/**
* *****************************************************************************
* @file twoDimensional.h
* @brief 二维数组 Pointers and 2-D arrays
* @author geovindu,Geovin Du,涂聚文 (geovindu@163.com)
* ide: vscode c11,c17 windows 10
* @date 2023-10-30
* @copyright geovindu 站在巨人的肩膀上 Standing on the Shoulders of Giants
* matrix => Points to base address of two-dimensional array.
Since array decays to pointer.
*(matrix) => Points to first row of two-dimensional array.
*(matrix + 0) => Points to first row of two-dimensional array.
*(matrix + 1) => Points to second row of two-dimensional array.
**matrix => Points to matrix[0][0]
*(*(matrix + 0)) => Points to matrix[0][0]
*(*(matrix + 0) + 0) => Points to matrix[0][0]
*(*matrix + 1) => Points to matrix[0][1]
*(*(matrix + 0) + 1) => Points to matrix[0][1]
*(*(matrix + 2) + 2) => Points to matrix[2][2]
* *****************************************************************************
*/
#ifndef TWODIMENSIONAL_H_
#define TWODIMENSIONAL_H_
#include <stddef.h>
#include <stdbool.h>
#define BUF_LEN 100 // Length of input buffer
#define COUNT 5 // Initial number of strings
/**
* @brief 输入字符排序
*
*/
void stringInputSort();
/**
* @brief
*
* @param arry 二维数组
* @param row 行长度
* @param col 列长度
* @return int
*/
int pointDisplay(const int** arry,int row,int col);
/**
* @brief
* @param arry 二维数组
* @param row 行长度
* @param col 列长度
* @return int
*/
int pointDisplay1(const** arry,int row,int col);
/**
* @brief
* @param arry 二维数组
* @param row 行长度
* @param col 列长度
* @return int
*/
int pointDisplay0(int arry[10][10],int row,int col);
/**
* @brief OK
*
* @param arry 二维数组
* @param intlength 行列共长度
* @return int
*/
int pointDisplay2(int arry[10][10],int intlength);
/**
* @brief
*
* @param arry 二维数组
* @param row 行长度
* @param col 列长度
* @return int
*/
int pointDisplay3(int** arry,int row,int col);
/**
* @brief Ok
* @param arry 二维数组
* @param row 行长度
* @param col 列长度
* @return int
*/
int pointDisplay4(int** arry,int row,int col);
/**
* @brief OK
* @param arry 二维数组
* @param row 行长度
* @param col 列长度
* @return int
*/
int pointDisplay5(int*** arry,int row,int col);
/**
* @brief ok
* @param arry 二维数组
* @param row 行长度
* @param col 列长度
* @return int
*/
int pointDisplay6(int** arry,int row,int col);
/**
* @brief 释放所有堆内存
* @param ps
* @param n
*
*/
void freeMemoryChar(char **ps,size_t n);
/**
* @brief 释放所有堆内存
* @param ps
* @param n
*
*/
void freeMemoryInt(int **ps,size_t n);
#endif/**
* *****************************************************************************
* @file twoDimensional.c
* @brief 二维数组 Pointers and 2-D arrays
* @author geovindu,Geovin Du,涂聚文 (geovindu@163.com)
* ide: vscode c11,c17 windows 10
* @date 2023-10-30
* @copyright geovindu 站在巨人的肩膀上 Standing on the Shoulders of Giants
* *****************************************************************************
*/
#include <stddef.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdbool.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <malloc.h>
#include "include/twoDimensional.h"
/**
* @brief 输入字符排序
*
*/
void stringInputSort()
{
char buf[BUF_LEN]; // Input buffer
size_t str_count = 0; // Current string count
size_t capacity = COUNT; // Current maximum number of strings
char **pS = calloc(capacity, sizeof(char*)); // Pointers to strings
char** psTemp = NULL; // Temporary pointer to pointer to char
char* pTemp = NULL; // Temporary pointer to char
size_t str_len = 0; // Length of a string
bool sorted = false; // Indicated when strings are sorted
printf("Enter strings to be sorted, one per line. Press Enter to end:\n");
// Read in all the strings
char *ptr = NULL;
while(true)
{
ptr = fgets(buf, BUF_LEN, stdin);
if(!ptr) // Check for read error
{
printf("Error reading string.\n");
free(pS);
pS = NULL;
return 1;
}
if(*ptr == '\n') break; // Empty line check
if(str_count == capacity)
{
capacity += capacity/4; // Increase capacity by 25%
if(!(psTemp = realloc(pS, capacity))) return 1;
pS = psTemp;
}
str_len = strnlen(buf, BUF_LEN) + 1; //strnlen_s
if(!(pS[str_count] = malloc(str_len))) return 2;
strcpy_s(pS[str_count++], str_len, buf);
}
// Sort the strings in ascending order
while(!sorted)
{
sorted = true;
for(size_t i = 0 ; i < str_count - 1 ; ++i)
{
if(strcmp(pS[i], pS[i + 1]) > 0)
{
sorted = false; // We were out of order so...
pTemp= pS[i]; // swap pointers pS[i]...
pS[i] = pS[i + 1]; // and...
pS[i + 1] = pTemp; // pS[i + 1]
}
}
}
// Output the sorted strings
printf("Your input sorted in ascending sequence is:\n\n");
for(size_t i = 0 ; i < str_count ; ++i)
{
printf("%s", pS[i] );
free(pS[i]); // Release memory for the word
pS[i] = NULL; // Reset the pointer
}
free(pS); // Release the memory for pointers
pS = NULL; // Reset the pointer
}
/**
* @brief 可以
*
* @param arry 二维数组
* @param row 行长度
* @param col 列长度
* @return int
*/
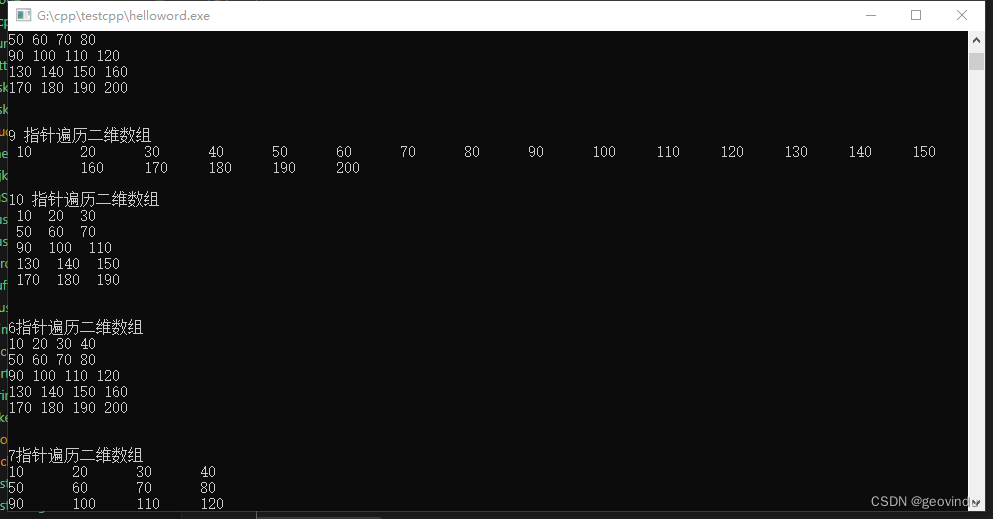
int pointDisplay(const** arry,int row,int col)
{
//在main 中直接使用可以
printf("\n6指针遍历二维数组\n");
int *dup;
//dup= arry[0]; //*(*(arry + 0));//*(arry + 0);//
for (int i = 0; i < row; i++) //sizeof(arry) / sizeof(int)
{
dup= arry[i];
for(int j=0;j<col;j++)
{
printf("%d ",*dup++);
}
printf("\n");
}
printf("\n");
}
/**
* @brief
* @param arry 二维数组
* @param row 行长度
* @param col 列长度
* @return int
*/
int pointDisplay1(const** arry,int row,int col)
{
//在main 中直接使用可以
printf("\n7指针遍历二维数组\n");
int* dup;
for (int i = 0; i < row; i++) //sizeof(arry) / sizeof(int)
{
dup=arry[i];//*arry;//
for(int j=0;j<col;j++)
{
// printf ("%d \t", *(dup+i)); //printf("\n"); //显示了第一行
printf ("%d \t", *(dup+j));
}
//printf("%d ",*dup++);
printf("\n");
}
printf("\n");
}
/**
* @brief
* @param arry 二维数组
* @param row 行长度
* @param col 列长度
* @return int
*/
int pointDisplay0(int arry[10][10],int row,int col)
{
printf("\n14指针遍历二维数组\n");
int *dup;
dup=&arry[0][0];
for (int i=0; i<row; i++){
for (int j=0; j<col; j++){
printf ("%d \t", *(dup+i*col+j));
}
printf("\n");
}
int (*pp)[col]=arry;
printf("\n1列的首位元素\n");
for(int k=0;k<row;k++)
{
printf(" %d ",*pp[k]); //列的首位元素
}
printf("\n");
printf("\n2第一行的遍历值\n");
for(int k=0;k<row;k++)
{
printf(" %d ",(*pp)[k]); //第一行的遍历值
}
printf("\n");
}
/**
* @brief
*
* @param arry 二维数组
* @param intlength 行列共长度 row*col
* @return int
*/
int pointDisplay2(int arry[10][10],int intlength)
{
printf("\n9 指针遍历二维数组\n");
//int llen=4*5;
for(int i=0;i<intlength;++i)
{
printf(" %d\t",*(*arry+i));
}
printf("\n");
}
/**
* @brief 可以
*
* @param arry 二维数组
* @param row 行长度
* @param col 列长度
* @return int
*/
int pointDisplay3(int** arry,int row,int col)
{
//在main 中直接使用可以
printf("\n10 指针遍历二维数组\n");
int *ddpp;//=*arry;
for(int i=0;i<row;++i)
{
ddpp=*(arry+i);
for (int j = 0; j < (col-1); j++) {
printf(" %d ",*(ddpp+j));
}
printf("\n");
}
printf("\n");
}
/**
* @brief Ok
* @param arry 二维数组
* @param row 行长度
* @param col 列长度
* @return int
*/
int pointDisplay4(int** arry,int row,int col)
{
printf("\n11 指针遍历二维数组\n");
for (int i = 0; i < row; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < col; j++) {
printf("%d ", arry[i][j]);
}
printf("\n");
}
printf("\n");
}
/**
* @brief ok
* @param arry 二维数组
* @param row 行长度
* @param col 列长度
* @return int
*/
int pointDisplay6(int** arry,int row,int col)
{
printf("\n13 指针遍历二维数组\n");
for (int i = 0; i < row; i++) {
//printf("Address of %d th array %u \n",i , *(arry + i));
for (int j = 0; j < col; j++) {
printf("%d ", *( *(arry + i) + j));
}
printf("\n");
}
printf("\n");
}
/**
* @brief OK
* @param arry 二维数组
* @param row 行长度
* @param col 列长度
* @return int
*/
int pointDisplay5(int*** arry,int row,int col)
{
printf("\n12 指针遍历二维数组\n");
for (int i = 0; i <row; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j <col; j++)
{
printf("%d ", *arry[i][j]);
}
printf("\n");
}
printf("\n");
}
/**
* @brief 释放所有堆内存
* @param ps
* @param n
*
*/
void freeMemoryChar(char **ps,size_t n)
{
for(size_t i=0;i<n;n++)
{
free(ps[i]);
ps[i]=NULL;
}
free(ps);
ps=NULL;
}
/**
* @brief 释放所有堆内存
* @param ps
* @param n
*
*/
void freeMemoryInt(int **ps,size_t n)
{
for(size_t i=0;i<n;n++)
{
free(ps[i]);
ps[i]=NULL;
}
free(ps);
ps=NULL;
}调用:
int main()
{
printf("hello c world \n");
printf("你好,中国\n");
// stringInputSort();
int arrdu[5][4]={
{10,20,30,40},
{50,60,70,80},
{90,100,110,120},
{130,140,150,160},
{170,180,190,200}
};
// 4 列
int dum=4;
//5 行
int dun=5;
for(int i = 0; i <dun ; i++)
{
for (int j = 0; j < dum; j++) {
printf("%d ", arrdu[i][j]);
}
printf("\n");
}
printf("\n\n");
for(int i = 0; i <dun ; i++)
{
printf("Address of %d th array %u \n",i , *(arrdu + i));
for(int j = 0; j <dum ; j++)
{
printf("arr[%d][%d]=%d\n", i, j, *( *(arrdu + i) + j) );
}
printf("\n\n");
}
int* ptr = malloc((dum * dun) * sizeof(int));
/* Putting 1 to 12 in the 1D array in a sequence */
for (int i = 0; i < dun * dum; i++)
ptr[i] = i + 1;
//int** pe;
//pe=arrdu;
/**/
//分配内存
int** pe = (int**)malloc(sizeof(int)*dum);
for(int i=0; i<dun; i++)
{
pe[i] = (int*)malloc(sizeof(int)*dum);
}
//初始化内存
//memset(*pe, 0, sizeof(int)*dum*dun);
//2分配内存
int*** arr2 = malloc(dum * sizeof(int**));
for (int i = 0; i < dun; i++)
arr2[i] = malloc(dun * sizeof(int*));
// Initialising each element of the
// pointer array with the address of
// element present in the other array
for (int i = 0; i <dun; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j <dum ; j++) {
arr2[i][j] = &arrdu[i][j];
}
}
printf("The values are\n");
for (int i = 0; i <dun ; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j <dum ; j++) {
printf("%d ", *arr2[i][j]);
}
printf("\n");
}
//strcpy(pe,arrdu);
for (int i = 0; i <dun ; i++)
{
for (int j = 0; j <dum ; j++)
{
pe[i][j]= arrdu[i][j];
//ptr[i][j]=arrdu[i][j];
//strcpy(pe[i][j],arrdu[i][j]);
printf("%d\n",arrdu[i][j]);
}
}
printf("PE The values are\n");
for (int i = 0; i < dun; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j <dum ; j++) {
printf("%d ", pe[i][j]);
}
printf("\n");
}
pointDisplay0(arrdu,dun,dum); //ok
pointDisplay4(pe,dun,dum); //ok
pointDisplay5(arr2,dun,dum); //ok
pointDisplay6(pe,dun,dum); //ok
pointDisplay2(arrdu,dum*dun); //ok
pointDisplay3(pe,dun,dum);
pointDisplay(pe,dun,dum); //12
pointDisplay1(pe,dun,dum); //12
//释放资源
free(pe);
free(arr2);
pe=NULL;
arr2=NULL;
system("pause");// linux 无效 ,只win 下有效
return 0;
}输出: