需要云服务器等云产品来学习Linux的同学可以移步/-->腾讯云<--/-->阿里云<--/-->华为云<--/官网,轻量型云服务器低至112元/年,新用户首次下单享超低折扣。
目录
一、Reactor介绍
二、基于epoll的ET模式下的Reactor计算器代码
1、TcpServer.hpp
2、Epoll.hpp
3、Main.cc
4、protocol.hpp
5、calServer.hpp
一、Reactor介绍
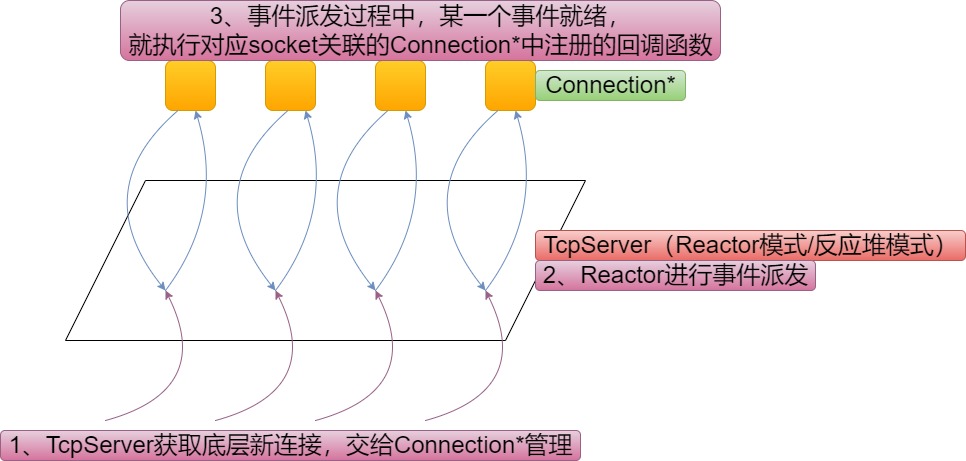
reactor模式是一种半同步(负责就绪事件的通知+IO)半异步(业务处理)IO,在Linux网络中,是使用最频繁的一种网络IO的设计模式。(还有一种比较少见的Proactor前摄器模式)Reactor模式中文译为反应堆模式,代码效果类似打地鼠游戏,玩家监控地鼠洞,哪个地鼠洞的“事件”就绪了,就去执行对应的回调方法。
注意,listen套接字也是非阻塞的,我们无法保证一次读取完毕所有的新连接,所以需要程序员使用while循环监听,读取新连接。
只要套接字被设置成非阻塞,即可不经过epoll直接发送(大不了发送失败用errno判断一下),但是我们无法保证数据是否一次被发完,所以必须保证一个socket一个发送缓冲区,否则残留的数据会被其他socket覆盖。
在处理发送事件时,其实非常不建议直接发送,因为程序员是无法保证写事件是就绪的,只有epoll有知晓写缓冲区是否就绪的能力。什么叫写事件就绪?就是发送缓冲区有空间,epoll就会提示写事件就绪。在大部分情况下,乃至服务器刚启动时,写事件其实都是就绪的。所以在epoll中,我们对读事件要常设关心,对写事件则按需设置(写事件常设时调用epoll_wait极大概率就绪)。
二、基于epoll的ET模式下的Reactor计算器代码
1、TcpServer.hpp
#pragma once
#include <iostream>
#include <functional>
#include <unordered_map>
#include <string>
#include <cassert>
#include "Err.hpp"
#include "Log.hpp"
#include "Sock.hpp"
#include "Epoll.hpp"
#include "Util.hpp"
#include "protocol.hpp"
namespace tcp_server
{
class Connection;
class TcpServer;
static const uint16_t defaultPort = 8080;
static const int num = 64;//表示最多可以存储多少个就绪事件
static const int timeout = 1000;//超时时间
using func_t = std::function<void (Connection*)>;//三种回调方法,读就绪,写就绪,异常就绪
//using hander_t = std::function<void(const std::string&)>;
class Connection//每一个套接字都要有自己的缓冲区(把每一个套接字看成Connection对象)
{
public:
Connection(int sock, TcpServer* pTS)
:_sock(sock)
,_pTS(pTS)
{}
~Connection(){}
public:
void Register(func_t readFunc, func_t writeFunc, func_t errFunc)//注册事件
{
_recver = readFunc;
_sender = writeFunc;
_excepter = errFunc;
}
void Close()
{
close(_sock);
}
public:
int _sock;
std::string _inBuffer;//输入缓冲区。注意图片和视频的传输格式,每个对象一个缓冲区,考科一防止数据读一半的情况
std::string _outBuffer;//输出缓冲区
func_t _recver;//从sock中读
func_t _sender;//向sock中写
func_t _excepter;//处理sock在io时的异常事件
TcpServer* _pTS;//tcpServer的指针,用于外部调用Connection对象可以控制TcpServer中的EnableReadWrite()接口
uint64_t lastTime;//最近一次访问时间,每一次读和写都更新一下时间
};
class TcpServer//Reactor
{
public:
TcpServer(func_t func, uint16_t port = defaultPort)
:_service(func)
,_port(port)
,_revs(nullptr)
{}
~TcpServer()
{
_sock.Close();
_epoll.Close();
if(nullptr != _revs) delete[] _revs;//还有unordered_map没有析构
}
public:
void InitServer()
{
//1、创建socket
_sock.Socket();
_sock.Bind(_port);
_sock.Listen();
//构建epoll对象
_epoll.Create();
//将listen套接字添加到epoll模型中
AddConnnection(_sock.GetListenSocket(), EPOLLIN | EPOLLET,
std::bind(&TcpServer::Accept, this, std::placeholders::_1), nullptr, nullptr);
_revs = new struct epoll_event[num];
_num = num;
}
void EnableReadWrite(Connection* conn, bool readAble, bool writeAble)//使能读、写
{
uint32_t event = (readAble ? EPOLLIN : 0) | (writeAble ? EPOLLOUT : 0) | EPOLLET;
_epoll.Control(conn->_sock, event, EPOLL_CTL_MOD);
}
void Dispatch()//事件派发
{
while(1)
{
Loop(timeout);
//所有事情做完后,遍历所有的连接,计算每一个连接已经多久没发消息了,现在时间和lastTime相减,超过5分钟就关闭连接
}
}
private:
void Accept(Connection* conn)//监听事件的回调函数
{
//获取新连接,监听套接字也是非阻塞的。
//Accept在非阻塞模式,返回值为-1时,判断errno即可知道是否读到所有的新连接
while(1)
{
std::string clientIp;
uint16_t clientPort;
int err = 0;//用于提取Accept的返回值
int sock = _sock.Accept(&clientIp, &clientPort, &err);
if(sock >= 0)
{
AddConnnection(sock, EPOLLIN | EPOLLET,
std::bind(&TcpServer::Read, this, std::placeholders::_1),
std::bind(&TcpServer::Write, this, std::placeholders::_1),
std::bind(&TcpServer::Except, this, std::placeholders::_1));
LogMessage(DEBUG, "git a new link, info: [%s:%d]", clientIp.c_str(), clientPort);
}
else
{
if(err == EAGAIN || err == EWOULDBLOCK) break;//次数说明Accept把文件描述符全部读完了
else if(err == EINTR) continue;//信号中断
else
{
break;//Accept出错了
}
}
}
}
void Read(Connection* conn)//普通读事件的回调
{
conn->lastTime = time(nullptr);
char buffer[1024];
while(1)
{
ssize_t s = recv(conn->_sock, buffer, sizeof(buffer)-1, 0);
if (s > 0)
{
buffer[s] = 0;
conn->_inBuffer += buffer;//将读到的数据存入string
_service(conn);//对读取到的数据进行处理
}
else if (s == 0)//对端关闭连接
{
if (conn->_excepter)//conn将会被释放,后续代码就不要操作conn指针了
{
conn->_excepter(conn);
return;
}
}
else//判断几种读取出异常的情况
{
if(errno == EINTR) continue;
else if(errno == EAGAIN || errno == EWOULDBLOCK) break;
else
{
if(conn->_excepter)
{
conn->_excepter(conn);
return;
}
}
}
}
}
void Write(Connection* conn)//普通写事件的回调
{
conn->lastTime = time(nullptr);
while(1)
{
ssize_t s = send(conn->_sock, conn->_outBuffer.c_str(), sizeof(conn->_outBuffer.size()), 0);
if (s > 0)
{
if (conn->_outBuffer.empty())
{
//EnableReadWrite(conn, true, false);//写事件写完了就关掉
break;
}
else
{
conn->_outBuffer.erase(0, s);
}
}
else
{
if (errno == EAGAIN || errno ==EWOULDBLOCK) { break; }
else if (errno == EINTR) { continue; }
else
{
if (conn->_excepter)
{
conn->_excepter(conn);
return;
}
}
}
}
if (!conn->_outBuffer.empty())//如果没发完
{
conn->_pTS->EnableReadWrite(conn, true, true);
}
else//如果发完了
{
conn->_pTS->EnableReadWrite(conn, true, false);
}
}
void Except(Connection* conn)//异常事件的回调
{
LogMessage(DEBUG, "Except");
_epoll.Control(conn->_sock, 0, EPOLL_CTL_DEL);//在del的时候不关心是何种事件,有fd即可
conn->Close();//关闭套接字
_connections.erase(conn->_sock);
delete conn;
}
void AddConnnection(int sock, uint32_t events, func_t readFunc, func_t writeFunc, func_t errFunc)//添加连接
{
//1、为该sock创建connection并初始化后添加到_connections
if(events & EPOLLET)
{
Util::SetNonBlock(sock);//将监听套接字设置为非阻塞
}
Connection* conn = new Connection(sock, this);//构建Connection对象
//2、给对应的sock设置对应的回调方法
conn->Register(readFunc, writeFunc, errFunc);
//3、将sock与它所关心的事件注册到epoll中
bool r = _epoll.AddEvent(sock, events);
assert(r);
(void)r;
//4、将k、v添加到_connection中
_connections.insert(std::pair<int, Connection*>(sock, conn));
LogMessage(DEBUG, "add new sock : %d in epoll and unordered_map", sock);
}
void Loop(int timeout)//事件派发中的循环函数
{
int n = _epoll.Wait(_revs, _num, timeout);//捞出就绪事件的_revs
for(int i = 0; i < n; ++i)
{
//通过_revs获得已就绪的fd和就绪事件
int sock = _revs[i].data.fd;
uint32_t events = _revs[i].events;
//将异常问题,全部转化为读写问题,因为在读写时,读写接口自带读写问题的异常处理方式
if((events & EPOLLERR)) events |= (EPOLLIN | EPOLLOUT);
if((events & EPOLLHUP)) events |= (EPOLLIN | EPOLLOUT);//对端关闭连接
if((events & EPOLLIN) && IsConnectionExist(sock))//监听事件及其他读事件就绪,保险起见,先判断connect对象是否存在
{
if(_connections[sock]->_recver)//检查存在,防止空指针
_connections[sock]->_recver(_connections[sock]);//从map中找到key值为sock的Connection对象
}
if((events & EPOLLOUT) && IsConnectionExist(sock))
{
if(_connections[sock]->_sender)//检查存在,防止空指针
_connections[sock]->_sender(_connections[sock]);
}
}
}
bool IsConnectionExist(int sock)
{
auto iter = _connections.find(sock);
return iter != _connections.end();
}
private:
uint16_t _port;
Sock _sock;//里面包含有listenS ocket
Epoll _epoll;
std::unordered_map<int, Connection*> _connections;//fd和Connection*
struct epoll_event* _revs;//捞出就绪的事件及其fd的数组,epoll_wait会去捞
int _num;//表示最多可以存储多少个就绪事件
// hander_t _handler;//解协议
func_t _service;
};
}2、Epoll.hpp
#pragma once
#include <iostream>
#include <sys/epoll.h>
#include <string>
#include <cstring>
#include "Err.hpp"
#include "Log.hpp"
const int size = 128;//epoll_create使用,大于0即可
class Epoll
{
public:
Epoll()
:_epfd(-1)
{}
~Epoll()
{
if(_epfd >= 0)
{
close(_epfd);
}
}
public:
void Create();
bool AddEvent(int sock, uint32_t events);
int Wait(struct epoll_event revs[], int num, int timeout);
void Close();
bool Control(int sock, uint32_t event, int action);
private:
int _epfd;
};
void Epoll::Create()
{
_epfd = epoll_create(size);
if(_epfd < 0)//创建epoll模型失败
{
LogMessage(FATAL, "epoll_create error, code: %d, errstring: %s",errno, strerror(errno));
exit(EPOLL_CREATE_ERR);
}
}
bool Epoll::AddEvent(int sock, uint32_t events)//用户到内核
{
struct epoll_event ev;
ev.events = events;
ev.data.fd = sock;
int n = epoll_ctl(_epfd, EPOLL_CTL_ADD, sock, &ev);
return n == 0;
}
int Epoll::Wait(struct epoll_event revs[], int num, int timeout)//revs是就绪的事件,num表示最多可以存储多少个就绪事件,均为输出型参数
{
int n = epoll_wait(_epfd, revs, num, timeout);
return n;//返回就绪事件的个数
}
void Epoll::Close()
{
if(_epfd >= 0)
{
close(_epfd);
}
}
bool Epoll::Control(int sock, uint32_t event, int action)
{
bool n = 0;
if (action == EPOLL_CTL_MOD)
{
struct epoll_event ev;
ev.events = event;
ev.data.fd = sock;
n = epoll_ctl(_epfd, action, sock, &ev);
}
else if (action == EPOLL_CTL_DEL)
{
n = epoll_ctl(_epfd, EPOLL_CTL_DEL, sock, nullptr);
}
else { n = -1; }
return n == 0;
}3、Main.cc
#include <memory>
#include "TcpServer.hpp"
using namespace tcp_server;
static void Usage(std::string proc)
{
std::cerr << "Usage:\n\t" << proc << "port" << "\n\n";
}
//根据传入的req,输出resp
bool Cal(const Request& req,Response& resp)
{
resp._exitCode = OK;
resp._result = OK;
switch(req._op)
{
case '+':
resp._result=req._x+req._y;
break;
case '-':
resp._result=req._x-req._y;
break;
case '*':
resp._result=req._x*req._y;
break;
case '/':
{
if(0==req._y){resp._exitCode=DIV_ZERO_ERR;}
else
resp._result=req._x/req._y;
}
break;
case '%':
{
if(0==req._y){resp._exitCode=MOD_ZERO_ERR;}
else
resp._result=req._x%req._y;
}
break;
default:
resp._exitCode=OP_ZERO_ERR;
return false;
}
return true;
}
void calculate(Connection* conn)//读就绪后,会进行回调,进行计算的处理
{
std::string onePackage;
while(ParseOncePackage(conn->_inBuffer, &onePackage))
{
std::string reqStr;//从一个报文中解析出来的正文部分
if(!deLength(onePackage, &reqStr)) { return; }//提取报文中的有效载荷
std::cout << "仅剩有效载荷的请求:\n" << reqStr << std::endl;
//二、对有效载荷进行反序列化。(将正文的string对象解析x,y,op存储至req对象中)
Request req;//运算数与运算符对象
if(!req.deserialize(reqStr)) { return; }
Response resp;
Cal(req, resp);
//四、对得到的Response计算结果对象,进行序列化,得到一个"字符串",发送给客户端
std::string respStr;//输出型参数,获取序列化string类型的内容(resp_str是序列化后的字符串)
resp.serialize(&respStr);//对计算结果对象resp进行序列化
//五、先构建一个完整的报文,再将其添加到发送缓冲区中
conn->_outBuffer = enLength(respStr);//对序列化数据添加自定义协议规则
std::cout << "result" << conn->_outBuffer << std::endl;
}
//处理完了,直接发回去
if (conn->_sender)
{
conn->_sender(conn);
}
//如果没有发送完毕,需要对对应的socket开启对写事件的关心,如果发完了,则关闭对写事件的关心
// if (!conn->_outBuffer.empty())//如果没发完
// {
// conn->_pTS->EnableReadWrite(conn, true, true);
// }
// else//如果发完了
// {
// conn->_pTS->EnableReadWrite(conn, true, false);
// }
}
int main(int argc, char* argv[])
{
if(argc != 2)
{
Usage(argv[0]);
exit(USAGE_ERR);
}
uint16_t port = atoi(argv[1]);
std::unique_ptr<TcpServer> tsvr(new TcpServer(calculate, port));
tsvr->InitServer();
tsvr->Dispatch();
return 0;
}4、protocol.hpp
#pragma once
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
#include <vector>
#include <cstring>
#include <jsoncpp/json/json.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/socket.h>
enum
{
OK=0,
DIV_ZERO_ERR,
MOD_ZERO_ERR,
OP_ZERO_ERR,
};
#define SEP " "
#define SEP_LEN strlen(SEP)//不能使用sizeof,用sizeof会统计到'\0'
#define LINE_SEP "\r\n"
#define LINE_SEP_LINE strlen(LINE_SEP)
//加包头包尾:"_exitcode result" -> "content_len"\r\n"_exitcode result"\r\n
//加包头包尾:"_x _op _y" 修改为 "content_len"\r\n"_x _op _y"\r\n
std::string enLength(const std::string& text)//text:_x _op _y。添加协议规则,用于构建一个完整的报文(类似"打包")
{
std::string send_string=std::to_string(text.size());//计算有效载荷的长度"_x _op _y"
send_string += LINE_SEP;
send_string += text;
send_string += LINE_SEP;
return send_string;
}
//去掉包头包尾"content_len"\r\n"_exitcode result"\r\n -> "_exitcode result"
bool deLength(const std::string& package,std::string* text)//获取报文中的有效载荷(类似"解包")
{
auto pos = package.find(LINE_SEP);
if(pos == std::string::npos) { return false; }
int textLen = std::stoi(package.substr(0, pos));//计算有效载荷的长度
*text = package.substr(pos + LINE_SEP_LINE, textLen);
return true;
}
class Request//请求类
{
public:
Request(int x,int y,char op)
:_x(x)
,_y(y)
,_op(op)
{}
Request()
:_x(0)
,_y(0)
,_op(0)
{}
bool serialize(std::string* out)//序列化,将成员变量转字符串
{
#ifdef MYSELF
//结构化->"_x _op _y"
*out="";//清空string对象
std::string x_tostring=std::to_string(_x);
std::string y_tostring=std::to_string(_y);
*out=x_tostring+SEP+_op+SEP+y_tostring;//_x _op _y
#else
//Json序列化
Json::Value root;//Json::Value万能对象,可接收任何对象
root["first"]=_x;//自动将_x转换为字符串
root["second"]=_y;
root["oper"]=_op;
//序列化
Json::FastWriter writer;//Json::StyledWriter write;等价
*out=writer.write(root);//将root进行序列化,返回值为string对象,接收即可
#endif
return true;
}
bool deserialize(const std::string& in)//反序列化
{
#ifdef MYSELF
//"_x _op _y"->结构化
auto leftSpace=in.find(SEP);//左边的空格
auto rightSpace=in.rfind(SEP);//右边的空格
if(leftSpace==std::string::npos||rightSpace==std::string::npos){return false;}
if(leftSpace==rightSpace){return false;}
//子串提取
std::string x_tostring=in.substr(0,leftSpace);
if(rightSpace-(leftSpace+SEP_LEN)!=1){return false;}//表示操作符一定只占1位
_op=in.substr(leftSpace+SEP_LEN,rightSpace-(leftSpace+SEP_LEN))[0];
std::string y_tostring=in.substr(rightSpace+SEP_LEN);
//对x,y进行转换
_x=std::stoi(x_tostring);
_y=std::stoi(y_tostring);
#else
//Json反序列化
Json::Value root;//Json::Value万能对象,可接收任何对象
Json::Reader reader;
reader.parse(in,root);//第一个参数:解析哪个流;第二个参数:将解析的数据存放到对象中
//反序列化
_x=root["first"].asInt();//默认是字符串,转换为整型
_y=root["second"].asInt();
_op=root["oper"].asInt();//转换为整型,整型可以给char类型。
#endif
return true;
}
public:
//_x _op _y
int _x;//左操作数
int _y;//右操作数
char _op;//操作符
};
class Response//响应类
{
public:
Response()
:_exitCode(0)
,_result(0)
{}
Response(int exitCode,int result)
:_exitCode(exitCode)
,_result(result)
{}
bool serialize(std::string* out)//序列化,将成员变量转string对象
{
#ifdef MYSELF
*out="";//清空string对象
std::string outString=std::to_string(_exitCode)+SEP+std::to_string(_result);
*out=outString;
#else
//Json序列化(对象被序列化为了对应的Json字符串)
Json::Value root;//Json::Value万能对象,可接收任何对象
root["exitCode"]=_exitCode;//自动将_exitCode转换为字符串
root["result"]=_result;
//序列化
Json::FastWriter writer;//Json::StyledWriter write;等价
*out=writer.write(root);//将root进行序列化,返回值为string对象,接收即可
#endif
return true;
}
bool deserialize(const std::string& in)//反序列化
{
#ifdef MYSELF
auto space=in.find(SEP);//找空格
if(space==std::string::npos){return false;}
std::string exitString=in.substr(0,space);
std::string resString=in.substr(space+SEP_LEN);
if(exitString.empty()||resString.empty()){return false;}//一个字符串为空就false
_exitCode=std::stoi(exitString);
_result=std::stoi(resString);
#else
//Json反序列化
Json::Value root;//Json::Value万能对象,可接收任何对象
Json::Reader reader;
reader.parse(in,root);//第一个参数:解析哪个流;第二个参数:将解析的数据存放到对象中
//反序列化
_exitCode=root["exitCode"].asInt();//默认是字符串,转换为整型
_result=root["result"].asInt();
#endif
return true;
}
public:
int _exitCode;//0表示计算成功,非零代表除零等错误
int _result;//运算结果
};
bool ParseOncePackage(std::string& inbuffer, std::string* text)//一次从缓冲区解析出一个报文
{
*text = "";
//拆分成一个个报文
auto pos = inbuffer.find(LINE_SEP);//找\r\n的起始位置
if(pos == std::string::npos)//没找到说明暂时还没找到\r\n分隔符,跳过本次循环,等待下次读取
{
return false;
}
std::string textLenString = inbuffer.substr(0, pos);
int textLen = std::stoi(textLenString);//拿出有效载荷的长度
int totalLen = textLenString.size() + 2 * LINE_SEP_LINE + textLen;//单个报文总长度
if(inbuffer.size() < totalLen)//说明缓冲区长度还不到一个报文大小,需要跳过本次循环继续读取
{
return false;
}
std::cout<<"截取报文前inbuffer中的内容:\n"<<inbuffer<<std::endl;
//走到这里,一定有一个完整的报文
*text = inbuffer.substr(0, totalLen);//取出一个报文
inbuffer.erase(0, totalLen);//删掉缓冲区中刚刚被提取走的报文数据
return true;
}5、calServer.hpp
#pragma once
#include <iostream>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/wait.h>
#include <sys/socket.h>
#include <arpa/inet.h>
#include <netinet/in.h>
#include <string>
#include <cstring>
#include <cstdlib>
#include <functional>
#include "Log.hpp"
#include "protoCal.hpp"
namespace Server
{
enum
{
USAGE_ERR=1,
SOCKET_ERR,
BIND_ERR,
LISTEN_ERR,
};
static const uint16_t gport=8080;//缺省的端口号
static const int gbacklog=5;//最大连接数=5+1
const static std::string defaultIp="0.0.0.0";//缺省的IP
//const Request&:输入型 Response&:输出型
typedef std::function<bool(const Request&,Response&)> func_t;
void handlerEntery(int sock,func_t func)
{
std::string inbuffer;//接收报文的缓冲区
while(1)
{
//一、如何保证服务器读到数据是完整的?
std::string req_text;//输出型参数,得到一条报文
std::string req_str;//输出型参数,得到报文中的有效载荷
if(!recvPackage(sock,inbuffer,&req_text)){return;}//服务器读取单条报文
std::cout<<"带报头的请求:\n"<<req_text<<std::endl;
if(!deLength(req_text,&req_str)){return;}//提取报文中的有效载荷
std::cout<<"仅剩有效载荷的请求:\n"<<req_text<<std::endl;
//二、对有效载荷进行反序列化,将提取到的数据存放至req中
Request req;//运算数与运算符对象
if(!req.deserialize(req_str)) return;
//三、计算业务处理,得到一个结构化的结果对象(Response对象)
Response resp;//计算结果对象
func(req,resp);//对req提供的运算数与运算符,通过func将计算结果存放至resp中
//四、对得到的Response计算结果对象,进行序列化,得到一个"字符串",发送给客户端
std::string resp_str;//输出型参数,获取序列化string类型的内容
resp.serialize(&resp_str);//对计算结果对象resp进行序列化
std::cout<<"计算完成的序列化string对象:"<<resp_str<<std::endl;
//五、先构建一个完整的报文,再进行发送
std::string send_string=enLength(resp_str);//对序列化数据添加自定义协议规则
std::cout<<"添加报头的序列化string对象:"<<send_string<<std::endl;
send(sock,send_string.c_str(),send_string.size(),0);//服务器发送序列化内容给客户端(此处存在问题)
}
}
class CalServer
{
public:
CalServer(const uint16_t& port=gport,const std::string& ip=defaultIp )
:_listenSocket(-1)
,_port(port)
,_ip(ip)
{
}
void InitServer()//初始化服务器
{
//1、创建监听socket套接字
_listenSocket=socket(AF_INET,SOCK_STREAM,0);
if(_listenSocket<0)
{
LogMessage(FATAL,"create socket error");
exit(SOCKET_ERR);
}
LogMessage(NORMAL,"create socket success");
//2、绑定端口号+ip地址
struct sockaddr_in local;
memset(&local,0,sizeof(local));
local.sin_addr.s_addr=inet_addr(_ip.c_str());
local.sin_family=AF_INET;
local.sin_port=htons(_port);
if(bind(_listenSocket,(struct sockaddr*)&local,sizeof(local))<0)
{
LogMessage(FATAL,"bind socket error");
exit(BIND_ERR);
}
LogMessage(NORMAL,"bind socket success");
//3、设置监听状态
if(-1==listen(_listenSocket,gbacklog))
{
LogMessage(FATAL,"listen socket error");
exit(LISTEN_ERR);
}
LogMessage(NORMAL,"listen socket success");
}
void Start(func_t func)//启动服务器
{
LogMessage(NORMAL,"Thread init success");
while(1)
{
//4、服务器获取客户端连接请求
struct sockaddr_in peer;//输出型参数,拿到客户端的信息
socklen_t len=sizeof(peer);
int sock=accept(_listenSocket,(struct sockaddr*)&peer,&len);
if(-1==sock)
{
LogMessage(ERROR,"accept error,next");
continue;
}
LogMessage(NORMAL,"accept a new link success");
//6、使用accept的返回值sock进行通信,均为文件操作
pid_t id=fork();
if(id==0)//子进程
{
close(_listenSocket);//关闭子进程的监听套接字,使监听套接字计数-1(防止下一步孙子进程拷贝)
if(fork()>0) exit(0);//让子进程退出,孙子进程成为孤儿进程,交给1号进程托管回收其退出资源
//ServerIO(sock);
handlerEntery(sock,func);//从sock读取请求
close(sock);//必须关闭使用完毕的sock,否则文件描述符泄漏(虽然下一句代码exit(0),孙子进程退出也会释放文件描述符,最好还是手动关一下)
exit(0);
}
close(sock);//这是用于通信的套接字fd,父进程和孙子进程都有这个文件描述符,父进程关了,该文件描述符引用技术-1,直至孙子进程退出,该fd才会减为0,关闭
//父进程
pid_t ret=waitpid(id,nullptr,0);//这里不能用非阻塞等待,否则父进程先跑去执行其他代码,可能会被卡在accept出不来了(没有新的客户端来连接的话)
if(ret>0)
{
LogMessage(NORMAL,"wait child success");
}
}
}
~CalServer()
{}
private:
int _listenSocket;//监听客户端的连接请求,不用于数据通信
uint16_t _port;//服务器端口号
std::string _ip;//服务器ip地址
};
}