目录
一、委托和lambda表达式
1.1 委托概述
1.2 委托类型的声明
1.3 委托的实例化
1.4 委托的内部机制
1.5 Lambda 表达式
1.6 语句lambda
1.7 表达式lambda
1.8 Lambda表达式
1.9 通用的委托
1.10 委托没有结构相等性
1.11 Lambda表达式和匿名方法的内部机制
1.12 外部变量
1.13 外部变量的CIL实现
二、事件
2.1 多播委托
2.2 使用多播委托来编码Observer模式
2.3 委托操作符
2.4 错误处理
2.5 事件的作用
2.6 事件的声明
2.7 编码规范
2.8 事件的内部机制
2.9 自定义事件的实现
一、委托和lambda表达式
1.1 委托概述
C/C++ 利用”函数指针”将方法的引用作为实参传给另一个方法。 C# 利用委托提供相同的功能。委托允许捕获对方法的引用,并像传递其他对象那样传递这个引用,像调用其他方法那样调用这个被捕获的方法。 例如:
public static void BubbleSort(int[] items, ComparisonHandler comparisonMethod)
{
int i, j, temp;
if(comparisonMethod == null)
throw new ArgumentNullException("comparisonMethod");
if(items == null)
return;
for(i = items.Length - 1; i >= 0; i--)
{
for(j = 1; j <= i; j++)
{
if(comparisonMethod(items[j - 1], items[j]))
{
temp = items[j - 1];
items[j - 1] = items[j];
items[j] = temp;
}
}
}
}1.2 委托类型的声明
为了声明委托,要使用delegate 关键字,后面跟着方法的签名。这个方法的签名是委托所引用的方法的签名。 例如:
public delegate bool ComparisonHandler(int first, int second);
委托可以嵌套在类中。 假如委托声明出现在另一个类的内部,则委托类型就会成为嵌套类型。
class DelegateSample
{
public delegate bool ComparisonHandler(int first, int second);
}
1.3 委托的实例化
为了实例化委托,需要一个和委托类型自身签名匹配的方法。 例如:
public delegate bool ComparisonHandler(int first, int second);
class DelegateSample
{
public static void BubbleSort(int[] items, ComparisonHandler comparisonMethod)
{
//…
}
public static bool GreaterThan(int first, int second)
{
return first > second;
}
static void Main()
{
int i;
int[] items = new int[5];
for(i = 0; i < items.Length; i++)
{
Console.Write("Enter an integer: ");
items[i] = int.Parse(Console.ReadLine());
}
BubbleSort(items, GreaterThan);
for(i = 0; i < items.Length; i++)
Console.WriteLine(items[i]);
}
}
1.4 委托的内部机制
委托是特殊的类,.Net 中的委托类型总是派生自System.MulticastDelegate, 后者又从 System.Delegate 派生。

C# 编译器不允许声明直接或间接从System.Delegate 或者System.MulicastDelegate 派生的类。
1.5 Lambda 表达式
C#2.0 引入非常精简的语法创建委托,相关的特性被称为匿名方法。 C# 3.0 相关的特性称为Lambda 表达式。这两种语法统称 匿名函数。Lambda 表达式本身分为两种类型: 语句lambda和表达式 lambda。

1.6 语句lambda
语句lambda 由形参列表,后面跟lambda 操作符=>, 然后跟一个代码块构成。 例如:
public class DelegateSample
{
//…..
public static void Main()
{
int i;
int[] items = new int[5];
for(i = 0; i < items.Length; i++)
{
Console.Write("Enter an integer: ");
items[i] = int.Parse(Console.ReadLine());
}
BubbleSort(items, (int first, int second) => { return first < second;});
for(i = 0; i < items.Length; i++)
{
Console.WriteLine(items[i]);
}
}
}
当编译器能从Lambda表达式转换成的委托推断出类型,所有Lambda都不需要显式声明参数类型。 在不能推断出类型时,C#要求显式指定Lambda类型。只要显式指定了一个Lambda参数类型,所有参数类型都必须被显式指定, 例如:
public static void ChapterMain()
{
int i;
int[] items = new int[5];
for(i = 0; i < items.Length; i++)
{
Console.Write("Enter an integer:");
items[i] = int.Parse(Console.ReadLine());
}
DelegateSample.BubbleSort(items, (first, second) => { return first < second;});
for(i = 0; i < items.Length; i++)
{
Console.WriteLine(items[i]);
}
}
当只有单个参数,而且类型可以推断时,这种Lambda 表达式可省略围绕参数列表的圆括号。如果Lambda没有参数, 或者有不止一个参数,或者显式指定了类型的单个参数,那么就必须将参数列表放到圆括号中。 例如:
public class Program
{
public static void ChapterMain()
{
IEnumerable<Process> processes = Process.GetProcesses().Where(
process => { return process.WorkingSet64 > 1000000000; });
}
}
无参数的语句Lambda
public static void ChapterMain()
{
Func<string> getUserInput = () =>
{
string input;
do
{
input = Console.ReadLine();
}
while(input.Trim().Length == 0);
return input;
};
}
1.7 表达式lambda
表达式lambda只有要返回的表达式,完全没有语句块。例如:
public static void Main()
{
int i;
int[] items = new int[5];
for(i = 0; i < items.Length; i++)
{
Console.Write("Enter an integer:");
items[i] = int.Parse(Console.ReadLine());
}
DelegateSample.BubbleSort(items, (first, second) => first < second);
for(i = 0; i < items.Length; i++)
{
Console.WriteLine(items[i]);
}
}
和null字面量相似,匿名函数不与任何类型关联。它的类型由它将要转换成的类型决定。所以不能对一个匿名方法使用typeof()操作符。另外,只有将匿名方法转换成一个特定类型后才能调用GetType
1.8 Lambda表达式
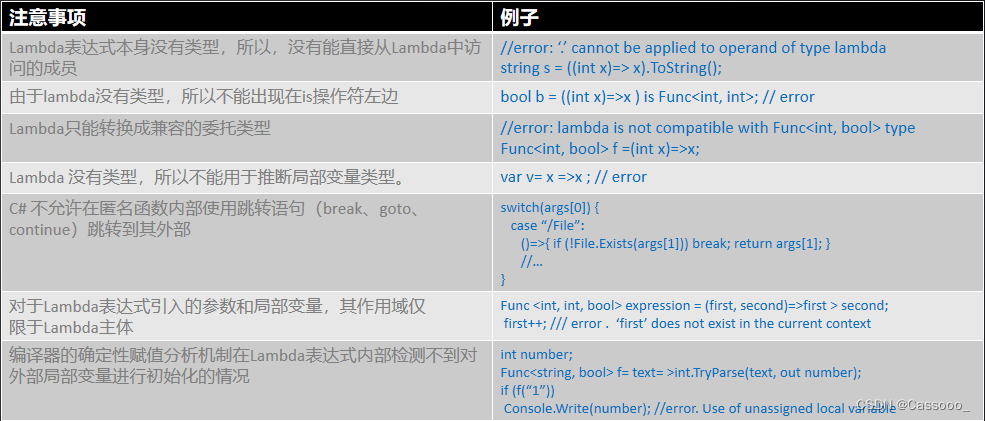
1.9 通用的委托
.Net 3.5 包含了一组通用的委托。System.Func 系列委托代表有返回值方法,而System.Action 系列委托代表返回void 的方法。Func 委托的最后一个参数总是委托的返回类型,其他参数依次对应于委托参数的类型。
//public delegate void Action();
//public delegate void Action<in T>(T arg);
//public delegate void Action<in T1, in T2>(T1 arg1, T2 arg2);
//public delegate void Action<in T1, in T2, in T3>(T1 arg1, T2 arg2, T3 arg3);
//public delegate void Action<in T1, in T2, in T3, in T4>(T1 arg1, T2 arg2, T3 arg3, T4 arg4);
// ...
//public delegate void Action<in T1, in T2, in T3, in T4, in T5, in T6, in T7, in T8, in T9, in T10, in T11, in T12, in T13, in T14, in T15, in T16>(
// T1 arg1, T2 arg2, T3 arg3, T4 arg4, T5 arg5, T6 arg6, T7 arg7, T8 arg8, T9 arg9, T10 arg10, T11 arg11, T12 arg12,
// T13 arg13, T14 arg14, T15 arg15, T16 arg16);
//public delegate TResult Func<out TResult>();
//public delegate TResult Func<in T, out TResult>(T arg);
//public delegate TResult Func<in T1, in T2, out TResult>(T1 arg1, T2 arg2);
//public delegate TResult Func<in T1, in T2, in T3, out TResult>(T1 arg1, T2 arg2, T3 arg3);
//public delegate TResult Func<in T1, in T2, in T3, in T4, out TResult>(T1 arg1, T2 arg2, T3 arg3, T4 arg4);
// ...
//public delegate TResult Func< in T1, in T2, in T3, in T4, in T5, in T6, in T7, in T8, in T9, in T10, in T11, in T12, in T13, in T14, in T15, in T16,
// out TResult>(T1 arg1, T2 arg2, T3 arg3, T4 arg4, T5 arg5, T6 arg6, T7 arg7, T8 arg8, T9 arg9, T10 arg10, T11 arg11, T12 arg12,
// T13 arg13, T14 arg14, T15 arg15, T16 arg16);
在许多情况下,.NET 3.5 添加的Func 委托能完全避免定义自己的委托类型。例如:
public static void BubbleSort(int[] items, Func<int, int, bool> comparisonMethod)
1.10 委托没有结构相等性
.NET 委托类型不具备结构相等性。也就是说,不能将某个委托类型的对象转换成不相关的委托类型,即使这两个委托类型的形参和返回类型完全一致。 然而,通过C# 4.0 添加的对可变性的支持,可以在某些引用类型之间进行引用转换。
public static void ChapterMain()
{
// Contravariance
Action<object> broadAction =
(object data) =>
{
Console.WriteLine(data);
};
Action<string> narrowAction = broadAction;
// Covariance
Func<string> narrowFunction =
() => Console.ReadLine();
Func<object> broadFunction = narrowFunction;
// Contravariance and covariance combined
Func<object, string> func1 =
(object data) => data.ToString();
Func<string, object> func2 = func1;
}
1.11 Lambda表达式和匿名方法的内部机制
当编译器遇到匿名方法时, 会把它转换为特殊的隐藏的类,字段和方法。 例如:
public static void Main()
{
int i;
int[] items = new int[5];
for(i = 0; i < items.Length; i++)
{
Console.Write("Enter an integer:");
items[i] = int.Parse(Console.ReadLine());
}
BubbleSort(items, DelegateSample.__AnonymousMethod_00000000);
for(i = 0; i < items.Length; i++)
{
Console.WriteLine(items[i]);
}
}
private static bool __AnonymousMethod_00000000(int first, int second)
{
return first < second;
}
1.12 外部变量
在Lambda表达式外部声明的局部变量称为表达式的外部变量。当Lambda主体使用一个外部变量时, 就说该变量被这个lambda捕获
public static void ChapterMain()
{
int i;
int[] items = new int[5];
int comparisonCount = 0;
for(i = 0; i < items.Length; i++)
{
Console.Write("Enter an integer:");
items[i] = int.Parse(Console.ReadLine());
}
DelegateSample.BubbleSort(items, (int first, int second) => {comparisonCount++; return first < second; });
for(i = 0; i < items.Length; i++)
Console.WriteLine(items[i]);
Console.WriteLine("Items were compared {0} times.", comparisonCount);
}
如果Lambda表达式捕获了外部变量,根据该表达式创建委托可能具有比局部变量更长的生存期。在此情况下,被捕获的变量的生存期变长了。
1.13 外部变量的CIL实现
在Lambda表达式外部声明的局部变量称为表达式的外部变量。当Lambda主体使用一个外部变量时, 就说该变量被这个lambda捕获
private sealed class __LocalsDisplayClass_00000001
{
public int comparisonCount;
public bool __AnonymousMethod_00000000(int first, int second)
{
comparisonCount++;
return first < second;
}
}
public static void Main()
{
int i;
__LocalsDisplayClass_00000001 locals = new __LocalsDisplayClass_00000001();
locals.comparisonCount = 0;
int[] items = new int[5];
for(i = 0; i < items.Length; i++)
{
Console.Write("Enter an integer:");
items[i] = int.Parse(Console.ReadLine());
}
DelegateSample.BubbleSort(items, locals.__AnonymousMethod_00000000);
for(i = 0; i < items.Length; i++)
Console.WriteLine(items[i]);
Console.WriteLine("Items were compared {0} times.", locals.comparisonCount);
}
二、事件
2.1 多播委托
委托本身是发布-订阅模式的基本单位
一个委托值可以引用一系列方法的, 这些方法将顺序调用。这样的委托称为多播委托。利用多播委托,单一事件的通知可以发布给多个订阅者
2.2 使用多播委托来编码Observer模式
定义订阅者方法
class Cooler
{
public Cooler(float temperature) {Temperature = temperature;}
public float Temperature { get; set; }
public void OnTemperatureChanged(float newTemperature)
{
if(newTemperature > Temperature)
System.Console.WriteLine("Cooler: On");
else
System.Console.WriteLine("Cooler: Off");
}
}
class Heater
{
public Heater(float temperature) {Temperature = temperature;}
public float Temperature { get; set; }
public void OnTemperatureChanged(float newTemperature)
{
if(newTemperature < Temperature)
System.Console.WriteLine("Heater: On");
else
System.Console.WriteLine("Heater: Off");
}
}
定义发布者
public class Thermostat
{
public Action<float> OnTemperatureChange { get; set; }
public float CurrentTemperature
{
get { return _CurrentTemperature; }
set
{
if(value != CurrentTemperature)
{
_CurrentTemperature = value;
}
}
}
private float _CurrentTemperature;
}
连接发布者和订阅者
public static void Main()
{
Thermostat thermostat = new Thermostat();
Heater heater = new Heater(60);
Cooler cooler = new Cooler(80);
string temperature; // Using C# 2.0 or later syntax.
thermostat.OnTemperatureChange += heater.OnTemperatureChanged;
thermostat.OnTemperatureChange += cooler.OnTemperatureChanged;
Console.Write("Enter temperature: ");
temperature = Console.ReadLine();
thermostat.CurrentTemperature = int.Parse(temperature);
}
调用委托
public class Thermostat
{
// Define the event publisher
public Action<float> OnTemperatureChange { get; set; }
public float CurrentTemperature
{
get { return _CurrentTemperature; }
set
{
if(value != CurrentTemperature)
{
_CurrentTemperature = value;
// INCOMPLETE: Check for null needed Call subscribers
OnTemperatureChange(value);
}
}
}
private float _CurrentTemperature;
}
检查null值
public static void ChapterMain()
{
Thermostat thermostat = new Thermostat();
Heater heater = new Heater(60);
Cooler cooler = new Cooler(80);
Action<float> delegate1;
Action<float> delegate2;
Action<float> delegate3;
// use Constructor syntax for C# 1.0.
delegate1 = heater.OnTemperatureChanged;
delegate2 = cooler.OnTemperatureChanged;
Console.WriteLine("Invoke both delegates:");
delegate3 = delegate1;
delegate3 += delegate2;
delegate3(90);
Console.WriteLine("Invoke only delegate2");
delegate3 -= delegate1;
delegate3(30);
}
2.3 委托操作符
为了合并多个订阅者,要使用+= 操作符。这个操作符会获取第一个委托,并将第二个委托添加到委托链中。 要从委托链中删除委托,则要使用-=操作符
public static void ChapterMain()
{
Thermostat thermostat = new Thermostat();
Heater heater = new Heater(60);
Cooler cooler = new Cooler(80);
Action<float> delegate1;
Action<float> delegate2;
Action<float> delegate3;
// use Constructor syntax for C# 1.0.
delegate1 = heater.OnTemperatureChanged;
delegate2 = cooler.OnTemperatureChanged;
Console.WriteLine("Invoke both delegates:");
delegate3 = delegate1;
delegate3 += delegate2;
delegate3(90);
Console.WriteLine("Invoke only delegate2");
delegate3 -= delegate1;
delegate3(30);
}
我们还可以使用+ 和- 合并委托
public static void ChapterMain()
{
Thermostat thermostat = new Thermostat();
Heater heater = new Heater(60);
Cooler cooler = new Cooler(80);
Action<float> delegate1, delegate2, delegate3;
delegate1 = heater.OnTemperatureChanged;
delegate2 = cooler.OnTemperatureChanged;
Console.WriteLine("Combine delegates using + operator:");
delegate3 = delegate1 + delegate2;
delegate3(60);
Console.WriteLine("Uncombine delegates using - operator:");
delegate3 = delegate3 - delegate2;
delegate3(60);
}
无论+ - 还是+= 、-=,在内部都是使用静态方法system.Delegate.combine() 和System.Delegate.Remove()来实现的。Combine 会连接两个参数,将两个委托的调用列表按顺序连接起来,Remove 则将第二个参数指定的委托删除
顺序调用
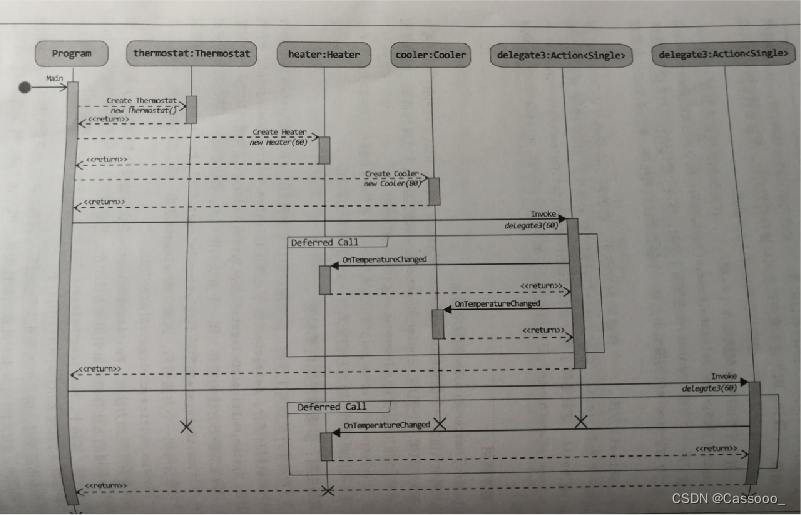
2.4 错误处理
假如一个订阅者发生了异常,链中后续的订阅者就收不到通知
public static void Main()
{
Thermostat thermostat = new Thermostat();
Heater heater = new Heater(60);
Cooler cooler = new Cooler(80);
string temperature;
thermostat.OnTemperatureChange +=heater.OnTemperatureChanged;
thermostat.OnTemperatureChange +=
(newTemperature) =>
{
throw new InvalidOperationException();
};
thermostat.OnTemperatureChange +=
cooler.OnTemperatureChanged;
Console.Write("Enter temperature: ");
temperature = Console.ReadLine();
thermostat.CurrentTemperature = int.Parse(temperature);
}
为了避免该问题,必须手动遍历委托链并单独调用委托
public class Thermostat {
public Action<float> OnTemperatureChange;
public float CurrentTemperature
{
get { return _CurrentTemperature; }
set
{
if(value != CurrentTemperature) {
_CurrentTemperature = value;
Action<float> onTemperatureChange = OnTemperatureChange;
if (onTemperatureChange != null) {
List<Exception> exceptionCollection = new List<Exception>();
foreach(Action<float> handler in onTemperatureChange.GetInvocationList())
{
try {
handler(value);
}
catch(Exception exception) {
exceptionCollection.Add(exception);
}
}
if(exceptionCollection.Count > 0)
throw new AggregateException( "There were exceptions thrown by " + "OnTemperatureChange Event subscribers.", exceptionCollection);
}
}
}
}
private float _CurrentTemperature;
}
2.5 事件的作用
封装订阅: 事件仅对包容类内部对象提供对赋值操作符的支持。
public static void Main()
{
Thermostat thermostat = new Thermostat();
Heater heater = new Heater(60);
Cooler cooler = new Cooler(80);
string temperature;
thermostat.OnTemperatureChange = heater.OnTemperatureChanged;
// Bug: Assignment operator overrides // previous assignment.
thermostat.OnTemperatureChange = cooler.OnTemperatureChanged;
Console.Write("Enter temperature: ");
temperature = Console.ReadLine();
thermostat.CurrentTemperature = int.Parse(temperature);
}
封装发布: 事件确保只有包容类才能触发异常
public static void ChapterMain()
{
//……..
thermostat.OnTemperatureChange += heater.OnTemperatureChanged;
thermostat.OnTemperatureChange +=cooler.OnTemperatureChanged;
// Bug: Should not be allowed
thermostat.OnTemperatureChange(42);
}
2.6 事件的声明
C# 使用事件解决了委托的两大问题。Event 定义了一个新的成员类型,例如:
public class Thermostat
{
public class TemperatureArgs : System.EventArgs
{
public TemperatureArgs(float newTemperature)
{
NewTemperature = newTemperature;
}
public float NewTemperature { get; set; }
}
// Define the event publisher
public event EventHandler<TemperatureArgs> OnTemperatureChange = delegate { };
public float CurrentTemperature
{
get { return _CurrentTemperature; }
set { _CurrentTemperature = value; }
}
private float _CurrentTemperature;
}
添加关键字event后,会禁止为一个public 委托字段使用赋值操作符,只有包容类才能调用向所有委托发出的通知委托; delegate{}表示一个空委托,代表由零个侦听者构成的集合。通过赋值空委托,可以引发事件而不必检查是否有侦听者
2.7 编码规范
为了获得所需功能,需要将原始委托变量声明为字段,然后添加event关键字。为了遵循C#编码规范,需要将原始委托替换成新的委托类型 EventHandle,例如:
public delegate void EventHandler<TEventArgs>(object sender, TEventArgs e)
where TEventArgs : EventArgs;
- 第一参数sender是object 类型, 它包含对调用委托的那个对象的一个引用(静态事件为null)
- 第二参数是System.EventArgs类型的,或者从System.EventArgs派生,但包含了事件的附加数据。
触发事件通知
public float CurrentTemperature
{
get { return _CurrentTemperature; }
set {
if(value != CurrentTemperature)
{
_CurrentTemperature = value;
// If there are any subscribers, notify them of changes in temperature by invoking said subcribers
OnTemperatureChange?.Invoke( this, new TemperatureArgs(value));
}
}
}
规范 :
- 要在调用委托前检查它的值不为null
- 不要为非静态事件的sender传递null 值
- 要为静态事件的sender传递null值
- 不要为eventArgs传递null值 要为事件使用EventHandler<TEventArgs> 委托类型
- 要为TEventArgs 使用System.EventArgs类型或者它的派生类型
- 考虑使用System.EventArgs的子类作为事件的实参类型,除非完全确定事件永远不需要携带任何数据
2.8 事件的内部机制
事件限制外部类只能通过+=向发布者添加订阅方法,并用-=取消订阅,除此之外任何事情不允许做。此外,它还禁止除包容类之外的任何类调用事件。为此,编译器会获取带有event修饰符的public 委托变了,并将委托声明为private,此外还添加两个方法和特殊的事件块。
public class Thermostat {
// ...
// Declaring the delegate field to save the list of subscribers.
private EventHandler<TemperatureArgs> _OnTemperatureChange;
public void add_OnTemperatureChange(EventHandler<TemperatureArgs> handler) {
System.Delegate.Combine(_OnTemperatureChange, handler);
}
public void remove_OnTemperatureChange( EventHandler<TemperatureArgs> handler) {
System.Delegate.Remove(_OnTemperatureChange, handler);
}
//public event EventHandler<TemperatureArgs> OnTemperatureChange
//{
// add
// {
// add_OnTemperatureChange(value);
// }
// remove
// {
// remove_OnTemperatureChange(value);
// }
//}
public class TemperatureArgs : System.EventArgs {
public TemperatureArgs(float newTemperature) {}
}
}
2.9 自定义事件的实现
编译器为+=和-=生成的代码是可以自定义的,例如
public class Thermostat {
public class TemperatureArgs : System.EventArgs
{
//….
}
// Define the delegate data type
public delegate void TemperatureChangeHandler(object sender, TemperatureArgs newTemperature);
// Define the event publisher
public event TemperatureChangeHandler OnTemperatureChange
{
add
{
_OnTemperatureChange = (TemperatureChangeHandler)System.Delegate.Combine(value, _OnTemperatureChange);
}
remove
{
_OnTemperatureChange = (TemperatureChangeHandler)System.Delegate.Remove(_OnTemperatureChange, value);
}
}
protected TemperatureChangeHandler _OnTemperatureChange;
public float CurrentTemperature
{
//......
}
}


![致远OA wpsAssistServlet任意文件读取漏洞复现 [附POC]](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/606343b4107546639b1b1afc1ca7da93.png)