欢迎关注更多精彩
关注我,学习常用算法与数据结构,一题多解,降维打击。
本期话题:给定二维点进行delaunay三角化
参考资料:
算法步骤与框架:
https://oi-wiki.org//geometry/triangulation/
空圆性深入解析:
【数字几何处理-中国科学技术大学-傅孝明】 【精准空降到 30:01】 https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV1B54y1B7Uc/?p=22&share_source=copy_web&vd_source=34b56bf81008e2621fca75c5166324c2&t=1801
定义
在数学和计算几何中,对于给定的平面中的离散点集 P,其 Delaunay 三角剖分 ,符号表示 为DT(P),应该满足:
- 三角部分后最外边界是一个凸包。
- 空圆性:在 DT(P) 中,任意三角形的外接圆范围内不会有其它点存在。
算法过程
大概步骤
- 排序: 对所有点按照x, y数值从小到大排序
- 分治: 如果小2个点则直接加入边,否则继续分治
- 合并:1)先找到一条基线(基线两点分别取待合并点集各一个),不与任何已经有边相交,如果有多条基线重合,则基线长越短越好。2)从基线2端点出发,找到直接相邻且邻边与基线夹角小于180的点作为候选点,如果没有候选点,则算法结束。3)从候选点中选出一个点(选中点)使得该点与基线两点的外接圆中不包含任意其他点(共圆除外)。4)添加一条边(ed), ed两端为选中点和基线中与选中点非同侧的点。5)删除与ed相交的所有边。更新基线一端为选中点,回到步骤2。
合并例子演示
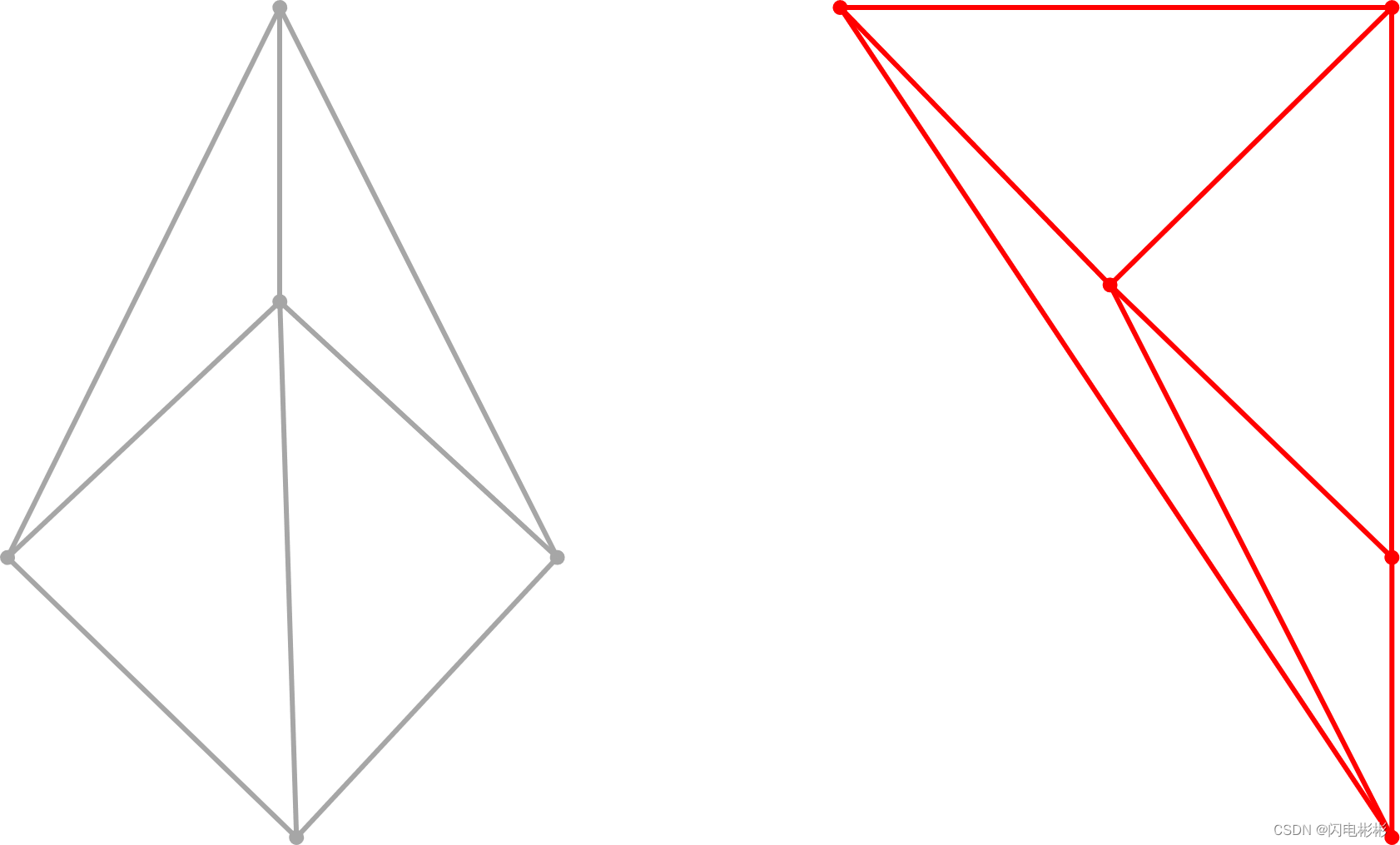
现在左右两边各自已经合并完成,需要整体合并。
1 找基线
具体查找方法在实现细节展示
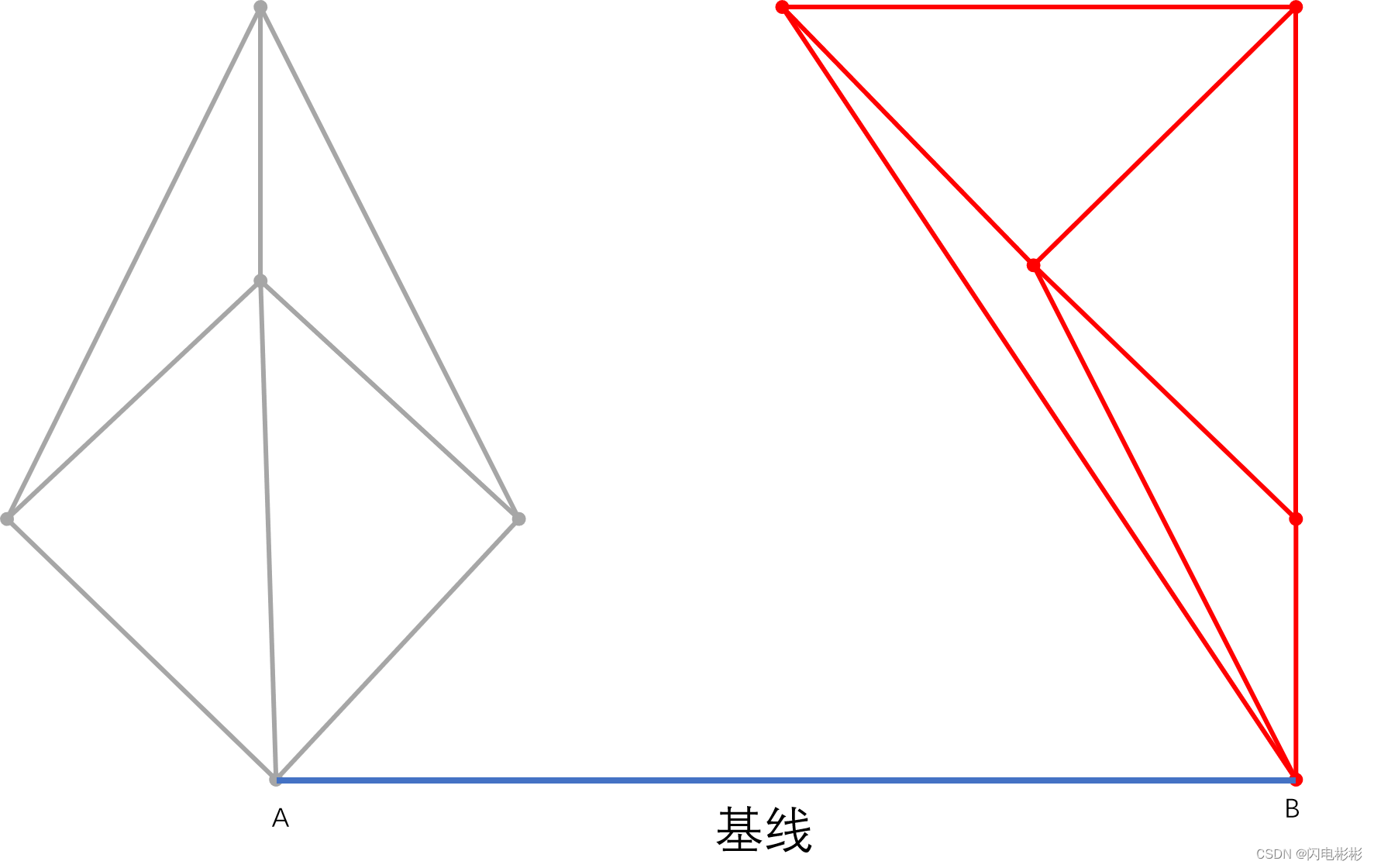
基线两点A, B分别位于左右两侧点集中。且所有点都处于基线上方。
2 候选点
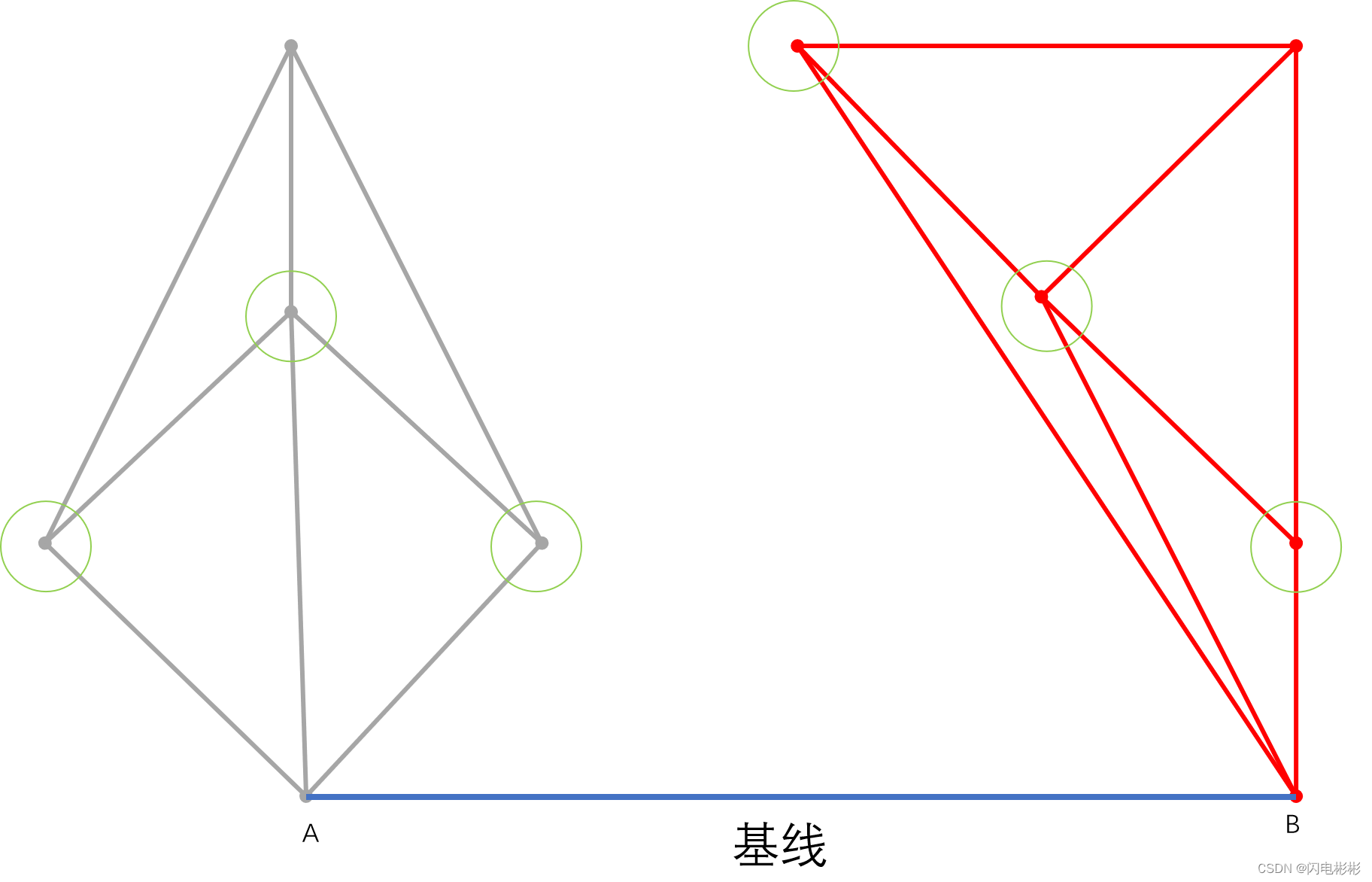
绿色圈中的点都为候选点,它们与A,B有边,且边与基线夹角小180度。
3 选中点,添加新边,更新基线
选中1个点p,使得pab所在外接圆不包含任何其他候选点。
具体算法在实现细节中给出。
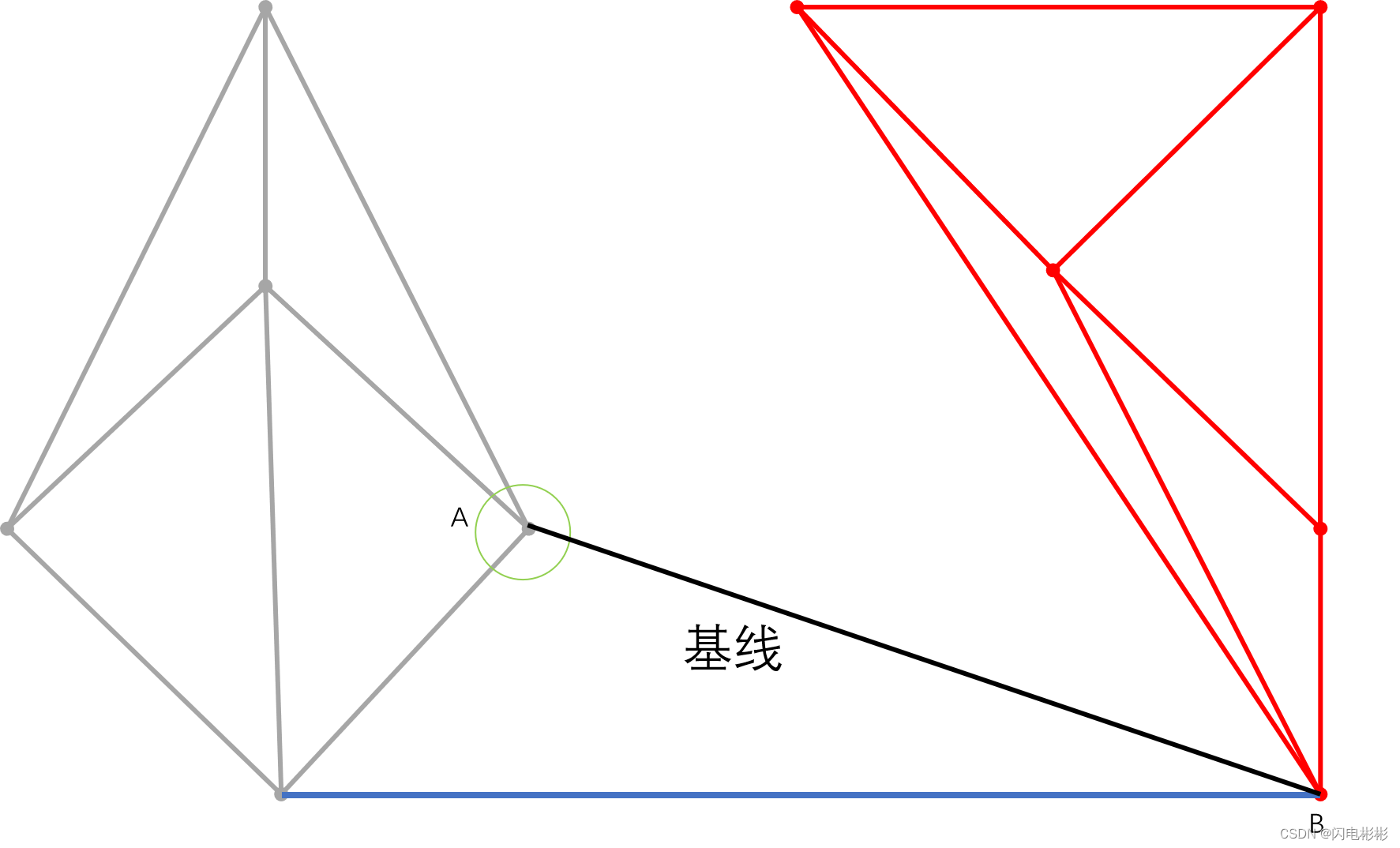
经过测试绿圆中的点为选中点, 添加边,更新基线位置。
到此,一次子操作就完成了。
继续上面步骤,依次添加和消失的边如下
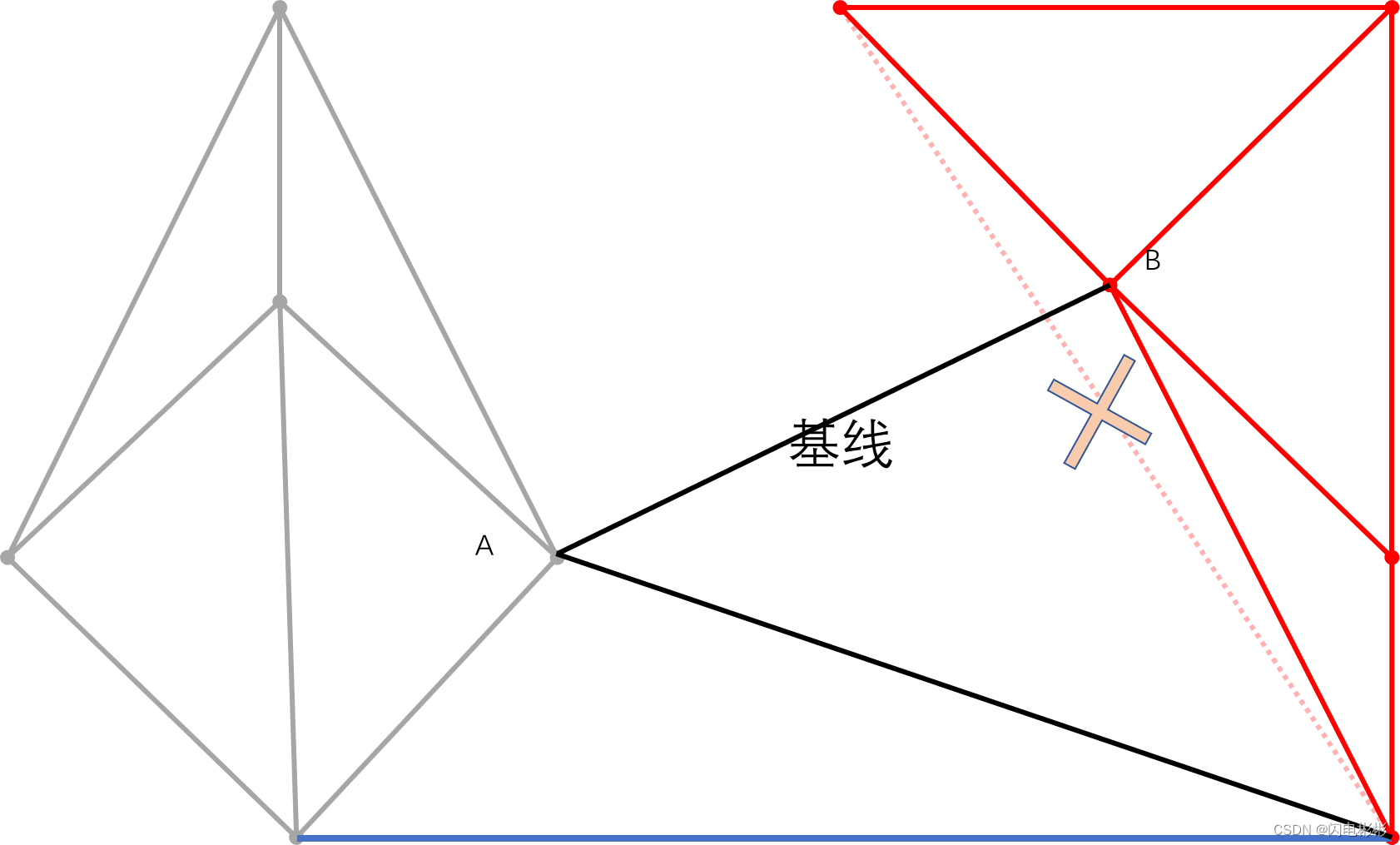
新的边与虚线有相交,需要删除。
继续加边
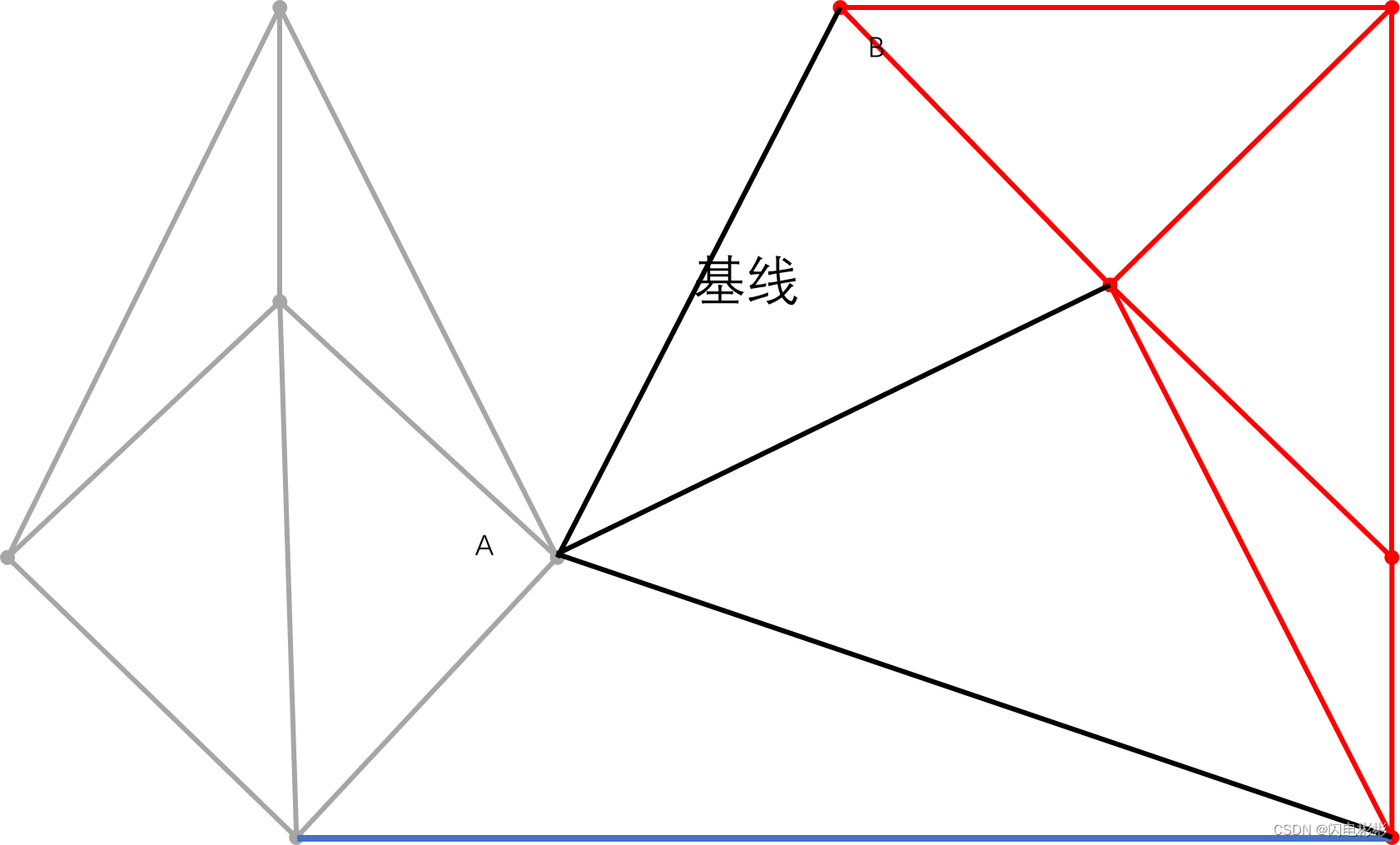
继续加边
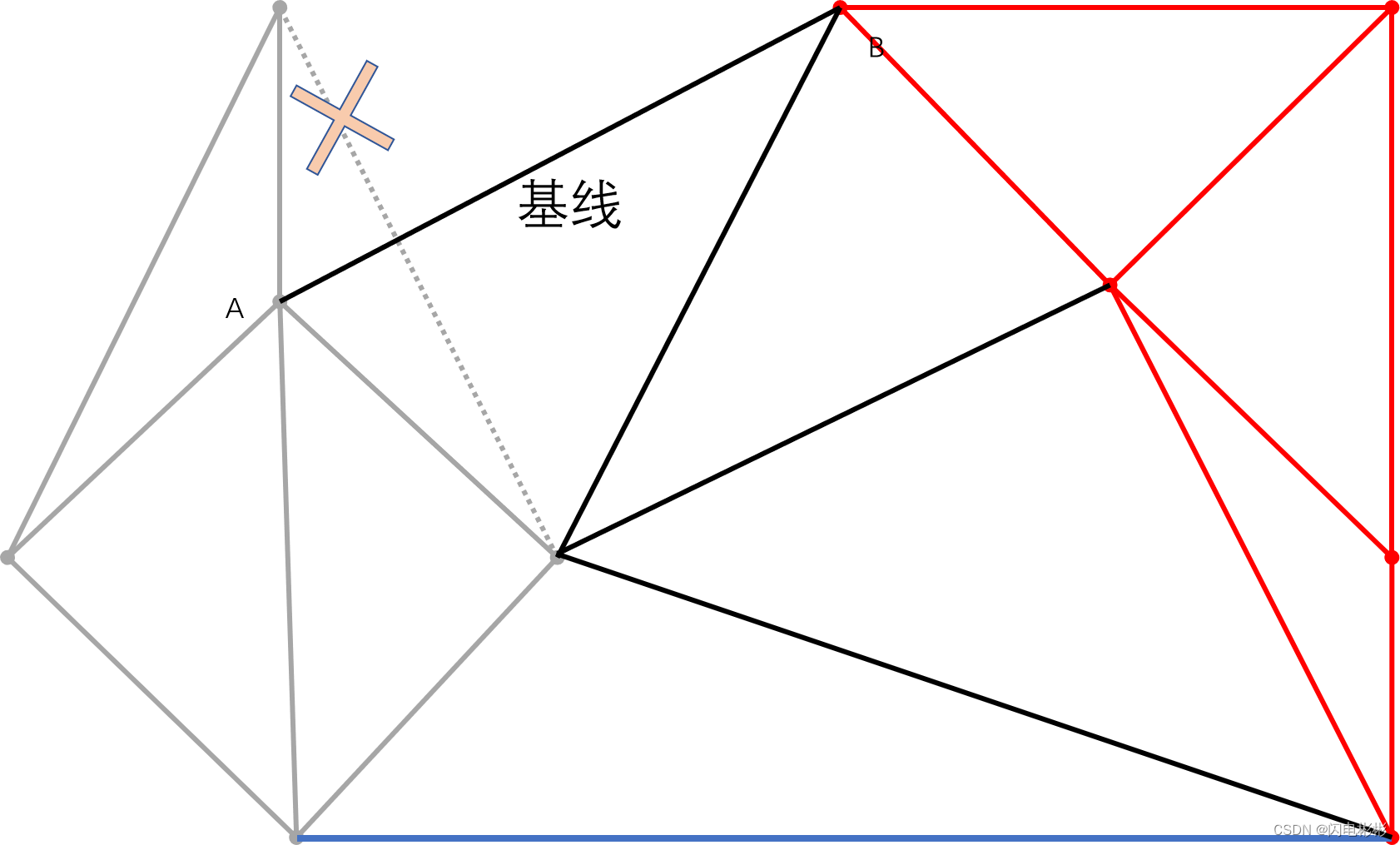
同样新边与现有边相交需要删除。
再添加新的边
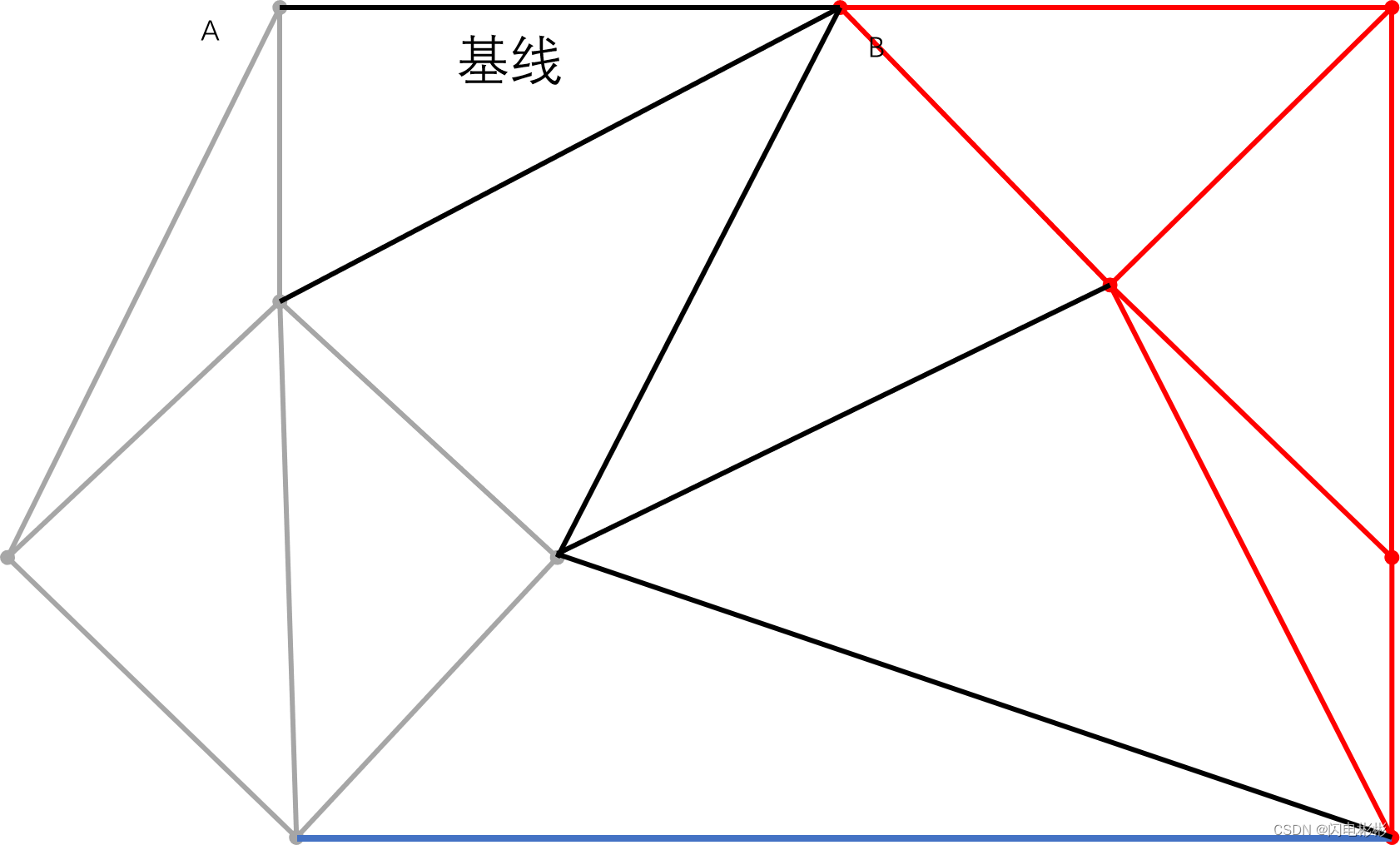
到此没有候选点在基线左上方。合并步骤结束。
实现细节
查找基线算法
由于点进行了排序,对于两个待合并的点集Q1(左边),Q2(右边)。
Q2的所有点肯定是在Q1的所有点的右上方。
已知Q1, Q2的外壳是一个凸包,所以基线的另一个性质是Q1,Q2中所有点都在基线的左上方。
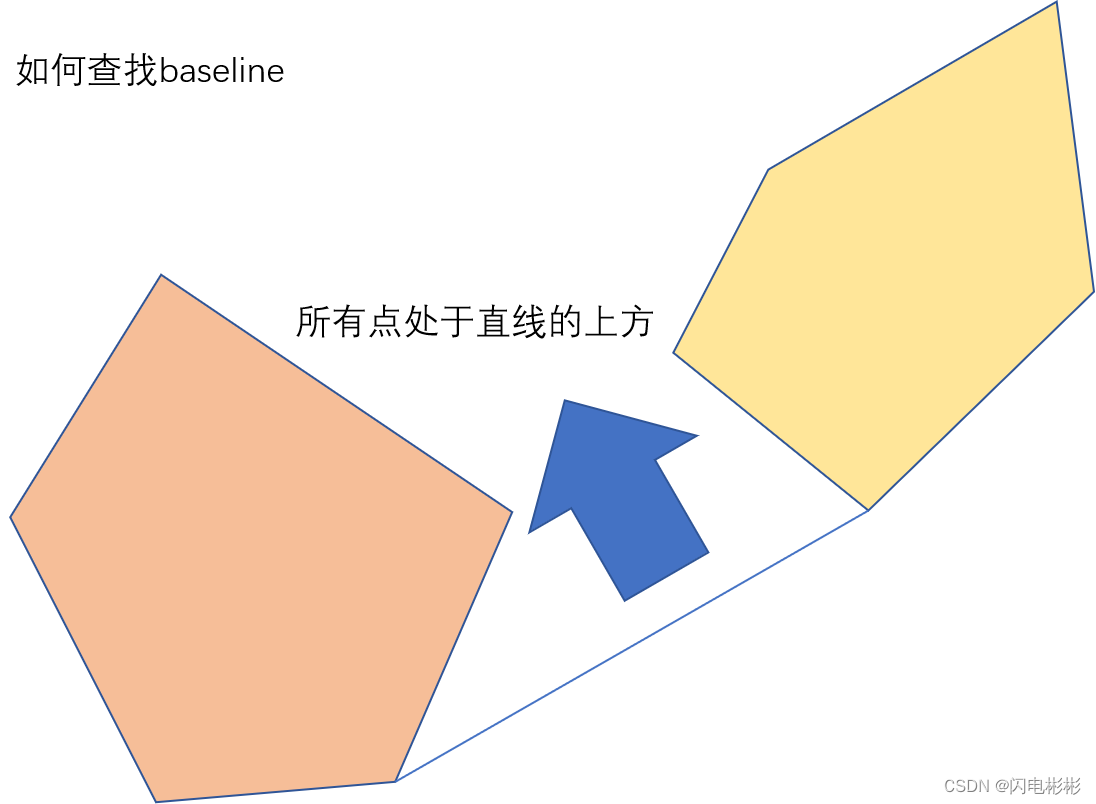
具体实现思路:
- 选择Q1中的任意点为基线的左点,选择Q2中的任意点为基线的右点。
- 依次遍历Q1中的点,如果不在基线的左上方,则把左点更新,如果重合则选择长度短的,直到左点不更新。
- 依次遍历Q2中的点,如果不在基线的左上方,则把右点更新,如果重合则选择长度短的,直到右点不更新,继续步骤2。
上述算法复杂度是O(n^2)
遍历优化:
在优化过程中,基线的点是不断往右下方移,之前遍历过的点是不需要再重复遍历。
所以,在遍历时可以根据当点的邻接点来遍历,不需要全部。
这样每个点最多被遍历一次,算法复杂度在O(n)。
如何从候选点找到选中点
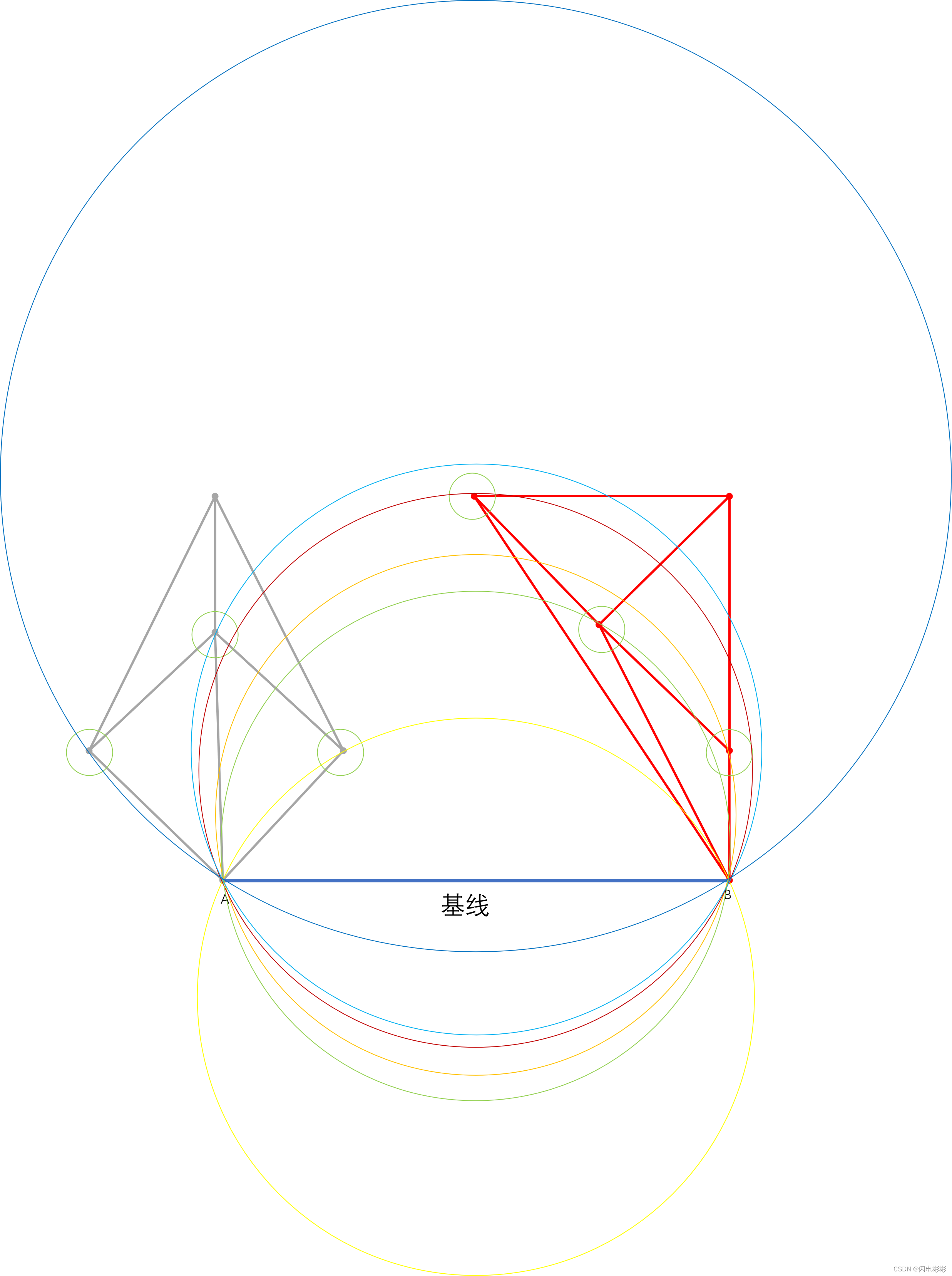
枚举出所有点形成的圆,可以看出只有基线往上面积最小的圆是符合要求的。
算法过程:
随机选中1点为选中点,遍历剩下的点,如果当前遍历点在外接圆里面,则更新当前遍历点为选中点。
删除边实现
- 相交判断参考往期文章,利用跨立测试进行判断。 点击前往
- 对边删除实现
使用双边数据结构,在每一条边结构里加入一个对边指针。
在删除自身时可以直接删除对边。
判断空圆性
利用三维抛物面判断点击前往
内存占用
主要是边数量的估计,点击前往
疑惑:新加入的边会之前构建三角形的空圆性
这里有一个疑惑需要解决。
在算法中每次检测空圆性只关注基线以上的点,有没有可能在加入新的边后影响到基线以下三角形的空圆性,如下图。
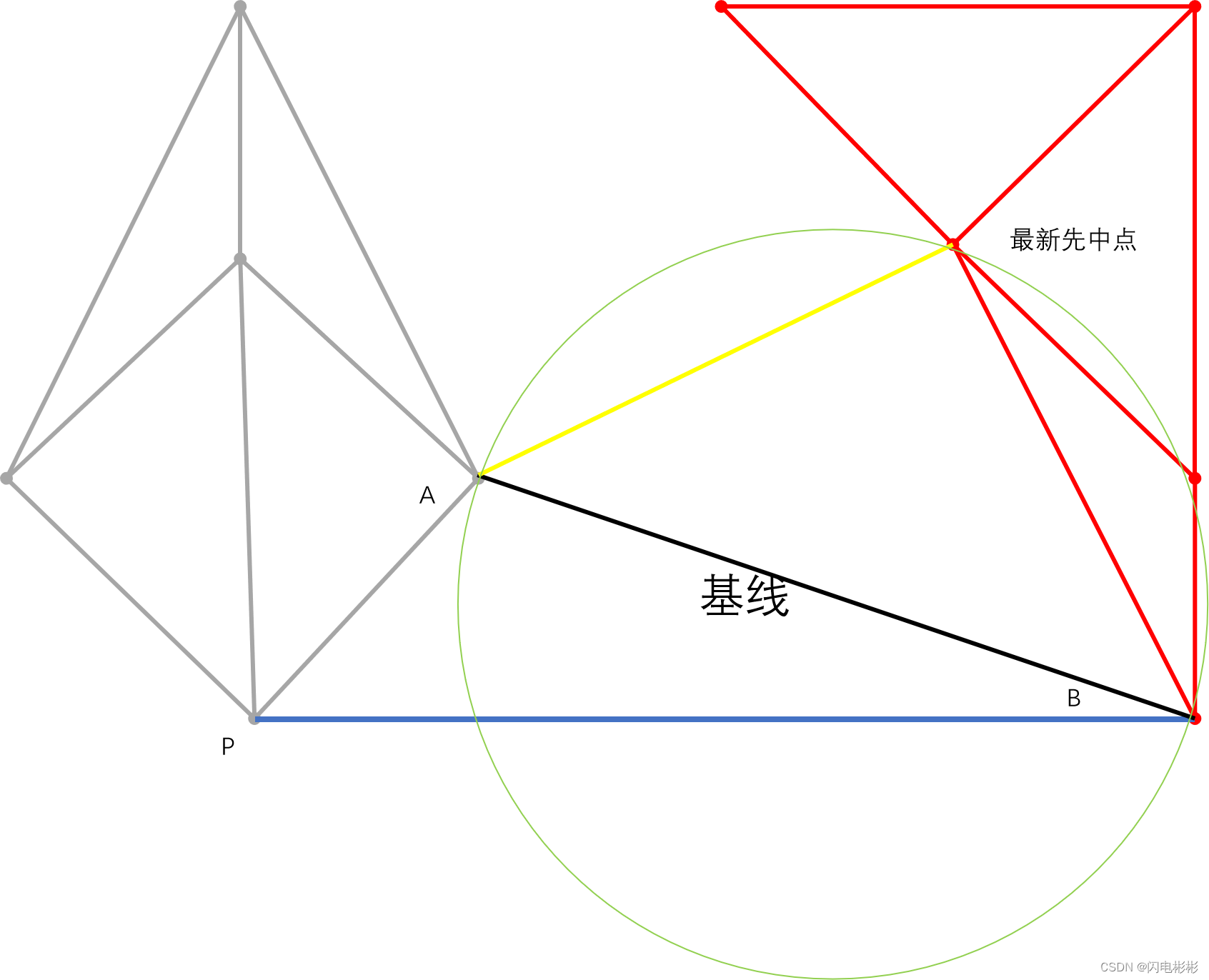
绿色圆有可能包含P点。
答案是不能。
先证明一个引理
引理1:如果一个4边形4点共圆,那么对角相加为180度
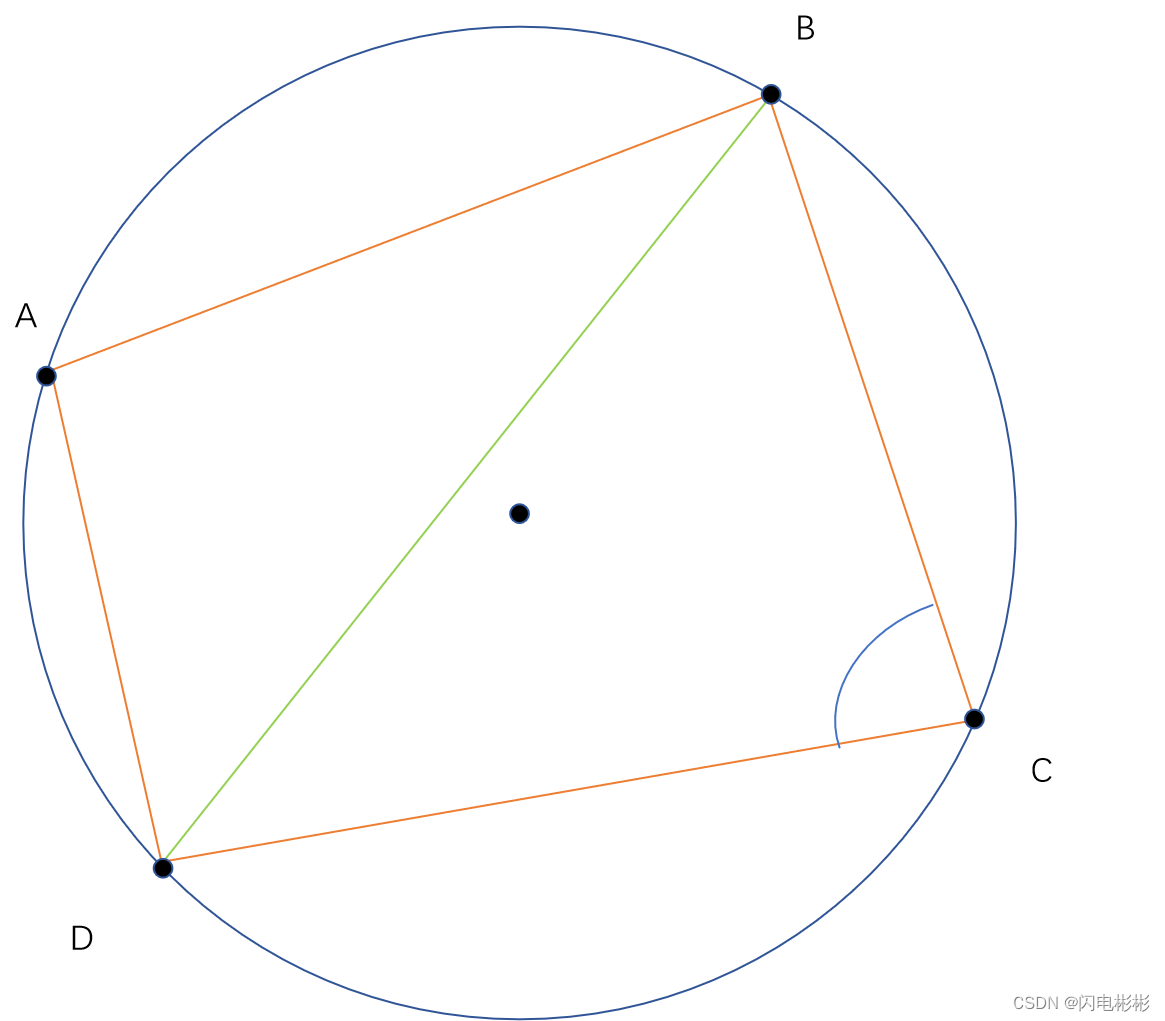
如上图,A,B,C,D 4点共圆。
则
∠
C
+
∠
A
=
180
则 \angle C+ \angle A=180
则∠C+∠A=180
证明:
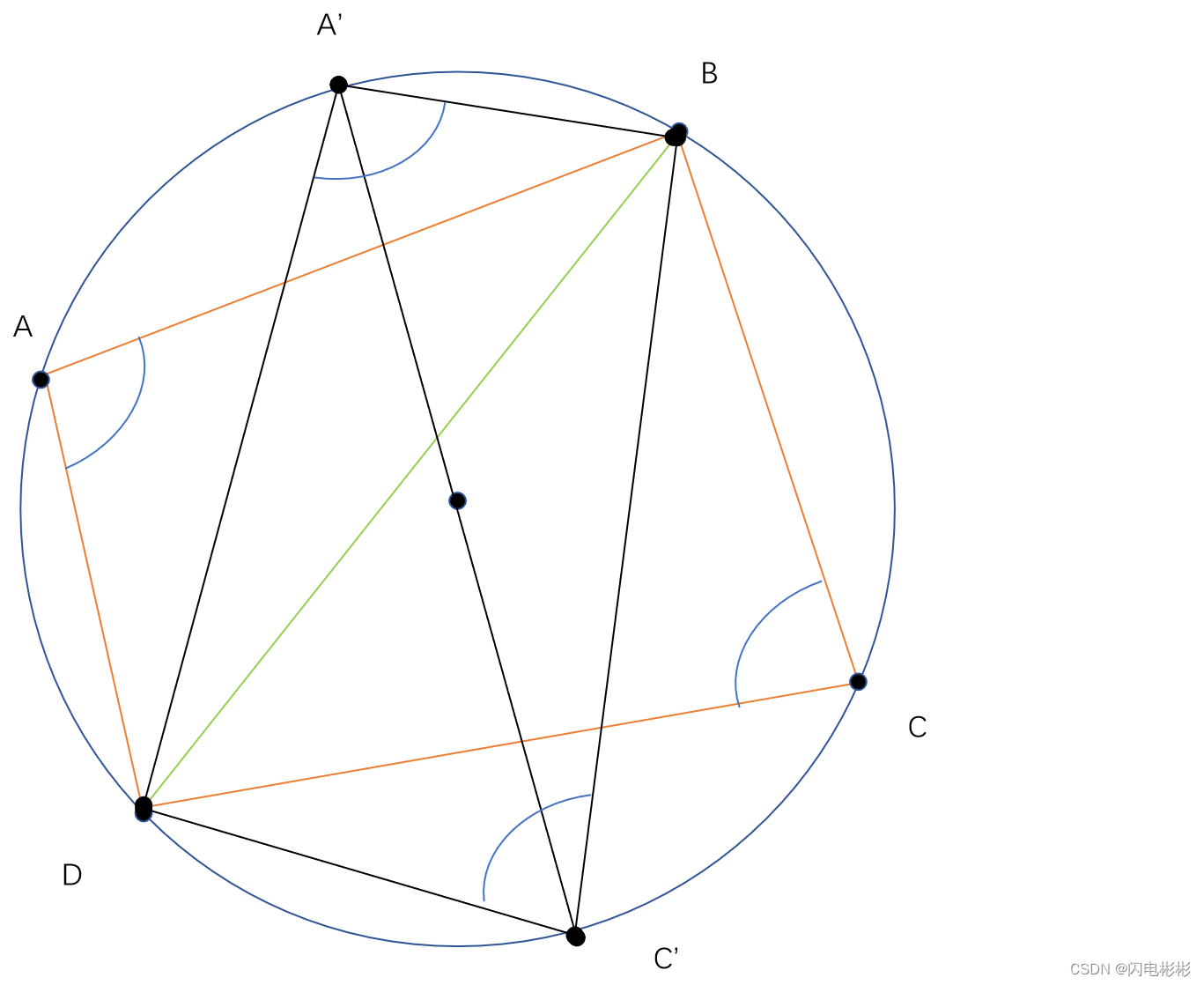
过圆心作一个直径A’C’, 连接A’D, A’B, C’D, C’B.
可知 ∠ A ′ D C ′ = ∠ C ′ B A ′ = 9 0 0 可知\angle A'DC'=\angle C'BA' = 90^0 可知∠A′DC′=∠C′BA′=900
根据四边形内角和为 36 0 0 , 可知 ∠ B C ′ D + ∠ B A ′ D = 18 0 0 根据四边形内角和为360^0, 可知\angle BC'D+\angle BA'D=180^0 根据四边形内角和为3600,可知∠BC′D+∠BA′D=1800
又 ∵ ∠ A 和 ∠ D A ′ B 为同弦同侧圆周角, ∠ C 和 ∠ D C ′ B 为同弦同侧圆周角 又\because \angle A和 \angle DA'B 为同弦同侧圆周角, \angle C 和 \angle DC'B为同弦同侧圆周角 又∵∠A和∠DA′B为同弦同侧圆周角,∠C和∠DC′B为同弦同侧圆周角
∴ ∠ A = ∠ D A ′ B , ∠ C = ∠ D C ′ B \therefore \angle A= \angle DA'B , \angle C = \angle DC'B ∴∠A=∠DA′B,∠C=∠DC′B
∴ ∠ A + ∠ C = ∠ D C ′ B + ∠ D A ′ B = 18 0 0 \therefore \angle A+ \angle C = \angle DC'B+\angle DA'B = 180^0 ∴∠A+∠C=∠DC′B+∠DA′B=1800
命题得证
引理2:4边形中如果1点所在角与对角和与180关系判断该点与另3点外接圆的关系
根据引理1可以得到如下结论:
4边形中如果1点所在角与对角和
1) >180: 在另三点外接圆内。
2)=180:在另三点外接圆上。
3)<180:在另三点外接圆外。
上述关系逆命题也成立。
之后加入的边不会影响之前的空圆性
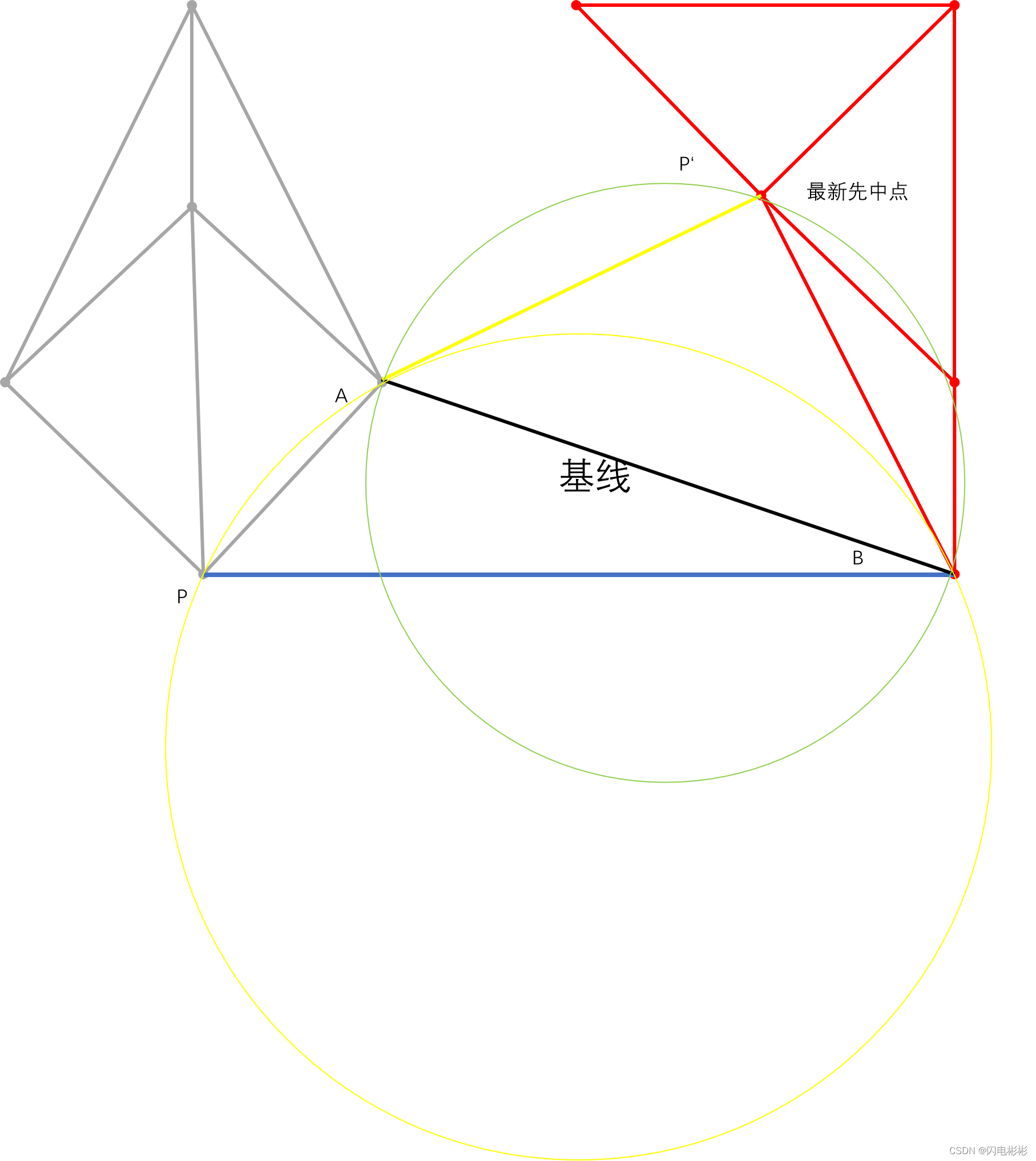
如上图,根据定义黄色的圆不会包含任何点
可知,点 p ′ 是在圆外面, ∠ A P B + ∠ B P ′ A < 18 0 0 可知,点p'是在圆外面,\angle APB + \angle BP'A < 180^0 可知,点p′是在圆外面,∠APB+∠BP′A<1800
所以,反过来绿色的圆也不会包含 P 点 所以,反过来绿色的圆也不会包含P点 所以,反过来绿色的圆也不会包含P点
代码模板
class Delaunay {
public:
std::list<EdgeDelaunay> head[N]; // graph
Point p[N];
int n=0;
void init(int psize, Point ps[]) {
this->n = psize;
memcpy(this->p, ps, sizeof(Point) * n);
std::sort(this->p, this->p + n);
divide(0, n - 1);
}
void addEdge(int u, int v) {
head[u].push_front(EdgeDelaunay(v));
head[v].push_front(EdgeDelaunay(u));
head[u].begin()->c = head[v].begin();
head[v].begin()->c = head[u].begin();
}
void divide(int l, int r) {
if (r - l <= 1) { // #point <= 2
for (int i = l; i <= r; i++)
for (int j = i + 1; j <= r; j++) addEdge(i, j);
return;
}
int mid = (l + r) / 2;
divide(l, mid);
divide(mid + 1, r);
std::list<EdgeDelaunay>::iterator it;
int nowl = l, nowr = r;
for (int update = 1; update;) {
// 查找左边最低线位置
update = 0;
Point ptL = p[nowl], ptR = p[nowr];
for (it = head[nowl].begin(); it != head[nowl].end(); it++) {
Point t = p[it->id];
double v = cross(ptL - ptR, t - ptR);
if (cmp(v) > 0 || (cmp(v) == 0 && (t - ptR).dis() < (ptL - ptR).dis())) {
nowl = it->id, update = 1;
break;
}
}
if (update) continue;
// 查找右边最低线位置
for (it = head[nowr].begin(); it != head[nowr].end(); it++) {
Point t = p[it->id];
double v = cross(ptR - ptL, t - ptL);
if (cmp(v) < 0 || (cmp(v) == 0 && (t - ptL).dis() < (ptL - ptR).dis())) {
nowr = it->id, update = 1;
break;
}
}
}
addEdge(nowl, nowr); // 添加基线
for (; true;) {
Point ptL = p[nowl], ptR = p[nowr];
int ch = -1, side = 0;
for (it = head[nowl].begin(); it != head[nowl].end(); it++) {
if (cmp(cross(ptR - ptL, p[it->id] - ptL)) <= 0)continue; // 判断夹角是否小于180
if (ch == -1 || inCircle(ptL, ptR, p[ch], p[it->id]) < 0) {
ch = it->id, side = -1;
}
}
for (it = head[nowr].begin(); it != head[nowr].end(); it++) {
if (cmp(cross(p[it->id] - ptR, ptL - ptR)) <= 0) continue;// 判断夹角是否小于180
if (ch == -1 || inCircle(ptL, ptR, p[ch], p[it->id]) < 0) {
ch = it->id, side = 1;
}
}
if (ch == -1) break; // 所有线已经加完
if (side == -1) {
for (it = head[nowl].begin(); it != head[nowl].end();) {
// 判断是否相交,边缘不算相交
if (cross(Line(ptL, p[it->id]), Line(ptR, p[ch]))) {
head[it->id].erase(it->c);
head[nowl].erase(it++);
}
else {
it++;
}
}
nowl = ch;
addEdge(nowl, nowr);
}
else {
for (it = head[nowr].begin(); it != head[nowr].end();) {
// 判断是否相交,边缘不算相交
if (cross(Line(ptR, p[it->id]), Line(ptL, p[ch]))) {
head[it->id].erase(it->c);
head[nowr].erase(it++);
}
else {
it++;
}
}
nowr = ch;
addEdge(nowl, nowr);
}
}
}
std::vector<std::pair<int, int> > getEdge() {
std::vector<std::pair<int, int> > ret;
ret.reserve(n);
std::list<EdgeDelaunay>::iterator it;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
//printf("%d : ", p[i].id);
for (it = head[i].begin(); it != head[i].end(); it++) {
//printf("%d, ", p[it->id].id);
if (it->id < i) continue;
ret.push_back(std::make_pair(p[i].id, p[it->id].id));
}
//puts("");
}
return ret;
}
};
练习一
题目链接:https://codeforces.com/problemsets/acmsguru/problem/99999/383
题目大意
沙漠中有很多绿洲用点表示。有很多支队伍,每支队都有自己的起点和终点,队伍在行进过程中都要经过很多绿洲休息,所以都希望从一个绿洲出发时尽快的到下一个绿洲(也就是希望经过两个绿洲越近越好)。
也就是希望经过所有绿洲中相邻两个绿洲距离最大值越小越好。
答案是求一支队伍在从起点到终点经过的绿洲中最远的2个绿洲距离。
思路分析
首先题目只给出点,没有给出点与点之间的通路。
那么首先就要确定1个点到周围哪些点需要有通路。这个可以通过delaunay三角化解决。
有很了边以后,需要去掉很多没有用的边,肯定是希望边距离越小越好,可以使用最小生树,只留下必要的边。最小生成树点击前往
最后求2点之最经过的最大边,使用最近公共祖先解决点击前往
代码
#include<stdio.h>
#include<cmath>
#include <algorithm>
#include <vector>
#include <list>
#include <cstring>
#include <utility>
using namespace std;
const double EPS = 1e-8;
const int N = 1e5 + 10;
const int M = 1e5 + 10;
int cmp(double d) {
if (abs(d) < EPS)return 0;
if (d > 0)return 1;
return -1;
}
class Point {
public:
double x, y;
int id;
Point() {}
Point(double a, double b) :x(a), y(b) {}
Point(const Point& p) :x(p.x), y(p.y), id(p.id) {}
void in() {
scanf("%lf %lf", &x, &y);
}
void out() {
printf("%f %f\n", x, y);
}
double dis() {
return sqrt(x * x + y * y);
}
double dis2() {
return x * x + y * y;
}
Point operator -() const {
return Point(-x, -y);
}
Point operator -(const Point& p) const {
return Point(x - p.x, y - p.y);
}
Point operator +(const Point& p) const {
return Point(x + p.x, y + p.y);
}
Point operator *(double d)const {
return Point(x * d, y * d);
}
Point operator /(double d)const {
return Point(x / d, y / d);
}
void operator -=(Point& p) {
x -= p.x;
y -= p.y;
}
void operator +=(Point& p) {
x += p.x;
y += p.y;
}
void operator *=(double d) {
x *= d;
y *= d;
}
void operator /=(double d) {
this ->operator*= (1 / d);
}
bool operator<(const Point& a) const {
return x < a.x || (abs(x - a.x) < EPS && y < a.y);
}
bool operator==(const Point& a) const {
return abs(x - a.x) < EPS && abs(y - a.y) < EPS;
}
};
// 向量操作
double cross(const Point& a, const Point& b) {
return a.x * b.y - a.y * b.x;
}
double dot(const Point& a, const Point& b) {
return a.x * b.x + a.y * b.y;
}
class Point3D {
public:
double x, y, z;
Point3D() {}
Point3D(double a, double b, double c) :x(a), y(b), z(c) {}
Point3D(const Point3D& p) :x(p.x), y(p.y), z(p.z) {}
double dis() {
return sqrt(x * x + y * y + z * z);
}
double dis2() {
return x * x + y * y + z * z;
}
Point3D operator -(const Point3D& p) const {
return Point3D(x - p.x, y - p.y, z - p.z);
}
Point3D operator +(const Point3D& p) const {
return Point3D(x + p.x, y + p.y, z + p.z);
}
Point3D operator *(double d)const {
return Point3D(x * d, y * d, z * d);
}
Point3D operator /(double d)const {
return Point3D(x / d, y / d, z / d);
}
void operator -=(Point3D& p) {
x -= p.x;
y -= p.y;
z -= p.z;
}
void operator +=(Point3D& p) {
x += p.x;
y += p.y;
z += p.z;
}
void operator *=(double d) {
x *= d;
y *= d;
z *= d;
}
void operator /=(double d) {
this ->operator*= (1 / d);
}
};
// 向量操作
Point3D cross(const Point3D& a, const Point3D& b) {
return Point3D(a.y * b.z - a.z * b.y, -a.x * b.z + a.z * b.x,
a.x * b.y - a.y * b.x);
}
double dot(const Point3D& a, const Point3D& b) {
return a.x * b.x + a.y * b.y + a.z * b.z;
}
class Line {
public:
Point front, tail;
Line() {}
Line(Point a, Point b) :front(a), tail(b) {}
};
/*
0 不相交
1 相交
0 平行/重合
*/
int cross(const Line& a, const Line& b) {
Point dir1 = a.front - a.tail;
Point dir2 = b.front - b.tail;
if (cmp(cross(dir1, dir2)) == 0) {
return 0;
}
if (cmp(cross(a.front - b.tail, dir2)) * cmp(cross(a.tail - b.tail, dir2)) >= 0)return 0;
if (cmp(cross(b.front - a.tail, dir1)) * cmp(cross(b.tail - a.tail, dir1)) >= 0)return 0;
return 1;
}
int inCircle(Point p0, Point p1, Point p2, Point p3) {
Point d1 = p1 - p0;
Point d2 = p2 - p0;
if (cross(d1, d2) < 0)return inCircle(p0, p2, p1, p3); // 保证平面法向向上
// 构建映射点
Point3D lift0(p0.x, p0.y, p0.dis2());
Point3D lift1(p1.x, p1.y, p1.dis2());
Point3D lift2(p2.x, p2.y, p2.dis2());
Point3D lift3(p3.x, p3.y, p3.dis2());
Point3D z1(lift1 - lift0), z2(lift2 - lift0);
Point3D normal = cross(z1, z2); // 计算平面法向
double project = dot(normal, lift3 - lift0); // 计算点到平面距离
return cmp(project);
}
// https://oi-wiki.org//geometry/inverse/#%E5%8F%82%E8%80%83%E8%B5%84%E6%96%99%E4%B8%8E%E6%8B%93%E5%B1%95%E9%98%85%E8%AF%BB
// 根据官方定义实现圆的反演
class Circle
{
public:
Point center;
double r;
Circle(const Point& c, double a) :center(c), r(a) {}
Circle() {}
void in() {
center.in();
scanf("%lf", &r);
}
void out() {
center.out();
printf("%f\n", r);
}
// 不过圆心的圆进行反演,得到1个圆
Circle invert(const Circle& A) {
Circle B;
double oa = (center - A.center).dis();
B.r = r * r / 2 * (1.0 / (oa - A.r) - 1.0 / (oa + A.r));
double ob = r * r / (oa + A.r) + B.r;
B.center = center + (A.center - center) * ob / oa;
return B;
}
// 过圆心的圆进行反演,得到1条直线
Point invert2line(const Circle& c) {
return Point();
}
// 求反演点
Point invertPoint(const Point& p) {
Point dir = p - center;
double dis = dir.dis();
dir /= dis;
dis = r * r / dis;
return center + dir * dis;
}
// 直线反演,得到圆
Circle invert2circle(const Line& l) {
Point dir = l.front - l.tail;
dir /= dir.dis();
Circle c(Point(0, 0), 0);
// 计算投影
Point cdir = center - l.tail;
Point project = l.tail + dir * (dir.x * cdir.x + dir.y * cdir.y);// 点乘得到投影长度
// 计算圆到直线的距离
Point op = project - center;
if (op.dis() < 1e-6)return c;// 直线与圆心重合非法
// 求解圆上的最远点
double d = r * r / op.dis();
Point pf = center + op / op.dis() * d;
c.center = (center + pf) / 2;
c.r = d / 2;
return c;
}
};
class Edge {
public:
Edge() {}
Edge(int t, int n, double w) :to(t), next(n), weight(w) {}
int index;
int from;
int to;
int next;
double weight;
bool isValid() const { return to >= 0; }
};
class EdgeDelaunay {
public:
int id;
std::list<EdgeDelaunay>::iterator c;
EdgeDelaunay(int id = 0) { this->id = id; }
};
class Delaunay {
public:
std::list<EdgeDelaunay> head[N]; // graph
Point p[N];
int n=0;
void init(int psize, Point ps[]) {
this->n = psize;
memcpy(this->p, ps, sizeof(Point) * n);
std::sort(this->p, this->p + n);
divide(0, n - 1);
}
void addEdge(int u, int v) {
head[u].push_front(EdgeDelaunay(v));
head[v].push_front(EdgeDelaunay(u));
head[u].begin()->c = head[v].begin();
head[v].begin()->c = head[u].begin();
}
void divide(int l, int r) {
if (r - l <= 1) { // #point <= 2
for (int i = l; i <= r; i++)
for (int j = i + 1; j <= r; j++) addEdge(i, j);
return;
}
int mid = (l + r) / 2;
divide(l, mid);
divide(mid + 1, r);
std::list<EdgeDelaunay>::iterator it;
int nowl = l, nowr = r;
for (int update = 1; update;) {
// 查找左边最低线位置
update = 0;
Point ptL = p[nowl], ptR = p[nowr];
for (it = head[nowl].begin(); it != head[nowl].end(); it++) {
Point t = p[it->id];
double v = cross(ptL - ptR, t - ptR);
if (cmp(v) > 0 || (cmp(v) == 0 && (t - ptR).dis() < (ptL - ptR).dis())) {
nowl = it->id, update = 1;
break;
}
}
if (update) continue;
// 查找右边最低线位置
for (it = head[nowr].begin(); it != head[nowr].end(); it++) {
Point t = p[it->id];
double v = cross(ptR - ptL, t - ptL);
if (cmp(v) < 0 || (cmp(v) == 0 && (t - ptL).dis() < (ptL - ptR).dis())) {
nowr = it->id, update = 1;
break;
}
}
}
addEdge(nowl, nowr); // 添加基线
for (; true;) {
Point ptL = p[nowl], ptR = p[nowr];
int ch = -1, side = 0;
for (it = head[nowl].begin(); it != head[nowl].end(); it++) {
if (cmp(cross(ptR - ptL, p[it->id] - ptL)) <= 0)continue; // 判断夹角是否小于180
if (ch == -1 || inCircle(ptL, ptR, p[ch], p[it->id]) < 0) {
ch = it->id, side = -1;
}
}
for (it = head[nowr].begin(); it != head[nowr].end(); it++) {
if (cmp(cross(p[it->id] - ptR, ptL - ptR)) <= 0) continue;// 判断夹角是否小于180
if (ch == -1 || inCircle(ptL, ptR, p[ch], p[it->id]) < 0) {
ch = it->id, side = 1;
}
}
if (ch == -1) break; // 所有线已经加完
if (side == -1) {
for (it = head[nowl].begin(); it != head[nowl].end();) {
// 判断是否相交,边缘不算相交
if (cross(Line(ptL, p[it->id]), Line(ptR, p[ch]))) {
head[it->id].erase(it->c);
head[nowl].erase(it++);
}
else {
it++;
}
}
nowl = ch;
addEdge(nowl, nowr);
}
else {
for (it = head[nowr].begin(); it != head[nowr].end();) {
// 判断是否相交,边缘不算相交
if (cross(Line(ptR, p[it->id]), Line(ptL, p[ch]))) {
head[it->id].erase(it->c);
head[nowr].erase(it++);
}
else {
it++;
}
}
nowr = ch;
addEdge(nowl, nowr);
}
}
}
std::vector<std::pair<int, int> > getEdge() {
std::vector<std::pair<int, int> > ret;
ret.reserve(n);
std::list<EdgeDelaunay>::iterator it;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
//printf("%d : ", p[i].id);
for (it = head[i].begin(); it != head[i].end(); it++) {
//printf("%d, ", p[it->id].id);
if (it->id < i) continue;
ret.push_back(std::make_pair(p[i].id, p[it->id].id));
}
//puts("");
}
return ret;
}
};
class Graph {
public:
int size;
Graph() {}
void init(int n) {
size = n;
head.assign(n, -1);
edge.resize(M * 4);
len = 0;
emptyEdge = Edge(-1, -1, 0);
}
Edge headEdge(int a) {
if (head[a] < 0)return emptyEdge;
return edge[head[a]];
}
Edge nextEdge(const Edge& ed) {
if (ed.next < 0)return emptyEdge;
return edge[ed.next];
}
void add(int a, int b, double w) {
//printf("add : %d %d %.6lf\n", a, b, w);
edge[len] = Edge(b, head[a], w);
edge[len].index = len;
head[a] = len;
len++;
}
private:
vector<int> head;
int len;
Edge emptyEdge;
vector<Edge> edge;
};
Graph g;
class UnionFindSet {
private:
vector<int> father; // 父结点定义,father[i]=i时,i为本集合的代表
vector<int> height; // 代表树高度,初始为1
int nodeNum; // 集合中的点数
public:
UnionFindSet(int n); // 初始化
bool Union(int x, int y); // 合并
int Find(int x);
bool UnionV2(int x, int y); // 合并
int FindV2(int x);
};
UnionFindSet::UnionFindSet(int n) : nodeNum(n + 1) {
father = vector<int>(nodeNum);
height = vector<int>(nodeNum);
for (int i = 0; i < nodeNum; ++i) father[i] = i, height[i] = 1; // 初始为自己
}
int UnionFindSet::Find(int x) {
while (father[x] != x) x = father[x];
return x;
}
bool UnionFindSet::Union(int x, int y) {
x = Find(x);
y = Find(y);
if (x == y)return false;
father[x] = y;
return true;
}
int UnionFindSet::FindV2(int x) {
int root = x; // 保存好路径上的头结点
while (father[root] != root) {
root = father[root];
}
/*
从头结点开始一直往根上遍历
把所有结点的father直接指向root。
*/
while (father[x] != x) {
// 一定要先保存好下一个结点,下一步是要对father[x]进行赋值
int temp = father[x];
father[x] = root;
x = temp;
}
return root;
}
/*
需要加入height[]属性,初始化为1.
*/
//合并结点
bool UnionFindSet::UnionV2(int x, int y) {
x = Find(x);
y = Find(y);
if (x == y) {
return false;
}
if (height[x] < height[y]) {
father[x] = y;
}
else if (height[x] > height[y]) {
father[y] = x;
}
else {
father[x] = y;
height[y]++;
}
return true;
}
// 最小生成树
class MST {
vector<Edge> edges;
UnionFindSet ufs;
public:
MST(int n, vector<Edge>& ed) :ufs(n), edges(ed) { g.init(n); }
void build() {
sort(edges.begin(), edges.end(), [=](Edge& a, Edge& b)->bool {return a.weight < b.weight; });
for (auto d : edges) {
if (ufs.UnionV2(d.from, d.to)) {
g.add(d.from, d.to, d.weight);
g.add(d.to, d.from, d.weight);
}
}
}
};
const int bitL = 22;
class LCA {
int h[N];
int father[bitL][N];
double dis[bitL][N];
public:
void dfs(int x, int fa, double w)
{
if (fa == -1) h[x] = 0;
else {
h[x] = h[fa] + 1;
father[0][x] = fa;
dis[0][x] = w;
for (int t = 1; t < bitL && (1 << t) <= h[x]; t++) {
father[t][x] = father[t - 1][father[t - 1][x]];
dis[t][x] = max(dis[t - 1][x], dis[t - 1][father[t - 1][x]]);
}
}
for (auto ed = g.headEdge(x); ed.isValid(); ed = g.nextEdge(ed))
{
int j = ed.to;
if (fa == j)continue;
dfs(j, x, ed.weight);
}
}
int lca(int a, int b) {
if (h[a] < h[b]) {
return lca(b, a);
}
int gap = h[a] - h[b];
for (int t = bitL - 1; t >= 0; t--) {
if (gap & (1 << t))a = father[t][a];
}
if (a == b)return a;
gap = h[a];
for (int t = bitL - 1; t >= 0; t--) {
if (gap <= (1 << t))continue;
if (father[t][a] == father[t][b])continue;
a = father[t][a];
b = father[t][b];
gap -= 1 << t;
}
return father[0][a];
}
double optDis(int a, int b) {
if (h[a] < h[b]) {
return optDis(b, a);
}
double d = 0;
int gap = h[a] - h[b];
for (int t = bitL - 1; t >= 0; t--) {
if (gap & (1 << t)) {
d = max(d, dis[t][a]);
a = father[t][a];
}
}
if (a == b)return d;
gap = h[a];
for (int t = bitL - 1; t >= 0; t--) {
if (gap <= (1 << t))continue;
if (father[t][a] == father[t][b])continue;
d = max(d, dis[t][a]);
d = max(d, dis[t][b]);
a = father[t][a];
b = father[t][b];
gap -= 1 << t;
}
d = max(d, max(dis[0][a], dis[0][b]));
return d;
}
};
Point oiPs[N];
Delaunay de;
LCA lc;
void solve() {
int n, m;
scanf("%d", &n);
int a, b;
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) {
scanf("%d%d", &a, &b);
oiPs[i].x = a;
oiPs[i].y = b;
oiPs[i].id = i;
}
de.init(n, oiPs);
auto oiedges = de.getEdge();
vector<Edge> edges;
for (auto oie : oiedges) {
Edge ed(oie.second, -1, (oiPs[oie.first] - oiPs[oie.second]).dis());
ed.from = oie.first;
edges.push_back(ed);
}
MST mst(n, edges);
mst.build();
/*for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) {
printf("%d : ", i);
for (Edge ed = g.headEdge(i); ed.isValid(); ed = g.nextEdge(ed)) {
printf("%d ", ed.to);
}
puts("");
}*/
lc.dfs(0, -1, 0);
scanf("%d", &m);
while (m--) {
scanf("%d%d", &a, &b);
a--, b--;
printf("%.11f\n", lc.optDis(a, b));
}
}
int main() {
solve();
return 0;
}
/*
3
0 0
50 10
150 0
3
1 2
1 3
2 3
4
0 1
1 0
1 1
0 0
4
1 2
2 3
4 1
1 3
4
0 0
0 1
1 0
1 1
4
1 2
2 3
4 1
1 3
6
0 0
0 1
0 2
0 3
0 4
0 5
4
1 2
2 3
4 1
1 3
6
1 0
5 0
0 0
2 0
3 0
4 0
4
1 2
2 3
4 1
1 3
10
0 0
1 1
1 2
2 1
2 3
2 9
3 2
4 6
7 9
9 8
10
1 2
2 3
3 4
4 5
5 6
6 7
7 8
8 9
9 10
10 1
7
0 0
1 1
1 2
2 1
2 3
2 9
3 2
1
1 2
10
1 2
2 1
1 1
9 8
7 9
2 3
4 6
2 9
0 0
3 2
10
1 2
2 3
3 4
4 5
5 6
6 7
7 8
8 9
9 10
10 1
*/
/*
10
1 2
1.00000000000
2 3
1.00000000000
3 4
4.24264068712
4 5
2.23606797750
5 6
4.24264068712
6 7
3.60555127546
7 8
3.60555127546
8 9
3.60555127546
9 10
1.41421356237
10 1
1.41421356237
4
1 2
1.00000000000
2 3
1.00000000000
4 1
1.00000000000
1 3
1.00000000000
*/
本人码农,希望通过自己的分享,让大家更容易学懂计算机知识。创作不易,帮忙点击公众号的链接。


![[Leetcode] 0108. 将有序数组转换为二叉搜索树](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/img_convert/9c970c6c3847ede3a76b5d6faa682f47.png)