文章目录
- 4.2.1 矩阵的数组表示
- 4.2.2 特殊矩阵的压缩存储
- a. 对角矩阵的压缩存储
- b~c. 三角、对称矩阵的压缩存储
- d. 稀疏矩阵的压缩存储——三元组表
- e. 压缩稀疏行(Compressed Sparse Row,CSR)矩阵
- f. 压缩稀疏列(Compressed Sparse Column,CSC)矩阵
- 结构体
- 创建CSC矩阵
- 元素设置
- 初始化
- 打印矩阵
- 销毁CSC矩阵
- 主函数
- 代码整合
4.2.1 矩阵的数组表示
【数据结构】数组和字符串(一):矩阵的数组表示
4.2.2 特殊矩阵的压缩存储
矩阵是以按行优先次序将所有矩阵元素存放在一个一维数组中。但是对于特殊矩阵,如对称矩阵、三角矩阵、对角矩阵和稀疏矩阵等, 如果用这种方式存储,会出现大量存储空间存放重复信息或零元素的情况,这样会造成很大的空间浪费。为节约存储空间和算法(程序)运行时间,通常会采用压缩存储的方法。
- 对角矩阵:指除了主对角线以外的元素都为零的矩阵,即对 任意 i ≠ j (1≤ i , j ≤n),都有M(i, j)=0。由于只有主对角线上有非零元素,只需存储主对角线上的元素即可。
- 三角矩阵:指上三角或下三角的元素都为零的矩阵。同样地,只需存储其中一部分非零元素,可以节省存储空间。
- 对称矩阵:指矩阵中的元素关于主对角线对称的矩阵。由于对称矩阵的非零元素有一定的规律,可以只存储其中一部分元素,从而减少存储空间。
- 稀疏矩阵:指大部分元素为零的矩阵。传统的按行优先次序存储方法会浪费大量空间来存储零元素,因此采用压缩存储的方法更为合适。常见的压缩存储方法有:压缩稠密行(CSR)、压缩稠密列(CSC)、坐标列表(COO)等。
a. 对角矩阵的压缩存储
【数据结构】数组和字符串(二):特殊矩阵的压缩存储:对角矩阵——一维数组
b~c. 三角、对称矩阵的压缩存储
【数据结构】数组和字符串(三):特殊矩阵的压缩存储:三角矩阵、对称矩阵——一维数组
d. 稀疏矩阵的压缩存储——三元组表
【数据结构】数组和字符串(四):特殊矩阵的压缩存储:稀疏矩阵——三元组表
e. 压缩稀疏行(Compressed Sparse Row,CSR)矩阵
【数据结构】数组和字符串(五):特殊矩阵的压缩存储:稀疏矩阵——压缩稀疏行(CSR)
f. 压缩稀疏列(Compressed Sparse Column,CSC)矩阵
压缩稀疏列(Compressed Sparse Column,CSC)以列为主要组织方式,将矩阵按列进行存储。它包含三个主要数组:
-
列指针数组(Column Pointer Array):该数组的长度为矩阵的列数加一(cols+1),每个元素存储对应列中第一个非零元素在元素数组中的索引位置。最后一个元素存储非零元素的总数以及元素数组的长度。
-
行索引数组(Row Index Array):该数组的长度等于非零元素的数量,每个元素存储对应非零元素所在的行索引。
-
元素数组(Element Array):该数组的长度等于非零元素的数量,每个元素存储非零元素的值以及它所在的列索引。
通过这种方式,CSC格式将稀疏矩阵的非零元素按列进行存储,并通过列指针数组和行索引数组提供了对非零元素在矩阵中位置的快速访问。
结构体
typedef struct {
int row;
int col;
int value;
} Element;
typedef struct {
int rows;
int cols;
int num_elements;
Element* elements;
int* col_ptr;
int* row_indices;
} CSCMatrix;
-
Element结构体表示矩阵中的一个元素,包含三个成员变量:row(行索引)、col(列索引)和value(元素值)。 -
CSCMatrix结构体表示一个CSC矩阵,包含了矩阵的行数rows、列数cols、非零元素的个数num_elements,以及三个指针成员变量elements、col_ptr和row_indices。
创建CSC矩阵
CSCMatrix createCSCMatrix(int rows, int cols, int num_elements) {
CSCMatrix matrix;
matrix.rows = rows;
matrix.cols = cols;
matrix.num_elements = num_elements;
matrix.elements = (Element*)malloc(num_elements * sizeof(Element));
matrix.col_ptr = (int*)malloc((cols + 1) * sizeof(int));
matrix.row_indices = (int*)malloc(num_elements * sizeof(int));
memset(matrix.col_ptr, 0, (cols + 1) * sizeof(int));
return matrix;
}
createCSCMatrix函数用于创建一个CSC矩阵。- 接受矩阵的行数、列数和非零元素的个数作为参数,并返回创建的CSC矩阵。
- 在函数内部,通过动态内存分配分别为
elements、col_ptr和row_indices分配内存空间,并将col_ptr数组的所有元素初始化为0,最后返回创建的矩阵。
元素设置
void setElement(CSCMatrix* matrix, int row, int col, int value) {
if (col < 0 || col >= matrix->cols) {
printf("Invalid column index.\n");
return;
}
int index = matrix->col_ptr[col];
matrix->elements[index].row = row;
matrix->elements[index].col = col;
matrix->elements[index].value = value;
matrix->row_indices[index] = row;
matrix->col_ptr[col]++; // 递增索引值
}
setElement 函数可用于设置(修改)CSC矩阵中某个位置的元素值。
- 接受一个指向CSC矩阵的指针
matrix,以及要设置的元素的行索引、列索引和值作为参数。 - 在函数内部,首先检查列索引是否有效,如果无效则打印错误信息并返回。
- 然后,根据列索引找到对应列的起始位置,将元素的行索引、列索引和值分别赋给对应的矩阵元素,并更新
row_indices数组和col_ptr数组中的值。
初始化
void initializeCSCMatrix(CSCMatrix* matrix, int* values, int* row_indices, int* col_indices, int num_elements) {
for (int i = 0; i < num_elements; i++) {
matrix->elements[i].value = values[i];
matrix->elements[i].row = row_indices[i];
matrix->elements[i].col = col_indices[i];
matrix->row_indices[i] = row_indices[i];
matrix->col_ptr[col_indices[i]]++;
}
int sum = 0;
for (int i = 0; i <= matrix->cols; i++) {
int temp = matrix->col_ptr[i];
matrix->col_ptr[i] = sum;
sum += temp;
}
}
initializeCSCMatrix 函数用于初始化CSC矩阵的数据。
- 接受一个指向CSC矩阵的指针
matrix,以及包含非零元素的值、行索引和列索引的数组,以及非零元素的个数作为参数。 - 通过遍历非零元素数组,将值、行索引和列索引分别赋给对应的矩阵元素,并更新
row_indices数组和col_ptr数组中的值。col_ptr数组的每个元素表示对应列的非零元素在elements数组中的起始位置,通过累加非零元素的个数来计算每列的结束位置。
打印矩阵
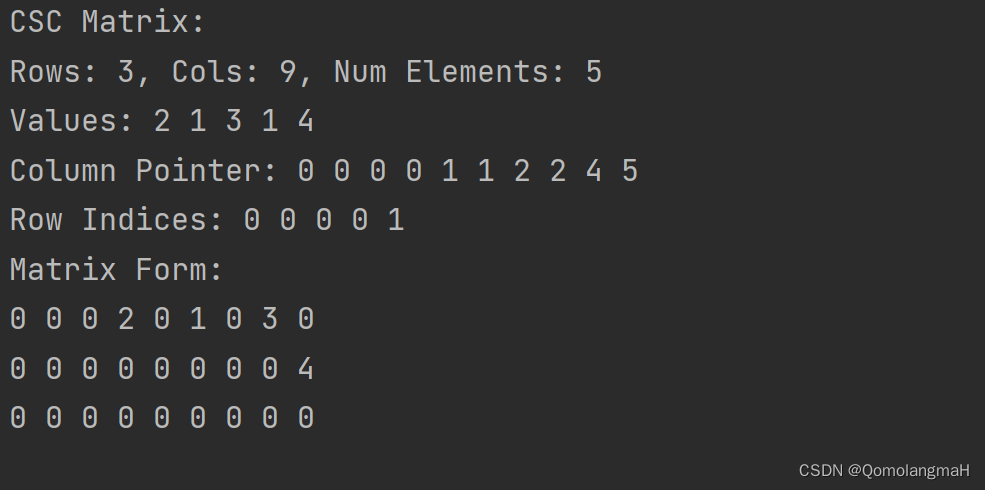
void printCSCMatrix(CSCMatrix matrix) {
printf("CSC Matrix:\n");
printf("Rows: %d, Cols: %d, Num Elements: %d\n", matrix.rows, matrix.cols, matrix.num_elements);
printf("Values: ");
for (int i = 0; i < matrix.num_elements; i++) {
printf("%d ", matrix.elements[i].value);
}
printf("\n");
printf("Column Pointer: ");
for (int i = 0; i <= matrix.cols; i++) {
printf("%d ", matrix.col_ptr[i]);
}
printf("\n");
printf("Row Indices: ");
for (int i = 0; i < matrix.num_elements; i++) {
printf("%d ", matrix.row_indices[i]);
}
printf("\n");
}
void printMatrixForm(CSCMatrix matrix) {
printf("Matrix Form:\n");
for (int i = 0; i < matrix.rows; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < matrix.cols; j++) {
int value = 0;
for (int k = matrix.col_ptr[j]; k < matrix.col_ptr[j + 1]; k++) {
if (matrix.elements[k].row == i) {
value = matrix.elements[k].value;
break;
}
}
printf("%d ", value);
}
printf("\n");
}
}
printCSCMatrix函数用于打印CSC矩阵的信息:它接受一个CSC矩阵作为参数,并打印矩阵的行数、列数、非零元素的个数以及elements、col_ptr和row_indices数组的内容。printMatrixForm函数用于以矩阵形式打印CSC矩阵。它接受一个CSC矩阵作为参数,并按矩阵的行数和列数遍历矩阵元素,通过遍历col_ptr数组和row_indices数组来获取每个位置的元素值,并打印出矩阵的形式。
销毁CSC矩阵
void destroyCSCMatrix(CSCMatrix* matrix) {
free(matrix->elements);
free(matrix->col_ptr);
free(matrix->row_indices);
matrix->elements = NULL;
matrix->col_ptr = NULL;
matrix->row_indices = NULL;
}
主函数
int main() {
int rows = 3;
int cols = 9;
int num_elements = 5;
CSCMatrix matrix = createCSCMatrix(rows, cols, num_elements);
int row_indices[] = {0, 0, 0, 0, 1};
int col_indices[] = {3, 5, 7, 8, 7};
int values[] = {2, 1, 3, 1, 4};
initializeCSCMatrix(&matrix, values, row_indices, col_indices, num_elements);
printCSCMatrix(matrix);
printMatrixForm(matrix);
destroyCSCMatrix(&matrix);
return 0;
}
代码整合
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
typedef struct {
int row;
int col;
int value;
} Element;
typedef struct {
int rows;
int cols;
int num_elements;
Element* elements;
int* col_ptr;
int* row_indices;
} CSCMatrix;
CSCMatrix createCSCMatrix(int rows, int cols, int num_elements) {
CSCMatrix matrix;
matrix.rows = rows;
matrix.cols = cols;
matrix.num_elements = num_elements;
matrix.elements = (Element*)malloc(num_elements * sizeof(Element));
matrix.col_ptr = (int*)malloc((cols + 1) * sizeof(int));
matrix.row_indices = (int*)malloc(num_elements * sizeof(int));
memset(matrix.col_ptr, 0, (cols + 1) * sizeof(int));
return matrix;
}
void setElement(CSCMatrix* matrix, int row, int col, int value) {
if (col < 0 || col >= matrix->cols) {
printf("Invalid column index.\n");
return;
}
int index = matrix->col_ptr[col];
matrix->elements[index].row = row;
matrix->elements[index].col = col;
matrix->elements[index].value = value;
matrix->row_indices[index] = row;
matrix->col_ptr[col]++; // 递增索引值
}
void printCSCMatrix(CSCMatrix matrix) {
printf("CSC Matrix:\n");
printf("Rows: %d, Cols: %d, Num Elements: %d\n", matrix.rows, matrix.cols, matrix.num_elements);
printf("Values: ");
for (int i = 0; i < matrix.num_elements; i++) {
printf("%d ", matrix.elements[i].value);
}
printf("\n");
printf("Column Pointer: ");
for (int i = 0; i <= matrix.cols; i++) {
printf("%d ", matrix.col_ptr[i]);
}
printf("\n");
printf("Row Indices: ");
for (int i = 0; i < matrix.num_elements; i++) {
printf("%d ", matrix.row_indices[i]);
}
printf("\n");
}
void printMatrixForm(CSCMatrix matrix) {
printf("Matrix Form:\n");
for (int i = 0; i < matrix.rows; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < matrix.cols; j++) {
int value = 0;
for (int k = matrix.col_ptr[j]; k < matrix.col_ptr[j + 1]; k++) {
if (matrix.elements[k].row == i) {
value = matrix.elements[k].value;
break;
}
}
printf("%d ", value);
}
printf("\n");
}
}
void destroyCSCMatrix(CSCMatrix* matrix) {
free(matrix->elements);
free(matrix->col_ptr);
free(matrix->row_indices);
matrix->elements = NULL;
matrix->col_ptr = NULL;
matrix->row_indices = NULL;
}
void initializeCSCMatrix(CSCMatrix* matrix, int* values, int* row_indices, int* col_indices, int num_elements) {
for (int i = 0; i < num_elements; i++) {
matrix->elements[i].value = values[i];
matrix->elements[i].row = row_indices[i];
matrix->elements[i].col = col_indices[i];
matrix->row_indices[i] = row_indices[i];
matrix->col_ptr[col_indices[i]]++;
}
int sum = 0;
for (int i = 0; i <= matrix->cols; i++) {
int temp = matrix->col_ptr[i];
matrix->col_ptr[i] = sum;
sum += temp;
}
}
int main() {
int rows = 3;
int cols = 9;
int num_elements = 5;
CSCMatrix matrix = createCSCMatrix(rows, cols, num_elements);
int row_indices[] = {0, 0, 0, 0, 1};
int col_indices[] = {3, 5, 7, 8, 7};
int values[] = {2, 1, 3, 1, 4};
initializeCSCMatrix(&matrix, values, row_indices, col_indices, num_elements);
printCSCMatrix(matrix);
printMatrixForm(matrix);
destroyCSCMatrix(&matrix);
return 0;
}