Android Framework系列之输入法服务
- 本文基于Android R(11),从Framework角度介绍Android输入法框架流程及常用调试方法。
写在前面
车载项目需要定制输入法,也有一些POC演示的项目使用原生比如LatinIME(源码路径为/packages/inputmethods/LatinIME),关于输入法可能会遇到以下一些问题
- 输入法进程启动崩溃
- 输入法画面被其他应用遮挡
- 输入法输入内容显示到错误的编辑框内
- 多屏情况下输入法显示异常
- 输入法未弹出或输入法未隐藏
- 定制多屏多客户端输入法
上面举了一些常见例子,实际开发过程中也会有定制输入法服务这类需求。所以对于Android输入法,作为Android Framework工程师对其要有一个整体框架性的了解。
专用术语
- IMMS: InputMethodManagerService
- IMS: InputMethodService
- IMM: InputMethodManager
- IME: InputMethodEditor
- MCIMMS:MultiClientInputMethodManagerService
输入法知识点
输入法框架
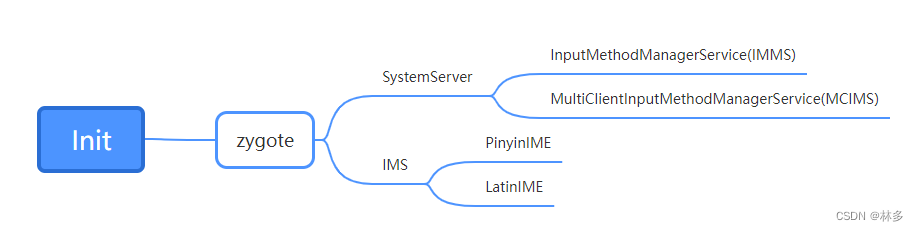
Android输入法框架包括:IMMS输入法管理服务、IMS输入法服务、IMM输入法管理(客户端)。
- IMMS:顾名思义,用于管理输入法的Service,包括打开、关闭、显示、隐藏、切换、绑定输入法等等。这个Service运行在SystemServer中。另外,Android中引入了MCIMMS用于支持多个输入法Client,MCIMMS目前仅作为一个Test功能,感兴趣的可自行研究。
- IMS: 输入法服务,比如Android原生自带的LatinIME通过继承InputMethodService的方式实现了一个IMS。IMS以 Application Service的形式运行在应用进程中,通过IMMS管理其状态(比如打开输入法)。
- IMM: 输入法管理(客户端),Android中经常将Client端被命名为 XXManager,比如AudioManager,WindowManager,输入法的客户端也是这样。IMM主要指InputMethodManager这个单例类,应用进程通过这个单例对象与IMMS/IMS进行交互。

输入法的启动
IMMS初始化

- Kernel拉起Init进程,Init启动Zygote,Zyogte启动SystemServer。SystemServer在startOtherServices阶段启动 IMMS,代码如下(本文下述代码中省略了部分源码)
// SystemServer.java
public static void main(String[] args) {
new SystemServer().run();
}
// SystemServer.java
private void run() {
// Start services.
try {
t.traceBegin("StartServices");
startBootstrapServices(t);
startCoreServices(t);
startOtherServices(t);
} catch (Throwable ex) {
Slog.e("System", "******************************************");
Slog.e("System", "************ Failure starting system services", ex);
throw ex;
} finally {
t.traceEnd(); // StartServices
}
}
// SystemServer.java
private void startOtherServices(@NonNull TimingsTraceAndSlog t) {
// Bring up services needed for UI.
if (mFactoryTestMode != FactoryTest.FACTORY_TEST_LOW_LEVEL) {
t.traceBegin("StartInputMethodManagerLifecycle");
if (InputMethodSystemProperty.MULTI_CLIENT_IME_ENABLED) {
// 多客户端(针对多屏情况下的一个Sample,默认不启用)
mSystemServiceManager.startService(
MultiClientInputMethodManagerService.Lifecycle.class);
} else {
mSystemServiceManager.startService(InputMethodManagerService.Lifecycle.class);
}
t.traceEnd();
}
}
- 执行InputMethodManagerService的Lifecycle的构造函数,初始化IMMS。
// InputMethodManagerService.java
public static final class Lifecycle extends SystemService {
private InputMethodManagerService mService;
public Lifecycle(Context context) {
super(context);
mService = new InputMethodManagerService(context);
}
@Override
public void onStart() {
// 填加到本地服务
LocalServices.addService(InputMethodManagerInternal.class,
new LocalServiceImpl(mService));
// push到binder service中,之后可以通过bind服务找到IMMS。
publishBinderService(Context.INPUT_METHOD_SERVICE, mService);
}
}
//InputMethodManagerService.java
public InputMethodManagerService(Context context) {
mIPackageManager = AppGlobals.getPackageManager();
mContext = context;
mRes = context.getResources();
mHandler = new Handler(this);
// Note: SettingsObserver doesn't register observers in its constructor.
// 监听输入法的设置,比如默认输入法
mSettingsObserver = new SettingsObserver(mHandler);
// 下面几行获取了相关服务的LocalService对象,IMMS与window、package、input进行交互。比如显示输入法时,需要利用WMS服务判定IME显示层级。
mIWindowManager = IWindowManager.Stub.asInterface(
ServiceManager.getService(Context.WINDOW_SERVICE));
mWindowManagerInternal = LocalServices.getService(WindowManagerInternal.class);
mPackageManagerInternal = LocalServices.getService(PackageManagerInternal.class);
mInputManagerInternal = LocalServices.getService(InputManagerInternal.class);
mDisplayManagerInternal = LocalServices.getService(DisplayManagerInternal.class);
// 这个写法比较特殊,是一个lambda表达式
mImeDisplayValidator = displayId -> mWindowManagerInternal.shouldShowIme(displayId);
mCaller = new HandlerCaller(context, null, new HandlerCaller.Callback() {
@Override
public void executeMessage(Message msg) {
handleMessage(msg);
}
}, true /*asyncHandler*/);
mAppOpsManager = mContext.getSystemService(AppOpsManager.class);
mUserManager = mContext.getSystemService(UserManager.class);
mUserManagerInternal = LocalServices.getService(UserManagerInternal.class);
mHardKeyboardListener = new HardKeyboardListener();
mHasFeature = context.getPackageManager().hasSystemFeature(
PackageManager.FEATURE_INPUT_METHODS);
mSlotIme = mContext.getString(com.android.internal.R.string.status_bar_ime);
// 判断是否为低内存模式
mIsLowRam = ActivityManager.isLowRamDeviceStatic();
Bundle extras = new Bundle();
extras.putBoolean(Notification.EXTRA_ALLOW_DURING_SETUP, true);
@ColorInt final int accentColor = mContext.getColor(
com.android.internal.R.color.system_notification_accent_color);
mImeSwitcherNotification =
new Notification.Builder(mContext, SystemNotificationChannels.VIRTUAL_KEYBOARD)
.setSmallIcon(com.android.internal.R.drawable.ic_notification_ime_default)
.setWhen(0)
.setOngoing(true)
.addExtras(extras)
.setCategory(Notification.CATEGORY_SYSTEM)
.setColor(accentColor);
Intent intent = new Intent(ACTION_SHOW_INPUT_METHOD_PICKER)
.setPackage(mContext.getPackageName());
mImeSwitchPendingIntent = PendingIntent.getBroadcast(mContext, 0, intent,
PendingIntent.FLAG_IMMUTABLE);
mShowOngoingImeSwitcherForPhones = false;
mNotificationShown = false;
int userId = 0;
try {
userId = ActivityManager.getService().getCurrentUser().id;
} catch (RemoteException e) {
Slog.w(TAG, "Couldn't get current user ID; guessing it's 0", e);
}
mLastSwitchUserId = userId;
// mSettings should be created before buildInputMethodListLocked
mSettings = new InputMethodSettings(
mRes, context.getContentResolver(), mMethodMap, userId, !mSystemReady);
updateCurrentProfileIds();
AdditionalSubtypeUtils.load(mAdditionalSubtypeMap, userId);
mSwitchingController = InputMethodSubtypeSwitchingController.createInstanceLocked(
mSettings, context);
}
- 上述代码中IMMS获取了许多其他服务的代理对象(WindowManager、PackageManager、InputManager等等),通过它们获取相关功能。从这里也可以看出,合理的功能模块划分,是有利于代码的开发维护。
IMM的初始化
- IMM是一个单例类,在每个应用中有一个实例。应用通过IMM请求IMMS启动输入法,IMMS通过Callback形式通知到IMM,进而告知应用相关输入法状态。

- 添加Window时会实例化ViewRootImpl,在ViewRootImpl中会初始化IMM。
// ViewRootImpl.java
public ViewRootImpl(Context context, Display display) {
this(context, display, WindowManagerGlobal.getWindowSession(),
false /* useSfChoreographer */);
}
// WindowManagerGlobal.java
public static IWindowSession getWindowSession() {
synchronized (WindowManagerGlobal.class) {
if (sWindowSession == null) {
try {
// Emulate the legacy behavior. The global instance of InputMethodManager
// was instantiated here.
// TODO(b/116157766): Remove this hack after cleaning up @UnsupportedAppUsage
InputMethodManager.ensureDefaultInstanceForDefaultDisplayIfNecessary();
IWindowManager windowManager = getWindowManagerService();
sWindowSession = windowManager.openSession(
new IWindowSessionCallback.Stub() {
@Override
public void onAnimatorScaleChanged(float scale) {
ValueAnimator.setDurationScale(scale);
}
});
} catch (RemoteException e) {
throw e.rethrowFromSystemServer();
}
}
return sWindowSession;
}
}
- 上面的代码调用了 InputMethodManager.ensureDefaultInstanceForDefaultDisplayIfNecessary(),在这个函数中对IMM进行了初始化。
// InputMethodManager.java
public static void ensureDefaultInstanceForDefaultDisplayIfNecessary() {
forContextInternal(Display.DEFAULT_DISPLAY, Looper.getMainLooper());
}
// InputMethodManager.java
private static InputMethodManager forContextInternal(int displayId, Looper looper) {
final boolean isDefaultDisplay = displayId == Display.DEFAULT_DISPLAY;
synchronized (sLock) {
// 从缓存map中根据displayID查找 imm,如果已经创建则返回。
InputMethodManager instance = sInstanceMap.get(displayId);
if (instance != null) {
return instance;
}
// 创建IMM实例
instance = createInstance(displayId, looper);
// For backward compatibility, store the instance also to sInstance for default display.
if (sInstance == null && isDefaultDisplay) {
sInstance = instance;
}
// IMM实例放入缓存map
sInstanceMap.put(displayId, instance);
return instance;
}
}
// InputMethodManager.java
private static InputMethodManager createRealInstance(int displayId, Looper looper) {
final IInputMethodManager service;
try {
// 取得IMMS服务对象。这里个INPUT_METHOD_SERVICE,就是IMMS初始化时push到binder中的service标志。
service = IInputMethodManager.Stub.asInterface(
ServiceManager.getServiceOrThrow(Context.INPUT_METHOD_SERVICE));
} catch (ServiceNotFoundException e) {
throw new IllegalStateException(e);
}
// 创建IMM实例对象
final InputMethodManager imm = new InputMethodManager(service, displayId, looper);
final long identity = Binder.clearCallingIdentity();
try {
// 将Client告知IMMS。IMMS内部会管理多个Client(每个应用都会有一个Client)
service.addClient(imm.mClient, imm.mIInputContext, displayId);
} catch (RemoteException e) {
e.rethrowFromSystemServer();
} finally {
Binder.restoreCallingIdentity(identity);
}
return imm;
}
- 到此创建了IMM对象,并获取了与IMMS服务交互的代理对象。每个IMM通过IMMS的addClient将自己的相关信息告诉IMMS,包括 mClient、mIInputContext、displayId。对于DisplayID,就是屏幕的逻辑ID。那么其他两个是什么?
// InputMethodManager.java
private InputMethodManager(IInputMethodManager service, int displayId, Looper looper) {
mService = service;
mMainLooper = looper;
mH = new H(looper);
mDisplayId = displayId;
// mIInputContext 实际上是IInputContext.Stub对象,输入法上下文。 这个对象会同过 IMMS 最终告知 IMS。通过这个对象,应用端接收输入的相关字符,让view进行处理。
mIInputContext = new ControlledInputConnectionWrapper(looper, mDummyInputConnection, this,
null);
}
// InputMethodManager.java
private static class ControlledInputConnectionWrapper extends IInputConnectionWrapper {}
// InputMethodManager.java
public abstract class IInputConnectionWrapper extends IInputContext.Stub {}
// InputMethodManager.java
// mClient实际上是IInputMethodClient.Stub对象,它作为Callback从IMMS获得输入法相关状态,使得应用可以做出相关动作。
final IInputMethodClient.Stub mClient = new IInputMethodClient.Stub() {}
// IInputMethodClient.aidl
/**
* Interface a client of the IInputMethodManager implements, to identify
* itself and receive information about changes to the global manager state.
*/
oneway interface IInputMethodClient {
// IInputContext.aidl
/**
* Interface from an input method to the application, allowing it to perform
* edits on the current input field and other interactions with the application.
* {@hide}
*/
oneway interface IInputContext {
}
IMS的初始化
-
IMS运行在输入法进程中,是一个Application里的service。可以通过BindService获取IMS服务对象。如果系统有多款输入法,那么就会有多个IMS(可以通过 ime list -s查看系统当前支持的输入法服务)。以Android原始自带的LatinIME为例。

-
AndroidManifest.xml中定义了Service
<!-- /packages/inputmethods/LatinIME/java/AndroidManifest.xml -->
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<manifest xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
coreApp="true"
package="com.android.inputmethod.latin"
android:versionCode="28">
<application android:label="@string/english_ime_name"
android:icon="@drawable/ic_launcher_keyboard"
android:supportsRtl="true"
android:allowBackup="true"
android:defaultToDeviceProtectedStorage="true"
android:directBootAware="true">
<!-- Services -->
<service android:name="LatinIME"
android:label="@string/english_ime_name"
android:permission="android.permission.BIND_INPUT_METHOD">
<intent-filter>
<action android:name="android.view.InputMethod" />
</intent-filter>
<meta-data android:name="android.view.im" android:resource="@xml/method" />
</service>
</application>
</manifest>
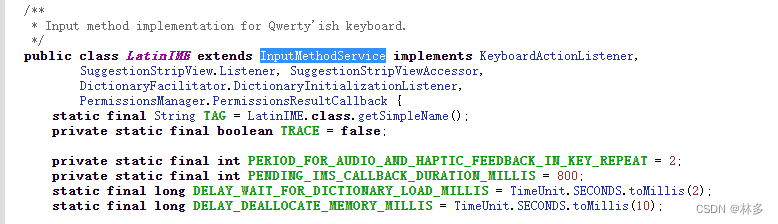
- LatinIME的实现类继承了InputMethodService,也就是实现了IMS。
/**
* Input method implementation for Qwerty'ish keyboard.
*/
public class LatinIME extends InputMethodService implements KeyboardActionListener,
SuggestionStripView.Listener, SuggestionStripViewAccessor,
DictionaryFacilitator.DictionaryInitializationListener,
PermissionsManager.PermissionsResultCallback { }
- 点击文本输入框触发Focus焦点变更是,IMM会告知IMMS启动IMS(这个流程在下章会介绍,这个关注IMS自身的初始化。),IMMS通过BindServic初始化IMS服务。
///packages/inputmethods/LatinIME/java/src/com/android/inputmethod/latin/LatinIME.java
public void onCreate() {
// LatinIME会进行自身的一些初始化,这里主要关注其InputMethodService的初始化。
super.onCreate();
}
// InputMethodService.java
@Override public void onCreate() {
mTheme = Resources.selectSystemTheme(mTheme,
getApplicationInfo().targetSdkVersion,
android.R.style.Theme_InputMethod,
android.R.style.Theme_Holo_InputMethod,
android.R.style.Theme_DeviceDefault_InputMethod,
android.R.style.Theme_DeviceDefault_InputMethod);
super.setTheme(mTheme);
super.onCreate();
// 获取IMMS服务对象
mImm = (InputMethodManager)getSystemService(INPUT_METHOD_SERVICE);
mSettingsObserver = SettingsObserver.createAndRegister(this);
// 判断是否为车载系统
mIsAutomotive = isAutomotive();
mAutomotiveHideNavBarForKeyboard = getApplicationContext().getResources().getBoolean(
com.android.internal.R.bool.config_automotiveHideNavBarForKeyboard);
// TODO(b/111364446) Need to address context lifecycle issue if need to re-create
// for update resources & configuration correctly when show soft input
// in non-default display.
mInflater = (LayoutInflater)getSystemService(
Context.LAYOUT_INFLATER_SERVICE);
// 创建输入法窗口(Dialog类型)
mWindow = new SoftInputWindow(this, "InputMethod", mTheme, null, null, mDispatcherState,
WindowManager.LayoutParams.TYPE_INPUT_METHOD, Gravity.BOTTOM, false);
mWindow.getWindow().getAttributes().setFitInsetsTypes(statusBars() | navigationBars());
mWindow.getWindow().getAttributes().setFitInsetsSides(Side.all() & ~Side.BOTTOM);
mWindow.getWindow().getAttributes().setFitInsetsIgnoringVisibility(true);
// IME layout should always be inset by navigation bar, no matter its current visibility,
// unless automotive requests it. Automotive devices may request the navigation bar to be
// hidden when the IME shows up (controlled via config_automotiveHideNavBarForKeyboard)
// in order to maximize the visible screen real estate. When this happens, the IME window
// should animate from the bottom of the screen to reduce the jank that happens from the
// lack of synchronization between the bottom system window and the IME window.
if (mIsAutomotive && mAutomotiveHideNavBarForKeyboard) {
mWindow.getWindow().setDecorFitsSystemWindows(false);
}
mWindow.getWindow().getDecorView().setOnApplyWindowInsetsListener(
(v, insets) -> v.onApplyWindowInsets(
new WindowInsets.Builder(insets).setInsets(
navigationBars(),
insets.getInsetsIgnoringVisibility(navigationBars()))
.build()));
// For ColorView in DecorView to work, FLAG_DRAWS_SYSTEM_BAR_BACKGROUNDS needs to be set
// by default (but IME developers can opt this out later if they want a new behavior).
mWindow.getWindow().setFlags(
FLAG_DRAWS_SYSTEM_BAR_BACKGROUNDS, FLAG_DRAWS_SYSTEM_BAR_BACKGROUNDS);
// 初始化View相关内容
initViews();
mWindow.getWindow().setLayout(MATCH_PARENT, WRAP_CONTENT);
mInlineSuggestionSessionController = new InlineSuggestionSessionController(
this::onCreateInlineSuggestionsRequest, this::getHostInputToken,
this::onInlineSuggestionsResponse);
}
// SoftInputWindow.java
public SoftInputWindow(Context context, String name, int theme, Callback callback,
KeyEvent.Callback keyEventCallback, KeyEvent.DispatcherState dispatcherState,
int windowType, int gravity, boolean takesFocus) {
super(context, theme);
mName = name;
mCallback = callback;
mKeyEventCallback = keyEventCallback;
mDispatcherState = dispatcherState;
mWindowType = windowType;
mGravity = gravity;
mTakesFocus = takesFocus;
initDockWindow();
}
// SoftInputWindow.java
private void initDockWindow() {
WindowManager.LayoutParams lp = getWindow().getAttributes();
// mWindowType是 WindowManager.LayoutParams.TYPE_INPUT_METHOD,可以通过改这里改变输入法WindowType,进行影响默认层级。
lp.type = mWindowType;
lp.setTitle(mName);
lp.gravity = mGravity;
updateWidthHeight(lp);
getWindow().setAttributes(lp);
int windowSetFlags = WindowManager.LayoutParams.FLAG_LAYOUT_IN_SCREEN;
int windowModFlags = WindowManager.LayoutParams.FLAG_LAYOUT_IN_SCREEN |
WindowManager.LayoutParams.FLAG_NOT_FOCUSABLE |
WindowManager.LayoutParams.FLAG_DIM_BEHIND;
// 默认走if里面,不获取焦点。
if (!mTakesFocus) {
windowSetFlags |= WindowManager.LayoutParams.FLAG_NOT_FOCUSABLE;
} else {
windowSetFlags |= WindowManager.LayoutParams.FLAG_NOT_TOUCH_MODAL;
windowModFlags |= WindowManager.LayoutParams.FLAG_NOT_TOUCH_MODAL;
}
getWindow().setFlags(windowSetFlags, windowModFlags);
}
- 上面对于IMS进行了一些初始化,主要是设置输入法窗口的一些属性。下面看一下,IMS通过onBind接口返回的Binder对象。Client端通过onBind时返回的对象与IMS服务交互。IMS继承了AbstractInputMethodService,onBind的 实现定义在这个类中。
// AbstractInputMethodService.java
public abstract class AbstractInputMethodService extends Service {
final public IBinder onBind(Intent intent) {
if (mInputMethod == null) {
mInputMethod = onCreateInputMethodInterface();
}
// IMMS通过这个对象控制 输入法服务(IMS)。IInputMethodWrapper 实际上是IInputMethod.Stub类型。
return new IInputMethodWrapper(this, mInputMethod);
}
}
// IInputMethodWrapper.java
class IInputMethodWrapper extends IInputMethod.Stub {}
// IInputMethod.aidl
oneway interface IInputMethod {}
- 综上,IMS启动完成。返回 IInputMethod.stub对象给IMMS用于操作IMS。
输入法的启动
-
上面的内容,主要关注 IMM、IMS、IMMS的初始化过程。在应用中点击文本输入框会弹出输入法界面。下面主要对这个流程进行分析。

-
点击文本输入框后,控件获取焦点,会触发ViewRootImpl的焦点变更流程。这个流程会调用IMM的startInput函数启动输入法。
// ViewRootImpl.java
public void windowFocusChanged(boolean hasFocus, boolean inTouchMode) {
Message msg = Message.obtain();
msg.what = MSG_WINDOW_FOCUS_CHANGED;
mHandler.sendMessage(msg);
}
// ViewRootImpl.java
public void handleMessage(Message msg)
// 省略
case MSG_WINDOW_FOCUS_CHANGED: {
handleWindowFocusChanged();
} break;
}
// ViewRootImpl.java
private void handleWindowFocusChanged() {
if (mAdded) {
// Note: must be done after the focus change callbacks,
// so all of the view state is set up correctly.
mImeFocusController.onPostWindowFocus(mView.findFocus(), hasWindowFocus,
mWindowAttributes);
}
}
// ImeFocusController.java
void onPostWindowFocus(View focusedView, boolean hasWindowFocus,
WindowManager.LayoutParams windowAttribute) {
// 没有焦点的话,不弹出输入法
if (!hasWindowFocus || !mHasImeFocus || isInLocalFocusMode(windowAttribute)) {
return;
}
// 获取Delegate对象(包装了IMM)
boolean forceFocus = false;
final InputMethodManagerDelegate immDelegate = getImmDelegate();
// 请求启动输入法
immDelegate.startInputAsyncOnWindowFocusGain(viewForWindowFocus,
windowAttribute.softInputMode, windowAttribute.flags, forceFocus);
}
// InputMethodManager.java
public void startInputAsyncOnWindowFocusGain(View focusedView,
@SoftInputModeFlags int softInputMode, int windowFlags, boolean forceNewFocus) {
if (controller.checkFocus(forceNewFocus, false)) {
// We need to restart input on the current focus view. This
// should be done in conjunction with telling the system service
// about the window gaining focus, to help make the transition
// smooth.
// 通常情况下会走到这里
if (startInput(StartInputReason.WINDOW_FOCUS_GAIN,
focusedView, startInputFlags, softInputMode, windowFlags)) {
return;
}
}
}
// InputMethodManager.java
public boolean startInput(@StartInputReason int startInputReason, View focusedView,
@StartInputFlags int startInputFlags, @SoftInputModeFlags int softInputMode,
int windowFlags) {
// 这些代码是在UIThread中执行的
return startInputInner(startInputReason,
focusedView != null ? focusedView.getWindowToken() : null, startInputFlags,
softInputMode, windowFlags);
}
// InputMethodManager.java
boolean startInputInner(@StartInputReason int startInputReason,
@Nullable IBinder windowGainingFocus, @StartInputFlags int startInputFlags,
@SoftInputModeFlags int softInputMode, int windowFlags) {
final View view;
synchronized (mH) {
view = getServedViewLocked();
}
// Okay we are now ready to call into the served view and have it
// do its stuff.
// Life is good: let's hook everything up!
// 记录编辑器相关信息的对象,输入法根据这些信息显示不同的效果
EditorInfo tba = new EditorInfo();
tba.packageName = view.getContext().getOpPackageName();
tba.autofillId = view.getAutofillId();
tba.fieldId = view.getId();
// 创建InputConnection,调用的是TextView中的对应函数。创建了EditableInputConnection类型对象
// 后续利用InputConnection对目标控件进行相关字符串操作
InputConnection ic = view.onCreateInputConnection(tba);
synchronized (mH) {
if (ic != null) {
// 这个对象实际上是 IInputContext.stub对象。上面创建的InpuConnection传给这个对象。
// IMS与 IInputContext.stub交互, IInputContext.stub通过 InpuConnection与控件交互。
servedContext = new ControlledInputConnectionWrapper(
icHandler != null ? icHandler.getLooper() : vh.getLooper(), ic, this, view);
} else {
servedContext = null;
missingMethodFlags = 0;
}
mServedInputConnectionWrapper = servedContext;
try {
// 真正启动输入法的地方,返回的InputBindResult是一个Parcelable
final InputBindResult res = mService.startInputOrWindowGainedFocus(
startInputReason, mClient, windowGainingFocus, startInputFlags,
softInputMode, windowFlags, tba, servedContext, missingMethodFlags,
view.getContext().getApplicationInfo().targetSdkVersion);
if (res == null) {
Log.wtf(TAG, "startInputOrWindowGainedFocus must not return"
+ " null. startInputReason="
+ InputMethodDebug.startInputReasonToString(startInputReason)
+ " editorInfo=" + tba
+ " startInputFlags="
+ InputMethodDebug.startInputFlagsToString(startInputFlags));
return false;
}
if (res.id != null) {
// 设置InputChannel
setInputChannelLocked(res.channel);
mBindSequence = res.sequence;
// IInputMethodSession类型对象,这个对象是IMS的Binder代理。通过它与IMS直接交互。
// 这样应用端就拿到了与IMS直接交互的对象
mCurMethod = res.method;
// 当前输入法的ID(不同输入法ID值不一样)
mCurId = res.id;
} else if (res.channel != null && res.channel != mCurChannel) {
res.channel.dispose();
}
} catch (RemoteException e) {
Log.w(TAG, "IME died: " + mCurId, e);
}
}
return true;
}
- 如果startInputInner执行成功的话,应用端的IMM中便会持有 IInputMethodSession类型对象,通过它与IMS进行交互。上面的mService是IMMS的客户端代理,在其startInputOrWindowGainedFocus函数会启动输入法。
public InputBindResult startInputOrWindowGainedFocus(
@StartInputReason int startInputReason, IInputMethodClient client, IBinder windowToken,
@StartInputFlags int startInputFlags, @SoftInputModeFlags int softInputMode,
int windowFlags, @Nullable EditorInfo attribute, IInputContext inputContext,
@MissingMethodFlags int missingMethods, int unverifiedTargetSdkVersion) {
final InputBindResult result;
synchronized (mMethodMap) {
final long ident = Binder.clearCallingIdentity();
try {
// 加锁调用
result = startInputOrWindowGainedFocusInternalLocked(startInputReason, client,
windowToken, startInputFlags, softInputMode, windowFlags, attribute,
inputContext, missingMethods, unverifiedTargetSdkVersion, userId);
} finally {
Binder.restoreCallingIdentity(ident);
}
}
return result;
}
// InputMethodManagerService.java
private InputBindResult startInputOrWindowGainedFocusInternalLocked(
@StartInputReason int startInputReason, IInputMethodClient client,
@NonNull IBinder windowToken, @StartInputFlags int startInputFlags,
@SoftInputModeFlags int softInputMode, int windowFlags, EditorInfo attribute,
IInputContext inputContext, @MissingMethodFlags int missingMethods,
int unverifiedTargetSdkVersion, @UserIdInt int userId) {
// 计算IME的TargeWindow,输入法窗口会根据TargetWindow动态计算显示层级
// 此函数会调用到WMS,并调用到DisplayContent::computeImeTarget函数中。
if (!mWindowManagerInternal.isInputMethodClientFocus(cs.uid, cs.pid,
cs.selfReportedDisplayId)) {
// Check with the window manager to make sure this client actually
// has a window with focus. If not, reject. This is thread safe
// because if the focus changes some time before or after, the
// next client receiving focus that has any interest in input will
// be calling through here after that change happens.
if (DEBUG) {
Slog.w(TAG, "Focus gain on non-focused client " + cs.client
+ " (uid=" + cs.uid + " pid=" + cs.pid + ")");
}
return InputBindResult.NOT_IME_TARGET_WINDOW;
}
// 判断是否是相同的Window获得了Focus
final boolean sameWindowFocused = mCurFocusedWindow == windowToken;
// 判断是不是文本编辑器
final boolean isTextEditor = (startInputFlags & StartInputFlags.IS_TEXT_EDITOR) != 0;
// 启动要因是否为得到焦点
final boolean startInputByWinGainedFocus =
(startInputFlags & StartInputFlags.WINDOW_GAINED_FOCUS) != 0;
// 如果焦点window一样,并且是本文编辑器。表示之前已经启动了输入法,直接启动。
if (sameWindowFocused && isTextEditor) {
if (DEBUG) {
Slog.w(TAG, "Window already focused, ignoring focus gain of: " + client
+ " attribute=" + attribute + ", token = " + windowToken
+ ", startInputReason="
+ InputMethodDebug.startInputReasonToString(startInputReason));
}
if (attribute != null) {
return startInputUncheckedLocked(cs, inputContext, missingMethods,
attribute, startInputFlags, startInputReason);
}
return new InputBindResult(
InputBindResult.ResultCode.SUCCESS_REPORT_WINDOW_FOCUS_ONLY,
null, null, null, -1, null);
}
// We want to start input before showing the IME, but after closing
// it. We want to do this after closing it to help the IME disappear
// more quickly (not get stuck behind it initializing itself for the
// new focused input, even if its window wants to hide the IME).
boolean didStart = false;
// 判断android:windowSoftInputMode
InputBindResult res = null;
switch (softInputMode & LayoutParams.SOFT_INPUT_MASK_STATE) {
// 默认情况下走这里
case LayoutParams.SOFT_INPUT_STATE_UNSPECIFIED:
if (!sameWindowFocused && (!isTextEditor || !doAutoShow)) {
if (LayoutParams.mayUseInputMethod(windowFlags)) {
// There is no focus view, and this window will
// be behind any soft input window, so hide the
// soft input window if it is shown.
if (DEBUG) Slog.v(TAG, "Unspecified window will hide input");
hideCurrentInputLocked(
mCurFocusedWindow, InputMethodManager.HIDE_NOT_ALWAYS, null,
SoftInputShowHideReason.HIDE_UNSPECIFIED_WINDOW);
// If focused display changed, we should unbind current method
// to make app window in previous display relayout after Ime
// window token removed.
// Note that we can trust client's display ID as long as it matches
// to the display ID obtained from the window.
if (cs.selfReportedDisplayId != mCurTokenDisplayId) {
unbindCurrentMethodLocked();
}
}
} else if (isTextEditor && doAutoShow
&& (softInputMode & LayoutParams.SOFT_INPUT_IS_FORWARD_NAVIGATION) != 0) {
// There is a focus view, and we are navigating forward
// into the window, so show the input window for the user.
// We only do this automatically if the window can resize
// to accommodate the IME (so what the user sees will give
// them good context without input information being obscured
// by the IME) or if running on a large screen where there
// is more room for the target window + IME.
if (DEBUG) Slog.v(TAG, "Unspecified window will show input");
if (attribute != null) {
// 启动输入法
res = startInputUncheckedLocked(cs, inputContext, missingMethods,
attribute, startInputFlags, startInputReason);
didStart = true;
}
// 显示输入法
showCurrentInputLocked(windowToken, InputMethodManager.SHOW_IMPLICIT, null,
SoftInputShowHideReason.SHOW_AUTO_EDITOR_FORWARD_NAV);
}
break;
case LayoutParams.SOFT_INPUT_STATE_UNCHANGED:
// 后面的代码省略。遇到问题时,可以根据具体情况,加log分析。
}
if (!didStart) {
// 如果没有启动的话,这里会做一下保护。感兴趣的可以看源码研究一下。
}
return res;
}
// InputMethodManagerService.java
InputBindResult startInputUncheckedLocked(@NonNull ClientState cs, IInputContext inputContext,
@MissingMethodFlags int missingMethods, @NonNull EditorInfo attribute,
@StartInputFlags int startInputFlags, @StartInputReason int startInputReason) {
// If no method is currently selected, do nothing.
// 如果当前没有输入法,直接返回
if (mCurMethodId == null) {
return InputBindResult.NO_IME;
}
// 启动没有ready,直接返回
if (!mSystemReady) {
// If the system is not yet ready, we shouldn't be running third
// party code.
return new InputBindResult(
InputBindResult.ResultCode.ERROR_SYSTEM_NOT_READY,
null, null, mCurMethodId, mCurSeq, null);
}
// 得到显示输入法的DisplayID
final int displayIdToShowIme = computeImeDisplayIdForTarget(cs.selfReportedDisplayId,
mImeDisplayValidator);
// Check if the input method is changing.
// We expect the caller has already verified that the client is allowed to access this
// display ID.
// 走到这个判断里面,基本上就是已经绑定过输入法了。直接返回结果就行。
if (mCurId != null && mCurId.equals(mCurMethodId)
&& displayIdToShowIme == mCurTokenDisplayId) {
}
// 没有绑定过,则重新开发绑定输入法。
InputMethodInfo info = mMethodMap.get(mCurMethodId);
if (info == null) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Unknown id: " + mCurMethodId);
}
unbindCurrentMethodLocked();
mCurIntent = new Intent(InputMethod.SERVICE_INTERFACE);
mCurIntent.setComponent(info.getComponent());
mCurIntent.putExtra(Intent.EXTRA_CLIENT_LABEL,
com.android.internal.R.string.input_method_binding_label);
mCurIntent.putExtra(Intent.EXTRA_CLIENT_INTENT, PendingIntent.getActivity(
mContext, 0, new Intent(Settings.ACTION_INPUT_METHOD_SETTINGS),
PendingIntent.FLAG_IMMUTABLE));
// 实际上是调用BindService,获取输入法服务(IMS)
if (bindCurrentInputMethodServiceLocked(mCurIntent, this, IME_CONNECTION_BIND_FLAGS)) {
mLastBindTime = SystemClock.uptimeMillis();
mHaveConnection = true;
mCurId = info.getId();
mCurToken = new Binder();
mCurTokenDisplayId = displayIdToShowIme;
try {
if (DEBUG) {
Slog.v(TAG, "Adding window token: " + mCurToken + " for display: "
+ mCurTokenDisplayId);
}
// 添加用于显示输入法的Token
mIWindowManager.addWindowToken(mCurToken, LayoutParams.TYPE_INPUT_METHOD,
mCurTokenDisplayId);
} catch (RemoteException e) {
}
// 成功:返回正在等待绑定IMS
return new InputBindResult(
InputBindResult.ResultCode.SUCCESS_WAITING_IME_BINDING,
null, null, mCurId, mCurSeq, null);
}
mCurIntent = null;
Slog.w(TAG, "Failure connecting to input method service: " + mCurIntent);
return InputBindResult.IME_NOT_CONNECTED;
}
// InputMethodManagerService.java
// BindService成功后的回调
public void onServiceConnected(ComponentName name, IBinder service) {
synchronized (mMethodMap) {
if (mCurIntent != null && name.equals(mCurIntent.getComponent())) {
//得到IInputMethod对象,IMMS通过这个对象与IMS交互。
mCurMethod = IInputMethod.Stub.asInterface(service);
//初始化输入法
executeOrSendMessage(mCurMethod, mCaller.obtainMessageIOO(
MSG_INITIALIZE_IME, mCurTokenDisplayId, mCurMethod, mCurToken));
scheduleNotifyImeUidToAudioService(mCurMethodUid);
if (mCurClient != null) {
// 接上述流程,此时有客户端等待。先清理session,然后创建session。session用于应用与输入法交互。
clearClientSessionLocked(mCurClient);
requestClientSessionLocked(mCurClient);
}
}
}
}
// InputMethodManagerService.java
void requestClientSessionLocked(ClientState cs) {
if (!cs.sessionRequested) {
if (DEBUG) Slog.v(TAG, "Creating new session for client " + cs);
InputChannel[] channels = InputChannel.openInputChannelPair(cs.toString());
cs.sessionRequested = true;
executeOrSendMessage(mCurMethod, mCaller.obtainMessageOOO(
MSG_CREATE_SESSION, mCurMethod, channels[1],
new MethodCallback(this, mCurMethod, channels[0])));
}
}
// IInputMethodWrapper.java
public void createSession(InputChannel channel, IInputSessionCallback callback) {
mCaller.executeOrSendMessage(mCaller.obtainMessageOO(DO_CREATE_SESSION,
channel, callback));
}
// IInputMethodWrapper.java
public void executeMessage(Message msg) {
case DO_CREATE_SESSION: {
SomeArgs args = (SomeArgs)msg.obj;
inputMethod.createSession(new InputMethodSessionCallbackWrapper(
mContext, (InputChannel)args.arg1,
(IInputSessionCallback)args.arg2));
args.recycle();
return;
}
}
// AbstractInputMethodService.java
public abstract class AbstractInputMethodImpl implements InputMethod {
/**
* Instantiate a new client session for the input method, by calling
* back to {@link AbstractInputMethodService#onCreateInputMethodSessionInterface()
* AbstractInputMethodService.onCreateInputMethodSessionInterface()}.
*/
@MainThread
public void createSession(SessionCallback callback) {
// 走这里,把session通知回去(IMS给IMMS通知)
callback.sessionCreated(onCreateInputMethodSessionInterface());
}
}
// InputMethodService.java
// InputMethodSessionImpl 这个对象,在IInputMethodWrapper.java中被 被InputMethodSessionCallbackWrapper包装成 IInputMethodSessionWrapper 对象。
// IInputMethodSessionWrapper 是IInputMethodSession.Stub 类型。
public AbstractInputMethodSessionImpl onCreateInputMethodSessionInterface() {
return new InputMethodSessionImpl();
}
- IMS创建了将IInputMethodSession的代理,并通过Callback返回给IMMS。
// InputMethodManagerService.java
// callback.sessionCreated 通过Binder回调到IMMS端的这个函数。
void onSessionCreated(IInputMethod method, IInputMethodSession session,
InputChannel channel) {
synchronized (mMethodMap) {
if (mCurMethod != null && method != null
&& mCurMethod.asBinder() == method.asBinder()) {
if (mCurClient != null) {
clearClientSessionLocked(mCurClient);
// 这个Client是IMM 通过addClient告知 IMMS的。它对应着某个应用端
mCurClient.curSession = new SessionState(mCurClient,
method, session, channel);
// 可以真正启动输入法了!!!
InputBindResult res = attachNewInputLocked(
StartInputReason.SESSION_CREATED_BY_IME, true);
if (res.method != null) {
// method 是 InputSession。如果非空,代表IMS已经创建了一个会话,那么 将这个会话与对应的应用Client端绑定。实际上调用了IInputMethodClient 的onBindMethod,将Parcelabled对象告知应用端。
executeOrSendMessage(mCurClient.client, mCaller.obtainMessageOO(
MSG_BIND_CLIENT, mCurClient.client, res));
}
return;
}
}
}
}
// InputMethodManagerService.java
InputBindResult attachNewInputLocked(@StartInputReason int startInputReason, boolean initial) {
if (!mBoundToMethod) {
// 将客户端绑定到IME(IMS),将InputConnection告知IMS。
// 调用InputMethod的bindInput API
executeOrSendMessage(mCurMethod, mCaller.obtainMessageOO(
MSG_BIND_INPUT, mCurMethod, mCurClient.binding));
mBoundToMethod = true;
}
// 启动输入法(告知IMS显示输入法)
final SessionState session = mCurClient.curSession;
executeOrSendMessage(session.method, mCaller.obtainMessageIIOOOO(
MSG_START_INPUT, mCurInputContextMissingMethods, initial ? 0 : 1 /* restarting */,
startInputToken, session, mCurInputContext, mCurAttribute));
if (mShowRequested) {
// 显示输入法,调用了InputMethod的showSoftInput
if (DEBUG) Slog.v(TAG, "Attach new input asks to show input");
showCurrentInputLocked(mCurFocusedWindow, getAppShowFlags(), null,
SoftInputShowHideReason.ATTACH_NEW_INPUT);
}
return new InputBindResult(InputBindResult.ResultCode.SUCCESS_WITH_IME_SESSION,
session.session, (session.channel != null ? session.channel.dup() : null),
mCurId, mCurSeq, mCurActivityViewToScreenMatrix);
}
// InputMethodManagerService.java
public boolean handleMessage(Message msg) {
case MSG_START_INPUT: {
final int missingMethods = msg.arg1;
final boolean restarting = msg.arg2 != 0;
args = (SomeArgs) msg.obj;
final IBinder startInputToken = (IBinder) args.arg1;
final SessionState session = (SessionState) args.arg2;
final IInputContext inputContext = (IInputContext) args.arg3;
final EditorInfo editorInfo = (EditorInfo) args.arg4;
try {
setEnabledSessionInMainThread(session);
session.method.startInput(startInputToken, inputContext, missingMethods,
editorInfo, restarting, session.client.shouldPreRenderIme);
} catch (RemoteException e) {
}
args.recycle();
return true;
}
}
- 到这里,输入法启动的大部分流程已经完成。当客户端的 onBindMethod被触发(InputMethodManager.java)应用客户端就收到了输入法对象,后续做了绑定以及再次请求启动输入法(此时已经启动过了)等操作。这些操作,遇到相关问题 时看代码分析即可。
输入法组件图
- 综上,总结一下IMS、IMM和IMMS的组件图。通过组件图可以了解个模块间的交互接口。
- IInputMethodManager: IMM通过它请求IMMS
- IInputMethodClient: IMMS通过它告知IMM相关通知及状态(包括Session对象)
- IInputMethod: IMMS用来请求IMS的对象
- IInputMethodSessionCallback: IMS通过这个Callback,把
- IInputMethodSession告知IMMS,进而告知IMM
- InputContext:IMM通过IMMS告知IMS的对象,IMS通过这个对象回调IMM
- IInputMethodSession:IMM用来请求IMS的对象

输入法调试
- 可以通过一下方式配置系统输入法(PS:原生Setting中有输入法设置画面,但实际项目中原始Setting一般都会被禁用或只能 以Debug方式启动。)
通过配置文件修改默认输入法
- 在framework的res文件中,定义def_input_method和config_default_input_method的值,并在DatabaseHelper.java的loadSecureSettings中加载定义的默认值(前提是输入法应用已被打包到系统)
<!-- frameworks/base/packages/SettingsProvider/res/values/defaults.xml -->
<string name="def_input_method" translatable="false">xxxx</string>
<string name="def_enabled_input_methods" translatable="false">xxxxx</string>
// /frameworks/base/packages/SettingsProvider/src/com/android/providers/settings/DatabaseHelper.java
private void loadSecureSettings(SQLiteDatabase db) {
loadStringSetting(stmt, Settings.Secure.ENABLED_INPUT_METHODS,R.string.def_enabled_input_methods);
loadStringSetting(stmt,Settings.Secure.DEFAULT_INPUT_METHOD,R.string.def_input_method);
}
通过ime命令调试
- 通过ime命令,配置当前系统的输入法
# xxx.apk 是输入法安装包
# root和remount非必须命令
adb root
adb remount
adb install xxx.apk
# 启用输入法,否则ims list -s 看不到输入法
adb shell
# 比如 com.android.inputmethod.leanback/.service.LeanbackImeService
# 根据自己安装的输入法信息设置
# 实在不知道的,可以通过 dumpsys package 包名 | grep Service 确认
ime enable 包名/.Service名
ime set 包名/.Service名
# 点击输入法测试即可
##### 查看输入法相关状态
dumpsys input_method

![2023年中国自动排气阀产业链、市场规模及存在问题分析]图[](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/img_convert/9cc8e72252ce081b74d8f2af16c45015.png)