这里写目录标题
- 一、所谓跨域:
- 二、不做任何处理
- 三、解决跨域请求
- 案例 一
- 案例 二
一、所谓跨域:
在前后端分离的项目中,前台一个服务,后台一个服务。
前台的一个Axios请求打进来,要访问后台Tomcat服务器Restful接口
浏览器出于安全的考虑,使用 XMLHttpRequest对象发起 HTTP请求时必须遵守同源策略
在默认的情况下跨域是被禁止。
IP不同或者端口号不同就是跨域
二、不做任何处理
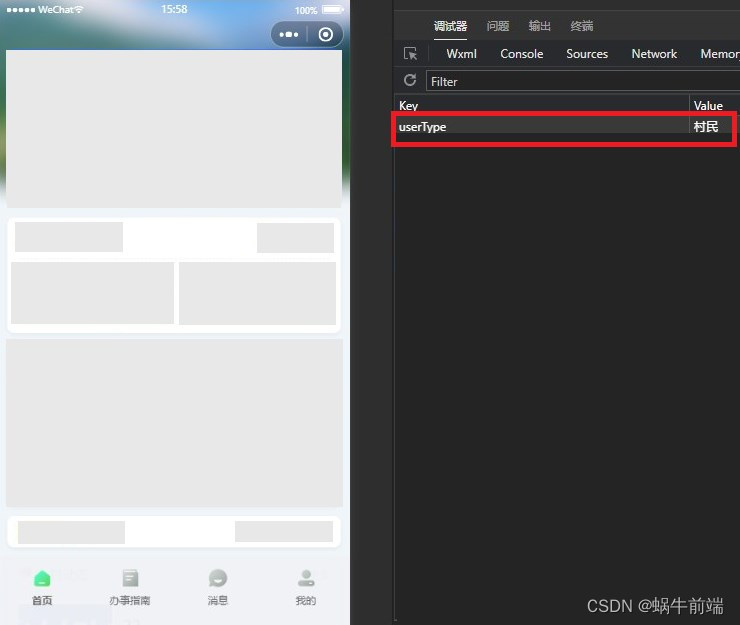
前后端交互的时候 跨域问题
已拦截跨源请求:同源策略禁止读取位于 http://localhost:8080/的远程资源。(原因:CORS
12打开后会发现控制台已经报错 Access-Control-Allow-Origin
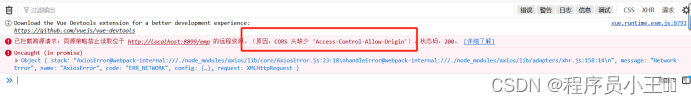
也就是说跨域的本质是靠Http的Header头中的Access-Control-Allow-Origin来实现跨域的
三、解决跨域请求
这两个用哪个都可以
案例 一
package com.aaa.common;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.web.servlet.config.annotation.CorsRegistry;
import org.springframework.web.servlet.config.annotation.WebMvcConfigurer;
// 案例 一 跨域请求
@Configuration
public class CorsConfig implements WebMvcConfigurer {
@Override
public void addCorsMappings(CorsRegistry registry) {
// 添加映射路径,“/”表示所有的路径都会被映射到该配置下。
registry.addMapping("/**")
//是否发送Cookie
.allowCredentials(true)
//放行哪些原始域
.allowedOriginPatterns("*")
// 允许的请求方法,包括GET、POST、PUT和DELETE。
.allowedMethods(new String[]{"GET", "POST", "PUT", "DELETE"})
// 允许的请求头信息,即任何请求头都允许。
.allowedHeaders("*")
// 允许的响应头信息,即任何响应头都允许。
.exposedHeaders("*");
}
}
案例 二
package com.aaa.common;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.web.servlet.config.annotation.CorsRegistry;
import org.springframework.web.servlet.config.annotation.WebMvcConfigurer;
// 案例 一 跨域请求
@Configuration
public class CorsConfig implements WebMvcConfigurer {
@Configuration
public class CorsConfig {
@Bean
public WebMvcConfigurer corsConfigurer() {
return new WebMvcConfigurer() {
@Override
public void addCorsMappings(CorsRegistry registry) {
registry.addMapping("/**")
.allowedOriginPatterns("*") // 修改为您允许的请求源
.allowCredentials(true)
.allowedMethods("*")
.allowedHeaders("*");
}
};
}
}