目录
- Spring Boot 中的自动装配是指什么?解决了什么问题?
- Spring Boot 自动装配的流程有哪些?
- Spring Boot 中实现自动装配的原理是什么?
- Spring 中的 ConfigurationClassPostProcessor 类有什么作用?
- Spring Boot 自动装配涉及的核心源码有哪些?
- Spring Boot 应用程序启动类
- 执行 SpringApplication 类中的构造方法
- 执行 SpringApplication 类中的 run 方法
- 执行 run 方法中的 prepareContext 方法
- 执行 run 方法中的 refreshContext 方法
- META-INF/spring.factories 文件有什么作用?
Spring Boot 中的自动装配是指什么?解决了什么问题?
(1)在 Spring Boot 中,自动装配是一种机制,它允许开发者无需显式地配置依赖项或组件,而是通过约定和默认值来实现自动配置。通过这种方式,Spring Boot能够简化开发过程并提高开发效率。
(2)自动装配能够解决以下问题:
- 依赖管理:Spring Boot 的自动配置机制能够根据项目的需求自动引入所需的依赖项,而无需手动维护和管理依赖关系。
- 配置管理:Spring Boot 提供了一种简化的配置方式,可以根据约定和默认值自动装配应用程序所需的配置参数,减少了繁琐的配置过程。
- 组件注册:Spring Boot 可以自动扫描项目中的组件,并将其注册为 Spring 容器中的 Bean,使得这些组件能够被其他组件自动注入和使用。
- 功能扩展:Spring Boot 提供了大量的自动配置模块,可以根据项目的需要自动启用或禁用某些功能,实现快速开发和定制。
(3)总的来说,自动装配的实现就是为了从 META-INF/spring.factories 文件中加载并创建对应的 Bean 对象,并且将它们交给 Spring 容器来进行统一管理。
Spring Boot 自动装配的流程有哪些?
(1)Spring Boot 的自动装配流程如下:
- Spring Boot 启动时,会扫描并加载所有的类路径下的
META-INF/spring.factories文件,并读取其中的配置信息。 - 通过读取
spring.factories文件中org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.EnableAutoConfiguration键对应的值,获取所有需要自动装配的配置类。 - Spring Boot 根据这些配置类的信息,按照特定的顺序进行自动装配。关键的自动装配注解有
@EnableAutoConfiguration和@SpringBootApplication。 - 自动装配过程中,Spring Boot 会根据配置类中的条件注解(以
@ConditionalOnXXX开头)来进行判断,决定是否装配某个组件。 - 自动装配过程还会考虑用户自定义的配置,可以通过在
application.properties或application.yml文件中添加配置信息,来覆盖默认的自动装配行为。 - 最后,Spring Boot 会根据自动装配的结果和应用的需要,创建相应的 Bean,并将其注册到 Spring 的应用上下文中,供应用程序使用。
(2)总的来说,Spring Boot 的自动装配机制通过扫描配置文件,加载配置类,并根据配置类和条件进行自动装配,从而简化了应用程序的配置工作。
Spring Boot 中实现自动装配的原理是什么?
(1)Spring Boot 中实现自动装配的原理入如下:
- 在启动类中的执行
SpringApplication.run方法,并且将启动类的class对象作为参数传入其中,方便 Spring Boot 能够扫描该类所在的包以及其子包,并解析该启动类上的注解。 - 加载 spring.factories:当启动 Spring Boot 应用程序的时候,会先创建
SpringApplication对象,并且在对象的构造方法中会进行一些初始化工作,最主要的是判断当前应用程序的类型以及设置初始化器和监听器,并且在这个过程中会加载整个应用程序中META-INF/spring.factories文件中的配置类,将文件的内容放到缓存对象中,方便后续获取。 - 执行两个关键方法:
SpringApplication对象创建完成之后,开始执行run方法,来完成整个启动,启动过程中有两个非常重要的方法,分别是prepareContext方法和refreshContext方法,在这两个关键步骤中完整了自动装配的核心功能:- 在
prepareContext方法中主要完成的是对上下文对象的初始化操作,包括了属性值的设置,比如环境对象,在整个过程中有一个非常重要的方法,叫做load,它主要完成一件事,将当前启动类做为一个beanDefinition对象注册到registry中,方便后续在进行BeanFactoryPostProcessor调用执行的时候,找到对应的主类,来完成@SpringBootApplicaiton等注解的解析工作; - 在
refreshContext方法中会进行整个容器的刷新过程,会调用AbstractApplicationContext类中的refresh方法,该方法中有13个非常关键的方法,来完成整个 Spring 应用程序的启动。在自动装配过程中,会调用 13 个方法中的invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessor方法,此方法主要是对ConfigurationClassPostProcessor类的处理,该类实现了BeanDefinitionRegisterProcessor接口(BeanFactoryPostProcessor的子接口)。在调用的时候会调用该类中的postProcessBeanDefinitionRegistry方法,该方法解析处理各种注解,包含@PropertySource、@ComponentScan、@ComponentScans、@Bean、@lmport等注解,最主要的是@lmport注解的解析:- 在解析
@lmport注解的时候,会有一个getImports的方法,从主类开始递归解析注解,把所有包含@lmport的注解都解析到,然后在processImport方法中对Import的类进行分类,其中AutoConfigurationImportSelect归属于ImportSelect的子类,在后续过程中会调用deferredlmportSelectorHandler中的process方法,来完整EnableAutoConfiguration的加载;
- 在解析
- 在
Spring 中的 ConfigurationClassPostProcessor 类有什么作用?
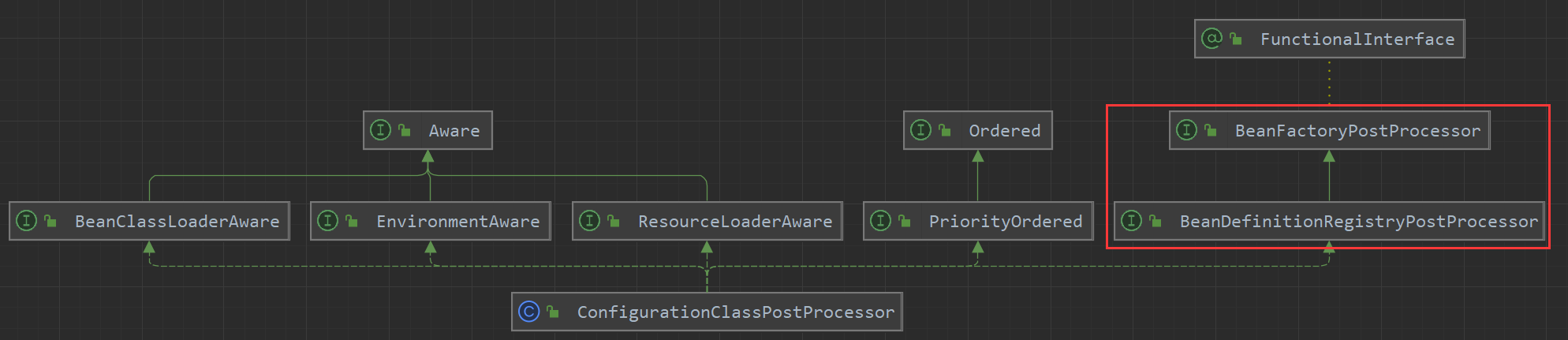
(1)在 Spring 中,ConfigurationClassPostProcessor类是一个重要的后置处理器,它实现了 BeanDefinitionRegisterProcessor 接口(BeanFactoryPostProcessor 的子接口,具体关系如下图所示),其作用是处理带有 @Configuration 注解的配置类。具体而言,ConfigurationClassPostProcessor 类完成以下几个主要的任务:
- 将配置类转换为
BeanDefinition对象:当Spring Boot应用启动时,ConfigurationClassPostProcessor会检查所有带有@Configuration注解的配置类,并将它们转换为BeanDefinition对象。这个过程包括解析配置类中的各种元数据,如 Bean 的定义、作用域、依赖关系等,并将其存储在Spring的BeanDefinition注册表中。 - 处理配置类中的特殊注解:
ConfigurationClassPostProcessor还会处理配置类中的一些特殊注解,比如@Conditional、@Import、@PropertySource等。它会根据这些注解的定义,对应进行处理并最终影响 Bean 的创建和配置。 - 处理配置类中的
@Bean注解:配置类中通常使用@Bean注解来定义 Bean 的创建和配置,而ConfigurationClassPostProcessor会解析这些@Bean方法,将其转换为对应的BeanDefinition对象,并存储在 Spring 容器的 Bean 定义注册表中。这样,当应用程序需要该 Bean 时,Spring 容器就可以根据这些注册信息进行创建和管理。
(2)总体来说,ConfigurationClassPostProcessor 类在 Spring Boot 中起到了非常重要的作用。它负责解析和处理配置类,将其转换为Spring 容器可以理解的 BeanDefinition 对象,并最终完成 Bean 的创建和配置过程。通过该后置处理器,Spring Boot 可以高效地管理和配置应用程序中的各种 Bean。
Spring Boot 自动装配涉及的核心源码有哪些?
Spring Boot 应用程序启动类
执行 SpringApplication 中的 run 方法,并且将启动类的 class 对象作为参数传入其中,方便 Spring Boot 能够扫描该类所在的包以及其子包,并解析该启动类上的注解。
@SpringBootApplication
public class ContentApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(ContentApplication.class, args);
}
}
执行 SpringApplication 类中的构造方法
在 SpringApplication 类的构造方法中会进行一些初始化工作,最重要的是加载 spring.factories 文件:
public class SpringApplication {
//...
public static ConfigurableApplicationContext run(Class<?> primarySource, String... args) {
return run(new Class<?>[] { primarySource }, args);
}
public static ConfigurableApplicationContext run(Class<?>[] primarySources, String[] args) {
return new SpringApplication(primarySources).run(args);
}
public SpringApplication(Class<?>... primarySources) {
this(null, primarySources);
}
//执行 SpringApplication 类中的构造方法
@SuppressWarnings({ "unchecked", "rawtypes" })
public SpringApplication(ResourceLoader resourceLoader, Class<?>... primarySources) {
this.resourceLoader = resourceLoader;
Assert.notNull(primarySources, "PrimarySources must not be null");
this.primarySources = new LinkedHashSet<>(Arrays.asList(primarySources));
this.webApplicationType = WebApplicationType.deduceFromClasspath();
//设置初始化器,此过程中会加载 spring.factories 文件
setInitializers((Collection) getSpringFactoriesInstances(ApplicationContextInitializer.class));
//设置监听器
setListeners((Collection) getSpringFactoriesInstances(ApplicationListener.class));
this.mainApplicationClass = deduceMainApplicationClass();
}
private <T> Collection<T> getSpringFactoriesInstances(Class<T> type) {
return getSpringFactoriesInstances(type, new Class<?>[] {});
}
private <T> Collection<T> getSpringFactoriesInstances(Class<T> type, Class<?>[] parameterTypes, Object... args) {
ClassLoader classLoader = getClassLoader();
// Use names and ensure unique to protect against duplicates
// loadFactoryNames 方法中会加载 spring.factories 文件,具体执行步骤在 SpringFactoriesLoader 类中
Set<String> names = new LinkedHashSet<>(SpringFactoriesLoader.loadFactoryNames(type, classLoader));
List<T> instances = createSpringFactoriesInstances(type, parameterTypes, classLoader, args, names);
AnnotationAwareOrderComparator.sort(instances);
return instances;
}
}
public final class SpringFactoriesLoader {
//...
public static final String FACTORIES_RESOURCE_LOCATION = "META-INF/spring.factories";
public static List<String> loadFactoryNames(Class<?> factoryType, @Nullable ClassLoader classLoader) {
String factoryTypeName = factoryType.getName();
return loadSpringFactories(classLoader).getOrDefault(factoryTypeName, Collections.emptyList());
}
private static Map<String, List<String>> loadSpringFactories(@Nullable ClassLoader classLoader) {
MultiValueMap<String, String> result = cache.get(classLoader);
if (result != null) {
return result;
}
try {
//下面的 FACTORIES_RESOURCE_LOCATION 即为 spring.factories 文件的路径
Enumeration<URL> urls = (classLoader != null ?
classLoader.getResources(FACTORIES_RESOURCE_LOCATION) :
ClassLoader.getSystemResources(FACTORIES_RESOURCE_LOCATION));
result = new LinkedMultiValueMap<>();
while (urls.hasMoreElements()) {
URL url = urls.nextElement();
UrlResource resource = new UrlResource(url);
Properties properties = PropertiesLoaderUtils.loadProperties(resource);
for (Map.Entry<?, ?> entry : properties.entrySet()) {
String factoryTypeName = ((String) entry.getKey()).trim();
for (String factoryImplementationName : StringUtils.commaDelimitedListToStringArray((String) entry.getValue())) {
result.add(factoryTypeName, factoryImplementationName.trim());
}
}
}
cache.put(classLoader, result);
return result;
}
catch (IOException ex) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Unable to load factories from location [" +
FACTORIES_RESOURCE_LOCATION + "]", ex);
}
}
}
执行 SpringApplication 类中的 run 方法
SpringApplication 类中 run 方法是整个过程的核心方法。
public class SpringApplication {
//...
public ConfigurableApplicationContext run(String... args) {
StopWatch stopWatch = new StopWatch();
stopWatch.start();
//上下文对象,保存当前操作前后的属性信息
ConfigurableApplicationContext context = null;
Collection<SpringBootExceptionReporter> exceptionReporters = new ArrayList<>();
configureHeadlessProperty();
SpringApplicationRunListeners listeners = getRunListeners(args);
listeners.starting();
try {
ApplicationArguments applicationArguments = new DefaultApplicationArguments(args);
ConfigurableEnvironment environment = prepareEnvironment(listeners, applicationArguments);
configureIgnoreBeanInfo(environment);
Banner printedBanner = printBanner(environment);
context = createApplicationContext();
exceptionReporters = getSpringFactoriesInstances(SpringBootExceptionReporter.class,
new Class[] { ConfigurableApplicationContext.class }, context);
//***准备上下文***
prepareContext(context, environment, listeners, applicationArguments, printedBanner);
//***刷新上下文***
refreshContext(context);
afterRefresh(context, applicationArguments);
stopWatch.stop();
if (this.logStartupInfo) {
new StartupInfoLogger(this.mainApplicationClass).logStarted(getApplicationLog(), stopWatch);
}
listeners.started(context);
callRunners(context, applicationArguments);
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
handleRunFailure(context, ex, exceptionReporters, listeners);
throw new IllegalStateException(ex);
}
try {
listeners.running(context);
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
handleRunFailure(context, ex, exceptionReporters, null);
throw new IllegalStateException(ex);
}
return context;
}
}
执行 run 方法中的 prepareContext 方法
public class SpringApplication {
//...
private void prepareContext(ConfigurableApplicationContext context, ConfigurableEnvironment environment,
SpringApplicationRunListeners listeners, ApplicationArguments applicationArguments, Banner printedBanner) {
context.setEnvironment(environment);
postProcessApplicationContext(context);
applyInitializers(context);
listeners.contextPrepared(context);
if (this.logStartupInfo) {
logStartupInfo(context.getParent() == null);
logStartupProfileInfo(context);
}
// Add boot specific singleton beans
ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory = context.getBeanFactory();
beanFactory.registerSingleton("springApplicationArguments", applicationArguments);
if (printedBanner != null) {
beanFactory.registerSingleton("springBootBanner", printedBanner);
}
if (beanFactory instanceof DefaultListableBeanFactory) {
((DefaultListableBeanFactory) beanFactory)
.setAllowBeanDefinitionOverriding(this.allowBeanDefinitionOverriding);
}
if (this.lazyInitialization) {
context.addBeanFactoryPostProcessor(new LazyInitializationBeanFactoryPostProcessor());
}
// Load the sources
Set<Object> sources = getAllSources();
Assert.notEmpty(sources, "Sources must not be empty");
/*
(1) sources 中保存了启动类 ContentApplication 的相关信息
(2) laod 方法将当前启动类做为一个 BeanDefinition 对象注册到 registry 中,方便后面解析到启动类上的注解
*/
load(context, sources.toArray(new Object[0]));
listeners.contextLoaded(context);
}
protected void load(ApplicationContext context, Object[] sources) {
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Loading source " + StringUtils.arrayToCommaDelimitedString(sources));
}
BeanDefinitionLoader loader = createBeanDefinitionLoader(getBeanDefinitionRegistry(context), sources);
if (this.beanNameGenerator != null) {
loader.setBeanNameGenerator(this.beanNameGenerator);
}
if (this.resourceLoader != null) {
loader.setResourceLoader(this.resourceLoader);
}
if (this.environment != null) {
loader.setEnvironment(this.environment);
}
loader.load();
}
}
执行 run 方法中的 refreshContext 方法
public class SpringApplication {
//...
private void refreshContext(ConfigurableApplicationContext context) {
if (this.registerShutdownHook) {
try {
context.registerShutdownHook();
}
catch (AccessControlException ex) {
// Not allowed in some environments.
}
}
refresh((ApplicationContext) context);
}
}
上面的方法会调用到 AbstractApplicationContext 类中的 refresh 方法:
public abstract class AbstractApplicationContext extends DefaultResourceLoader
implements ConfigurableApplicationContext {
//...
@Override
public void refresh() throws BeansException, IllegalStateException {
synchronized (this.startupShutdownMonitor) {
// Prepare this context for refreshing.
prepareRefresh();
// Tell the subclass to refresh the internal bean factory.
ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory = obtainFreshBeanFactory();
// Prepare the bean factory for use in this context.
prepareBeanFactory(beanFactory);
try {
// Allows post-processing of the bean factory in context subclasses.
postProcessBeanFactory(beanFactory);
// Invoke factory processors registered as beans in the context.
invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(beanFactory);
// Register bean processors that intercept bean creation.
registerBeanPostProcessors(beanFactory);
// Initialize message source for this context.
initMessageSource();
// Initialize event multicaster for this context.
initApplicationEventMulticaster();
// Initialize other special beans in specific context subclasses.
onRefresh();
// Check for listener beans and register them.
registerListeners();
// Instantiate all remaining (non-lazy-init) singletons.
finishBeanFactoryInitialization(beanFactory);
// Last step: publish corresponding event.
finishRefresh();
}
catch (BeansException ex) {
if (logger.isWarnEnabled()) {
logger.warn("Exception encountered during context initialization - " +
"cancelling refresh attempt: " + ex);
}
// Destroy already created singletons to avoid dangling resources.
destroyBeans();
// Reset 'active' flag.
cancelRefresh(ex);
// Propagate exception to caller.
throw ex;
}
finally {
// Reset common introspection caches in Spring's core, since we
// might not ever need metadata for singleton beans anymore...
resetCommonCaches();
}
}
}
}
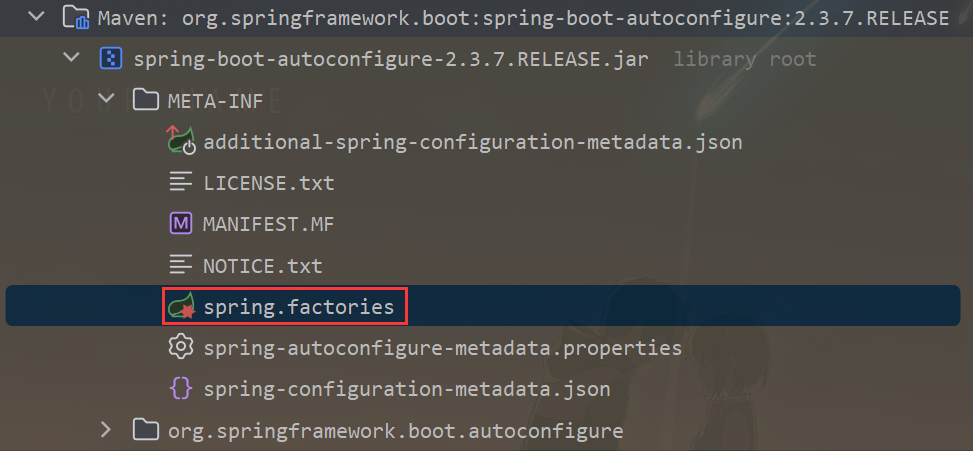
META-INF/spring.factories 文件有什么作用?
(1)META-INF/spring.factories 文件是在使用 Spring 框架的项目中常见的一个文件,它用于进行 Spring 框架的扩展和自动装配。spring.factories 文件采用键值对的形式,其中键表示一个接口或抽象类的全限定名,值表示具体的实现类或配置类的全限定名。这个文件的作用是告诉 Spring 框架在启动时自动加载和注册这些实现类或配置类,从而进行自动装配。
(2)下面是 Spring Boot 框架中 spring.factories 文件的部分内容:
# Initializers
org.springframework.context.ApplicationContextInitializer=\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SharedMetadataReaderFactoryContextInitializer,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.logging.ConditionEvaluationReportLoggingListener
# Application Listeners
org.springframework.context.ApplicationListener=\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.BackgroundPreinitializer
# Auto Configuration Import Listeners
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.AutoConfigurationImportListener=\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.condition.ConditionEvaluationReportAutoConfigurationImportListener
# Auto Configuration Import Filters
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.AutoConfigurationImportFilter=\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.condition.OnBeanCondition,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.condition.OnClassCondition,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.condition.OnWebApplicationCondition
//...