由于 performTraversals 方法比较长,看一个简化版:
// ViewRootImpl 类
private void performTraversals() {
// 这个方法代码非常多,但是重点就是执行这三个方法
// 执行测量
performMeasure(childWidthMeasureSpec, childHeightMeasureSpec);
// 执行布局(ViewGroup)中才会有
performLayout(lp, mWidth, mHeight);
// 执行绘制
performDraw();
}其流程具体如下:
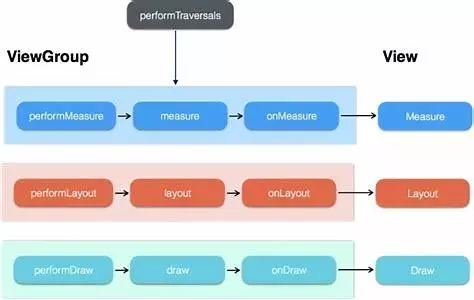
View的整个绘制流程可以分为以下三个阶段:
-
measure: 判断是否需要重新计算 View 的大小,需要的话则计算;
-
layout: 判断是否需要重新计算 View 的位置,需要的话则计算;
-
draw: 判断是否需要重新绘制 View,需要的话则重绘制。
MeasureSpec
在介绍绘制前,先了解下 MeasureSpec。MeasureSpec 封装了父布局传递给子布局的布局要求,它通过一个 32 位 int 类型的值来表示,该值包含了两种信息,高两位表示的是 SpecMode(测量模式),低 30 位表示的是 SpecSize(测量的具体大小)。下面通过注释的方式来分析来类:
/**
* 三种SpecMode:
* 1.UNSPECIFIED
* 父 ViewGroup 没有对子View施加任何约束,子 view 可以是任意大小。这种情况比较少见,主要用于系统内部多次measure的情形,
* 用到的一般都是可以滚动的容器中的子view,比如ListView、GridView、RecyclerView中某些情况下的子view就是这种模式。
* 一般来说,我们不需要关注此模式。
* 2.EXACTLY
* 该 view 必须使用父 ViewGroup 给其指定的尺寸。对应 match_parent 或者具体数值(比如30dp)
* 3.AT_MOST
* 该 View 最大可以取父ViewGroup给其指定的尺寸。对应wrap_content
*
* MeasureSpec使用了二进制去减少对象的分配。
*/
public class MeasureSpec {
// 进位大小为2的30次方(int的大小为32位,所以进位30位就是要使用int的最高位和第二高位也就是32和31位做标志位)
private static final int MODE_SHIFT = 30;
// 运算遮罩,0x3为16进制,10进制为3,二进制为11。3向左进位30,就是11 00000000000(11后跟30个0)
// (遮罩的作用是用1标注需要的值,0标注不要的值。因为1与任何数做与运算都得任何数,0与任何数做与运算都得0)
private static final int MODE_MASK = 0x3 << MODE_SHIFT;
// 0向左进位30,就是00 00000000000(00后跟30个0)
public static final int UNSPECIFIED = 0 << MODE_SHIFT;
// 1向左进位30,就是01 00000000000(01后跟30个0)
public static final int EXACTLY = 1 << MODE_SHIFT;
// 2向左进位30,就是10 00000000000(10后跟30个0)
public static final int AT_MOST = 2 << MODE_SHIFT;
/**
* 根据提供的size和mode得到一个详细的测量结果
*/
// 第一个return:
// measureSpec = size + mode; (注意:二进制的加法,不是十进制的加法!)
// 这里设计的目的就是使用一个32位的二进制数,32和31位代表了mode的值,后30位代表size的值
// 例如size=100(4),mode=AT_MOST,则measureSpec=100+10000...00=10000..00100
//
// 第二个return:
// size &; ~MODE_MASK就是取size 的后30位,mode & MODE_MASK就是取mode的前两位,最后执行或运算,得出来的数字,前面2位包含代表mode,后面30位代表size
public static int makeMeasureSpec(int size, int mode) {
if (sUseBrokenMakeMeasureSpec) {
return size + mode;
} else {
return (size & ~MODE_MASK) | (mode & MODE_MASK);
}
}
/**
* 获得SpecMode
*/
// mode = measureSpec & MODE_MASK;
// MODE_MASK = 11 00000000000(11后跟30个0),原理是用MODE_MASK后30位的0替换掉measureSpec后30位中的1,再保留32和31位的mode值。
// 例如10 00..00100 & 11 00..00(11后跟30个0) = 10 00..00(AT_MOST),这样就得到了mode的值
public static int getMode(int measureSpec) {
return (measureSpec & MODE_MASK);
}
/**
* 获得SpecSize
*/
// size = measureSpec & ~MODE_MASK;
// 原理同上,不过这次是将MODE_MASK取反,也就是变成了00 111111(00后跟30个1),将32,31替换成0也就是去掉mode,保留后30位的size
public static int getSize(int measureSpec) {
return (measureSpec & ~MODE_MASK);
}
}顺便提下 MATCH_PARENT 和 WRAP_CONTENT 这两个代表的值,分别是 -1 和 -2。
/**
* Special value for the height or width requested by a View.
* MATCH_PARENT means that the view wants to be as big as its parent,
* minus the parent's padding, if any. Introduced in API Level 8.
*/
public static final int MATCH_PARENT = -1;
/**
* Special value for the height or width requested by a View.
* WRAP_CONTENT means that the view wants to be just large enough to fit
* its own internal content, taking its own padding into account.
*/
public static final int WRAP_CONTENT = -2;Decorview 尺寸的确定
在 performTraversals 中,首先是要确定 DecorView 的尺寸。只有当 DecorView 尺寸确定了,其子 View 才可以知道自己能有多大。具体是如何去确定的,可以看下面的代码:
//Activity窗口的宽度和高度
int desiredWindowWidth;
int desiredWindowHeight;
...
//用来保存窗口宽度和高度,来自于全局变量mWinFrame,这个mWinFrame保存了窗口最新尺寸
Rect frame = mWinFrame;
//构造方法里mFirst赋值为true,意思是第一次执行遍历吗
if (mFirst) {
//是否需要重绘
mFullRedrawNeeded = true;
//是否需要重新确定Layout
mLayoutRequested = true;
// 这里又包含两种情况:是否包括状态栏
//判断要绘制的窗口是否包含状态栏,有就去掉,然后确定要绘制的Decorview的高度和宽度
if (shouldUseDisplaySize(lp)) {
// NOTE -- system code, won't try to do compat mode.
Point size = new Point();
mDisplay.getRealSize(size);
desiredWindowWidth = size.x;
desiredWindowHeight = size.y;
} else {
//宽度和高度为整个屏幕的值
Configuration config = mContext.getResources().getConfiguration();
desiredWindowWidth = dipToPx(config.screenWidthDp);
desiredWindowHeight = dipToPx(config.screenHeightDp);
}
...
else{
// 这是window的长和宽改变了的情况,需要对改变的进行数据记录
//如果不是第一次进来这个方法,它的当前宽度和高度就从之前的mWinFrame获取
desiredWindowWidth = frame.width();
desiredWindowHeight = frame.height();
/**
* mWidth和mHeight是由WindowManagerService服务计算出的窗口大小,
* 如果这次测量的窗口大小与这两个值不同,说明WMS单方面改变了窗口的尺寸
*/
if (desiredWindowWidth != mWidth || desiredWindowHeight != mHeight) {
if (DEBUG_ORIENTATION) Log.v(mTag, "View " + host + " resized to: " + frame);
//需要进行完整的重绘以适应新的窗口尺寸
mFullRedrawNeeded = true;
//需要对控件树进行重新布局
mLayoutRequested = true;
//window窗口大小改变
windowSizeMayChange = true;
}
}
...
// 进行预测量
if (layoutRequested){
...
if (mFirst) {
// 视图窗口当前是否处于触摸模式。
mAttachInfo.mInTouchMode = !mAddedTouchMode;
//确保这个Window的触摸模式已经被设置
ensureTouchModeLocally(mAddedTouchMode);
} else {
//六个if语句,判断insects值和上一次比有什么变化,不同的话就改变insetsChanged
//insects值包括了一些屏幕需要预留的区域、记录一些被遮挡的区域等信息
if (!mPendingOverscanInsets.equals(mAttachInfo.mOverscanInsets)) {
insetsChanged = true;
}
...
// 这里有一种情况,我们在写dialog时,会手动添加布局,当设定宽高为Wrap_content时,会把屏幕的宽高进行赋值,给出尽量长的宽度
/**
* 如果当前窗口的根布局的width或height被指定为 WRAP_CONTENT 时,
* 比如Dialog,那我们还是给它尽量大的长宽,这里是将屏幕长宽赋值给它
*/
if (lp.width == ViewGroup.LayoutParams.WRAP_CONTENT
|| lp.height == ViewGroup.LayoutParams.WRAP_CONTENT) {
windowSizeMayChange = true;
//判断要绘制的窗口是否包含状态栏,有就去掉,然后确定要绘制的Decorview的高度和宽度
if (shouldUseDisplaySize(lp)) {
// NOTE -- system code, won't try to do compat mode.
Point size = new Point();
mDisplay.getRealSize(size);
desiredWindowWidth = size.x;
desiredWindowHeight = size.y;
} else {
Configuration config = res.getConfiguration();
desiredWindowWidth = dipToPx(config.screenWidthDp);
desiredWindowHeight = dipToPx(config.screenHeightDp);
}
}
}
}
}这里主要是分两步走:
-
如果是第一次测量,那么根据是否有状态栏,来确定是直接使用屏幕的高度,还是真正的显示区高度。
-
如果不是第一次,那么从 mWinFrame 获取,并和之前保存的长宽高进行比较,不相等的话就需要重新测量确定高度。
当确定了 DecorView 的具体尺寸之后,然后就会调用 measureHierarchy 来确定其 MeasureSpec :
// Ask host how big it wants to be
windowSizeMayChange |= measureHierarchy(host, lp, res,
desiredWindowWidth, desiredWindowHeight); 其中 host 就是 DecorView,lp 是 wm 在添加时候传给 DecorView 的,最后两个就是刚刚确定显示宽高 ,看下方法的具体逻辑 :
private boolean measureHierarchy(final View host, final WindowManager.LayoutParams lp,
final Resources res, final int desiredWindowWidth, final int desiredWindowHeight) {
int childWidthMeasureSpec;
int childHeightMeasureSpec;
boolean windowSizeMayChange = false;boolean goodMeasure = false;
// 说明是 dialog
if (lp.width == ViewGroup.LayoutParams.WRAP_CONTENT) {
// On large screens, we don't want to allow dialogs to just
// stretch to fill the entire width of the screen to display
// one line of text. First try doing the layout at a smaller
// size to see if it will fit.
final DisplayMetrics packageMetrics = res.getDisplayMetrics();
res.getValue(com.android.internal.R.dimen.config_prefDialogWidth, mTmpValue, true);
int baseSize = 0;
// 获取一个基本的尺寸
if (mTmpValue.type == TypedValue.TYPE_DIMENSION) {
baseSize = (int)mTmpValue.getDimension(packageMetrics);
}
if (DEBUG_DIALOG) Log.v(mTag, "Window " + mView + ": baseSize=" + baseSize
+ ", desiredWindowWidth=" + desiredWindowWidth);
// 如果大于基本尺寸
if (baseSize != 0 && desiredWindowWidth > baseSize) {
childWidthMeasureSpec = getRootMeasureSpec(baseSize, lp.width);
childHeightMeasureSpec = getRootMeasureSpec(desiredWindowHeight, lp.height);
performMeasure(childWidthMeasureSpec, childHeightMeasureSpec);
if (DEBUG_DIALOG) Log.v(mTag, "Window " + mView + ": measured ("
+ host.getMeasuredWidth() + "," + host.getMeasuredHeight()
+ ") from width spec: " + MeasureSpec.toString(childWidthMeasureSpec)
+ " and height spec: " + MeasureSpec.toString(childHeightMeasureSpec));
// 判断测量是否准确
if ((host.getMeasuredWidthAndState()&View.MEASURED_STATE_TOO_SMALL) == 0) {
goodMeasure = true;
} else {
// Didn't fit in that size... try expanding a bit.
baseSize = (baseSize+desiredWindowWidth)/2;
if (DEBUG_DIALOG) Log.v(mTag, "Window " + mView + ": next baseSize="
+ baseSize);
childWidthMeasureSpec = getRootMeasureSpec(baseSize, lp.width);
performMeasure(childWidthMeasureSpec, childHeightMeasureSpec);
if (DEBUG_DIALOG) Log.v(mTag, "Window " + mView + ": measured ("
+ host.getMeasuredWidth() + "," + host.getMeasuredHeight() + ")");
if ((host.getMeasuredWidthAndState()&View.MEASURED_STATE_TOO_SMALL) == 0) {
if (DEBUG_DIALOG) Log.v(mTag, "Good!");
goodMeasure = true;
}
}
}
}
// 这里就是一般 DecorView 会走的逻辑
if (!goodMeasure) {
childWidthMeasureSpec = getRootMeasureSpec(desiredWindowWidth, lp.width);
childHeightMeasureSpec = getRootMeasureSpec(desiredWindowHeight, lp.height);
performMeasure(childWidthMeasureSpec, childHeightMeasureSpec);
// 与之前的尺寸进行对比,看看是否相等,不想等,说明尺寸可能发生了变化
if (mWidth != host.getMeasuredWidth() || mHeight != host.getMeasuredHeight()) {
windowSizeMayChange = true;
}
}
return windowSizeMayChange;
}上面主要主要做的就是来确定父 View 的 MeasureSpec。但是分了两种不同类型:
-
如果宽是 WRAP_CONTENT 类型,说明这是 dialog,会有一些针对 dialog 的处理,最终会调用 performMeasure 进行测量;
-
对于一般 Activity 的尺寸,会调用 getRootMeasureSpec MeasureSpec 。
下面看下 DecorView MeasureSpec 的计算方法:
private static int getRootMeasureSpec(int windowSize, int rootDimension) {
int measureSpec;
switch (rootDimension) {
case ViewGroup.LayoutParams.MATCH_PARENT:
// Window can't resize. Force root view to be windowSize.
measureSpec = MeasureSpec.makeMeasureSpec(windowSize, MeasureSpec.EXACTLY);
break;
case ViewGroup.LayoutParams.WRAP_CONTENT:
// Window can resize. Set max size for root view.
measureSpec = MeasureSpec.makeMeasureSpec(windowSize, MeasureSpec.AT_MOST);
break;
default:
// Window wants to be an exact size. Force root view to be that size.
measureSpec = MeasureSpec.makeMeasureSpec(rootDimension, MeasureSpec.EXACTLY);
break;
}
return measureSpec;
}该方法主要是根据 View 的 MeasureSpec 是根据宽高的参数来划分的。
-
MATCH_PARENT :精确模式,大小就是窗口的大小;
-
WRAP_CONTENT :最大模式,大小不定,但是不能超过窗口的大小;
-
固定大小:精确模式,大小就是指定的具体宽高,比如100dp。
对于 DecorView 来说就是走第一个 case,到这里 DecorView 的 MeasureSpec 就确定了,从 MeasureSpec 可以得出 DecorView 的宽高的约束信息。
获取子 view 的 MeasureSpec
当父 ViewGroup 对子 View 进行测量时,会调用 View 类的 measure 方法,这是一个 final 方法,无法被重写。ViewGroup 会传入自己的 widthMeasureSpec 和 heightMeasureSpec,分别表示父 View 对子 View 的宽度和高度的一些限制条件。尤其是当 ViewGroup 是 WRAP_CONTENT 的时候,需要优先测量子 View,只有子 View 宽高确定,ViewGroup 才能确定自己到底需要多大的宽高。
当 DecorView 的 MeasureSpec 确定以后,ViewRootImpl 内部会调用 performMeasure 方法:
private void performMeasure(int childWidthMeasureSpec, int childHeightMeasureSpec) {
if (mView == null) {
return;
}
Trace.traceBegin(Trace.TRACE_TAG_VIEW, "measure");
try {
mView.measure(childWidthMeasureSpec, childHeightMeasureSpec);
} finally {
Trace.traceEnd(Trace.TRACE_TAG_VIEW);
}
}该方法传入的是对 DecorView 的 MeasureSpec,其中 mView 就是 DecorView 的实例,接下来看 measure() 的具体逻辑:
/**
* 调用这个方法来算出一个View应该为多大。参数为父View对其宽高的约束信息。
* 实际的测量工作在onMeasure()方法中进行
*/
public final void measure(int widthMeasureSpec, int heightMeasureSpec) {
......
// Suppress sign extension for the low bytes
long key = (long) widthMeasureSpec << 32 | (long) heightMeasureSpec & 0xffffffffL;
if (mMeasureCache == null) mMeasureCache = new LongSparseLongArray(2);
// 若mPrivateFlags中包含PFLAG_FORCE_LAYOUT标记,则强制重新布局
// 比如调用View.requestLayout()会在mPrivateFlags中加入此标记
final boolean forceLayout = (mPrivateFlags & PFLAG_FORCE_LAYOUT) == PFLAG_FORCE_LAYOUT;
final boolean specChanged = widthMeasureSpec != mOldWidthMeasureSpec
|| heightMeasureSpec != mOldHeightMeasureSpec; // 说明上一次测量已经失效
final boolean isSpecExactly = MeasureSpec.getMode(widthMeasureSpec) == MeasureSpec.EXACTLY
&& MeasureSpec.getMode(heightMeasureSpec) == MeasureSpec.EXACTLY;
final boolean matchesSpecSize = getMeasuredWidth() == MeasureSpec.getSize(widthMeasureSpec)
&& getMeasuredHeight() == MeasureSpec.getSize(heightMeasureSpec);
final boolean needsLayout = specChanged
&& (sAlwaysRemeasureExactly || !isSpecExactly || !matchesSpecSize);
// 需要重新布局
if (forceLayout || needsLayout) {
// first clears the measured dimension flag 标记为未测量状态
mPrivateFlags &= ~PFLAG_MEASURED_DIMENSION_SET;
// 对阿拉伯语、希伯来语等从右到左书写、布局的语言进行特殊处理
resolveRtlPropertiesIfNeeded();
// 先尝试从缓从中获取,若forceLayout为true或是缓存中不存在或是
// 忽略缓存,则调用onMeasure()重新进行测量工作
int cacheIndex = forceLayout ? -1 : mMeasureCache.indexOfKey(key);
if (cacheIndex < 0 || sIgnoreMeasureCache) {
// measure ourselves, this should set the measured dimension flag back
onMeasure(widthMeasureSpec, heightMeasureSpec);
. . .
} else {
// 缓存命中,直接从缓存中取值即可,不必再测量
long value = mMeasureCache.valueAt(cacheIndex);
// Casting a long to int drops the high 32 bits, no mask needed
setMeasuredDimensionRaw((int) (value >> 32), (int) value);
mPrivateFlags3 |= PFLAG3_MEASURE_NEEDED_BEFORE_LAYOUT;
}
// 如果自定义的View重写了onMeasure方法,但是没有调用setMeasuredDimension()方法就会在这里抛出错误;
// flag not set, setMeasuredDimension() was not invoked, we raise
// an exception to warn the developer
if ((mPrivateFlags & PFLAG_MEASURED_DIMENSION_SET) != PFLAG_MEASURED_DIMENSION_SET) {
throw new IllegalStateException("View with id " + getId() + ": "
+ getClass().getName() + "#onMeasure() did not set the"
+ " measured dimension by calling"
+ " setMeasuredDimension()");
}
//到了这里,View已经测量完了并且将测量的结果保存在View的mMeasuredWidth和mMeasuredHeight中,将标志位置为可以layout的状态
mPrivateFlags |= PFLAG_LAYOUT_REQUIRED;
}
mOldWidthMeasureSpec = widthMeasureSpec;
mOldHeightMeasureSpec = heightMeasureSpec;
// 保存到缓存中
mMeasureCache.put(key, ((long) mMeasuredWidth) << 32 |
(long) mMeasuredHeight & 0xffffffffL); // suppress sign extension
}
这里要注意的是,这是一个 final 方法,不能被继承。这个方法只在 View 类里面。总结一下 measure() 都干了什么事:
-
调用
View.measure()方法时 View 并不是立即就去测量,而是先判断一下要不要进行测量操作,如果没必要,那么 View 就不需要重新测量了,避免浪费时间资源 -
如果需要测量,在测量之前,会先判断是否存在缓存,存在直接从缓存中获取就可以了,再调用一下
setMeasuredDimensionRaw方法,将从缓存中读到的测量结果保存到成员变量mMeasuredWidth和mMeasuredHeight中。 -
如果不能从
mMeasureCache中读到缓存过的测量结果,调用onMeasure()方法去完成实际的测量工作,并且将尺寸限制条件widthMeasureSpec和heightMeasureSpec传递给onMeasure()方法。关于onMeasure()方法,会在下面详细介绍。 -
将结果保存到
mMeasuredWidth和mMeasuredHeight这两个成员变量中,同时缓存到成员变量mMeasureCache中,以便下次执行measure()方法时能够从其中读取缓存值。 -
需要说明的是,View 有一个成员变量
mPrivateFlags,用以保存 View 的各种状态位,在测量开始前,会将其设置为未测量状态,在测量完成后会将其设置为已测量状态。
DecorView 是 FrameLayout 子类,这时候应该去看 FrameLayout 中的 onMeasure() 方法,代码具体如下:
protected void onMeasure(int widthMeasureSpec, int heightMeasureSpec) {
// 获取子view的个数
int count = getChildCount();
final boolean measureMatchParentChildren =
MeasureSpec.getMode(widthMeasureSpec) != MeasureSpec.EXACTLY ||
MeasureSpec.getMode(heightMeasureSpec) != MeasureSpec.EXACTLY;
mMatchParentChildren.clear();
int maxHeight = 0;
int maxWidth = 0;
int childState = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < count; i++) {
final View child = getChildAt(i);
// mMeasureAllChildren 默认为FALSE,表示是否全部子 view 都要测量,子view不为GONE就要测量
if (mMeasureAllChildren || child.getVisibility() != GONE) {
// 测量子view
measureChildWithMargins(child, widthMeasureSpec, 0, heightMeasureSpec, 0);
// 获取子view的布局参数
final LayoutParams lp = (LayoutParams) child.getLayoutParams();
// 记录子view的最大宽度和高度
maxWidth = Math.max(maxWidth,
child.getMeasuredWidth() + lp.leftMargin + lp.rightMargin);
maxHeight = Math.max(maxHeight,
child.getMeasuredHeight() + lp.topMargin + lp.bottomMargin);
childState = combineMeasuredStates(childState, child.getMeasuredState());
// 记录所有跟父布局有着相同宽或高的子view
if (measureMatchParentChildren) {
if (lp.width == LayoutParams.MATCH_PARENT ||
lp.height == LayoutParams.MATCH_PARENT) {
mMatchParentChildren.add(child);
}
}
}
}
// Account for padding too 子view的最大宽高计算出来后,还要加上父View自身的padding
maxWidth += getPaddingLeftWithForeground() + getPaddingRightWithForeground();
maxHeight += getPaddingTopWithForeground() + getPaddingBottomWithForeground();
// Check against our minimum height and width
maxHeight = Math.max(maxHeight, getSuggestedMinimumHeight());
maxWidth = Math.max(maxWidth, getSuggestedMinimumWidth());
// Check against our foreground's minimum height and width
final Drawable drawable = getForeground();
if (drawable != null) {
maxHeight = Math.max(maxHeight, drawable.getMinimumHeight());
maxWidth = Math.max(maxWidth, drawable.getMinimumWidth());
}
// 确定父 view 的宽高
setMeasuredDimension(resolveSizeAndState(maxWidth, widthMeasureSpec, childState),
resolveSizeAndState(maxHeight, heightMeasureSpec,
childState << MEASURED_HEIGHT_STATE_SHIFT));
count = mMatchParentChildren.size();
if (count > 1) {
for (int i = 0; i < count; i++) {
final View child = mMatchParentChildren.get(i);
final MarginLayoutParams lp = (MarginLayoutParams) child.getLayoutParams();
final int childWidthMeasureSpec;
// 如果子view的宽是MATCH_PARENT,那么宽度 = 父view的宽 - 父Padding - 子Margin
if (lp.width == LayoutParams.MATCH_PARENT) {
final int width = Math.max(0, getMeasuredWidth()
- getPaddingLeftWithForeground() - getPaddingRightWithForeground()
- lp.leftMargin - lp.rightMargin);
childWidthMeasureSpec = MeasureSpec.makeMeasureSpec(
width, MeasureSpec.EXACTLY);
} else {
childWidthMeasureSpec = getChildMeasureSpec(widthMeasureSpec,
getPaddingLeftWithForeground() + getPaddingRightWithForeground() +
lp.leftMargin + lp.rightMargin,
lp.width);
}
final int childHeightMeasureSpec;
// 同理
if (lp.height == LayoutParams.MATCH_PARENT) {
final int height = Math.max(0, getMeasuredHeight()
- getPaddingTopWithForeground() - getPaddingBottomWithForeground()
- lp.topMargin - lp.bottomMargin);
childHeightMeasureSpec = MeasureSpec.makeMeasureSpec(
height, MeasureSpec.EXACTLY);
} else {
childHeightMeasureSpec = getChildMeasureSpec(heightMeasureSpec,
getPaddingTopWithForeground() + getPaddingBottomWithForeground() +
lp.topMargin + lp.bottomMargin,
lp.height);
}
child.measure(childWidthMeasureSpec, childHeightMeasureSpec);
}
}
}FrameLayout 是 ViewGroup 的子类,后者有一个 View[] 类型的成员变量 mChildren,代表了其子 View 集合。通过 getChildAt(i) 能获取指定索引处的子 View,通过 getChildCount() 可以获得子 View 的总数。
在上面的源码中,首先调用 measureChildWithMargins() 方法对所有子 View 进行了一遍测量,并计算出所有子 View 的最大宽度和最大高度。而后将得到的最大高度和宽度加上padding,这里的 padding 包括了父 View 的 padding 和前景区域的 padding。然后会检查是否设置了最小宽高,并与其比较,将两者中较大的设为最终的最大宽高。最后,若设置了前景图像,我们还要检查前景图像的最小宽高。
经过了以上一系列步骤后,我们就得到了 maxHeight 和 maxWidth 的最终值,表示当前容器 View 用这个尺寸就能够正常显示其所有子 View(同时考虑了 padding 和 margin )。而后我们需要调用 resolveSizeAndState() 方法来结合传来的 MeasureSpec 来获取最终的测量宽高,并保存到 mMeasuredWidth 与 mMeasuredHeight 成员变量中。
如果存在一些子 View 的宽或高是 MATCH_PARENT,那么需要等父 View 的尺寸计算出来后,重新计算这些子 View 的 MeasureSpec,再来测量这些子 view 的宽高。
这里提醒我们在自定义 View 的时候需要考虑你的子 View 是不是和你自定义的 View 的大小是一样,如果一样,就需要等自定义 View 的大小确定了,再重新测量一遍。
下面看看 measureChildWithMargins() 方法具体逻辑:
/**
* Ask one of the children of this view to measure itself, taking into
* account both the MeasureSpec requirements for this view and its padding
* and margins. The child must have MarginLayoutParams The heavy lifting is
* done in getChildMeasureSpec.
*
* @param child The child to measure
* @param parentWidthMeasureSpec The width requirements for this view
* @param widthUsed Extra space that has been used up by the parent
* horizontally (possibly by other children of the parent)
* @param parentHeightMeasureSpec The height requirements for this view
* @param heightUsed Extra space that has been used up by the parent
* vertically (possibly by other children of the parent)
*/
protected void measureChildWithMargins(View child,
int parentWidthMeasureSpec, int widthUsed,
int parentHeightMeasureSpec, int heightUsed) {
final MarginLayoutParams lp = (MarginLayoutParams) child.getLayoutParams();
final int childWidthMeasureSpec = getChildMeasureSpec(parentWidthMeasureSpec,
mPaddingLeft + mPaddingRight + lp.leftMargin + lp.rightMargin
+ widthUsed, lp.width);
final int childHeightMeasureSpec = getChildMeasureSpec(parentHeightMeasureSpec,
mPaddingTop + mPaddingBottom + lp.topMargin + lp.bottomMargin
+ heightUsed, lp.height);
child.measure(childWidthMeasureSpec, childHeightMeasureSpec);
}该方法主要是获取子 View 的 MeasureSpec,然后调用 child.measure() 来完成子 View 的测量。下面看看子 View 获取 MeasureSpec 的具体逻辑:
public static int getChildMeasureSpec(int spec, int padding, int childDimension) {
// 父 view 的 mode 和 size
int specMode = MeasureSpec.getMode(spec);
int specSize = MeasureSpec.getSize(spec);
// 去掉 padding
int size = Math.max(0, specSize - padding);
int resultSize = 0;
int resultMode = 0;
switch (specMode) {
// Parent has imposed an exact size on us
case MeasureSpec.EXACTLY:
if (childDimension >= 0) {
resultSize = childDimension;
resultMode = MeasureSpec.EXACTLY;
} else if (childDimension == LayoutParams.MATCH_PARENT) {
// Child wants to be our size. So be it.
resultSize = size;
resultMode = MeasureSpec.EXACTLY;
} else if (childDimension == LayoutParams.WRAP_CONTENT) {
// Child wants to determine its own size. It can't be
// bigger than us.
resultSize = size;
resultMode = MeasureSpec.AT_MOST;
}
break;
// Parent has imposed a maximum size on us
case MeasureSpec.AT_MOST:
if (childDimension >= 0) {
// Child wants a specific size... so be it
resultSize = childDimension;
resultMode = MeasureSpec.EXACTLY;
} else if (childDimension == LayoutParams.MATCH_PARENT) {
// Child wants to be our size, but our size is not fixed.
// Constrain child to not be bigger than us.
resultSize = size;
resultMode = MeasureSpec.AT_MOST;
} else if (childDimension == LayoutParams.WRAP_CONTENT) {
// Child wants to determine its own size. It can't be
// bigger than us.
resultSize = size;
resultMode = MeasureSpec.AT_MOST;
}
break;
// Parent asked to see how big we want to be
case MeasureSpec.UNSPECIFIED:
if (childDimension >= 0) {
// Child wants a specific size... let him have it
resultSize = childDimension;
resultMode = MeasureSpec.EXACTLY;
} else if (childDimension == LayoutParams.MATCH_PARENT) {
// Child wants to be our size... find out how big it should
// be
resultSize = View.sUseZeroUnspecifiedMeasureSpec ? 0 : size;
resultMode = MeasureSpec.UNSPECIFIED;
} else if (childDimension == LayoutParams.WRAP_CONTENT) {
// Child wants to determine its own size.... find out how
// big it should be
resultSize = View.sUseZeroUnspecifiedMeasureSpec ? 0 : size;
resultMode = MeasureSpec.UNSPECIFIED;
}
break;
}
//noinspection ResourceType
return MeasureSpec.makeMeasureSpec(resultSize, resultMode);
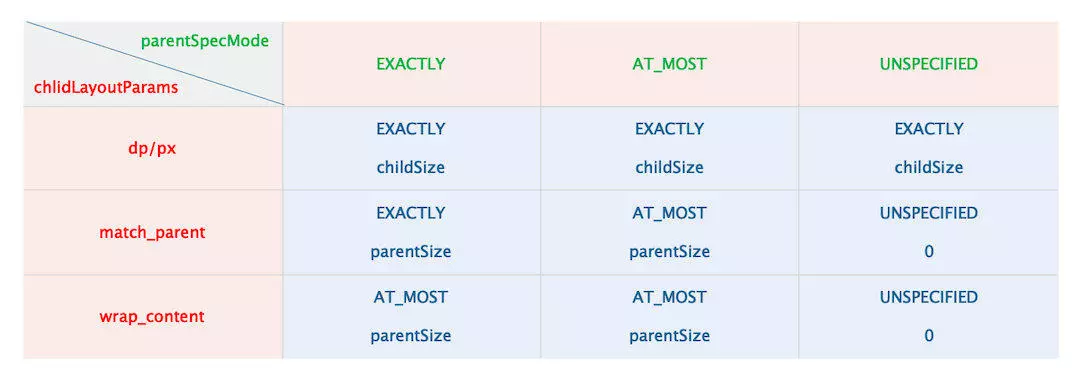
} 该方法清楚展示了普通 View 的 MeasureSpec 的创建规则,每个 View 的 MeasureSpec 状态量由其直接父 View 的 MeasureSpec 和 View 自身的属性 LayoutParams (LayoutParams 有宽高尺寸值等信息)共同决定。
从上面的代码可以知道,返回 View 的 MeasureSpec 大致可以分为一下机制情况:
-
子 View 为
具体的宽/高,那么 View 的 MeasureSpec 都为 LayoutParams 中大小。 -
子 View 为
match_parent,父元素为精度模式(EXACTLY),那么 View 的 MeasureSpec 也是精准模式他的大小不会超过父容器的剩余空间。 -
子 View 为
wrap_content,不管父元素是精准模式还是最大化模式(AT_MOST),View 的 MeasureSpec 总是为最大化模式并且大小不超过父容器的剩余空间。 -
父容器为 UNSPECIFIED 模式主要用于系统多次 Measure 的情形,一般我们不需要关心。
总结为下表:
View.measure() 代码逻辑前面已经分析过了,最终会调用 onMeasure 方法,下面看下 View.onMeasure() 的代码:
protected void onMeasure(int widthMeasureSpec, int heightMeasureSpec) {
setMeasuredDimension(getDefaultSize(getSuggestedMinimumWidth(), widthMeasureSpec),
getDefaultSize(getSuggestedMinimumHeight(), heightMeasureSpec));
}上面方法中调用了 方法中调用了 setMeasuredDimension()方法,setMeasuredDimension()又调用了 getDefaultSize() 方法。getDefaultSize() 又调用了getSuggestedMinimumWidth()和 getSuggestedMinimumHeight(),那反向研究一下,先看下 getSuggestedMinimumWidth() 方法 (getSuggestedMinimumHeight() 原理 getSuggestedMinimumWidth() 跟一样)。
protected int getSuggestedMinimumWidth() {
return (mBackground == null) ? mMinWidth : max(mMinWidth, mBackground.getMinimumWidth());
}
源码很简单,如果 View 没有背景,就直接返回 View 本身的最小宽度 mMinWidth;如果给 View 设置了背景,就取 View 本身的最小宽度 mMinWidth 和背景的最小宽度的最大值.
那么 mMinWidth 是哪里来的?搜索下源码就可以知道,View 的最小宽度 mMinWidth 可以有两种方式进行设置:
- 第一种是在 View 的构造方法中进行赋值的,View 通过读取 XML 文件中View设置的
minWidth属性来为mMinWidth赋值:
case R.styleable.View_minWidth:
mMinWidth = a.getDimensionPixelSize(attr, 0);
break;- 第二种是在调用 View 的
setMinimumWidth方法为mMinWidth赋值
public void setMinimumWidth(int minWidth) {
mMinWidth = minWidth;
requestLayout();
}下面看下 getDefaultSize() 的代码逻辑:
public static int getDefaultSize(int size, int measureSpec) {
int result = size;
int specMode = MeasureSpec.getMode(measureSpec);
int specSize = MeasureSpec.getSize(measureSpec);
switch (specMode) {
case MeasureSpec.UNSPECIFIED:
result = size;
break;
case MeasureSpec.AT_MOST:
case MeasureSpec.EXACTLY:
result = specSize;
break;
}
return result;
}从注释可以看出,getDefaultSize()这个测量方法并没有适配 wrap_content 这一种布局模式,只是简单地将 wrap_content 跟 match_parent 等同起来。
到了这里,我们要注意一个问题:
getDefaultSize()方法中 wrap_content 和 match_parent 属性的效果是一样的,而该方法是 View 的 onMeasure()中默认调用的,也就是说,对于一个直接继承自 View 的自定义 View 来说,它的 wrap_content 和 match_parent 属性是一样的效果,因此如果要实现自定义 View 的 wrap_content,则要重写 onMeasure() 方法,对 wrap_content 属性进行处理。
如何处理呢?也很简单,代码如下所示:
protected void onMeasure(int widthMeasureSpec, int heightMeasureSpec){
super.onMeasure(widthMeasureSpec, heightMeasureSpec);
//取得父ViewGroup指定的宽高测量模式和尺寸
int widthSpecMode = MeasureSpec.getMode(widthMeasureSpec);
int widthSpecSize = MeasureSpec.getSize(widthMeasureSpec);
int heightSpecMode = MeasureSpec.getMode(heightMeasureSpec);
int heightSpecSize = MeasureSpec.getSize(heightMeasureSpec);
if (widthSpecMode == MeasureSpec.AT_MOST && heightSpecMode == MeasureSpec.AT_MOST) {
//如果宽高都是AT_MOST的话,即都是wrap_content布局模式,就用View自己想要的宽高值
setMeasuredDimension(mWidth, mHeight);
}else if (widthSpecMode == MeasureSpec.AT_MOST) {
//如果只有宽度都是AT_MOST的话,即只有宽度是wrap_content布局模式,宽度就用View自己想要的宽度值,高度就用父ViewGroup指定的高度值
setMeasuredDimension(mWidth, heightSpecSize);
}else if (heightSpecMode == MeasureSpec.AT_MOST) {
//如果只有高度都是AT_MOST的话,即只有高度是wrap_content布局模式,高度就用View自己想要的宽度值,宽度就用父ViewGroup指定的高度值
setMeasuredDimension(widthSpecSize, mHeight);
}
} 在上面的代码中,我们要给 View 指定一个默认的内部宽/高(mWidth 和 mHeight),并在 wrap_content 时设置此宽/高即可。最后将在将宽高设置到 View 上:
// View
protected final void setMeasuredDimension(int measuredWidth, int measuredHeight) {
boolean optical = isLayoutModeOptical(this);
if (optical != isLayoutModeOptical(mParent)) {
Insets insets = getOpticalInsets();
int opticalWidth = insets.left + insets.right;
int opticalHeight = insets.top + insets.bottom;
measuredWidth += optical ? opticalWidth : -opticalWidth;
measuredHeight += optical ? opticalHeight : -opticalHeight;
}
setMeasuredDimensionRaw(measuredWidth, measuredHeight);
}
private void setMeasuredDimensionRaw(int measuredWidth, int measuredHeight) {
mMeasuredWidth = measuredWidth;
mMeasuredHeight = measuredHeight;
mPrivateFlags |= PFLAG_MEASURED_DIMENSION_SET;
}这里就是把测量完的宽高值赋值给 mMeasuredWidth、mMeasuredHeight 这两个 View 的属性,然后将标志位置为已测量状态。
子 View 测量完成以后,会计算 childState,看下 combineMeasuredStates 方法 :
public static int combineMeasuredStates(int curState, int newState) {
return curState | newState;
}当前 curState 为 0, newState 是调用 child.getMeasuredState() 方法得到的,来看下这个方法的具体逻辑:
/**
* Return only the state bits of {@link #getMeasuredWidthAndState()}
* and {@link #getMeasuredHeightAndState()}, combined into one integer.
* The width component is in the regular bits {@link #MEASURED_STATE_MASK}
* and the height component is at the shifted bits
* {@link #MEASURED_HEIGHT_STATE_SHIFT}>>{@link #MEASURED_STATE_MASK}.
*/
public final int getMeasuredState() {
return (mMeasuredWidth&MEASURED_STATE_MASK)
| ((mMeasuredHeight>>MEASURED_HEIGHT_STATE_SHIFT)
& (MEASURED_STATE_MASK>>MEASURED_HEIGHT_STATE_SHIFT));
}该方法返回一个 int 值,该值同时包含宽度的 state 以及高度的 state 信息,不包含任何的尺寸信息。
-
MEASURED_STATE_MASK 的值为 0xff000000,其高字节的 8 位全部为 1,低字节的 24 位全部为 0。
-
MEASURED_HEIGHT_STATE_SHIFT 值为 16。
-
将 MEASURED_STATE_MASK 与
mMeasuredWidth做与操作之后就取出了存储在宽度首字节中的 state 信息,过滤掉低位三个字节的尺寸信息。 -
由于 int 有四个字节,首字节已经存了宽度的 state 信息,那么高度的 state 信息就不能存在首位字节。MEASURED_STATE_MASK 向右移 16 位,变成了 0x0000ff00,这个值与高度值
mMeasuredHeight做与操作就取出了mMeasuredHeight第三个字节中的信息。而mMeasuredHeight的 state 信息是存在首字节中,所以也得对mMeasuredHeight向右移相同的位置,这样就把 state 信息移到了第三个字节中。 -
最后,将得到的宽度 state 与高度 state 按位或操作,这样就拼接成一个 int 值,该值首个字节存储宽度的 state 信息,第三个字节存储高度的 state 信息。
这些都得到之后,就可以开始去计算父 View 的尺寸了:
// 确定父 View 的宽高
setMeasuredDimension(resolveSizeAndState(maxWidth, widthMeasureSpec, childState),
resolveSizeAndState(maxHeight, heightMeasureSpec,
childState << MEASURED_HEIGHT_STATE_SHIFT));下面开始看 resolveSizeAndState 具体逻辑:
// View 的静态方法
public static int resolveSizeAndState(int size, int measureSpec, int childMeasuredState) {
final int specMode = MeasureSpec.getMode(measureSpec);
final int specSize = MeasureSpec.getSize(measureSpec);
final int result;
switch (specMode) {
case MeasureSpec.AT_MOST:
if (specSize < size) {
result = specSize | MEASURED_STATE_TOO_SMALL;
} else {
result = size;
}
break;
case MeasureSpec.EXACTLY:
result = specSize;
break;
case MeasureSpec.UNSPECIFIED:
default:
result = size;
}
return result | (childMeasuredState & MEASURED_STATE_MASK);
}这个方法的代码结构跟前文提到的 getDefaultSize()方法很相似,主要的区别在于 specMode 为 AT_MOST 的情况。我们当时说 getDefaultSize() 方法是没有适配wrap_content 这种情况,而这个 resolveSizeAndState() 方法是已经适配了 wrap_content 的布局方式,那具体怎么实现 AT_MOST 测量逻辑的呢?有两种情况:
-
当父 ViewGroup 指定的最大尺寸比 View 想要的尺寸还要小时,会给这个父 ViewGroup 的指定的最大值
specSize加入一个尺寸太小的标志 MEASURED_STATE_TOO_SMALL,然后将这个带有标志的尺寸返回,父 ViewGroup 通过该标志就可以知道分配给 View 的空间太小了,在窗口协商测量的时候会根据这个标志位来做窗口大小的决策。 -
当父 ViewGroup 指定的最大尺寸比没有比 View 想要的尺寸小时(相等或者 View 想要的尺寸更小),直接取 View 想要的尺寸,然后返回该尺寸。
getDefaultSize() 方法只是 onMeasure() 方法中获取最终尺寸的默认实现,其返回的信息比 resolveSizeAndState() 要少,那么什么时候才会调用 resolveSizeAndState() 方法呢? 主要有两种情况:
-
Android 中的大部分 ViewGroup 类都调用了
resolveSizeAndState()方法,比如 LinearLayout 在测量过程中会调用resolveSizeAndState()方法而非getDefaultSize()方法。 -
我们自己在实现自定义的 View 或 ViewGroup 时,我们可以重写
onMeasure()方法,并在该方法内调用resolveSizeAndState()方法。
到此,终于把 View 测量过程讲完了。
![[EFI]asus strix b760-i 13900F电脑 Hackintosh 黑苹果efi引导文件](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/ec76ad13cf4a473cbda6286ec5fb40c6.png)
![[AUTOSAR][诊断管理][ECU][$28] 通信控制](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/5e9e08cdf4a34151859727cd34acea35.png)