基于注解的IOC配置
一、先来说一下放在对象上面的注解
Component:
* 作用:用于把当前类对象存入spring容器中
* 属性:
* value:用于指定bean的id。当我们不写时,它的默认值是当前类名,且首字母改小写。
* Controller:一般用在表现层
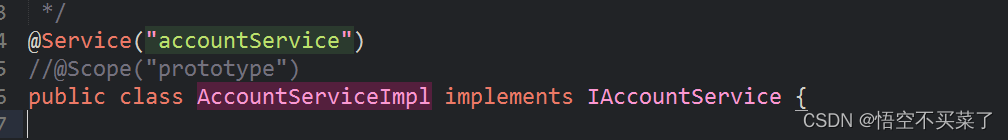
* Service:一般用在业务层
* Repository:一般用在持久层
* 以上三个注解他们的作用和属性与Component是一模一样。
* 他们三个是spring框架为我们提供明确的三层使用的注解,使我们的三层对象更加清晰
也就是说指定了此注解,就会自动给我们创建一个对象
二、再来说一下用于注入数据的
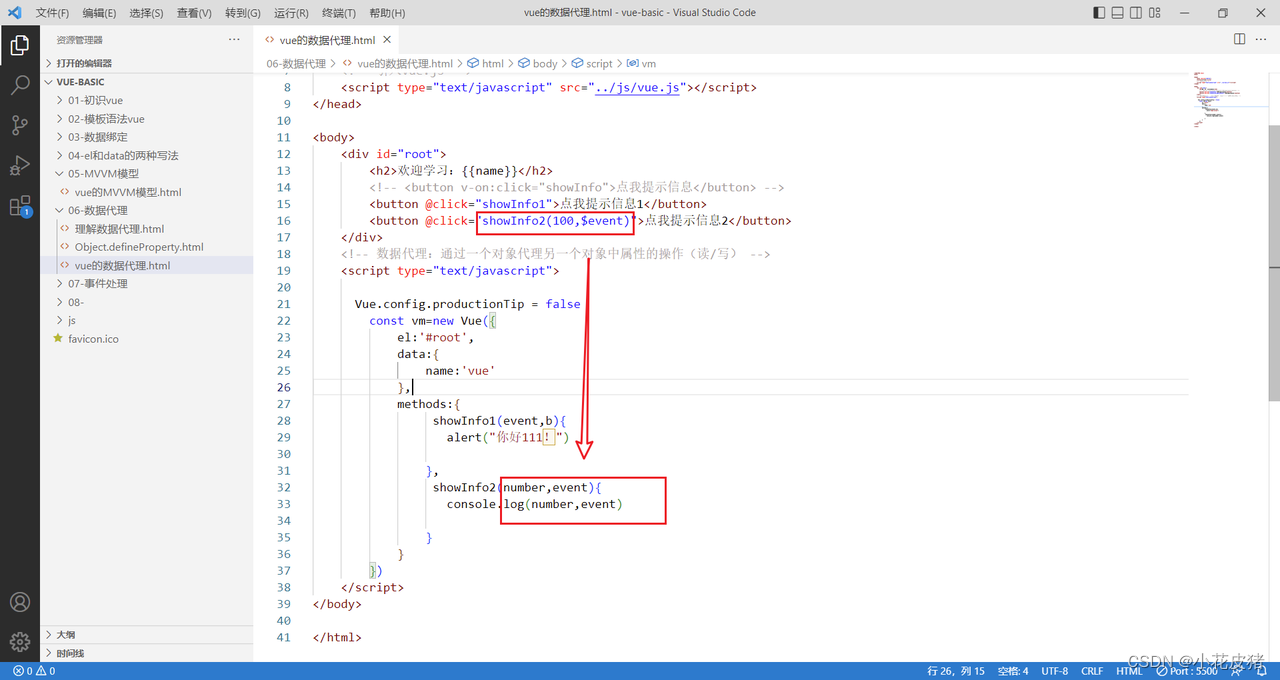
Autowired
 Qualifier
Qualifier

Resource

Value

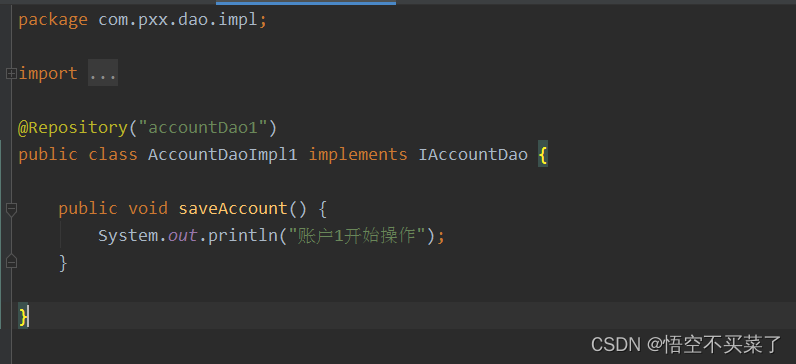
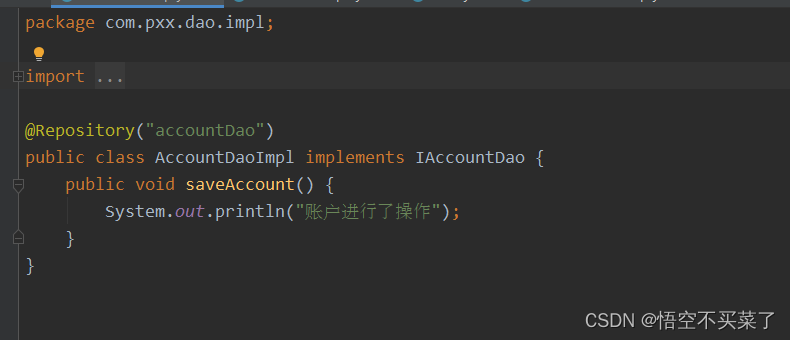
下面做了两个持久层
在service层里面
然后在客户端里面
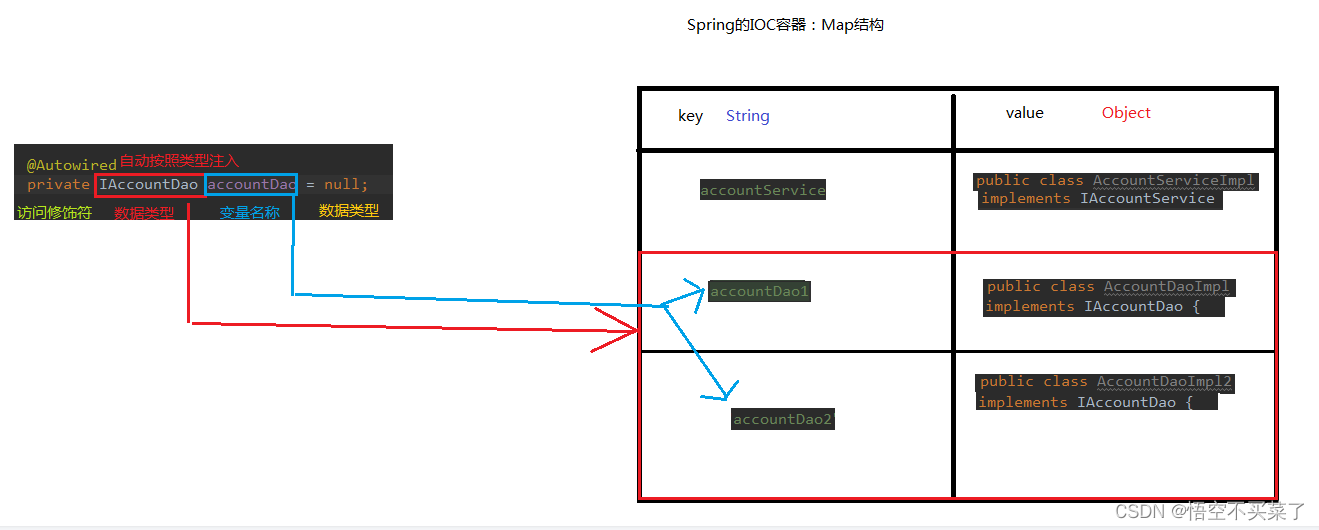

在整体使用注解的时候
运行结果:
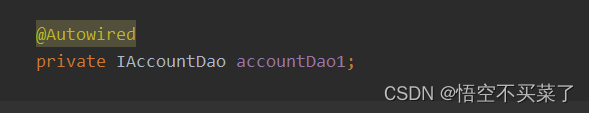
上面解释出一个,如果单独用一个@AutoWired的时候,就是根据变量名称来找对象的
但是我们也可以指定我们需要需要用到的类名
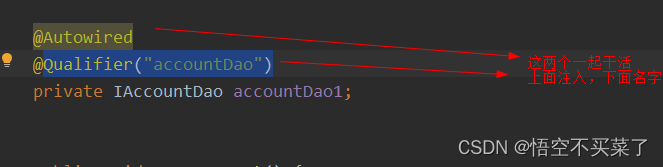
但是有一个注解可以单独用,就是Resource
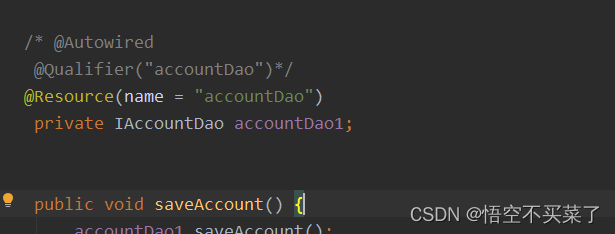
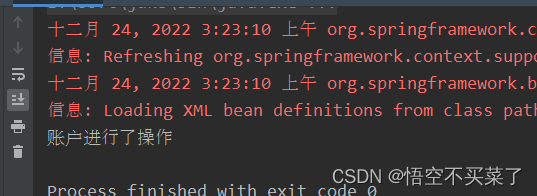
下面来说一下基于XML的IOC的案例
一、配置相关的依赖jar包并搭建数据库环境
先把pom.xml给拿过来
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 http://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd">
<modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion>
<groupId>com.pxx</groupId>
<artifactId>spring1_copy_normal</artifactId>
<version>1.0</version>
<packaging>jar</packaging>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-context</artifactId>
<version>5.0.2.RELEASE</version>
</dependency>
<!--apache提供的一个JDBC工具类库
是对jdbc的一个简单封装
-->
<dependency>
<groupId>commons-dbutils</groupId>
<artifactId>commons-dbutils</artifactId>
<version>1.4</version>
</dependency>
<!--
MySQL数据库连接jar包
-->
<dependency>
<groupId>mysql</groupId>
<artifactId>mysql-connector-java</artifactId>
<version>5.1.6</version>
</dependency>
<!--
c3p0的数据库连接池
-->
<dependency>
<groupId>c3p0</groupId>
<artifactId>c3p0</artifactId>
<version>0.9.1.2</version>
</dependency>
<!--
junit单元测试jar包
-->
<dependency>
<groupId>junit</groupId>
<artifactId>junit</artifactId>
<version>4.12</version>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
</project>创建数据库
sql代码直接贴过来
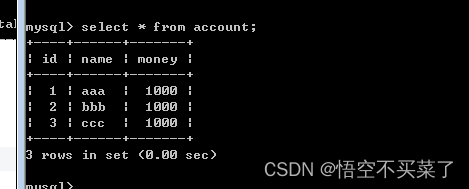
create table account(
id int primary key auto_increment,
name varchar(40),
money float
)character set utf8 collate utf8_general_ci;
insert into account(name,money) values('aaa',1000);
insert into account(name,money) values('bbb',1000);
insert into account(name,money) values('ccc',1000);
我这个sql是放到D盘下面的,那么就是直接执行sql
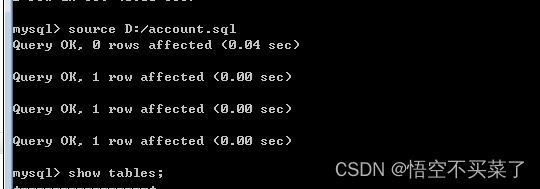
二、创建好每一个类
先创建一个关于表的实体类
Account.java
package com.pxx.domain;
import java.io.Serializable;
public class Account implements Serializable {
private Integer id;
private String name;
private Float money;
public Integer getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(Integer id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public Float getMoney() {
return money;
}
public void setMoney(Float money) {
this.money = money;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Account{" +
"id=" + id +
", name='" + name + '\'' +
", money=" + money +
'}';
}
}
再来创建IAccountDao.java
package com.pxx.dao;
import com.pxx.domain.Account;
import java.util.List;
/**
* 账户持久层接口
*/
public interface IAccountDao {
/**
* 查询所有
* @return
*/
List<Account> findAllAccount();
/**
* 查询一个
* @return
*/
Account findAccountById(Integer accountId);
/**
* 保存
* @param account
*/
void saveAccount(Account account);
/**
* 更新
* @param account
*/
void updateAccount(Account account);
/**
* 删除
* @param acccountId
*/
void deleteAccount(Integer acccountId);
}
然后完成AccountDaoImpl.java
package com.pxx.dao.impl;
import com.pxx.dao.IAccountDao;
import com.pxx.domain.Account;
import org.apache.commons.dbutils.QueryRunner;
import org.apache.commons.dbutils.handlers.BeanHandler;
import org.apache.commons.dbutils.handlers.BeanListHandler;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Repository;
import java.util.Date;
import java.util.List;
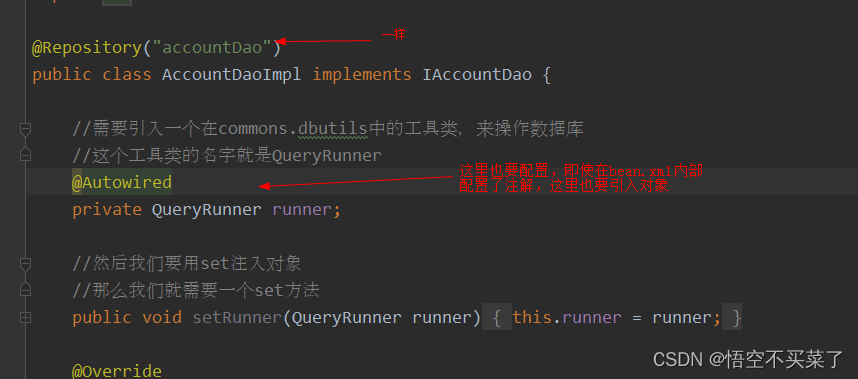
@Repository("accountDao")
public class AccountDaoImpl implements IAccountDao {
//需要引入一个在commons.dbutils中的工具类,来操作数据库
//这个工具类的名字就是QueryRunner
private QueryRunner runner;
//然后我们要用set注入对象
//那么我们就需要一个set方法
public void setRunnner(QueryRunner runner) {
this.runner = runner;
}
@Override
public List<Account> findAllAccount() {
try{
return runner.query("select * from account",new BeanListHandler<Account>(Account.class));
}catch (Exception e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
@Override
public Account findAccountById(Integer accountId) {
try{
return runner.query("select * from account where id = ? ",new BeanHandler<Account>(Account.class),accountId);
}catch (Exception e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
@Override
public void saveAccount(Account account) {
try{
runner.update("insert into account(name,money)values(?,?)",account.getName(),account.getMoney());
}catch (Exception e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
@Override
public void updateAccount(Account account) {
try{
runner.update("update account set name=?,money=? where id=?",account.getName(),account.getMoney(),account.getId());
}catch (Exception e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
@Override
public void deleteAccount(Integer accountId) {
try{
runner.update("delete from account where id=?",accountId);
}catch (Exception e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
}
现在去做业务层的service
IAccountService.java
package com.pxx.service;
import com.pxx.domain.Account;
import java.util.List;
public interface IAccountService {
/**
* 查询所有
* @return
*/
List<Account> findAllAccount();
/**
* 查询一个
* @return
*/
Account findAccountById(Integer accountId);
/**
* 保存
* @param account
*/
void saveAccount(Account account);
/**
* 更新
* @param account
*/
void updateAccount(Account account);
/**
* 删除
* @param acccountId
*/
void deleteAccount(Integer acccountId);
}
AccountServiceImpl.java
package com.pxx.service.impl;
import com.pxx.dao.IAccountDao;
import com.pxx.dao.impl.AccountDaoImpl;
import com.pxx.domain.Account;
import com.pxx.service.IAccountService;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Qualifier;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
import javax.annotation.Resource;
import java.util.List;
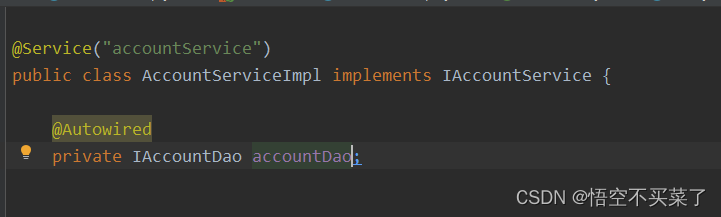
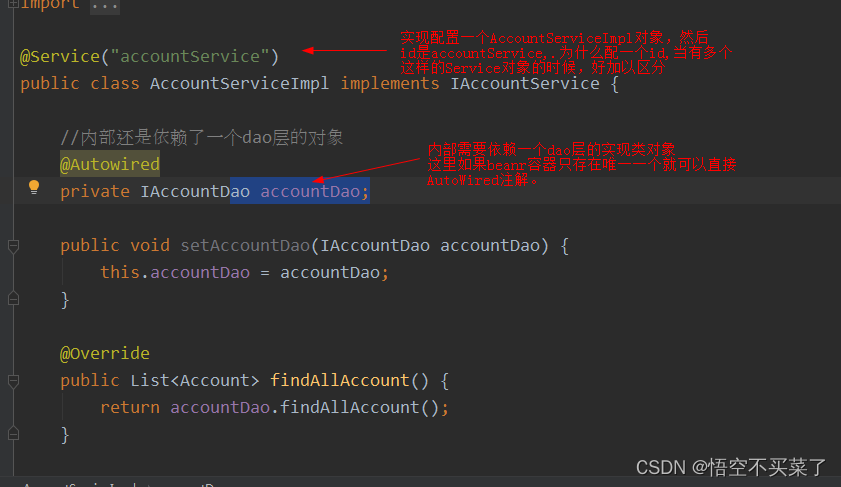
@Service("accountService")
public class AccountServiceImpl implements IAccountService {
//内部还是依赖了一个dao层的对象
private IAccountDao accountDao;
public void setAccountDao(IAccountDao accountDao) {
this.accountDao = accountDao;
}
@Override
public List<Account> findAllAccount() {
return accountDao.findAllAccount();
}
@Override
public Account findAccountById(Integer accountId) {
return accountDao.findAccountById(accountId);
}
@Override
public void saveAccount(Account account) {
accountDao.saveAccount(account);
}
@Override
public void updateAccount(Account account) {
accountDao.updateAccount(account);
}
@Override
public void deleteAccount(Integer acccountId) {
accountDao.deleteAccount(acccountId);
}
}
三、配置bean.xml文件
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd">
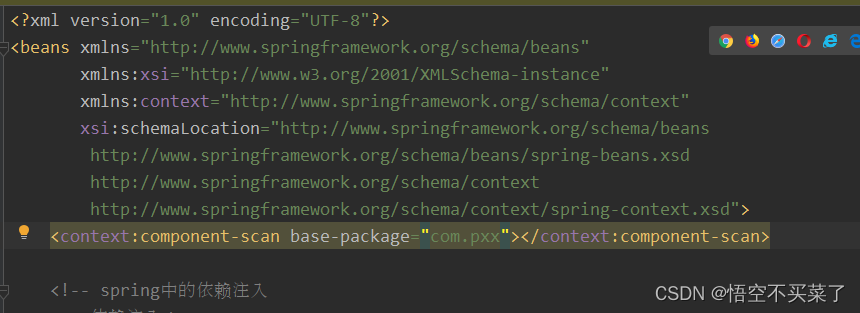
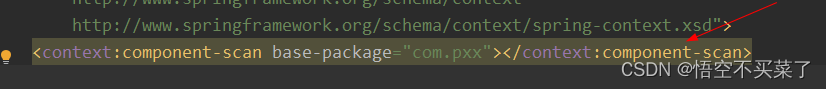
<context:component-scan base-package="com.pxx"></context:component-scan>
<!--配置service-->
<bean id="accountService" class="com.pxx.service.impl.AccountServiceImpl">
<!--内部有一个dao层的实现对象,我们set注解-->
<property name="accountDao" ref="accountDao"></property>
</bean>
<!--
现在就开配这个dao对象
-->
<bean id="accountDao" class="com.pxx.dao.impl.AccountDaoImpl">
<!--
它内部又有一个依赖,就是QueryRunner类
-->
<property name="runner" ref="runner"></property>
</bean>
<!--
开始配置QueryRunner对象
这个在commons.dbutil包里面
它是封装了数据库操作的
-->
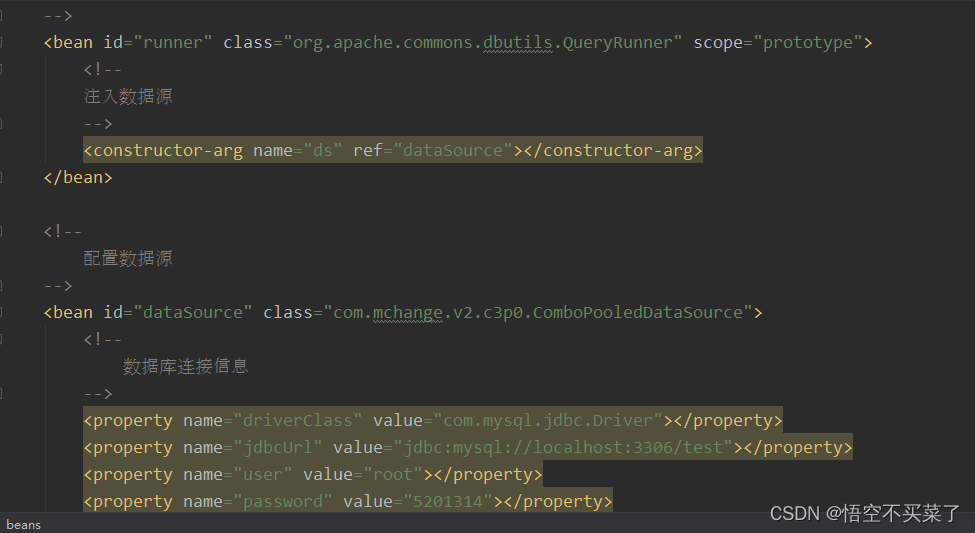
<bean id="runner" class="org.apache.commons.dbutils.QueryRunner" scope="prototype">
<!--
注入数据源
-->
<constructor-arg name="ds" ref="dataSource"></constructor-arg>
</bean>
<!--
配置数据源
-->
<bean id="dataSource" class="com.mchange.v2.c3p0.ComboPooledDataSource">
<!--
数据库连接信息
-->
<property name="driverClass" value="com.mysql.jdbc.Driver"></property>
<property name="jdbcUrl" value="jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/test"></property>
<property name="user" value="root"></property>
<property name="password" value="5201314"></property>
</bean>
</beans>现在写一个测试类,测试一下
在pom.xml上面添加上spring的测试依赖包
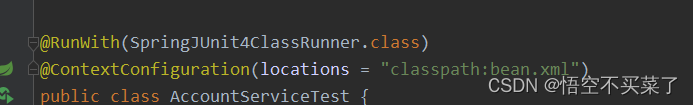
添加上测试需要的注解信息
整个代码文件AccountServiceTest
package com.pxx;
import com.pxx.domain.Account;
import com.pxx.service.IAccountService;
import org.junit.Test;
import org.junit.runner.RunWith;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.test.context.ContextConfiguration;
import org.springframework.test.context.junit4.SpringJUnit4ClassRunner;
import java.util.List;
@RunWith(SpringJUnit4ClassRunner.class)
@ContextConfiguration(locations = "classpath:bean.xml")
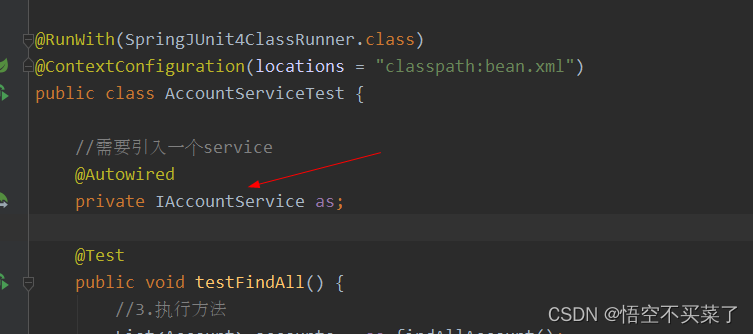
public class AccountServiceTest {
//需要引入一个service
@Autowired
private IAccountService as;
@Test
public void testFindAll() {
//3.执行方法
List<Account> accounts = as.findAllAccount();
for(Account account : accounts){
System.out.println(account);
}
}
@Test
public void testFindOne() {
//3.执行方法
Account account = as.findAccountById(1);
System.out.println(account);
}
@Test
public void testSave() {
Account account = new Account();
account.setName("test");
account.setMoney(12345f);
//3.执行方法
as.saveAccount(account);
}
@Test
public void testUpdate() {
//3.执行方法
Account account = as.findAccountById(4);
account.setMoney(23456f);
as.updateAccount(account);
}
@Test
public void testDelete() {
//3.执行方法
as.deleteAccount(4);
}
}
下面把这个项目改成基于注解的配置
首先我们先去修改bean.xml文件
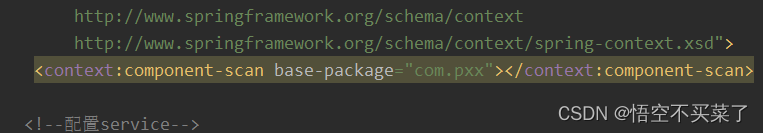
其实采用注解的方式我们就是需要把注入的对象或者注入数据类型全部删除。首先看一下上面这个容器是我们即使采用注解也需要引入的 ,他告诉我们要解析哪一个包下面的类。如果有些类不在这个包下面,我们是不可以采用注解的比如QueryRunner对象和它内部的一个连接池对象
所以这个bean.xml文档就变成了如下
bean.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd">
<context:component-scan base-package="com.pxx"></context:component-scan>
<!--
开始配置QueryRunner对象
这个在commons.dbutil包里面
它是封装了数据库操作的
-->
<bean id="runner" class="org.apache.commons.dbutils.QueryRunner" scope="prototype">
<!--
注入数据源
-->
<constructor-arg name="ds" ref="dataSource"></constructor-arg>
</bean>
<!--
配置数据源
-->
<bean id="dataSource" class="com.mchange.v2.c3p0.ComboPooledDataSource">
<!--
数据库连接信息
-->
<property name="driverClass" value="com.mysql.jdbc.Driver"></property>
<property name="jdbcUrl" value="jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/test"></property>
<property name="user" value="root"></property>
<property name="password" value="5201314"></property>
</bean>
</beans>项目改成基于注解配置的思路
1.首先在bean.xml里面配置需要在spring容器中存在的对象

2.配置每一个类的注解以及内部对象数据注解
关于Service的注解
关于Dao的注解
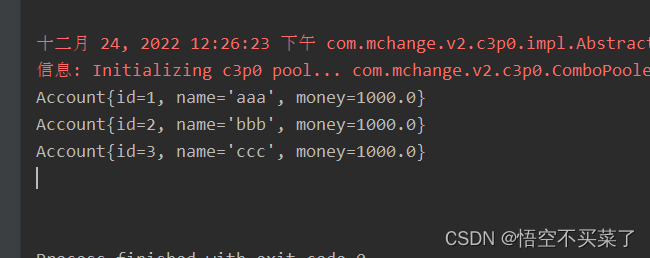
运行结果
Spring的新注解
现在我们面临一个问题,就算是我们写了注解但是还是脱离不了bean.xml文件
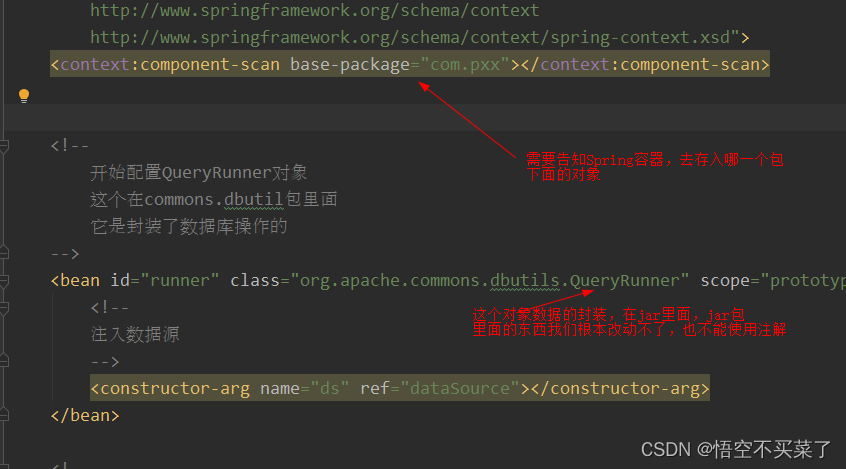
那我们就把Spring的这个配置文件做成一个类来使用SpringConfiguration.java
先来看两个注解




然后在bean.xml中就可以删除context配置
下面又诞生一个问题,就是如下这些数据又该怎么配置
先来说一个注解

先来分析一下配置文件

上面有Bean了还有类的方法抽取,接下来写代码
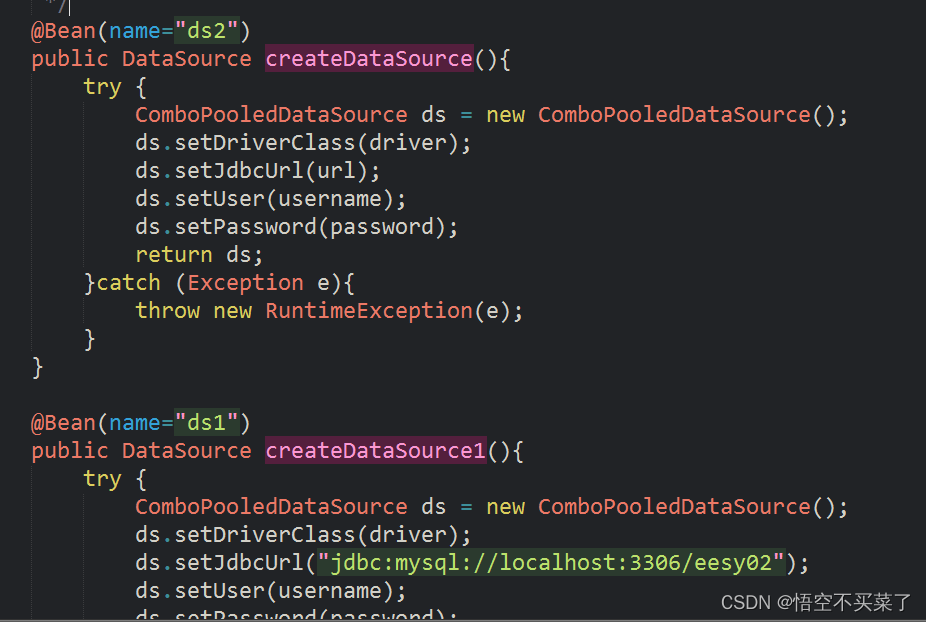
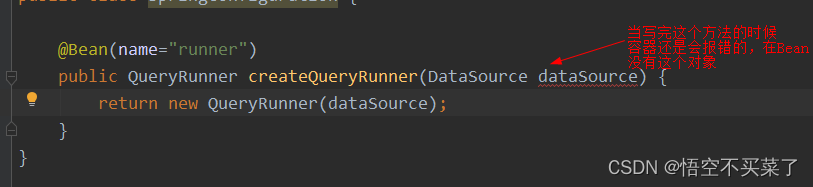 那么现在就要把DataSource这部分给补全
那么现在就要把DataSource这部分给补全
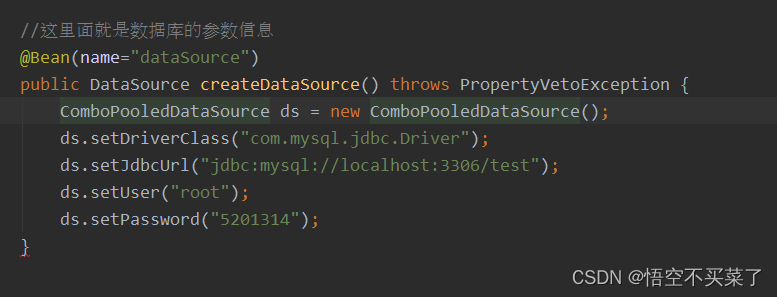
那么这个时候就可以删掉配置文件了
下面来说一下AnnotationConfigApplicationContext的使用

这个就是引入了配置文件
下面我们去修改一下AccountServcieTest里面的代码,看看能不能用
之前的业务代码是这样的啊,全部引入的是xml文件
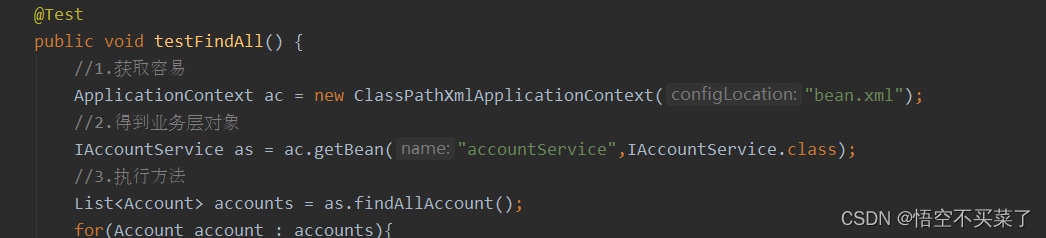
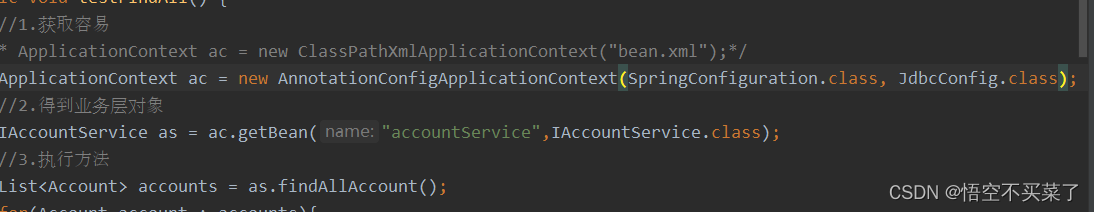
现在我们要去得到配置文件,也就是class文件,就需要用到
AnnotationConfigApplicationContext
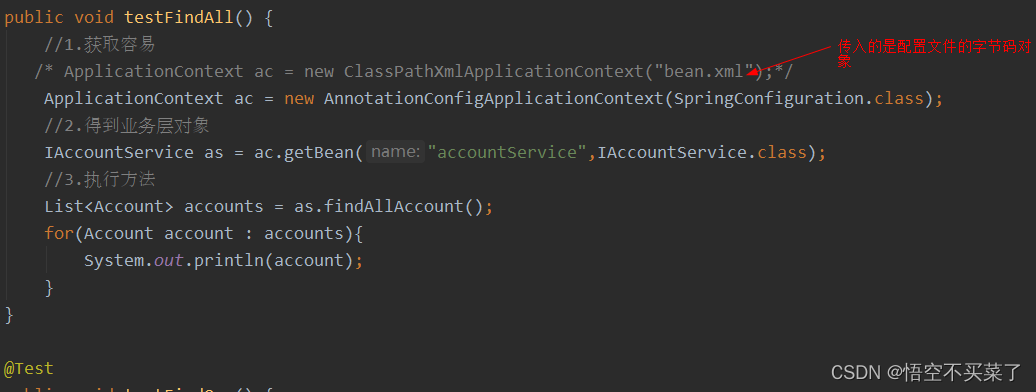
测试一把:
下面来说一下SpringConfiguration中的细节
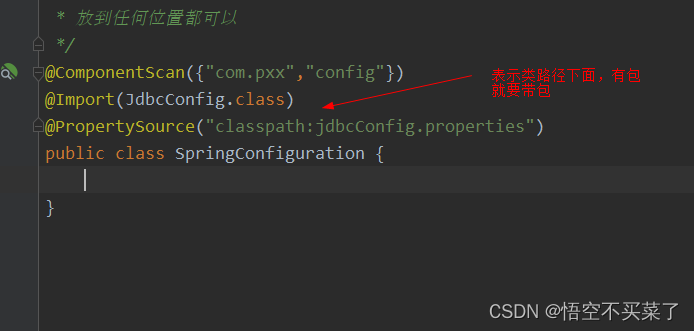
下面在来说一个注解@Import注解

细节1:配置类作为AnnotationConfigApplicationContext对象创建的参数时,该注解可以不写。
但是这句话也不绝对。
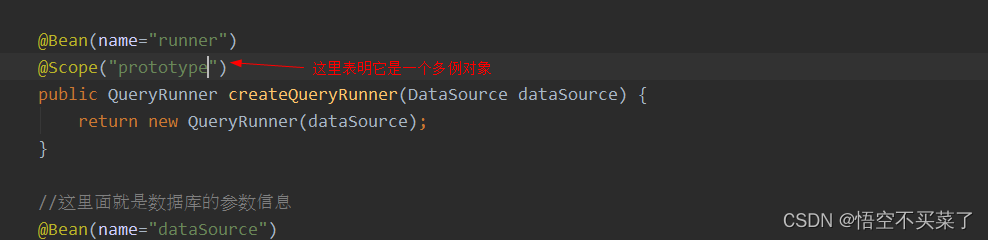
假如我们重新在写一个JdbcConfig.java的配置文件
这个是JdbcConfig.java
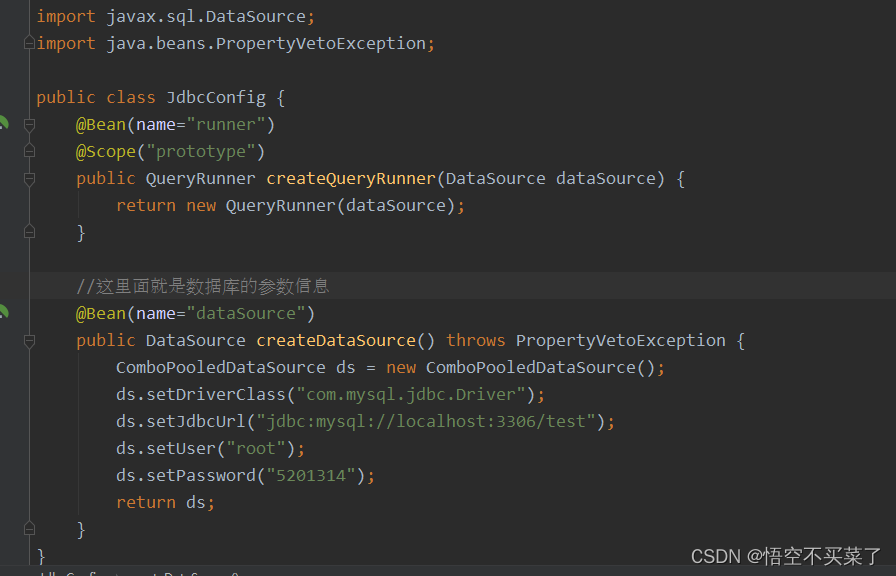
把SpringConfiguration的东西给切掉

上面没有显示声明JdbcConfig,测试代码肯定会报错,如果你想不报错,就把这个配置文件放到这里面去
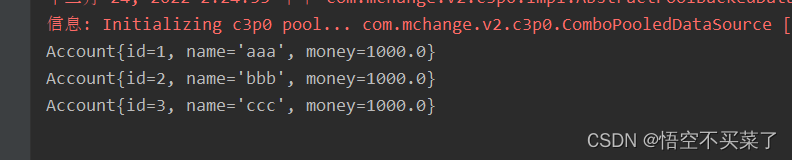
运行结果:
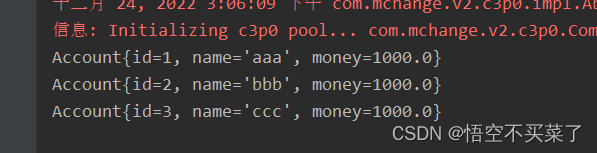
现在有一个问题就是,我们不想再SpringConfiguration上面写@Configuration,也不想在JdbcConfig上面写注解类,而且我们不想像下面一样导入两个配置文件
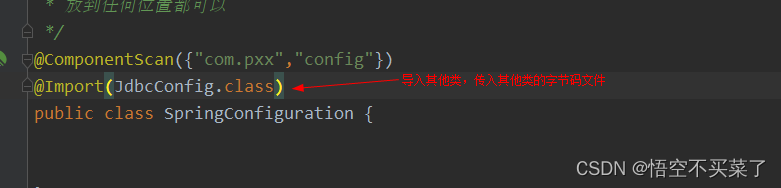
它的作用是导入其他配置类,参数是传入其他配置类的字节码对象
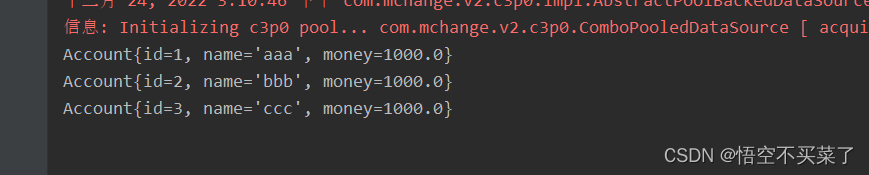
运行结果:
再来说一个注解

先来定义一个配置文件放到resources目录下面,因为这个注解主要是读取配置文件的数据嘛

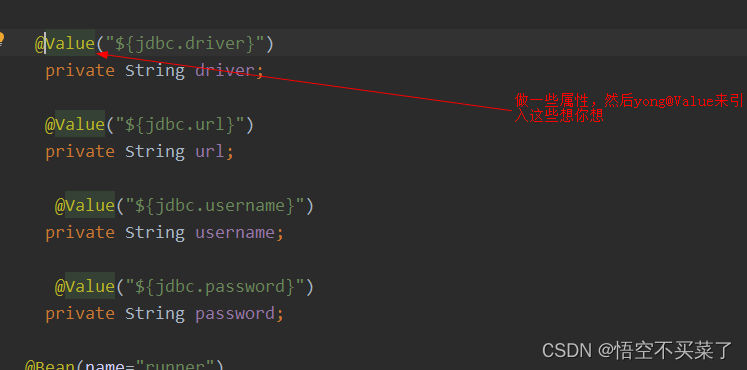
运行结果:
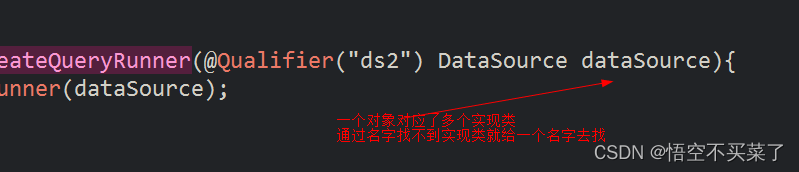
下面多说一句Qualifier注解的另外一种用法
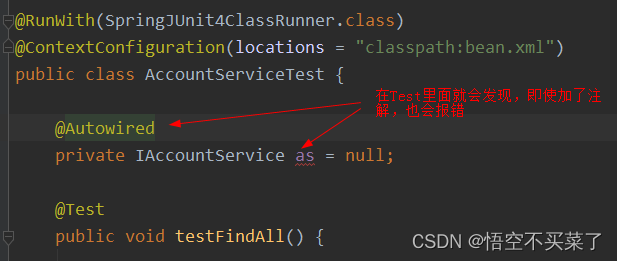
 Spring整合junit问题分析
Spring整合junit问题分析
下面来分析一下AccountServiceTest.java中的代码
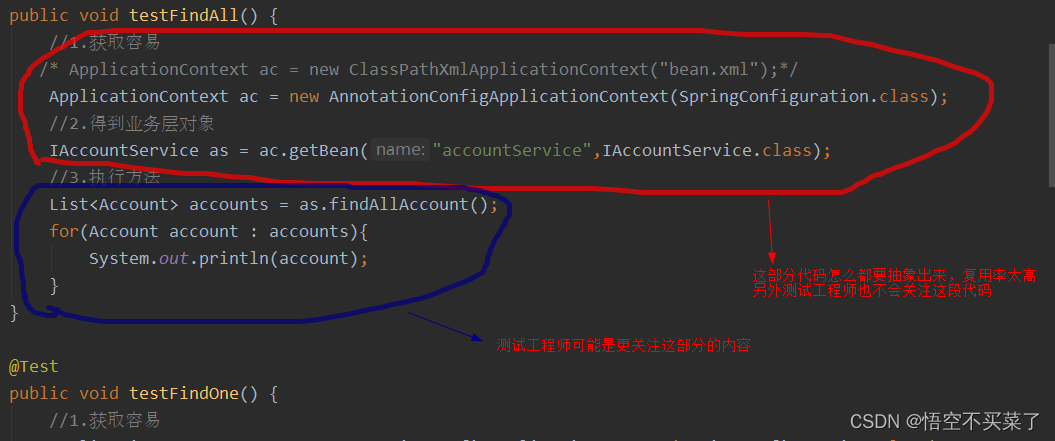
于是,我们想了一个办法直接通过注解方式获取一个IAccountService对象然后去调用里面dao层的方法,但是
那么下面我们就来分析一下

下面我们把Spring与junit进行整合一下
使用Junit单元测试:测试我们的配置
Spring整合junit的配置
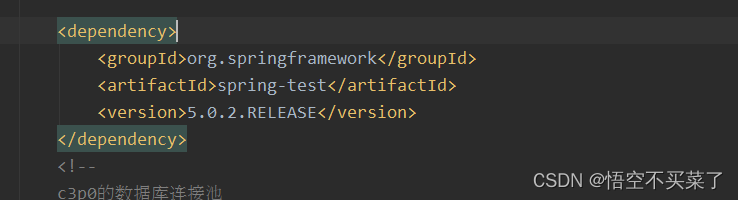
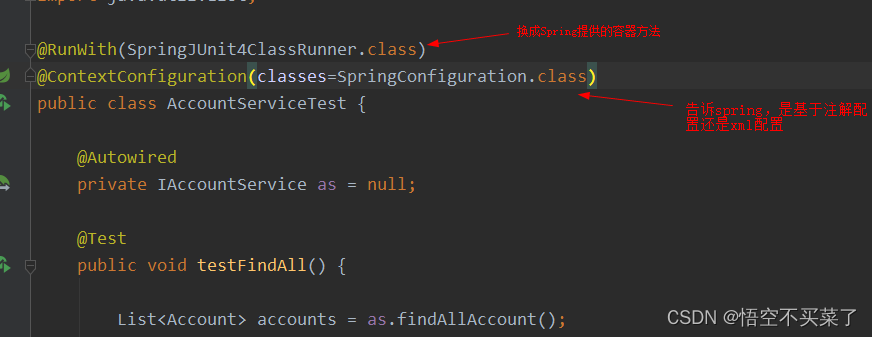
1、导入spring整合junit的jar(坐标)
2、使用Junit提供的一个注解把原有的main方法替换了,替换成spring提供的
@Runwith
3、告知spring的运行器,spring和ioc创建是基于xml还是注解的,并且说明位置
@ContextConfiguration
locations:指定xml文件的位置,加上classpath关键字,表示在类路径下
classes:指定注解类所在地位置
当我们使用spring 5.x版本的时候,要求junit的jar必须是4.12及以上
整体业务代码:spring1_copy_normal