欢迎关注更多精彩
关注我,学习常用算法与数据结构,一题多解,降维打击。
voronoi 图求解点击前往
题目链接:https://vjudge.net/problem/URAL-1504
题目大意
有一个桌子,形状是圆形。
桌上放着很多蛋糕,每个蛋糕有大小。
人可以坐在桌子边缘的任意位置,坐下后可以拿离自己最近的一块蛋糕,求坐在哪个位置可以拿到尽可能大的蛋糕。
思考&分析
先求出每个蛋糕所在voronoi区域。
查看区域与圆有没有交点。
遍历有交点的蛋糕,选择可以拿到最大蛋糕的交点。
算法细节
1)判断区域与圆有交
可以求出区域所有顶点,判断有没有顶点在圆上或外面。
2)直线与圆求交
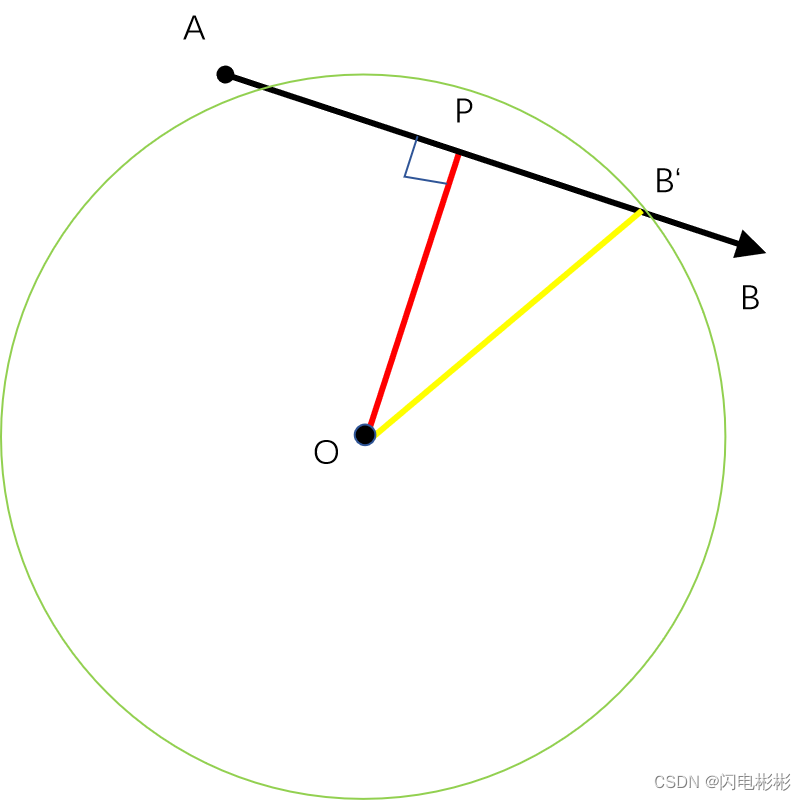
可以利用投影先求到P点,利用直角三角形可知PB’长度
从P点沿AB方向就可以得到B’坐标,同理,反向还有一个交点。
3)特殊情况
只有2个蛋糕或者所有蛋糕在一条线上时,不能进行三角化。
此时,选择最大的蛋糕,作垂线与圆求交点即可。
算法过程
step 1 对边界点进行delaunay三角化
step 2 遍历每个边界点,收集邻边,并按照逆时针排序。
求解出每个邻边的中垂线,分别与边界和其他中垂线求交(邻近的中垂线才有交点)判断是否与圆有交集
step 3 求解与圆的交点,并判断交点是否在voronoi区域内。
step 4 选取可以拿到最大蛋糕的位置点
代码
#include<stdio.h>
#include<cmath>
#include <algorithm>
#include <vector>
#include <list>
#include <cstring>
#include <utility>
using namespace std;
const double EPS = 1e-8;
const int N = 1e6 + 10;
const int M = 1e6 + 10;
int cmp(double d) {
if (abs(d) < EPS)return 0;
if (d > 0)return 1;
return -1;
}
class Point {
public:
double x, y;
int id;
Point() {}
Point(double a, double b) :x(a), y(b) {}
Point(const Point& p) :x(p.x), y(p.y), id(p.id) {}
void in() {
scanf("%lf %lf", &x, &y);
}
void out() {
printf("%f %f\n", x, y);
}
double dis() {
return sqrt(x * x + y * y);
}
double dis2() {
return x * x + y * y;
}
Point operator -() const {
return Point(-x, -y);
}
Point operator -(const Point& p) const {
return Point(x - p.x, y - p.y);
}
Point operator +(const Point& p) const {
return Point(x + p.x, y + p.y);
}
Point operator *(double d)const {
return Point(x * d, y * d);
}
Point operator /(double d)const {
return Point(x / d, y / d);
}
void operator -=(Point& p) {
x -= p.x;
y -= p.y;
}
void operator +=(Point& p) {
x += p.x;
y += p.y;
}
void operator *=(double d) {
x *= d;
y *= d;
}
void operator /=(double d) {
this ->operator*= (1 / d);
}
bool operator<(const Point& a) const {
return x < a.x || (abs(x - a.x) < EPS && y < a.y);
}
bool operator==(const Point& a) const {
return abs(x - a.x) < EPS && abs(y - a.y) < EPS;
}
};
// 向量操作
double cross(const Point& a, const Point& b) {
return a.x * b.y - a.y * b.x;
}
double dot(const Point& a, const Point& b) {
return a.x * b.x + a.y * b.y;
}
class Point3D {
public:
double x, y, z;
Point3D() {}
Point3D(double a, double b, double c) :x(a), y(b), z(c) {}
Point3D(const Point3D& p) :x(p.x), y(p.y), z(p.z) {}
double dis() {
return sqrt(x * x + y * y + z * z);
}
double dis2() {
return x * x + y * y + z * z;
}
Point3D operator -(const Point3D& p) const {
return Point3D(x - p.x, y - p.y, z - p.z);
}
Point3D operator +(const Point3D& p) const {
return Point3D(x + p.x, y + p.y, z + p.z);
}
Point3D operator *(double d)const {
return Point3D(x * d, y * d, z * d);
}
Point3D operator /(double d)const {
return Point3D(x / d, y / d, z / d);
}
void operator -=(Point3D& p) {
x -= p.x;
y -= p.y;
z -= p.z;
}
void operator +=(Point3D& p) {
x += p.x;
y += p.y;
z += p.z;
}
void operator *=(double d) {
x *= d;
y *= d;
z *= d;
}
void operator /=(double d) {
this ->operator*= (1 / d);
}
};
// 向量操作
Point3D cross(const Point3D& a, const Point3D& b) {
return Point3D(a.y * b.z - a.z * b.y, -a.x * b.z + a.z * b.x,
a.x * b.y - a.y * b.x);
}
double dot(const Point3D& a, const Point3D& b) {
return a.x * b.x + a.y * b.y + a.z * b.z;
}
class Line {
public:
Point front, tail;
Line() {}
Line(Point a, Point b) :front(a), tail(b) {}
};
/*
0 不相交
1 相交
0 平行/重合
*/
int cross(const Line& a, const Line& b) {
Point dir1 = a.front - a.tail;
Point dir2 = b.front - b.tail;
if (cmp(cross(dir1, dir2)) == 0) {
return 0;
}
if (cmp(cross(a.front - b.tail, dir2)) * cmp(cross(a.tail - b.tail, dir2)) >= 0)return 0;
if (cmp(cross(b.front - a.tail, dir1)) * cmp(cross(b.tail - a.tail, dir1)) >= 0)return 0;
return 1;
}
int inCircle(Point p0, Point p1, Point p2, Point p3) {
Point d1 = p1 - p0;
Point d2 = p2 - p0;
if (cross(d1, d2) < 0)return inCircle(p0, p2, p1, p3); // 保证平面法向向上
// 构建映射点
Point3D lift0(p0.x, p0.y, p0.dis2());
Point3D lift1(p1.x, p1.y, p1.dis2());
Point3D lift2(p2.x, p2.y, p2.dis2());
Point3D lift3(p3.x, p3.y, p3.dis2());
Point3D z1(lift1 - lift0), z2(lift2 - lift0);
Point3D normal = cross(z1, z2); // 计算平面法向
double project = dot(normal, lift3 - lift0); // 计算点到平面距离
return cmp(project);
}
class EdgeDelaunay {
public:
int id;
std::list<EdgeDelaunay>::iterator c;
EdgeDelaunay(int id = 0) { this->id = id; }
};
class Delaunay {
public:
std::list<EdgeDelaunay> head[N]; // graph
Point p[N];
int n = 0;
void init(int psize, Point ps[]) {
this->n = psize;
memcpy(this->p, ps, sizeof(Point) * n);
std::sort(this->p, this->p + n);
divide(0, n - 1);
}
void addEdge(int u, int v) {
head[u].push_front(EdgeDelaunay(v));
head[v].push_front(EdgeDelaunay(u));
head[u].begin()->c = head[v].begin();
head[v].begin()->c = head[u].begin();
}
void divide(int l, int r) {
if (r - l <= 1) { // #point <= 2
for (int i = l; i <= r; i++)
for (int j = i + 1; j <= r; j++) addEdge(i, j);
return;
}
int mid = (l + r) / 2;
divide(l, mid);
divide(mid + 1, r);
std::list<EdgeDelaunay>::iterator it;
int nowl = l, nowr = r;
for (int update = 1; update;) {
// 查找左边最低线位置
update = 0;
Point ptL = p[nowl], ptR = p[nowr];
for (it = head[nowl].begin(); it != head[nowl].end(); it++) {
Point t = p[it->id];
double v = cross(ptL - ptR, t - ptR);
if (cmp(v) > 0 || (cmp(v) == 0 && (t - ptR).dis() < (ptL - ptR).dis())) {
nowl = it->id, update = 1;
break;
}
}
if (update) continue;
// 查找右边最低线位置
for (it = head[nowr].begin(); it != head[nowr].end(); it++) {
Point t = p[it->id];
double v = cross(ptR - ptL, t - ptL);
if (cmp(v) < 0 || (cmp(v) == 0 && (t - ptL).dis() < (ptL - ptR).dis())) {
nowr = it->id, update = 1;
break;
}
}
}
addEdge(nowl, nowr); // 添加基线
for (; true;) {
Point ptL = p[nowl], ptR = p[nowr];
int ch = -1, side = 0;
for (it = head[nowl].begin(); it != head[nowl].end(); it++) {
if (cmp(cross(ptR - ptL, p[it->id] - ptL)) <= 0)continue; // 判断夹角是否小于180
if (ch == -1 || inCircle(ptL, ptR, p[ch], p[it->id]) < 0) {
ch = it->id, side = -1;
}
}
for (it = head[nowr].begin(); it != head[nowr].end(); it++) {
if (cmp(cross(p[it->id] - ptR, ptL - ptR)) <= 0) continue;// 判断夹角是否小于180
if (ch == -1 || inCircle(ptL, ptR, p[ch], p[it->id]) < 0) {
ch = it->id, side = 1;
}
}
if (ch == -1) break; // 所有线已经加完
if (side == -1) {
for (it = head[nowl].begin(); it != head[nowl].end();) {
// 判断是否相交,边缘不算相交
if (cross(Line(ptL, p[it->id]), Line(ptR, p[ch]))) {
head[it->id].erase(it->c);
head[nowl].erase(it++);
}
else {
it++;
}
}
nowl = ch;
addEdge(nowl, nowr);
}
else {
for (it = head[nowr].begin(); it != head[nowr].end();) {
// 判断是否相交,边缘不算相交
if (cross(Line(ptR, p[it->id]), Line(ptL, p[ch]))) {
head[it->id].erase(it->c);
head[nowr].erase(it++);
}
else {
it++;
}
}
nowr = ch;
addEdge(nowl, nowr);
}
}
}
std::vector<std::pair<int, int> > getEdge() {
std::vector<std::pair<int, int> > ret;
ret.reserve(n);
std::list<EdgeDelaunay>::iterator it;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
for (it = head[i].begin(); it != head[i].end(); it++) {
ret.push_back(std::make_pair(p[i].id, p[it->id].id));
}
}
return ret;
}
};
/*
点p 到 p+r 表示线段1
点q 到 q+s 表示线段2
线段1 上1点用 p' = p+t*r (0<=t<=1)
线段2 上1点用 q' = q+u*s (0<=u<=1)
让两式相等求交点 p+t*r = q+u*s
两边都叉乘s
(p+t*r)Xs = (q+u*s)Xs
pXs + t*rXs = qXs
t = (q-p)Xs/(rXs)
同理,
u = (p-q)Xr/(sXr) -> u = (q-p)Xr/(rXs)
以下分4种情况:
1. 共线,sXr==0 && (q-p)Xr==0, 计算 (q-p)在r上的投影在r长度上的占比t0,
计算(q+s-p)在r上的投影在r长度上的占比t1,查看[t0, t1]是否与范围[0,1]有交集。
如果t0>t1, 则比较[t1, t0]是否与范围[0,1]有交集。
t0 = (q-p)*r/(r*r)
t1 = (q+s-p)*r/(r*r) = t0 + s · r / (r · r)
2. 平行sXr==0 && (q-p)Xr!=0
3. 0<=u<=1 && 0<=t<=1 有交点
4. 其他u, t不在0到范围内,没有交点。
*/
pair<double, double> intersection(const Point& q, const Point& s, const Point& p, const Point& r) {
// 计算 (q-p)Xr
auto qpr = cross(q - p, r);
auto qps = cross(q - p, s);
auto rXs = cross(r, s);
if (cmp(rXs) == 0)return { -1, -1 }; // 平行或共线
// 求解t, u
// t = (q-p)Xs/(rXs)
auto t = qps / rXs;
// u = (q-p)Xr/(rXs)
auto u = qpr / rXs;
return { u, t };
}
Point oiPs[N];
Delaunay de;
Point lowPoint;
int ind[M];
Point tmpPs[N]; // 存储与边界的交点
int cakeSize[N];
vector<Point> insectCircle(const Point& A, const Point& dir, double r) {
vector<Point> ans;
Point P = A + dir * dot(dir, -A);
double op = abs(cross(dir, A));
if (cmp(op - r) > 0)return ans;
double Pb = sqrt(r * r - op * op);
if (cmp(Pb) == 0) ans.push_back(P);
else {
ans.push_back(P + dir * Pb);
ans.push_back(P - dir * Pb);
}
return ans;
}
// 按照极坐标排序
bool sortcmp(int i, int j) {
Point pi = oiPs[i] - lowPoint;
Point pj = oiPs[j] - lowPoint;
// 在上下半区不同侧,上半区优先
if (cmp(pi.y * pj.y) < 0) return pi.y > pj.y;
pi /= pi.dis();
pj /= pj.dis();
// 有一条为1,0, x大的优化
if (cmp(pi.x - 1) == 0 || 0 == cmp(pj.x - 1)) return pi.x > pj.x;
double d = cmp(cross(pi, pj)); // 同侧判断是否逆时针旋转
return d > 0;
}
bool oneLine(int n) {
if (n < 3)return true;
for (int i = 2; i < n; ++i) {
if (cmp(cross(oiPs[1] - oiPs[0], oiPs[i] - oiPs[0])) != 0) return false;
}
return true;
}
void solve() {
int n, r;
scanf("%d%d", &r, &n);
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) {
scanf("%lf%lf", &oiPs[i].x, &oiPs[i].y);
scanf("%d", cakeSize+i);
oiPs[i].id = i;
}
// 判断是否共线
if (oneLine(n)) {
// 选取最大的
int indbig = 0;
for (int i = 1; i < n; ++i) {
if (cakeSize[i] > cakeSize[indbig])indbig = i;
}
Point dir = oiPs[n - 1] - oiPs[0];
dir = { -dir.y, dir.x };
dir /= dir.dis();
auto insectPs = insectCircle(oiPs[indbig], dir, r);
Point seat = insectPs[0];
printf("%.10f %.10f\n", seat.x, seat.y);
return;
}
oiPs[n] = oiPs[0];
de.init(n, oiPs);
auto oiedges = de.getEdge();
vector<vector<int>> link(n, vector<int>());
for (auto oie : oiedges) {
link[oie.first].push_back(oie.second);
}
int maxSize = 0;
Point seat;
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) {
// 遍历每个边界点,收集邻边,并按照逆时针排序。
int len = 0;
for (auto to : link[i]) {
ind[len++] = to;
}
lowPoint = oiPs[i];
sort(ind, ind + len, sortcmp);
ind[len] = ind[0];// 添加循环优化
// 求voronoi 边界之间交点
bool isInsect = false; // 标记vonoroi cell 与圆是否有交集
for (int i = 0; i < len && !isInsect; ++i) {
Point mid = (lowPoint + oiPs[ind[i]]) / 2;
Point dir = oiPs[ind[i]] - lowPoint;
dir = { -dir.y, dir.x }; // 旋转90度
Point mid2 = (lowPoint + oiPs[ind[i + 1]]) / 2;
Point dir2 = oiPs[ind[i + 1]] - lowPoint;
dir2 = { -dir2.y, dir2.x }; // 旋转90度
// 判断是否为都边界(夹角不能大于180)
if (cmp(cross(dir, dir2)) <= 0) {
isInsect = true;
break;
}
// 求交点
auto pr = intersection(mid, dir, mid2, dir2);
Point ablePoint = mid2 + dir2 * pr.second;
if (cmp(ablePoint.dis() - r) >= 0)isInsect = true;
}
int k = 0;
// 求与圆的交点
for (int i = 0; i < len && isInsect; ++i) {
Point mid = (lowPoint + oiPs[ind[i]]) / 2;
Point dir = oiPs[ind[i]] - lowPoint;
dir = { -dir.y, dir.x }; // 旋转90度
dir /= dir.dis();
auto insectPs = insectCircle(mid, dir, r);
for (auto& c : insectPs) {
tmpPs[k++] = c;
//c.out();
}
}
// 排除无效交点
for (int i = 0; i < len; ++i) {
Point mid = (lowPoint + oiPs[ind[i]]) / 2;
Point dir = oiPs[ind[i]] - lowPoint;
dir = { -dir.y, dir.x }; // 旋转90度
for (int j = 0; j < k; ++j) {
// 判断点是否与Lowpoint 在同一半平面内
if (cmp(cross(lowPoint - mid, dir) * cross(dir, tmpPs[j] - mid)) > 0) {
swap(tmpPs[k - 1], tmpPs[j]);
k--;
j--;
continue;
}
}
}
for (int j = 0; j < k; ++j) {
if (cakeSize[i] > maxSize) {
maxSize = cakeSize[i];
seat = tmpPs[j];
//seat.out();
}
}
}
printf("%.10f %.10f\n", seat.x, seat.y);
//printf("%d\n", maxSize);
//printf("%.10f\n", seat.dis());
}
int main() {
solve();
return 0;
}
/*
10 5
0 0 100
1 0 1
0 1 2
0 -1 3
-1 0 4
10 3
1 -1 100
2 2 200
-2.5 -2.56 1
10 5
0.2 0 100
1 0 1
2 0 2
3 0 1
4 0 4
10 5
9.89 0 100
1 0 1
2 0 2
3 0 1
4 0 4
10 2
10 0 100
1 0 1
*/
本人码农,希望通过自己的分享,让大家更容易学懂计算机知识。创作不易,帮忙点击公众号的链接。








![[C++ ]:5.类和对象中(运算符重载补充)+ 类和对象下(初始化列表)](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/7d0323bb689d4d47a9731da34721b591.png)