boa配置流程详解
- 前期准备
- boa介绍
- 操作目的
- 下载boa
- 配置流程
- 1.解压boa服务器
- 2.配置Makefile
- 3.编译boa服务器
- 4.修改boa配置文件
- 5.增加权限并编译cgi
- 6.测试demo
- 7.错误示例
- 附录A history
- 附录B boa.conf
前期准备
boa介绍
Boa服务器是一个小巧高效的web服务器,是一个运行于unix或linux下的,支持CGI的、适合于嵌入式系统的单任务的http服务器,源代码开放、性能高。Boa是一种非常小巧的Web服务器,其可执行代码只有大约60KB左右。作为一种单任务Web服务器,Boa只能依次完成用户的请求,而不会fork出新的进程来处理并发连接请求。但Boa支持CGI,能够为CGI程序fork出一个进程来执行。Boa的设计目标是速度和安全。
操作目的
本次流程目的是在飞凌开发板部署配置boa服务器,平台为aarch64,通过简单逻辑登录页面来验证流程是否成功,并将流程中的报错一并托出。
下载boa
boa官网地址:www.boa.org
记得不要选0.94.14rc21,这个解压后src目录下没有configure文件,选择0.94.13的here下载。下载的格式是boa-0.94.13.tar.gz
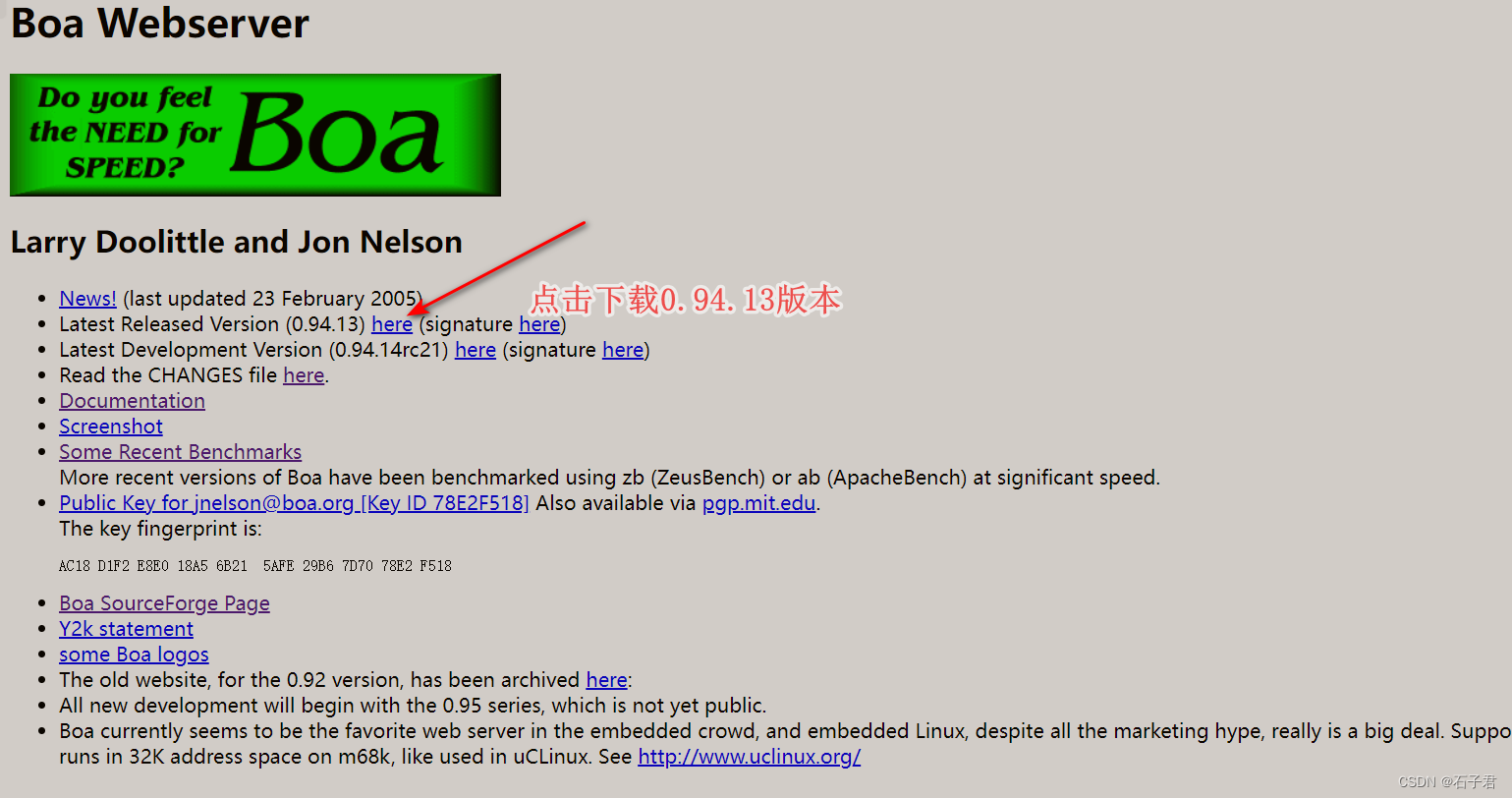
配置流程
首先先连接好目标ip将boa的压缩包传进去,例:如果使用ubuntu的小伙伴那就使用xftp或者MobaXterm或者FileZilla Client将boa-0.94.13.tar.gz传入Ubuntu。
(本文会将history附在最后,暂记附录A)
1.解压boa服务器
我们假设你已经进入到Ubuntu的home路径下,开始解压boa
sudo tar zxvf boa-0.94.13.tar.gz
cd boa-0.94.13
sudo apt-get install bison flex
cd src
./configure 生成Makefile
2.配置Makefile
这里需要注意的是,假使你的目标是X86平台,可以跳过步骤2,如果你的目标平台是aarch64 arm等,需要改动makefile
查看平台架构:uname -m
文件显示行号:按键Esc,输入英文:set nu 或者:set number
makefile改动CC CPP两点,如图示例。
执行
sudo vi Makefile
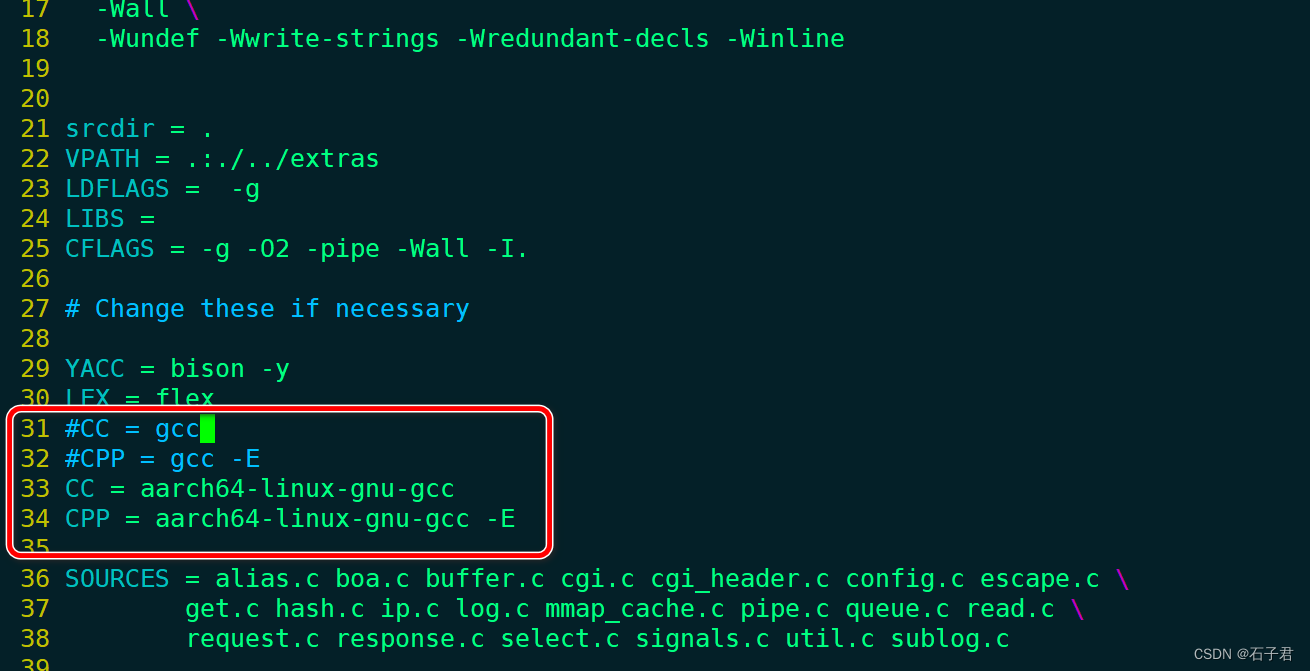
小伙伴们注意哈,aarch64-linux-gnu-gcc是tab补全的,千万别自己傻傻敲哈。
3.编译boa服务器
目前是在src目录下,即当前路径(以我为例)为/home/graysen/boa-0.94.13/src
3.1 编辑defines.h
sudo vi defines.h
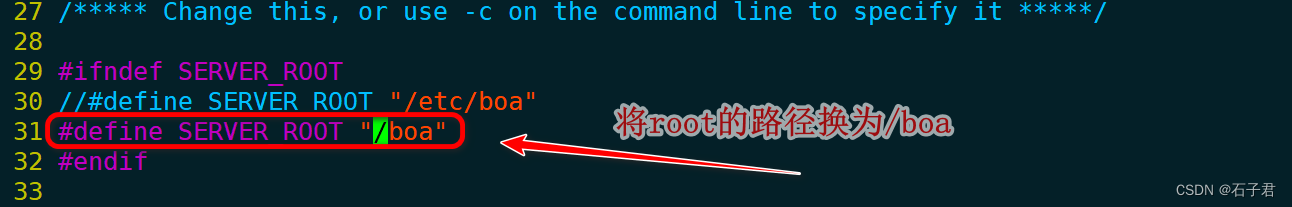
这里是web服务器根目录,也就是web,cgi的存放位置。
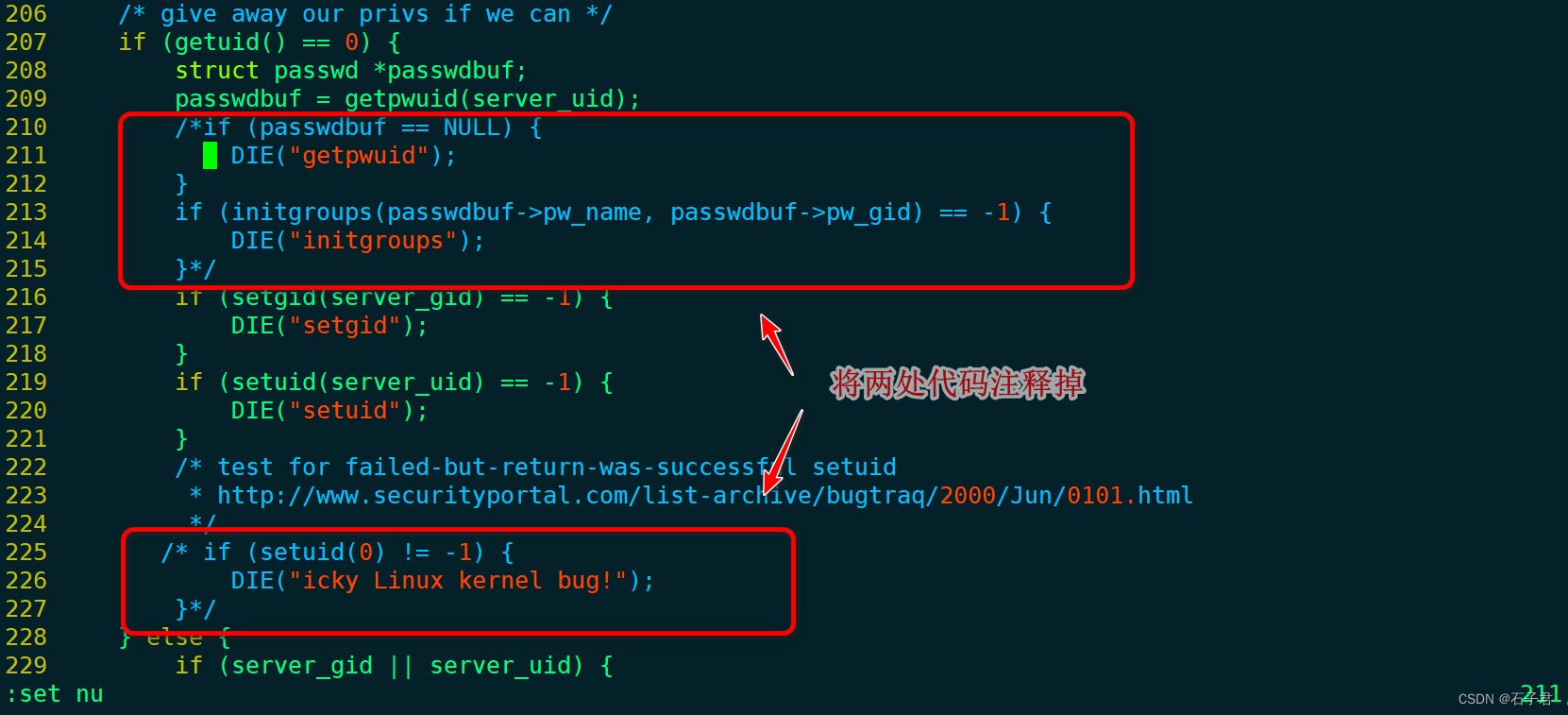
3.2 编辑boa.c
sudo vi boa.c
3.3 编辑compat.h
sudo vi compat.h
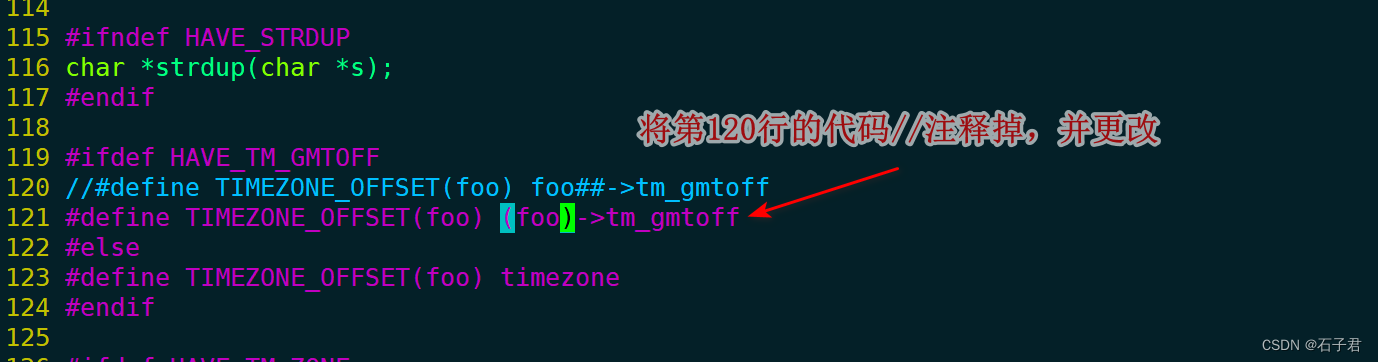
3.4 编辑log.c
sudo vi log.c
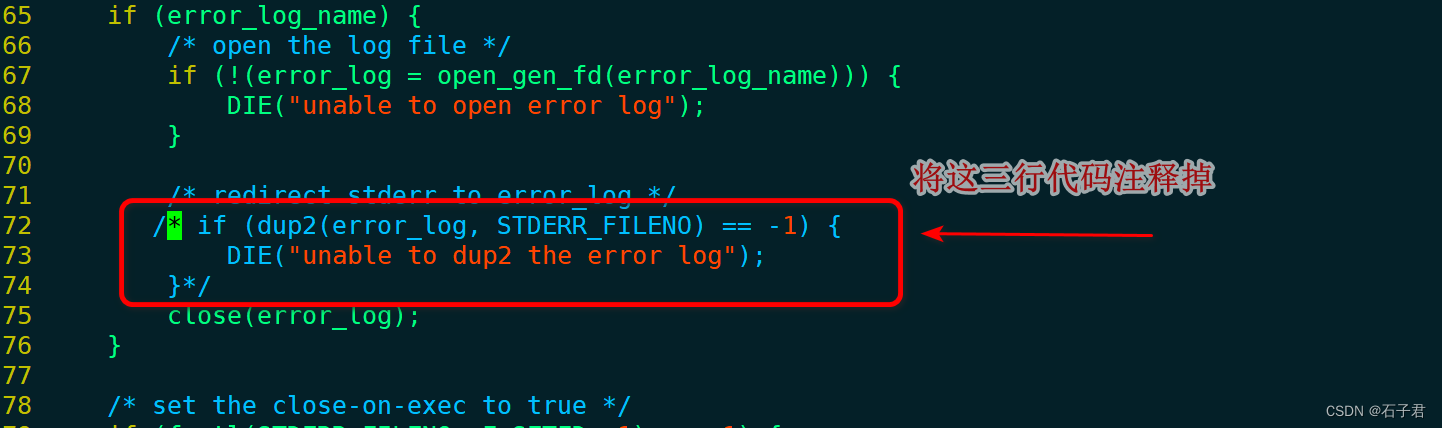
这里需要注意下,注释log.c的作用是决定是否显示启动boa服务器的打印输出,比如我注释了,在启动boa时会在shell中显示详细执行情况;如果不注释,启动完boa无任何输出(无论注释或者不注释结果都会显示在/boa/log目录下)
编辑修改文件工作已经完成
当前在src目录下
执行
sudo make
开始编译
编译完成后,开始安装boa服务器
在src目录下
sudo mkdir -p /boa /boa/www /boa/cgi-bin /boa/log

cd …
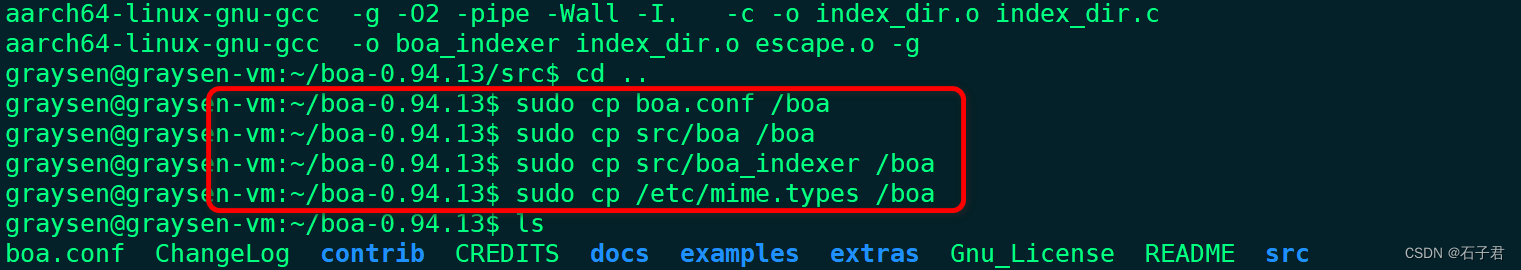
回到boa-0.94.13目录,将编译后的文件copy到boa服务器位置
执行
sudo cp boa.conf /boa
sudo cp src/boa /boa
sudo cp src/boa_indexer /boa
sudo cp /etc/mime.types /boa
4.修改boa配置文件
我们将boa服务器放在了根目录下
cd /boa
sudo vim boa.conf


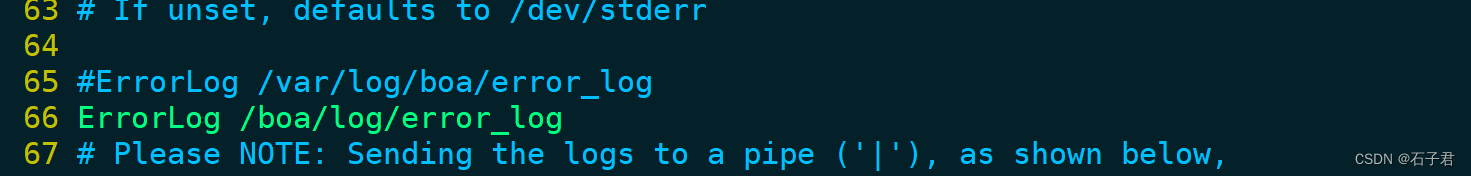
#ErrorLog /var/log/boa/error_log是定向输出到这的错误日志,如果您不想记录错误,请设置为 /dev/null。
DocumentRoot /boa/www是你的web的目录,存放web的地方
ScriptAlias /cgi-bin/ /boa/cgi-bin/是存放.c .cgi文件的地方,当然可以指定任何地方,可以在www下建立cgi-bin进行存放,那么这里就需要修改为:
ScriptAlias /cgi-bin/ /boa/www/cgi-bin/
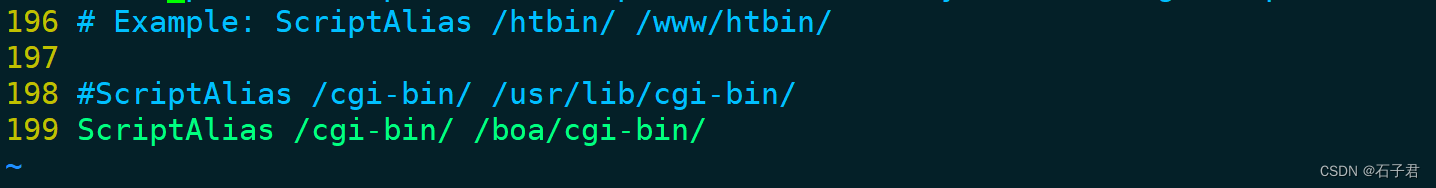
里面字段的具体含义可以参考官网解释http://www.boa.org/documentation/boa-2.html#ss2.3
(本文会将boa.conf全文放置最后,暂且记附录B)
5.增加权限并编译cgi
修改boa权限
cd /boa
sudo chmod 777 *
编写简单html demo存放至/boa/www下
<html>
<head>
<title>CGI login</title>
<meta http-equiv="Content-Type" content="text/html; charset=utf-8">
</head>
<body>
<form name="login" action="../cgi-bin/login.cgi">name:<input type="text" name="name" />
<br/>password:<input type="password" name="pwd" />
<br/>true:<input type="submit" value="login" />
</form>
</body>
</html>
编写简单c demo编译后存放至/boa/cgi-bin下
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
int main()
{
char *date;
char name[50],pwd[20];
printf("content-type:text/html;charset=utf-8\n\n");
printf("<TITLE>login ret</TITLE>");
printf("<H3>login ret</h3>");
date=getenv("QUERY_STRING");
if(date==NULL)
printf("<p>err</p>");
else
{
sscanf(date,"name=%[^&]&pwd=%s",name,pwd);
printf("<p>name=%s</p>",name);
printf("<p>pwd=%s</p>",pwd);
printf("%s",date);
}
return 0;
}
printf("content-type:text/html;charset=utf-8\n\n"); 如果你自己C文件这句话一定要加上
注意:
如果你是X86平台运行,请使用gcc编译
如果你是aarch64 arm平台运行,请使用aarch64-linux-gnu-gcc或者arm-linux-gnueabi-gcc编译
以我为例,使用aarch64-linux-gnu-gcc编译
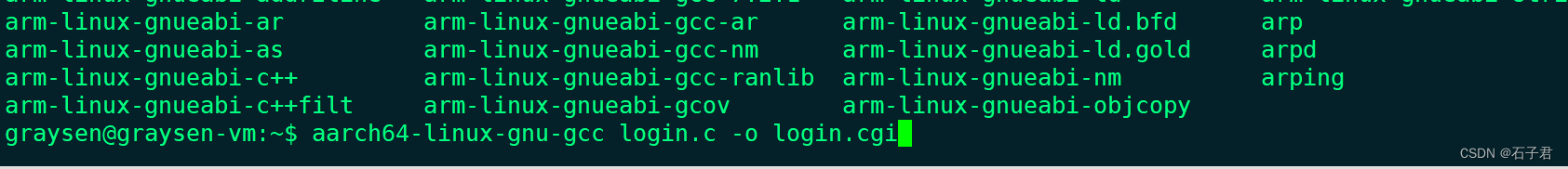
将我的示例代码login.cgi存放至/boa/cgi-bin下
sudo cp login.cgi /boa/cgi-bin
并增加权限
(当前我已经切换到/boa/cgi-bin目录下)
sudo chmod 777 *(或者sudo chmod 777 login.cgi)
6.测试demo
在/boa目录下会看到boa
执行
./boa
启动服务器
打开浏览器输入 (你的ubuntu ip或者开发板ip)(boa.conf设置的端口)
以我为例:192.168.31.201:8080
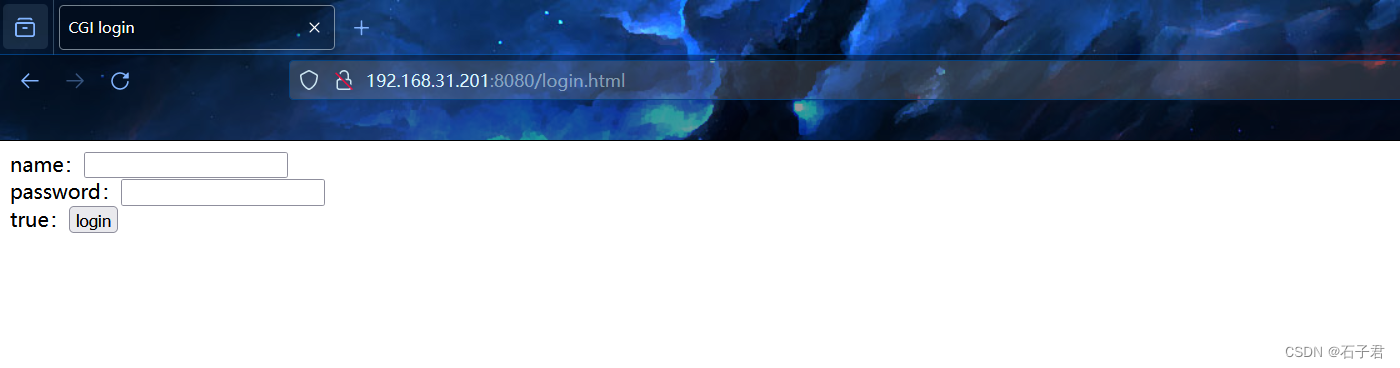
成功显示页面,并输入账号密码
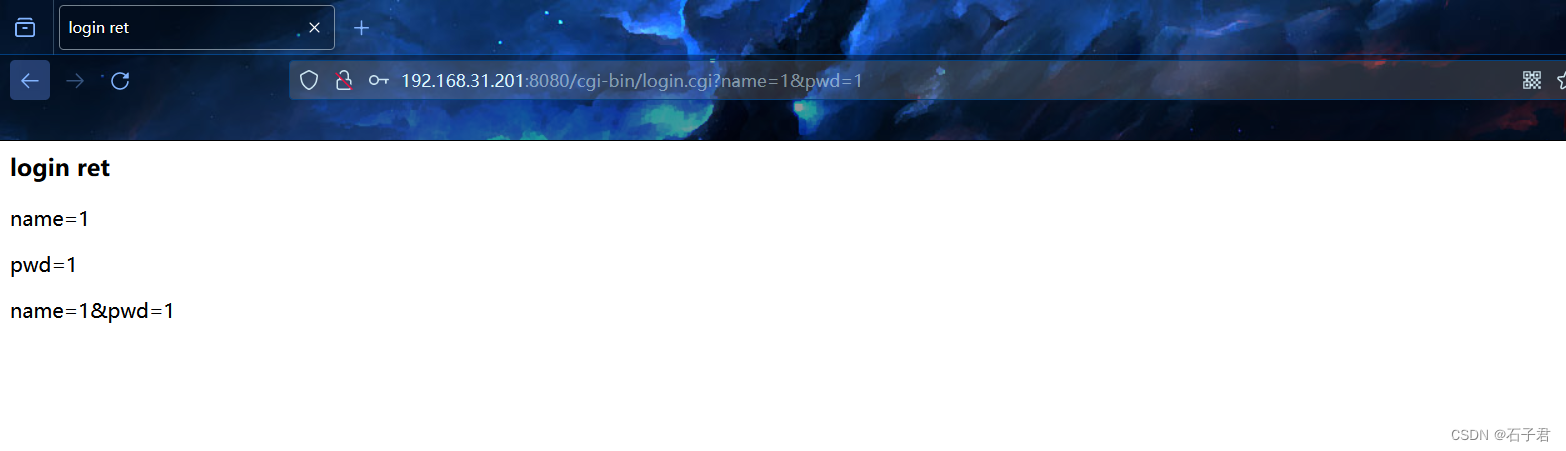
成功跳转到/cgi-bin/login.cgi,显示正确
7.错误示例
7.1 -bash: ./boa: cannot execute binary file: Exec format error
出现-bash: ./boa: cannot execute binary file: Exec format error错误可能是因为你的交叉编译出问题了,有可能是你的目标环境是aarch64,但是你是用gcc编译的C文件,请尝试修改makefile,使用正确的编译器编译,遵循makefile-编译C-目标环境一致。
7.2Could not chdir to “/etc/boa”: aborting
关于该目录的定义在 defines.h中,可能你的boa服务器目录没有配置或者配置路径出错,按照我们示例,是将#define SERVER_ROOT修改为 “/boa”
7.3 502 Bad GatewayThe CGI was not CGI/1.1 compliant
出现
502 Bad Gateway
The CGI was not CGI/1.1 compliant
cgi_header: unable to find LFLF
原因有以下几点:
1.可能是网址打错了(路径是否和配置文件对应)
2.配置有问题
3.权限没给足 chmod 777 test.cgi
4.代码本身有问题(先测测 cgi-test.cgi)
5.c代码使用错误的编译器生成了cgi

6.试试关闭两端防火墙,关闭火绒等
依次检查完无误后如果还是不行,可以尝试重新配置并移植boa
7.4 GET http://192.168.77.149:888/favicon.ico
在网络调试抓捕中出现GET http://192.168.77.149:888/favicon.ico
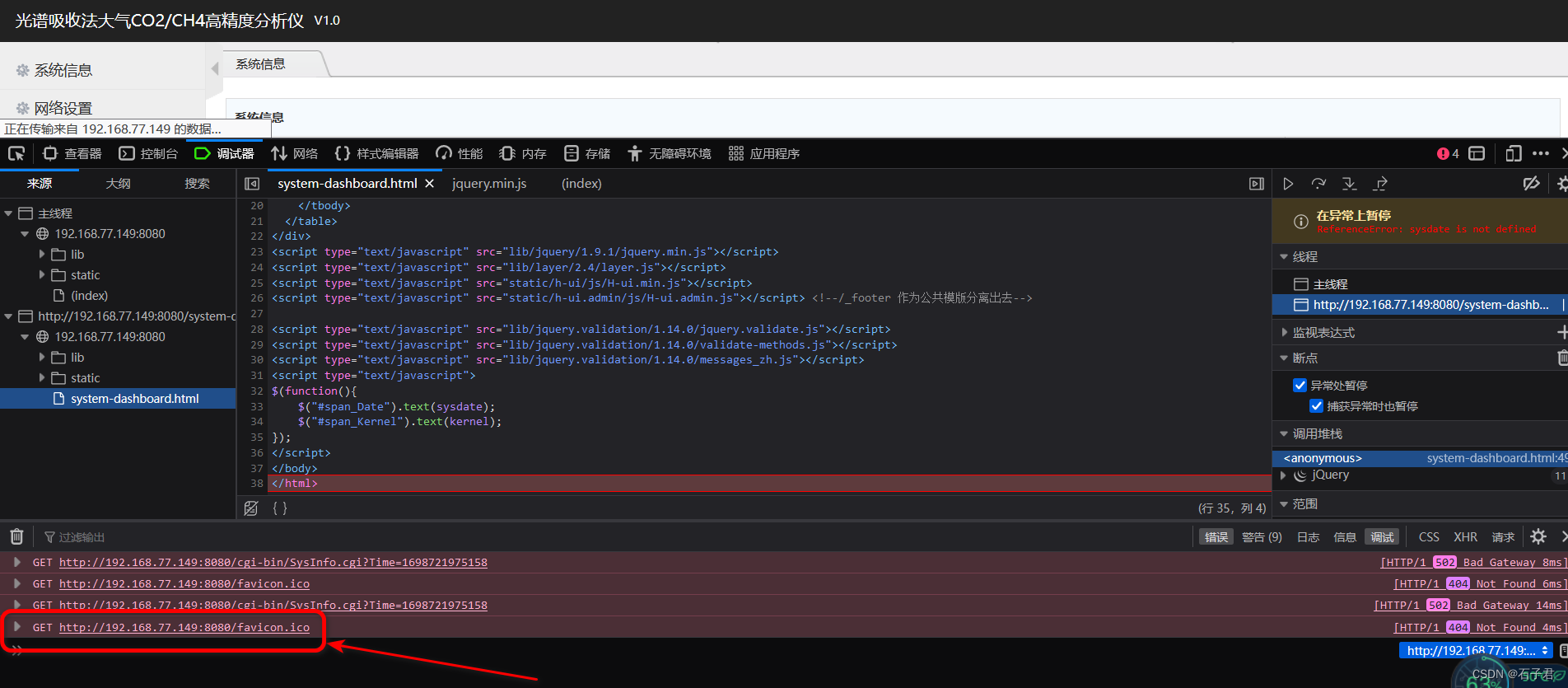
显示你没有favicon.ico文件,在/boa/www下传入favicon.ico文件即可
favicon.ico一般用于作为缩略的网站标志,它显示在浏览器的地址栏、浏览器标签上或者在收藏夹上,是展示网站个性的缩略logo标志。
你可以使用在线转换网页来将任意图片转换为favicon.ico
附录A history
cd boa-0.94.13/
ls
sudo apt-get install bison flex
cd src/
sudo ./configure
ls
sudo vi defines.h
sudo vi boa.c
sudo vi compat.h
sudo make
sudo mkdir -p /boa /boa/www /boa/cgi-bin /boa/log
sudo cp boa.conf /boa
sudo cp src/boa /boa
sudo cp src/boa_indexer /boa
sudo cp /etc/mime.types /boa
sudo cp test.html /boa/www/
sudo cp test.c /boa/cgi-bin/
sudo ufw disable
附录B boa.conf
# Boa v0.94 configuration file
# File format has not changed from 0.93
# File format has changed little from 0.92
# version changes are noted in the comments
#
# The Boa configuration file is parsed with a lex/yacc or flex/bison
# generated parser. If it reports an error, the line number will be
# provided; it should be easy to spot. The syntax of each of these
# rules is very simple, and they can occur in any order. Where possible
# these directives mimic those of NCSA httpd 1.3; I saw no reason to
# introduce gratuitous differences.
# $Id: boa.conf,v 1.25 2002/03/22 04:33:09 jnelson Exp $
# The "ServerRoot" is not in this configuration file. It can be compiled
# into the server (see defines.h) or specified on the command line with
# the -c option, for example:
#
# boa -c /usr/local/boa
# Port: The port Boa runs on. The default port for http servers is 80.
# If it is less than 1024, the server must be started as root.
#Port 80
Port 8080
# Listen: the Internet address to bind(2) to. If you leave it out,
# it takes the behavior before 0.93.17.2, which is to bind to all
# addresses (INADDR_ANY). You only get one "Listen" directive,
# if you want service on multiple IP addresses, you have three choices:
# 1. Run boa without a "Listen" directive
# a. All addresses are treated the same; makes sense if the addresses
# are localhost, ppp, and eth0.
# b. Use the VirtualHost directive below to point requests to different
# files. Should be good for a very large number of addresses (web
# hosting clients).
# 2. Run one copy of boa per IP address, each has its own configuration
# with a "Listen" directive. No big deal up to a few tens of addresses.
# Nice separation between clients.
# The name you provide gets run through inet_aton(3), so you have to use dotted
# quad notation. This configuration is too important to trust some DNS.
#Listen 192.68.0.5
# User: The name or UID the server should run as.
# Group: The group name or GID the server should run as.
User nobody
#Group nogroup
Group nobody
# ServerAdmin: The email address where server problems should be sent.
# Note: this is not currently used, except as an environment variable
# for CGIs.
#ServerAdmin root@localhost
# ErrorLog: The location of the error log file. If this does not start
# with /, it is considered relative to the server root.
# Set to /dev/null if you don't want errors logged.
# If unset, defaults to /dev/stderr
#ErrorLog /var/log/boa/error_log
ErrorLog /boa/log/error_log
# Please NOTE: Sending the logs to a pipe ('|'), as shown below,
# is somewhat experimental and might fail under heavy load.
# "Usual libc implementations of printf will stall the whole
# process if the receiving end of a pipe stops reading."
#ErrorLog "|/usr/sbin/cronolog --symlink=/var/log/boa/error_log /var/log/boa/error-%Y%m%d.log"
# AccessLog: The location of the access log file. If this does not
# start with /, it is considered relative to the server root.
# Comment out or set to /dev/null (less effective) to disable
# Access logging.
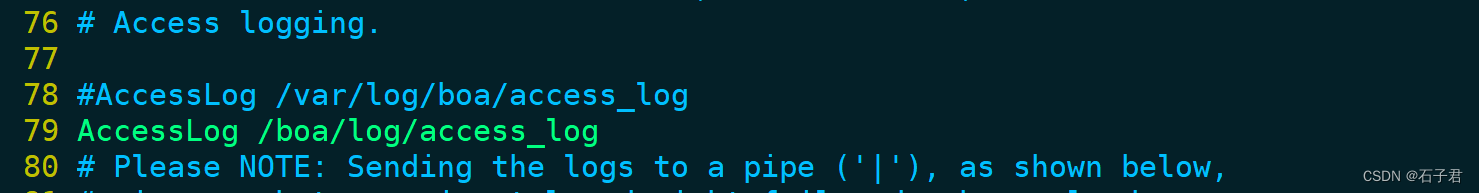
#AccessLog /var/log/boa/access_log
AccessLog /boa/log/access_log
# Please NOTE: Sending the logs to a pipe ('|'), as shown below,
# is somewhat experimental and might fail under heavy load.
# "Usual libc implementations of printf will stall the whole
# process if the receiving end of a pipe stops reading."
#AccessLog "|/usr/sbin/cronolog --symlink=/var/log/boa/access_log /var/log/boa/access-%Y%m%d.log"
# UseLocaltime: Logical switch. Uncomment to use localtime
# instead of UTC time
#UseLocaltime
# VerboseCGILogs: this is just a logical switch.
# It simply notes the start and stop times of cgis in the error log
# Comment out to disable.
#VerboseCGILogs
# ServerName: the name of this server that should be sent back to
# clients if different than that returned by gethostname + gethostbyname
#ServerName www.your.org.here
# VirtualHost: a logical switch.
# Comment out to disable.
# Given DocumentRoot /var/www, requests on interface 'A' or IP 'IP-A'
# become /var/www/IP-A.
# Example: http://localhost/ becomes /var/www/127.0.0.1
#
# Not used until version 0.93.17.2. This "feature" also breaks commonlog
# output rules, it prepends the interface number to each access_log line.
# You are expected to fix that problem with a postprocessing script.
#VirtualHost
# DocumentRoot: The root directory of the HTML documents.
# Comment out to disable server non user files.
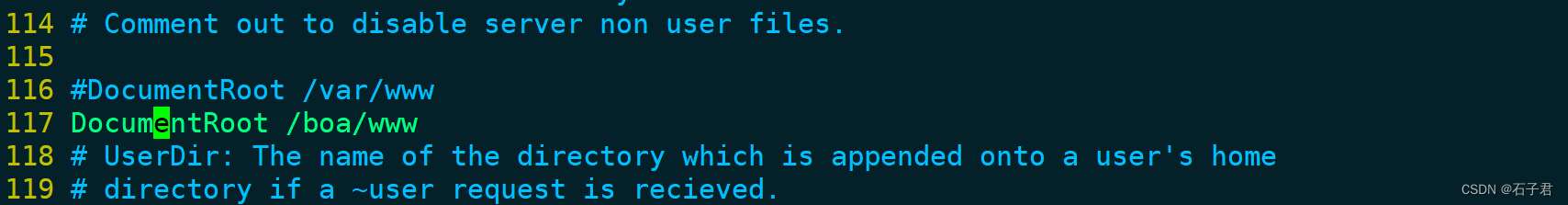
#DocumentRoot /var/www
DocumentRoot /boa/www
# UserDir: The name of the directory which is appended onto a user's home
# directory if a ~user request is recieved.
UserDir public_html
# DirectoryIndex: Name of the file to use as a pre-written HTML
# directory index. Please MAKE AND USE THESE FILES. On the
# fly creation of directory indexes can be _slow_.
# Comment out to always use DirectoryMaker
DirectoryIndex index.html
# DirectoryMaker: Name of program used to create a directory listing.
# Comment out to disable directory listings. If both this and
# DirectoryIndex are commented out, accessing a directory will give
# an error (though accessing files in the directory are still ok).
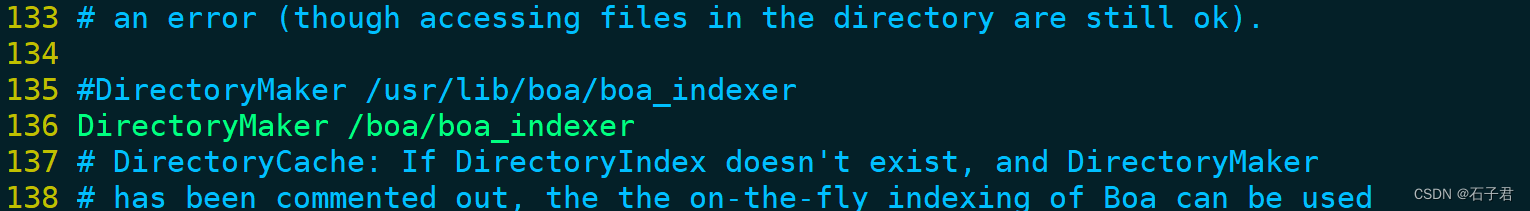
#DirectoryMaker /usr/lib/boa/boa_indexer
DirectoryMaker /boa/boa_indexer
# DirectoryCache: If DirectoryIndex doesn't exist, and DirectoryMaker
# has been commented out, the the on-the-fly indexing of Boa can be used
# to generate indexes of directories. Be warned that the output is
# extremely minimal and can cause delays when slow disks are used.
# Note: The DirectoryCache must be writable by the same user/group that
# Boa runs as.
# DirectoryCache /var/spool/boa/dircache
# KeepAliveMax: Number of KeepAlive requests to allow per connection
# Comment out, or set to 0 to disable keepalive processing
KeepAliveMax 1000
# KeepAliveTimeout: seconds to wait before keepalive connection times out
KeepAliveTimeout 10
# MimeTypes: This is the file that is used to generate mime type pairs
# and Content-Type fields for boa.
# Set to /dev/null if you do not want to load a mime types file.
# Do *not* comment out (better use AddType!)
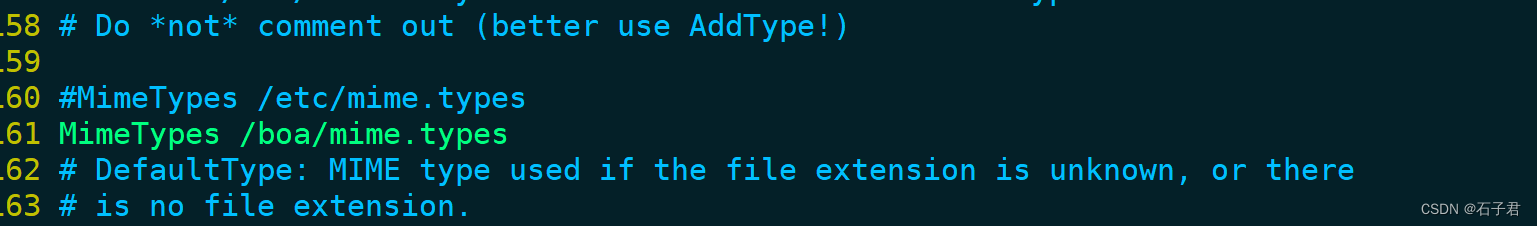
#MimeTypes /etc/mime.types
MimeTypes /boa/mime.types
# DefaultType: MIME type used if the file extension is unknown, or there
# is no file extension.
DefaultType text/plain
# CGIPath: The value of the $PATH environment variable given to CGI progs.
CGIPath /bin:/usr/bin:/usr/local/bin
# SinglePostLimit: The maximum allowable number of bytes in
# a single POST. Default is normally 1MB.
# AddType: adds types without editing mime.types
# Example: AddType type extension [extension ...]
# Uncomment the next line if you want .cgi files to execute from anywhere
#AddType application/x-httpd-cgi cgi
# Redirect, Alias, and ScriptAlias all have the same semantics -- they
# match the beginning of a request and take appropriate action. Use
# Redirect for other servers, Alias for the same server, and ScriptAlias
# to enable directories for script execution.
# Redirect allows you to tell clients about documents which used to exist in
# your server's namespace, but do not anymore. This allows you to tell the
# clients where to look for the relocated document.
# Example: Redirect /bar http://elsewhere/feh/bar
# Aliases: Aliases one path to another.
# Example: Alias /path1/bar /path2/foo
Alias /doc /usr/doc
# ScriptAlias: Maps a virtual path to a directory for serving scripts
# Example: ScriptAlias /htbin/ /www/htbin/
#ScriptAlias /cgi-bin/ /usr/lib/cgi-bin/
ScriptAlias /cgi-bin/ /boa/cgi-bin/

![map的operator[]原理](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/b5b68a919e614c2ebdacfe1caa0c266d.png)




![【蓝桥每日一题]-二分精确(保姆级教程 篇4) #kotori的设备 #银行贷款 #一元三次方程求解](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/6392744afbf14007a3545eaff1474d6e.png)
