = true; try { boolean interrupted = false; // 自旋 for (;;) { final Node p = node.predecessor(); // 在 p 为头节点的时候就再次尝试获得锁 // 获取成功就不入队:failed = false // 否则就会在 finally 入队 if (p == head && tryAcquire(arg)) { setHead(node); p.next = null; // help GC failed = false; return interrupted; } if (shouldParkAfterFailedAcquire(p, node) && parkAndCheckInterrupt()) interrupted = true; } } finally { if (failed) cancelAcquire(node); } }
-
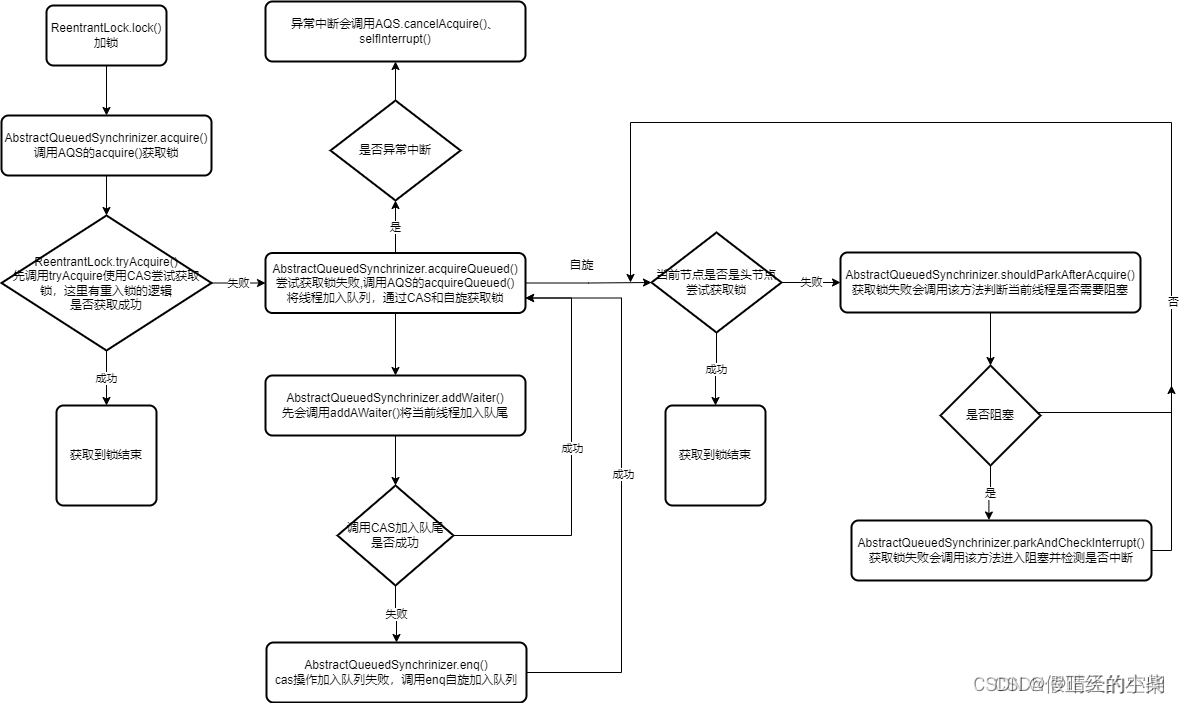 总的聊就是非公平锁去加锁的时候会尝试去抢俩次,也可以说三次,因为第三次抢锁条件是当当前节点的前一个节点是头节点的时候,即是空的时候,这个时候才会去再次尝试抢锁,也就是后面前面没人排队购票了,然后我正好去购票了。
总的聊就是非公平锁去加锁的时候会尝试去抢俩次,也可以说三次,因为第三次抢锁条件是当当前节点的前一个节点是头节点的时候,即是空的时候,这个时候才会去再次尝试抢锁,也就是后面前面没人排队购票了,然后我正好去购票了。
前俩次抢锁一个是在加锁的时候就会进行抢锁,没成功的话,调用 tryAcquire 的时候又会去进行一次抢锁,这里还包括了可重入操作,即更新 state+=1(arg)。
否则最后进入队列然后将线程挂起。
三、可重入锁解锁流程
非公平的可重入锁的解锁流程核心部分如下:
- new ReentrantLock().unlock()
- AQS.release(1)
- Sync.tryRelease(1)
- 判断当前线程是否是有锁线程,不是则抛出
IllegalMonitorStateException非法监控状态异常; - 对 state 的值进行减 1 之后,判断 state 的值是否为 0,为 0 则解锁成功,返回 true;
- 如果减 1 后的值不为 0,则返回 false。
protected final boolean tryRelease(int releases) {
int c = getState() - releases;
// 判断当前线程是否是有锁线程
if (Thread.currentThread() != getExclusiveOwnerThread())
throw new IllegalMonitorStateException();
boolean free = false;
if (c == 0) {
free = true;
setExclusiveOwnerThread(null);
}
setState(c);
return free;
}
- 如果释放锁(解锁成功)的话,去对队列首个线程挂起的进行取消挂起,也就是去唤醒它。
public final boolean release(int arg) {
if (tryRelease(arg)) {
Node h = head;
if (h != null && h.waitStatus != 0)
unparkSuccessor(h);
return true;
}
return false;
}
非公平锁的解锁流程很简单,就是去尝试去更新 state 直至为 0,state -= 1(arg)。最后 tryRelease 为 true 后然后让队列头个元素唤醒(除head之外的头个元素)。
引用了
Java锁(二):AbstractQueuedSynchronizer、ReentrantLock详解
的流程图。