文件相关命令:
ps -aux|grep init? //搜索包含init名称的进程
top //linux下的资源管理器(动态)
//open 返回的int 是给后面的读/写/光标移动 用的fd,没有open就不能进行后面的操作;
int open(const char *pathname, int flags);
int open(const char *pathname, int flags, mode_t mode);
close(fd); //关闭文件
// _t 都是返回的int数字;写write,读read,光标移动lseek
ssize_t write(int fd, const void *buf, size_t count);
ssize_t read(int fd, void *buf, size_t count);
off_t lseek(int fd, off_t offset, int whence);
//同时打开两个文件
vimdiff demo1.c demo2.c
//fopen注意mode就行,有:r r+ w w+ a ,返回的文件指针是给后面的读 写 偏移用
FILE *fopen(const char *pathname, const char *mode);
fclose(FILE *); //关闭文件
//跟上面的差不多一样用
//fread/fwrite(读写的数组,读写的大小, 读写的最大次数?, 读写的文件指针)
(读写返回次数的区别:读为有效次数,能一次读完就算你写10次,也返回只读1次)
size_t fread(void *ptr, size_t size, size_t nmemb, FILE *stream);
size_t fwrite(const void *ptr, size_t size, size_t nmemb,FILE *stream);
int fseek(FILE *stream, long offset, int whence);
fputc();//写入一个字符;
fgetc();//读取一个字符
feof();/检测是否到达文件末尾,到了返回1;文件结束符为EOF=-1;
//注意:读写操作都会使光标偏移,但也可以利用这点来遍历读写文件;
例:
while(!feof(FILE* fd)){
printf("%c ",fgetc(FILE* fd));
}进程相关命令:
getpid(); fork(); vfork();
//_t 一律返回的是int
//获取进程ID 就是pid
pid_t getpid(void);
//fork创建子进程
pid_t fork(void);
//这里返回的是的pid = 0 就是子进程,pid > 0 就是父进程;
//所以可以通过判断pid的值,来区别父子进程需要执行的代码;
//注意fork开辟的子进程,没有等待一说,父子进程谁抢到就先运行谁,
//【子进程为僵尸进程】;
//例:
#include<stdio.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
int main()
{
pid_t pid;
int num = 0;
pid = getpid();
printf("this pid:%d\n",getpid());
pid_t return_pid = fork();
if(return_pid > 0){
while(1){
printf("this father pid:%d return_pid:%d \n",getpid(),return_pid);
printf("father now num:%d\n",num);
sleep(1);
}
}else if(return_pid == 0){
printf("this son pid:%d return_pid:%d \n",getpid(),return_pid);
num += 2;
printf("child now num:%d\n",num);
exit(6);
}
}
//vfork创建子进程
pid_t vfork(void);
//注意fork开辟的子进程,会等待子进程执行完并exit(num)后,父子进程才继续执行,
//【子进程不会成为僵尸进程】;
//例:
#include<stdio.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
int main()
{
pid_t pid;
pid = getpid();
printf("this pid:%d\n",getpid());
int num = 0;
printf("start_father_num:%d \n",num);
pid_t return_pid = vfork();
if(return_pid > 0){
while(1){
printf("this father pid:%d return_pid:%d \n",getpid(),return_pid);
printf("num = %d\n",num);
sleep(1);
}
}
else if(return_pid == 0){
int i;
for(i=0;i<3;i++){
printf("this son pid:%d return_pid:%d \n",getpid(),return_pid);
num++;
sleep(1);
}
exit(0);
}
return 0;
}
exit(6); wait(status); WEXITSTATUS(status);
子进程退出; 等待子进程; 获取子进程退出状态码;
//wait() 返回的是子进程的ID 即pid;
//里面的 int *status 是子进程的exit(num)的num码;
//后续使用WEXITSTATUS(status),即可打印出来子进程退出时的状态码;
pid_t wait(int *status);
//例:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
int main()
{
pid_t pid;
int status = 0;
pid = getpid();
printf("start father pid:%d\n",getpid());
pid_t return_pid = fork();
if(return_pid > 0 ){
pid_t child_pid = wait(&status);
printf("\n\nwait_return_childe_pid:%d\n",child_pid);
printf("child exit code:%d \n",WEXITSTATUS(status));
while(1){
printf("this father pid:%d fork_return_pid:%d > 0 \n",getpid(),return_pid);
sleep(1);
}
}else if(return_pid == 0){
int i;
for(i=0;i<3;i++){
printf("this son pid:%d fork_return_pid:%d == 0 \n",getpid(),return_pid);
}
exit (6);
}
return 0;
}
exec组函数 对比 system + popen :(程序/进程跳转)
大佬精彩博文: https://blog.csdn.net/u014530704/article/details/73848573
观后感:
跟着execl/execlp指定的程序跑了,不回来了!
// date 获取时间的程序
execl("./PATH","date","NULL");
// execl(程序所在路径,程序名,结尾必须为NULL)
// 就像这样用,在当前程序运行到这句代码时,
// 便将替换为后续执行execl所指的程序,不带回头的那种!
execlp("date","date",NULL);
// execlp(程序名,程序名,结尾必须为NULL)
// 就像这样用,它带p,能自己在环境变量下搜索对应的程序并替换后续执行;
// 也是不带回头的那种!相比较之下 system 执行完指定程序后,还会回来,挺好!
system("cat demo1.c");
//执行完成后返回原程序,继续执行后续代码;
而对比popen 而言,popen除了将指定程序/代码执行完之后,继续执行后续代码外,还将读/写的内容放在管道内,并以文件指针的形式返回;
#include <stdio.h>
#include <unistd.h>
int main()
{
printf("------------------------------------------------\nPS:\n");
char* p = "ps";
FILE *fd = popen(p,"r");
char data[1024];
fread(&data,1024,1,fd);
printf("%s\n",data);
perror("why");
return 0;
}
进程间通讯:
int pipe(int pipefd[2]); (无名管道,在文件里看不到)
里面的fd[2]数组,其中 fd[0] : 读的fd, fd[1] : 写的fd;
例:通过在父子进程中 close (fd[0]/fd[1]) 配合read(); write(); 实现进程间通讯;
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <unistd.h>
int main()
{
printf("------------------------------------------------:\n");
int fd[2];
int n_pipe = pipe(fd);
char data1[128];
if(n_pipe < 0){
printf("error: can not creat pipe!\n");
perror("why");
}
int pid = fork();
if(pid < 0){
printf("error: creat child failed!\n");
perror("why");
}
if(pid > 0){
// sleep(2);
printf("this is father pc\n");
close(fd[0]);
write(fd[1],"hello pipe from father;",strlen("hello pipe from father;"));
close(fd[1]);
}
if(pid == 0){
printf("this is child pc\n");
close(fd[1]);
read(fd[0],data1,128);
printf("data : %s\n",data1);
exit(9);
}
return 0;
}
打印:

mkfifo创建有名管道文件;成功返回0;失败返回-1并设置erron = -1;
返回值判断报错值:EEXIST,可以锁定报错为文件已存在目录中;
/*
int mkfifo(const char *pathname, mode_t mode);
RETURN VALUE
On success mkfifo() and mkfifoat() return 0. In the case of
an error, -1 is returned (in which case, errno is set appro‐
priately).
EEXIST pathname already exists. This includes the case where
pathname is a symbolic link, dangling or not.
*/
//例:
#include<stdio.h>
#include <errno.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
int main()
{
if(mkfifo("./demo1.txt",0666) < 0 && errno == EEXIST ){
printf("mkfifo error:\n");
perror("why");
}
return 0;
}mkfifo() 有名管道(会生成临时文件); 配合 open(); read(); write(); 实现进程间通讯;
例 mkread + mkwrite:
//demo mkread:
#include<stdio.h>
#include <errno.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <unistd.h>
int main()
{
char buf[30]={0};
int nff = mkfifo("./demo10.txt",0600);
if(nff < 0 || errno == EEXIST ){
printf("mkfifo error:\n");
perror("why");
}
if(nff == 0){
printf("mkfifo OK! \n");
}
int fd = open("./demo10.txt",O_RDONLY);
printf("open success\n");
int n_read = read(fd,buf,30);
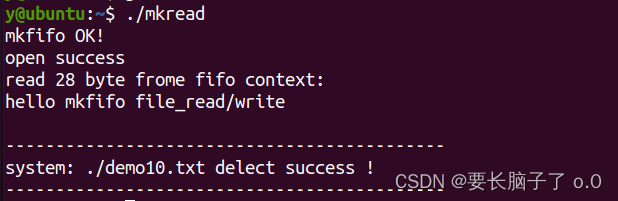
printf("read %d byte frome fifo context:\n%s\n",n_read,buf);
int n_sys = system("rm ./demo10.txt");
if(n_sys < 0 || n_sys ==127 ){
printf("./demo10.txt delect error! \n");
perror("why");
}else{
printf("\n--------------------------------------------");
printf("\nsystem: ./demo10.txt delect success !\n");
printf("--------------------------------------------\n");
}
close(fd);
return 0;
}//demo mkwrite:
#include<stdio.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <unistd.h>
int main()
{
char buf[30]={"hello mkfifo file_read/write"};
int fd = open("./demo10.txt",O_WRONLY);
printf("open success\n");
int n_write = write(fd,buf,strlen(buf));
printf("write %d byte give fifo context:\n%s\n",n_write,buf);
close(fd);
return 0;
}
打印:



![[SQL开发笔记]LIKE操作符:在 WHERE 子句中搜索列中的指定模式](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/0e3e4b0e5dc7424da8e210b34a594116.png)



![buuctf_练[GYCTF2020]FlaskApp](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/img_convert/16756c3a126348e1e74c0cd16fa55e0f.png)