目录
1. 175组合两个表
左外连接
2. 181. 超过经理收入的员工
3. 182. 查找重复的电子邮箱
4. 196. 删除重复的电子邮箱
5. 197. 上升的温度
日期作差
6. 511. 游戏玩法分析 I
7. 577. 员工奖金
null条件运算
8. 584. 寻找用户推荐人
9. 586. 订单最多的客户
10. 595. 大的国家
11. 596. 超过5名学生的课
聚合加条件
🦍12. 607. 销售员
13. 610. 判断三角形
if语句
14. 619. 只出现一次的最大数字
仅独立使用select
15. 620. 有趣的电影
16. 627.update替换
17. 1050. 合作过至少三次的演员和导演
group by两个参数
18. 1068. 产品销售分析 I
19. 1084. 销售分析III
日期比较
20. 1075. 项目员工 I
小数点位数 round(x,2)
21. 1141. 查询近30天活跃用户数
22. 1148. 文章浏览 I
🦍23. 1179. 重新格式化部门表
行转列暴力解法
24. 1211. 查询结果的质量和占比
分组后求算式
25. 1251. 平均售价
ifnull(算式,空时的值)
26. 1280. 学生们参加各科测试的次数
连接多
27. 1327. 列出指定时间段内所有的下单产品
日期函数YEAR()
28. 1378. 使用唯一标识码替换员工ID
29. 1407. 排名靠前的旅行者
陷阱
30. 1484. 按日期分组销售产品
group_concat(distinct product)
31. 1527. 患某种疾病的患者
字符串占位符
32. 1587. 银行账户概要 II
33. 1581. 进店却未进行过交易的顾客
null统计不到个数,要使用count(*)
34. 1517. 查找拥有有效邮箱的用户
正则表达式!🌿!
35. 1633. 各赛事的用户注册率
36. 1661. 每台机器的进程平均运行时间
37. 1667. 修复表中的名字
38. 1683. 无效的推文
39. 1693. 每天的领导和合伙人
40. 1729. 求关注者的数量
41. 1731. 每位经理的下属员工数量
42. 1741. 查找每个员工花费的总时间
43. 1757. 可回收且低脂的产品
44. 1789. 员工的直属部门
union
45.🦍 1795. 每个产品在不同商店的价格
46. 1873. 计算特殊奖金
if嵌套
47. 1890. 2020年最后一次登录
48.1965. 丢失信息的雇员
49. 1978. 上级经理已离职的公司员工
50. 2356. 每位教师所教授的科目种类的数量

1. 175组合两个表
左外连接
Q:
表: Person
+-------------+---------+
| 列名 | 类型 |
+-------------+---------+
| PersonId | int |
| FirstName | varchar |
| LastName | varchar |
+-------------+---------+
personId 是该表的主键(具有唯一值的列)。
该表包含一些人的 ID 和他们的姓和名的信息。
表: Address
+-------------+---------+
| 列名 | 类型 |
+-------------+---------+
| AddressId | int |
| PersonId | int |
| City | varchar |
| State | varchar |
+-------------+---------+
addressId 是该表的主键(具有唯一值的列)。
该表的每一行都包含一个 ID = PersonId 的人的城市和州的信息。
编写解决方案,报告 Person 表中每个人的姓、名、城市和州。如果 personId 的地址不在 Address 表中,则报告为 null 。
以 任意顺序 返回结果表。
结果格式如下所示。
示例 1:
输入:
Person表:
+----------+----------+-----------+
| personId | lastName | firstName |
+----------+----------+-----------+
| 1 | Wang | Allen |
| 2 | Alice | Bob |
+----------+----------+-----------+
Address表:
+-----------+----------+---------------+------------+
| addressId | personId | city | state |
+-----------+----------+---------------+------------+
| 1 | 2 | New York City | New York |
| 2 | 3 | Leetcode | California |
+-----------+----------+---------------+------------+
输出:
+-----------+----------+---------------+----------+
| firstName | lastName | city | state |
+-----------+----------+---------------+----------+
| Allen | Wang | Null | Null |
| Bob | Alice | New York City | New York |
+-----------+----------+---------------+----------+
解释:
地址表中没有 personId = 1 的地址,所以它们的城市和州返回 null。
addressId = 1 包含了 personId = 2 的地址信息。SELECT firstName, lastName, city, state from Person left join Address on Person.personId=Address.personId; 2. 181. 超过经理收入的员工
表:Employee
+-------------+---------+
| Column Name | Type |
+-------------+---------+
| id | int |
| name | varchar |
| salary | int |
| managerId | int |
+-------------+---------+
id 是该表的主键(具有唯一值的列)。
该表的每一行都表示雇员的ID、姓名、工资和经理的ID。
编写解决方案,找出收入比经理高的员工。
以 任意顺序 返回结果表。
结果格式如下所示。
示例 1:
输入:
Employee 表:
+----+-------+--------+-----------+
| id | name | salary | managerId |
+----+-------+--------+-----------+
| 1 | Joe | 70000 | 3 |
| 2 | Henry | 80000 | 4 |
| 3 | Sam | 60000 | Null |
| 4 | Max | 90000 | Null |
+----+-------+--------+-----------+
输出:
+----------+
| Employee |
+----------+
| Joe |
+----------+
解释: Joe 是唯一挣得比经理多的雇员。SELECT a.name Employee FROM Employee a join Employee b on a.managerId=b.id where a.salary>b.salary;3. 182. 查找重复的电子邮箱
输入:
Person 表:
+----+---------+
| id | email |
+----+---------+
| 1 | a@b.com |
| 2 | c@d.com |
| 3 | a@b.com |
+----+---------+
输出:
+---------+
| Email |
+---------+
| a@b.com |
+---------+
解释: a@b.com 出现了两次。select email as Email from Person group by email having count(email) > 14. 183. 从不订购的客户

select t.name as Customers from (select C.id as i,name,O.id as ii,customerId from Customers as C left join Orders as O on C.id=O.customerId) as t where t.customerId is null
or
select name as Customers from Customers as C left join Orders as O on C.id=O.customerId where O.customerId is null4. 196. 删除重复的电子邮箱
编写解决方案 删除 所有重复的电子邮件,只保留一个具有最小 id 的唯一电子邮件。
(对于 SQL 用户,请注意你应该编写一个 DELETE 语句而不是 SELECT 语句。)
| id | email |
| -- | ---------------- |
| 1 | john@example.com |
| 2 | bob@example.com |
| 3 | john@example.com |DELETE FROM Person
WHERE id NOT IN (
# 筛出所有的单个最小id,删掉不在里面的
SELECT id FROM (
SELECT MIN(id) AS id FROM Person GROUP BY email
) AS u
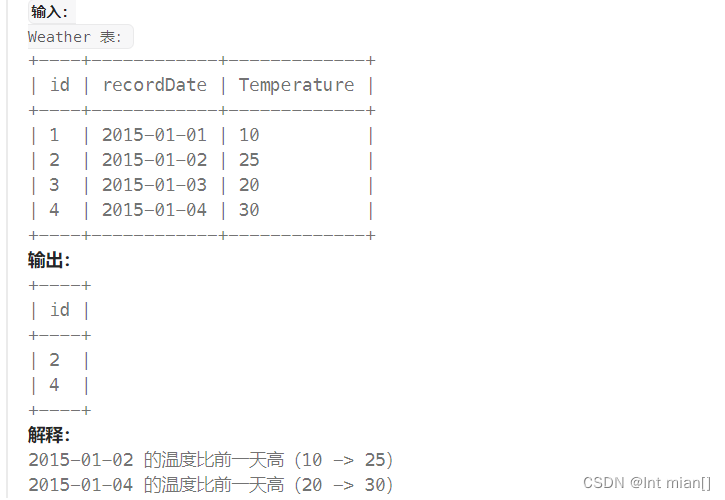
);5. 197. 上升的温度
日期作差
编写解决方案,找出与之前(昨天的)日期相比温度更高的所有日期的 id 。
返回结果 无顺序要求 。
结果格式如下例子所示。
# Write your MySQL query statement below
select t.id1 id from (
select w1.id id1,w1.recordDate re1,w1.temperature te1,w2.id id2,w2.recordDate re2,w2.temperature te2
from Weather as w1 left join Weather as w2 on TIMESTAMPDIFF(DAY,w2.recordDate, w1.recordDate)=1
) as t where t.te1>t.te26. 511. 游戏玩法分析 I
查询每位玩家 第一次登陆平台的日期。
查询结果的格式如下所示:
Activity 表:
+-----------+-----------+------------+--------------+
| player_id | device_id | event_date | games_played |
+-----------+-----------+------------+--------------+
| 1 | 2 | 2016-03-01 | 5 |
| 1 | 2 | 2016-05-02 | 6 |
| 2 | 3 | 2017-06-25 | 1 |
| 3 | 1 | 2016-03-02 | 0 |
| 3 | 4 | 2018-07-03 | 5 |
+-----------+-----------+------------+--------------+
Result 表:
+-----------+-------------+
| player_id | first_login |
+-----------+-------------+
| 1 | 2016-03-01 |
| 2 | 2017-06-25 |
| 3 | 2016-03-02 |
+-----------+-------------+# Write your MySQL query statement below
select player_id,min(event_date) first_login from(
select player_id,event_date from Activity
) as t group by player_id7. 577. 员工奖金
null条件运算
编写解决方案,报告每个奖金 少于 1000 的员工的姓名和奖金数额。
结果格式如下所示。
示例 1:
输入:
Employee table:
+-------+--------+------------+--------+
| empId | name | supervisor | salary |
+-------+--------+------------+--------+
| 3 | Brad | null | 4000 |
| 1 | John | 3 | 1000 |
| 2 | Dan | 3 | 2000 |
| 4 | Thomas | 3 | 4000 |
+-------+--------+------------+--------+
Bonus table:
+-------+-------+
| empId | bonus |
+-------+-------+
| 2 | 500 |
| 4 | 2000 |
+-------+-------+
输出:
+------+-------+
| name | bonus |
+------+-------+
| Brad | null |
| John | null |
| Dan | 500 |
+------+-------+select name,bonus from Employee as e left join Bonus as b
on e.empId=b.empId
where b.bonus < 1000 or b.bonus is nullQ:在这个语句里我筛选出了bonus小于1000的数据,但是bonus为null为什么筛选不出来?
A: 这是因为在MySQL中,当你使用条件筛选时,NULL 值的处理方式会有些不同。通常情况下,比较 NULL 值需要使用
IS NULL或IS NOT NULL,而不是使用比较运算符(如<、>、=)。
8. 584. 寻找用户推荐人
找出那些 没有被 id = 2 的客户 推荐 的客户的姓名。
以 任意顺序 返回结果表。
结果格式如下所示。
示例 1:
输入:
Customer 表:
+----+------+------------+
| id | name | referee_id |
+----+------+------------+
| 1 | Will | null |
| 2 | Jane | null |
| 3 | Alex | 2 |
| 4 | Bill | null |
| 5 | Zack | 1 |
| 6 | Mark | 2 |
+----+------+------------+easy
9. 586. 订单最多的客户
查找下了 最多订单 的客户的 customer_number 。
测试用例生成后, 恰好有一个客户 比任何其他客户下了更多的订单。
查询结果格式如下所示。
示例 1:
输入:
Orders 表:
+--------------+-----------------+
| order_number | customer_number |
+--------------+-----------------+
| 1 | 1 |
| 2 | 2 |
| 3 | 3 |
| 4 | 3 |
+--------------+-----------------+
输出:
+-----------------+
| customer_number |
+-----------------+
| 3 |
+-----------------+select customer_number
from orders
group by customer_number
order by count(*) desc
limit 110. 595. 大的国家
如果一个国家满足下述两个条件之一,则认为该国是 大国 :
- 面积至少为 300 万平方公里(即,
3000000 km2),或者 - 人口至少为 2500 万(即
25000000)送分题
11. 596. 超过5名学生的课
聚合加条件
查询 至少有5个学生 的所有班级。
以 任意顺序 返回结果表。
查询结果格式如下所示。
示例 1:
输入:
Courses table:
+---------+----------+
| student | class |
+---------+----------+
| A | Math |
| B | English |
| C | Math |
| D | Biology |
| E | Math |
| F | Computer |
| G | Math |
| H | Math |
| I | Math |
+---------+----------+
输出:
+---------+
| class |
+---------+
| Math |
+---------+select class from Courses
group by class
having count(student)>=5🦍12. 607. 销售员
编写解决方案,找出没有任何与名为 “RED” 的公司相关的订单的所有销售人员的姓名。
以 任意顺序 返回结果表。
返回结果格式如下所示。
示例 1:
输入:
SalesPerson 表:
+----------+------+--------+-----------------+------------+
| sales_id | name | salary | commission_rate | hire_date |
+----------+------+--------+-----------------+------------+
| 1 | John | 100000 | 6 | 4/1/2006 |
| 2 | Amy | 12000 | 5 | 5/1/2010 |
| 3 | Mark | 65000 | 12 | 12/25/2008 |
| 4 | Pam | 25000 | 25 | 1/1/2005 |
| 5 | Alex | 5000 | 10 | 2/3/2007 |
+----------+------+--------+-----------------+------------+
Company 表:
+--------+--------+----------+
| com_id | name | city |
+--------+--------+----------+
| 1 | RED | Boston |
| 2 | ORANGE | New York |
| 3 | YELLOW | Boston |
| 4 | GREEN | Austin |
+--------+--------+----------+
Orders 表:
+----------+------------+--------+----------+--------+
| order_id | order_date | com_id | sales_id | amount |
+----------+------------+--------+----------+--------+
| 1 | 1/1/2014 | 3 | 4 | 10000 |
| 2 | 2/1/2014 | 4 | 5 | 5000 |
| 3 | 3/1/2014 | 1 | 1 | 50000 |
| 4 | 4/1/2014 | 1 | 4 | 25000 |
+----------+------------+--------+----------+--------+
输出:
+------+
| name |
+------+
| Amy |
| Mark |
| Alex |
+------+select tem.name name from (
select s.sales_id id,s.name name,o.com_id com_id from SalesPerson as s left join Orders as o on s.sales_id=o.sales_id
) as tem left join Company as c on tem.com_id=c.com_id or tem.name is null
group by tem.id
having sum(if(c.name='RED',1,0))=013. 610. 判断三角形
if语句
输入:
Triangle 表:
+----+----+----+
| x | y | z |
+----+----+----+
| 13 | 15 | 30 |
| 10 | 20 | 15 |
+----+----+----+
输出:
+----+----+----+----------+
| x | y | z | triangle |
+----+----+----+----------+
| 13 | 15 | 30 | No |
| 10 | 20 | 15 | Yes |
+----+----+----+----------+select x,y,z,(if(x+y>z and x+z>y and y+z>x,'Yes','No')) as triangle from Triangle; 14. 619. 只出现一次的最大数字
仅独立使用select
单一数字 是在 MyNumbers 表中只出现一次的数字。
找出最大的 单一数字 。如果不存在 单一数字 ,则返回 null 。
查询结果如下例所示。
示例 1:
输入:
MyNumbers 表:
+-----+
| num |
+-----+
| 8 |
| 8 |
| 3 |
| 3 |
| 1 |
| 4 |
| 5 |
| 6 |
+-----+
输出:
+-----+
| num |
+-----+
| 6 |
+-----+
还有null的情况# Write your MySQL query statement below
select (
select num from MyNumbers
group by num
having count(num)=1
order by num desc
limit 1
) as num
select null as num
| num |
| ---- |
| null |15. 620. 有趣的电影
编写解决方案,找出所有影片描述为 非 boring (不无聊) 的并且 id 为奇数 的影片。
返回结果按 rating 降序排列。
结果格式如下示例。送分题
select * from cinema where id%2=1 and description!='boring'
order by rating desc 
16. 627.update替换
请你编写一个解决方案来交换所有的 'f' 和 'm' (即,将所有 'f' 变为 'm' ,反之亦然),仅使用 单个 update 语句 ,且不产生中间临时表。
注意,你必须仅使用一条 update 语句,且 不能 使用 select 语句。
update Salary
set sex = if(sex='m','f','m')17. 1050. 合作过至少三次的演员和导演
group by两个参数
编写解决方案找出合作过至少三次的演员和导演的 id 对 (actor_id, director_id)

# Write your MySQL query statement below
select Ac.actor_id,Ac.director_id from ActorDirector as Ac
group by Ac.actor_id,Ac.director_id
having count(*)>=318. 1068. 产品销售分析 I
送分题
select p.product_name,s.year,s.price from Sales as s left join Product as p on s.product_id=p.product_id19. 1084. 销售分析III
日期比较
即仅在2019-01-01至2019-03-31(含)之间出售的商品。

# Write your MySQL query statement below
select t.product_id,p.product_name from (
select s.product_id from Sales as s
group by s.product_id having max(s.sale_date)<'2019-04-01' and min(s.sale_date)>='2019-01-01'
) as t left join Product as p on t.product_id=p.product_id20. 1075. 项目员工 I
小数点位数 round(x,2)
Project 表:
+-------------+-------------+
| project_id | employee_id |
+-------------+-------------+
| 1 | 1 |
| 1 | 2 |
| 1 | 3 |
| 2 | 1 |
| 2 | 4 |
+-------------+-------------+
Employee 表:
+-------------+--------+------------------+
| employee_id | name | experience_years |
+-------------+--------+------------------+
| 1 | Khaled | 3 |
| 2 | Ali | 2 |
| 3 | John | 1 |
| 4 | Doe | 2 |
+-------------+--------+------------------+
Result 表:
+-------------+---------------+
| project_id | average_years |
+-------------+---------------+
| 1 | 2.00 |
| 2 | 2.50 |
+-------------+---------------+
第一个项目中,员工的平均工作年限是 (3 + 2 + 1) / 3 = 2.00;第二个项目中,员工的平均工作年限是 (3 + 2) / 2 = 2.50select p.project_id,round(avg(e.experience_years),2) as average_years from Project as p join Employee as e on p.employee_id=e.employee_id
group by p.project_id21. 1141. 查询近30天活跃用户数
编写解决方案,统计截至 2019-07-27(包含2019-07-27),近 30 天的每日活跃用户数(当天只要有一条活动记录,即为活跃用户)
输入:
Activity table:
+---------+------------+---------------+---------------+
| user_id | session_id | activity_date | activity_type |
+---------+------------+---------------+---------------+
| 1 | 1 | 2019-07-20 | open_session |
| 1 | 1 | 2019-07-20 | scroll_down |
| 1 | 1 | 2019-07-20 | end_session |
| 2 | 4 | 2019-07-20 | open_session |
| 2 | 4 | 2019-07-21 | send_message |
| 2 | 4 | 2019-07-21 | end_session |
| 3 | 2 | 2019-07-21 | open_session |
| 3 | 2 | 2019-07-21 | send_message |
| 3 | 2 | 2019-07-21 | end_session |
| 4 | 3 | 2019-06-25 | open_session |
| 4 | 3 | 2019-06-25 | end_session |
+---------+------------+---------------+---------------+
输出:
+------------+--------------+
| day | active_users |
+------------+--------------+
| 2019-07-20 | 2 |
| 2019-07-21 | 2 |
+------------+--------------+ select day,count(active_users) as active_users from (
select distinct a.activity_date as day,a.user_id as active_users from Activity as a
where a.activity_date>'2019-06-27' and a.activity_date<'2019-07-28'
)as t
group by day 22. 1148. 文章浏览 I
请查询出所有浏览过自己文章的作者
秒了
输入:
Views 表:
+------------+-----------+-----------+------------+
| article_id | author_id | viewer_id | view_date |
+------------+-----------+-----------+------------+
| 1 | 3 | 5 | 2019-08-01 |
| 1 | 3 | 6 | 2019-08-02 |
| 2 | 7 | 7 | 2019-08-01 |
| 2 | 7 | 6 | 2019-08-02 |
| 4 | 7 | 1 | 2019-07-22 |
| 3 | 4 | 4 | 2019-07-21 |
| 3 | 4 | 4 | 2019-07-21 |
+------------+-----------+-----------+------------+
输出:
+------+
| id |
+------+
| 4 |
| 7 |
+------+select distinct v.viewer_id as id from Views as v
where v.author_id=v.viewer_id
order by id🦍23. 1179. 重新格式化部门表
行转列暴力解法

SELECT
DISTINCT
a.id,
Jan.revenue AS Jan_Revenue,
Feb.revenue AS Feb_Revenue,
Mar.revenue AS Mar_Revenue,
Apr.revenue AS Apr_Revenue,
May.revenue AS May_Revenue,
Jun.revenue AS Jun_Revenue,
Jul.revenue AS Jul_Revenue,
Aug.revenue AS Aug_Revenue,
Sep.revenue AS Sep_Revenue,
Octo.revenue AS Oct_Revenue,
Nov.revenue AS Nov_Revenue,
Dece.revenue AS Dec_Revenue
FROM
Department a LEFT JOIN Department Jan ON a.id = Jan.id
AND
Jan.month = 'Jan'LEFT JOIN Department Feb ON a.id = Feb.id
AND
Feb.month = 'Feb' LEFT JOIN Department Mar ON a.id = Mar.id
AND
Mar.month = 'Mar' LEFT JOIN Department Apr ON a.id = Apr.id
AND
Apr.month = 'Apr' LEFT JOIN Department May ON a.id = May.id
AND
May.month = 'May' LEFT JOIN Department Jun ON a.id = Jun.id
AND
Jun.month = 'Jun' LEFT JOIN Department Jul ON a.id = Jul.id
AND
Jul.month = 'Jul' LEFT JOIN Department Aug ON a.id = Aug.id
AND
Aug.month = 'Aug' LEFT JOIN Department Sep ON a.id = Sep.id
AND
Sep.month = 'Sep' LEFT JOIN Department Octo ON a.id = Octo.id
AND
Octo.month = 'Oct'LEFT JOIN Department Nov ON a.id = Nov.id
AND
Nov.month = 'Nov' LEFT JOIN Department Dece ON a.id = Dece.id
AND
Dece.month = 'Dec'当一个单元格中有多个数据时,case when只会提取当中的第一个数据。
那该如何解决单元格内含多个数据的情况呢?答案就是使用聚合函数,聚合函数就用来输入多个数据,输出一个数据的。如SUM()或MAX(),而每个聚合函数的输入就是每一个多数据的单元格。
24. 1211. 查询结果的质量和占比
分组后求算式
将查询结果的质量 quality 定义为:
各查询结果的评分与其位置之间比率的平均值。
将劣质查询百分比 poor_query_percentage 为:
评分小于 3 的查询结果占全部查询结果的百分比。
输入:
Queries table:
+------------+-------------------+----------+--------+
| query_name | result | position | rating |
+------------+-------------------+----------+--------+
| Dog | Golden Retriever | 1 | 5 |
| Dog | German Shepherd | 2 | 5 |
| Dog | Mule | 200 | 1 |
| Cat | Shirazi | 5 | 2 |
| Cat | Siamese | 3 | 3 |
| Cat | Sphynx | 7 | 4 |
+------------+-------------------+----------+--------+
输出:
+------------+---------+-----------------------+
| query_name | quality | poor_query_percentage |
+------------+---------+-----------------------+
| Dog | 2.50 | 33.33 |
| Cat | 0.66 | 33.33 |
+------------+---------+-----------------------+
解释:
Dog 查询结果的质量为 ((5 / 1) + (5 / 2) + (1 / 200)) / 3 = 2.50
Dog 查询结果的劣质查询百分比为 (1 / 3) * 100 = 33.33
Cat 查询结果的质量为 ((2 / 5) + (3 / 3) + (4 / 7)) / 3 = 0.66
Cat 查询结果的劣质查询百分比为 (1 / 3) * 100 = 33.33select query_name,round(avg(rating/position),2) as quality,round(sum(if(rating<3,1,0))/count(rating)*100,2) as poor_query_percentage
from Queries
group by query_name 25. 1251. 平均售价
ifnull(算式,空时的值)
计算题
示例 1:
输入:
Prices table:
+------------+------------+------------+--------+
| product_id | start_date | end_date | price |
+------------+------------+------------+--------+
| 1 | 2019-02-17 | 2019-02-28 | 5 |
| 1 | 2019-03-01 | 2019-03-22 | 20 |
| 2 | 2019-02-01 | 2019-02-20 | 15 |
| 2 | 2019-02-21 | 2019-03-31 | 30 |
+------------+------------+------------+--------+
UnitsSold table:
+------------+---------------+-------+
| product_id | purchase_date | units |
+------------+---------------+-------+
| 1 | 2019-02-25 | 100 |
| 1 | 2019-03-01 | 15 |
| 2 | 2019-02-10 | 200 |
| 2 | 2019-03-22 | 30 |
+------------+---------------+-------+
输出:
+------------+---------------+
| product_id | average_price |
+------------+---------------+
| 1 | 6.96 |
| 2 | 16.96 |
+------------+---------------+
解释:
平均售价 = 产品总价 / 销售的产品数量。
产品 1 的平均售价 = ((100 * 5)+(15 * 20) )/ 115 = 6.96
产品 2 的平均售价 = ((200 * 15)+(30 * 30) )/ 230 = 16.96# Write your MySQL query statement below
select p.product_id as product_id,ifnull(round(sum(u.units*p.price) / sum(u.units),2),0) as average_price
from Prices as p left join UnitsSold as u
on u.purchase_date <= p.end_date and u.purchase_date>=p.start_date and u.product_id=p.product_id
group by p.product_id26. 1280. 学生们参加各科测试的次数
连接多
查询出每个学生参加每一门科目测试的次数,结果按 student_id 和 subject_name 排序。
查询结构格式如下所示。
示例 1:
输入:
Students table:
+------------+--------------+
| student_id | student_name |
+------------+--------------+
| 1 | Alice |
| 2 | Bob |
| 13 | John |
| 6 | Alex |
+------------+--------------+
Subjects table:
+--------------+
| subject_name |
+--------------+
| Math |
| Physics |
| Programming |
+--------------+
Examinations table:
+------------+--------------+
| student_id | subject_name |
+------------+--------------+
| 1 | Math |
| 1 | Physics |
| 1 | Programming |
| 2 | Programming |
| 1 | Physics |
| 1 | Math |
| 13 | Math |
| 13 | Programming |
| 13 | Physics |
| 2 | Math |
| 1 | Math |
+------------+--------------+
输出:
+------------+--------------+--------------+----------------+
| student_id | student_name | subject_name | attended_exams |
+------------+--------------+--------------+----------------+
| 1 | Alice | Math | 3 |
| 1 | Alice | Physics | 2 |
| 1 | Alice | Programming | 1 |
| 2 | Bob | Math | 1 |
| 2 | Bob | Physics | 0 |
| 2 | Bob | Programming | 1 |
| 6 | Alex | Math | 0 |
| 6 | Alex | Physics | 0 |
| 6 | Alex | Programming | 0 |
| 13 | John | Math | 1 |
| 13 | John | Physics | 1 |
| 13 | John | Programming | 1 |
+------------+--------------+--------------+----------------+
解释:
结果表需包含所有学生和所有科目(即便测试次数为0):
Alice 参加了 3 次数学测试, 2 次物理测试,以及 1 次编程测试;
Bob 参加了 1 次数学测试, 1 次编程测试,没有参加物理测试;
Alex 啥测试都没参加;
John 参加了数学、物理、编程测试各 1 次。select tem.student_id,tem.student_name,tem.subject_name,sum(if (tem.subject_name=cishu.subject_name,1,0)) as attended_exams from (
select stu.student_id as student_id,stu.student_name as student_name,sub.subject_name as subject_name from Students as stu join Subjects as sub
) as tem left join Examinations as cishu on tem.student_id=cishu.student_id and tem.subject_name=cishu.subject_name
group by tem.student_id,tem.subject_name
order by tem.student_id,tem.subject_name27. 1327. 列出指定时间段内所有的下单产品
日期函数YEAR()
select p.product_name,t.unit from (
select product_id,sum(unit) unit from Orders
where MONTH(order_date)=2 and YEAR(order_date)=2020
group by product_id
having sum(unit)>=100
)as t left join Products as p on t.product_id=p.product_id28. 1378. 使用唯一标识码替换员工ID
秒了送分题
select uni.unique_id as unique_id,e.name from Employees as e left join EmployeeUNI as uni on e.id=uni.id29. 1407. 排名靠前的旅行者
陷阱
编写解决方案,报告每个用户的旅行距离。
返回的结果表单,以 travelled_distance 降序排列 ,如果有两个或者更多的用户旅行了相同的距离, 那么再以 name 升序排列 。
返回结果格式如下例所示。
示例 1:
输入:
Users 表:
+------+-----------+
| id | name |
+------+-----------+
| 1 | Alice |
| 2 | Bob |
| 3 | Alex |
| 4 | Donald |
| 7 | Lee |
| 13 | Jonathan |
| 19 | Elvis |
+------+-----------+
Rides 表:
+------+----------+----------+
| id | user_id | distance |
+------+----------+----------+
| 1 | 1 | 120 |
| 2 | 2 | 317 |
| 3 | 3 | 222 |
| 4 | 7 | 100 |
| 5 | 13 | 312 |
| 6 | 19 | 50 |
| 7 | 7 | 120 |
| 8 | 19 | 400 |
| 9 | 7 | 230 |
+------+----------+----------+
输出:
+----------+--------------------+
| name | travelled_distance |
+----------+--------------------+
| Elvis | 450 |
| Lee | 450 |
| Bob | 317 |
| Jonathan | 312 |
| Alex | 222 |
| Alice | 120 |
| Donald | 0 |
+----------+--------------------+# Write your MySQL query statement below
select user.name name,IFNULL(sum(distance),0) travelled_distance
from Users user left join Rides r on r.user_id = user.id
group by user.id
order by travelled_distance desc,name30. 1484. 按日期分组销售产品
group_concat(distinct product)
select sell_date,count(distinct product) num_sold,group_concat(distinct product) products from Activities
group by sell_date
GROUP_CONCAT是 MySQL 中的聚合函数,用于将分组后的结果集中的多个行合并成一个字符串,并以指定的分隔符分隔它们。它的一般语法如下:GROUP_CONCAT(column_name [ORDER BY column_name] [SEPARATOR separator])
column_name:要合并的列的名称。ORDER BY column_name:可选,用于指定如何对合并的值进行排序。SEPARATOR separator:可选,用于指定合并后的字符串中的分隔符。以下是一个示例,假设我们有一个名为 "students" 的表,其中包含学生的姓名,并且每个学生都属于一个特定的班级:
SELECT class_id, GROUP_CONCAT(student_name ORDER BY student_name SEPARATOR ',') AS students FROM students GROUP BY class_id;

31. 1527. 患某种疾病的患者
字符串占位符
查询患有 I 类糖尿病的患者 ID (patient_id)、患者姓名(patient_name)以及其患有的所有疾病代码(conditions)。I 类糖尿病的代码总是包含前缀 DIAB1 。
按 任意顺序 返回结果表。
查询结果格式如下示例所示。
示例 1:
输入:
Patients表:
+------------+--------------+--------------+
| patient_id | patient_name | conditions |
+------------+--------------+--------------+
| 1 | Daniel | YFEV COUGH |
| 2 | Alice | |
| 3 | Bob | DIAB100 MYOP |
| 4 | George | ACNE DIAB100 |
| 5 | Alain | DIAB201 |
+------------+--------------+--------------+
输出:
+------------+--------------+--------------+
| patient_id | patient_name | conditions |
+------------+--------------+--------------+
| 3 | Bob | DIAB100 MYOP |
| 4 | George | ACNE DIAB100 |
+------------+--------------+--------------+
解释:Bob 和 George 都患有代码以 DIAB1 开头的疾病。select * from Patients
where conditions like 'DIAB1%' or conditions like '% DIAB1%'
32. 1587. 银行账户概要 II
送分题
select Users.name as NAME,tem.BALANCE from (
select account, sum(amount) as BALANCE from Transactions as t
group by account
having sum(amount)>10000) as tem join Users on tem.account=Users.account 33. 1581. 进店却未进行过交易的顾客
null统计不到个数,要使用count(*)
有一些顾客可能光顾了购物中心但没有进行交易。请你编写一个解决方案,来查找这些顾客的 ID ,以及他们只光顾不交易的次数。
返回以 任何顺序 排序的结果表。
返回结果格式如下例所示。
示例 1:
输入:
Visits
+----------+-------------+
| visit_id | customer_id |
+----------+-------------+
| 1 | 23 |
| 2 | 9 |
| 4 | 30 |
| 5 | 54 |
| 6 | 96 |
| 7 | 54 |
| 8 | 54 |
+----------+-------------+
Transactions
+----------------+----------+--------+
| transaction_id | visit_id | amount |
+----------------+----------+--------+
| 2 | 5 | 310 |
| 3 | 5 | 300 |
| 9 | 5 | 200 |
| 12 | 1 | 910 |
| 13 | 2 | 970 |
+----------------+----------+--------+
输出:
+-------------+----------------+
| customer_id | count_no_trans |
+-------------+----------------+
| 54 | 2 |
| 30 | 1 |
| 96 | 1 |
+-------------+----------------+
解释:
ID = 23 的顾客曾经逛过一次购物中心,并在 ID = 12 的访问期间进行了一笔交易。
ID = 9 的顾客曾经逛过一次购物中心,并在 ID = 13 的访问期间进行了一笔交易。
ID = 30 的顾客曾经去过购物中心,并且没有进行任何交易。
ID = 54 的顾客三度造访了购物中心。在 2 次访问中,他们没有进行任何交易,在 1 次访问中,他们进行了 3 次交易。
ID = 96 的顾客曾经去过购物中心,并且没有进行任何交易。
如我们所见,ID 为 30 和 96 的顾客一次没有进行任何交易就去了购物中心。顾客 54 也两次访问了购物中心并且没有进行任何交易。select v.customer_id,count(*) as count_no_trans from Visits as v left join Transactions as t on v.visit_id=t.visit_id
where t.transaction_id is null
group by v.customer_id34. 1517. 查找拥有有效邮箱的用户
正则表达式!🌿!
select * from Users
where mail regexp '^[a-zA-Z]+[a-zA-Z0-9_\\.\\/\\-]*@leetcode\\.com$';35. 1633. 各赛事的用户注册率
算数
select contest_id,round(100*count(user.user_name)/(select count(*) from Users),2) as percentage
from Register as re left join Users as user on re.user_id = user.user_id
group by re.contest_id
order by percentage desc,contest_id36. 1661. 每台机器的进程平均运行时间
作差,思路清奇
输入:
Activity table:
+------------+------------+---------------+-----------+
| machine_id | process_id | activity_type | timestamp |
+------------+------------+---------------+-----------+
| 0 | 0 | start | 0.712 |
| 0 | 0 | end | 1.520 |
| 0 | 1 | start | 3.140 |
| 0 | 1 | end | 4.120 |
| 1 | 0 | start | 0.550 |
| 1 | 0 | end | 1.550 |
| 1 | 1 | start | 0.430 |
| 1 | 1 | end | 1.420 |
| 2 | 0 | start | 4.100 |
| 2 | 0 | end | 4.512 |
| 2 | 1 | start | 2.500 |
| 2 | 1 | end | 5.000 |
+------------+------------+---------------+-----------+
输出:
+------------+-----------------+
| machine_id | processing_time |
+------------+-----------------+
| 0 | 0.894 |
| 1 | 0.995 |
| 2 | 1.456 |
+------------+-----------------+
解释:
一共有3台机器,每台机器运行着两个进程.
机器 0 的平均耗时: ((1.520 - 0.712) + (4.120 - 3.140)) / 2 = 0.894
机器 1 的平均耗时: ((1.550 - 0.550) + (1.420 - 0.430)) / 2 = 0.995select machine_id,round(sum(if(activity_type='start',-timestamp,timestamp))/(0.5*count(process_id)),3) as processing_time from Activity
group by machine_id37. 1667. 修复表中的名字
大小写转换
# Write your MySQL query statement below
select user_id, concat(upper(left(name,1)),lower(right(name,length(name)-1))) as name from Users
order by user_id 38. 1683. 无效的推文
送分题
select tweet_id from Tweets
where length(content)>1539. 1693. 每天的领导和合伙人
好几个去重
其实没必要对日期去重,后面的已经去过了
# Write your MySQL query statement below
select distinct date_id,make_name,count(distinct lead_id) unique_leads,count(distinct partner_id) unique_partners from DailySales
group by date_id,make_name40. 1729. 求关注者的数量
送
select user_id,count(follower_id) as followers_count from Followers
group by user_id
order by user_id41. 1731. 每位经理的下属员工数量
对于此问题,我们将至少有一个其他员工需要向他汇报的员工,视为一个经理。
编写SQL查询需要听取汇报的所有经理的ID、名称、直接向该经理汇报的员工人数,以及这些员工的平均年龄,其中该平均年龄需要四舍五入到最接近的整数。
返回的结果集需要按照 employee_id 进行排序。
查询结果的格式如下:
Employees table:
+-------------+---------+------------+-----+
| employee_id | name | reports_to | age |
+-------------+---------+------------+-----+
| 9 | Hercy | null | 43 |
| 6 | Alice | 9 | 41 |
| 4 | Bob | 9 | 36 |
| 2 | Winston | null | 37 |
+-------------+---------+------------+-----+
Result table:
+-------------+-------+---------------+-------------+
| employee_id | name | reports_count | average_age |
+-------------+-------+---------------+-------------+
| 9 | Hercy | 2 | 39 |
+-------------+-------+---------------+-------------+
Hercy 有两个需要向他汇报的员工, 他们是 Alice and Bob. 他们的平均年龄是 (41+36)/2 = 38.5, 四舍五入的结果是 39.select tem.id1 employee_id,tem.name1 name,count(tem.id2) reports_count,round(avg(tem.age2),0) average_age from
(select e1.employee_id id1,e1.name name1,e1.reports_to to1,e1.age age1,
e2.employee_id id2,e2.name name2,e2.reports_to to2,e2.age age2 from Employees as e1 left join Employees as e2 on e1.employee_id=e2.reports_to
where e2.employee_id is not null) tem
group by tem.id1
order by employee_id42. 1741. 查找每个员工花费的总时间
送分
select event_day day, emp_id,sum(out_time-in_time) total_time from Employees
group by event_day,emp_id43. 1757. 可回收且低脂的产品
送分
select product_id from Products
where low_fats='Y' and recyclable='Y'44. 1789. 员工的直属部门
union
select employee_id, min(department_id) department_id from Employee
group by employee_id
having count(primary_flag) = 1
union
select employee_id, department_id from Employee
where primary_flag = 'Y'45.🦍 1795. 每个产品在不同商店的价格
请你重构 Products 表,查询每个产品在不同商店的价格,使得输出的格式变为(product_id, store, price) 。如果这一产品在商店里没有出售,则不输出这一行。
输出结果表中的 顺序不作要求 。
查询输出格式请参考下面示例。
示例 1:
输入:
Products table:
+------------+--------+--------+--------+
| product_id | store1 | store2 | store3 |
+------------+--------+--------+--------+
| 0 | 95 | 100 | 105 |
| 1 | 70 | null | 80 |
+------------+--------+--------+--------+
输出:
+------------+--------+-------+
| product_id | store | price |
+------------+--------+-------+
| 0 | store1 | 95 |
| 0 | store2 | 100 |
| 0 | store3 | 105 |
| 1 | store1 | 70 |
| 1 | store3 | 80 |
+------------+--------+-------+
解释:
产品 0 在 store1、store2、store3 的价格分别为 95、100、105。
产品 1 在 store1、store3 的价格分别为 70、80。在 store2 无法买到。行列转换
# Write your MySQL query statement below
select product_id, 'store1' as store, store1 as price from Products where store1 is not null
union all
select product_id, 'store2' as store, store2 as price from Products where store2 is not null
union all
select product_id, 'store3' as store, store3 as price from Products where store3 is not null 
46. 1873. 计算特殊奖金
if嵌套
select employee_id,if(employee_id%2=1,if(left(name,1)!='M',salary,0),0) bonus from Employees
order by employee_id47. 1890. 2020年最后一次登录
送
select user_id ,max(time_stamp) last_stamp from Logins
where time_stamp>='2020-01-01 00:00:00' and time_stamp<='2020-12-31 23:59:59'
group by user_id 48.1965. 丢失信息的雇员
第七穿插连
select employee_id from Employees where employee_id not in (select employee_id from salaries)
union
select employee_id from Salaries where employee_id not in (select employee_id from Employees)
order by employee_id49. 1978. 上级经理已离职的公司员工
查找这些员工的id,他们的薪水严格少于$30000 并且他们的上级经理已离职。当一个经理离开公司时,他们的信息需要从员工表中删除掉,但是表中的员工的manager_id 这一列还是设置的离职经理的id 。
返回的结果按照employee_id 从小到大排序。
查询结果如下所示:
示例:
输入:
Employees table:
+-------------+-----------+------------+--------+
| employee_id | name | manager_id | salary |
+-------------+-----------+------------+--------+
| 3 | Mila | 9 | 60301 |
| 12 | Antonella | null | 31000 |
| 13 | Emery | null | 67084 |
| 1 | Kalel | 11 | 21241 |
| 9 | Mikaela | null | 50937 |
| 11 | Joziah | 6 | 28485 |
+-------------+-----------+------------+--------+
输出:
+-------------+
| employee_id |
+-------------+
| 11 |
+-------------+
解释:
薪水少于 30000 美元的员工有 1 号(Kalel) 和 11号 (Joziah)。
Kalel 的上级经理是 11 号员工,他还在公司上班(他是 Joziah )。
Joziah 的上级经理是 6 号员工,他已经离职,因为员工表里面已经没有 6 号员工的信息了,它被删除了。表述不清
select e.employee_id
from Employees e
left join Employees ee
on e.manager_id = ee.employee_id
where e.manager_id is not null and ee.employee_id is null and e.salary < 30000
order by e.employee_id50. 2356. 每位教师所教授的科目种类的数量
送
select teacher_id,count(distinct subject_id) cnt from Teacher
group by teacher_id