文章目录
- 1. 代码仓库
- 2. 图的基本表示的比较
- 3. 邻接矩阵:Array和TreeSet
- 3.1 图示
- 3.2 Array主要代码解析
- 3.3 测试输出
- 3.4 使用TreeSet的代码
- 4. 邻接表:LinkedList
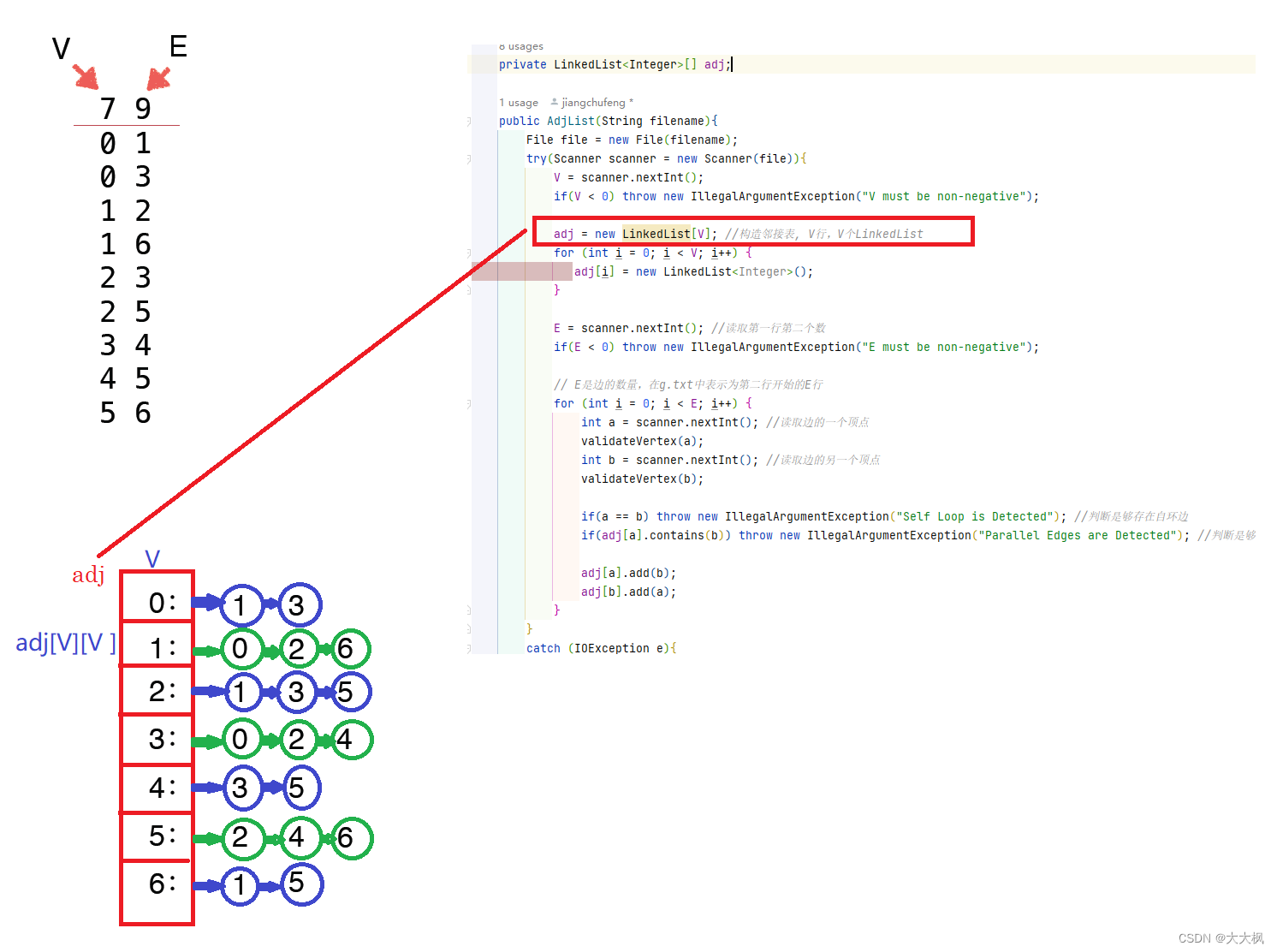
- 4.1 图示
- 4.2 LinkedList主要代码解析
- 4.3 测试输出
- 5. 完整代码
- 5.1 邻接表 - Array
- 5.2 邻接表-TreeSet
- 5.3 邻接矩阵-LinkedList
- 5.4 输入文件
1. 代码仓库
https://github.com/Chufeng-Jiang/Graph-Theory/tree/main/src/Chapt01_Adjacency
2. 图的基本表示的比较
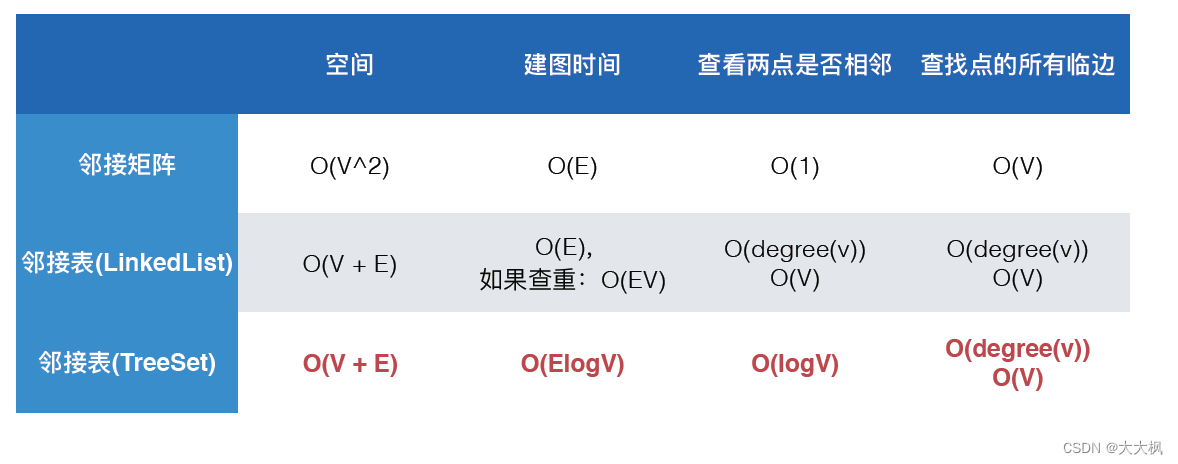
3. 邻接矩阵:Array和TreeSet
3.1 图示

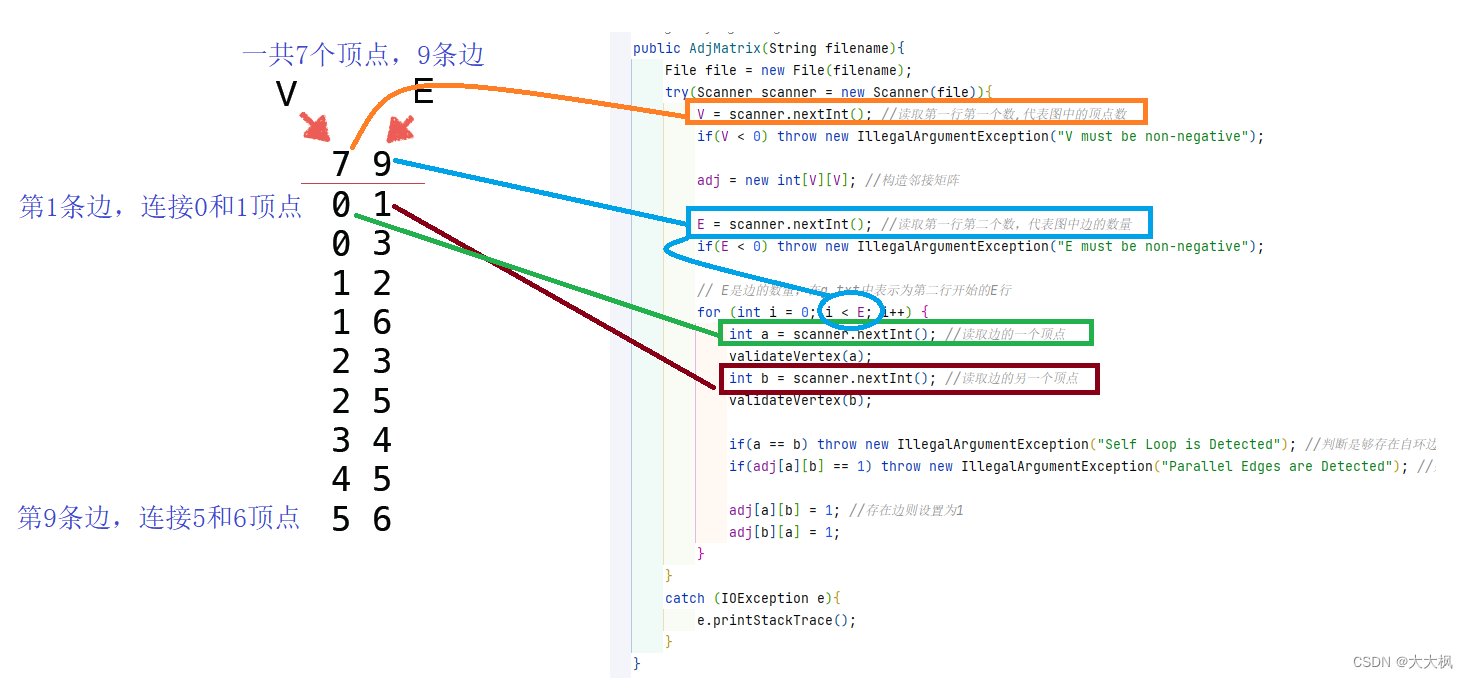
3.2 Array主要代码解析
代码有删减
public AdjMatrix(String filename){
File file = new File(filename);
try(Scanner scanner = new Scanner(file)){
V = scanner.nextInt(); //读取第一行第一个数,代表图中的顶点数
//构造邻接矩阵
adj = new int[V][V];
E = scanner.nextInt(); //读取第一行第二个数,代表图中边的数量
// E是边的数量,在g.txt中表示为第二行开始的E行
for (int i = 0; i < E; i++) {
int a = scanner.nextInt(); //读取边的一个顶点
int b = scanner.nextInt(); //读取边的另一个顶点
adj[a][b] = 1; //存在边则设置为1
adj[b][a] = 1;
}
}
}
3.3 测试输出
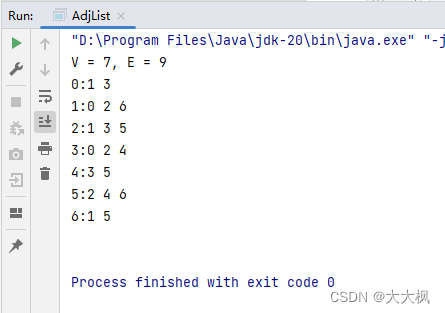
3.4 使用TreeSet的代码
代码有删减
只需要改动一行
adj = new TreeSet[V]; //构造邻接表, V行,V个LinkedList
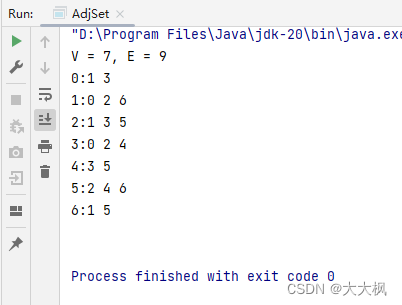
4. 邻接表:LinkedList
4.1 图示

4.2 LinkedList主要代码解析
代码有删减
public class AdjList {
private int V;
private int E;
private LinkedList<Integer>[] adj;
public AdjList(String filename){
File file = new File(filename);
try(Scanner scanner = new Scanner(file)){
V = scanner.nextInt();
/*构造邻接表, V行,V个LinkedList*/
adj = new LinkedList[V];
for (int i = 0; i < V; i++) {
adj[i] = new LinkedList<Integer>();
}
E = scanner.nextInt(); //读取第一行第二个数
// E是边的数量,在g.txt中表示为第二行开始的E行
for (int i = 0; i < E; i++) {
int a = scanner.nextInt(); //读取边的一个顶点
int b = scanner.nextInt(); //读取边的另一个顶点
adj[a].add(b);
adj[b].add(a);
}
}
}
4.3 测试输出
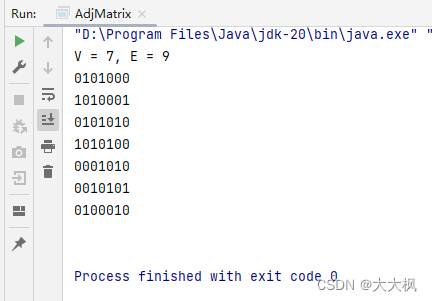
5. 完整代码
5.1 邻接表 - Array
package Chapt01_Adjacency;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.util.LinkedList;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class AdjList {
private int V;
private int E;
private LinkedList<Integer>[] adj;
public AdjList(String filename){
File file = new File(filename);
try(Scanner scanner = new Scanner(file)){
V = scanner.nextInt();
if(V < 0) throw new IllegalArgumentException("V must be non-negative");
adj = new LinkedList[V]; //构造邻接表, V行,V个LinkedList
for (int i = 0; i < V; i++) {
adj[i] = new LinkedList<Integer>();
}
E = scanner.nextInt(); //读取第一行第二个数
if(E < 0) throw new IllegalArgumentException("E must be non-negative");
// E是边的数量,在g.txt中表示为第二行开始的E行
for (int i = 0; i < E; i++) {
int a = scanner.nextInt(); //读取边的一个顶点
validateVertex(a);
int b = scanner.nextInt(); //读取边的另一个顶点
validateVertex(b);
if(a == b) throw new IllegalArgumentException("Self Loop is Detected"); //判断是够存在自环边
if(adj[a].contains(b)) throw new IllegalArgumentException("Parallel Edges are Detected"); //判断是够存在平行l边
adj[a].add(b);
adj[b].add(a);
}
}
catch (IOException e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
private void validateVertex(int v){
if(v < 0 || v >= V)
throw new IllegalArgumentException("vertex" + v + "is invalid");
}
public int V(){
return V;
}
public int E(){
return E;
}
public boolean hasEdge(int v, int w){
validateVertex(v);
validateVertex(w);
return adj[v].contains(w);
}
public LinkedList<Integer> adj(int v){
validateVertex(v);
return adj[v];
}
public int degree(int v){
return adj(v).size();
}
@Override
public String toString(){
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
sb.append(String.format("V = %d, E = %d\n", V, E));
for (int i = 0; i < V; i++) {
sb.append(String.format("%d:",i));
for (int w: adj[i]) {
sb.append(String.format("%d ",w));
}
sb.append('\n');
}
return sb.toString();
}
public static void main(String[] args){
AdjList adjList = new AdjList("g1.txt"); //新建邻接矩阵,并从文件内容初始化
System.out.println(adjList);
}
}
5.2 邻接表-TreeSet
package Chapt01_Adjacency;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.util.Scanner;
import java.util.TreeSet;
public class AdjSet {
private int V;
private int E;
private TreeSet<Integer>[] adj;
public AdjSet(String filename){
File file = new File(filename);
try(Scanner scanner = new Scanner(file)){
V = scanner.nextInt();
if(V < 0) throw new IllegalArgumentException("V must be non-negative");
adj = new TreeSet[V]; //构造邻接表, V行,V个LinkedList
for (int i = 0; i < V; i++) {
adj[i] = new TreeSet<Integer>();
}
E = scanner.nextInt(); //读取第一行第二个数
if(E < 0) throw new IllegalArgumentException("E must be non-negative");
// E是边的数量,在g.txt中表示为第二行开始的E行
for (int i = 0; i < E; i++) {
int a = scanner.nextInt(); //读取边的一个顶点
validateVertex(a);
int b = scanner.nextInt(); //读取边的另一个顶点
validateVertex(b);
if(a == b) throw new IllegalArgumentException("Self Loop is Detected"); //判断是够存在自环边
if(adj[a].contains(b)) throw new IllegalArgumentException("Parallel Edges are Detected"); //判断是够存在平行l边
adj[a].add(b);
adj[b].add(a);
}
}
catch (IOException e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
private void validateVertex(int v){
if(v < 0 || v >= V)
throw new IllegalArgumentException("vertex" + v + "is invalid");
}
public int V(){
return V;
}
public int E(){
return E;
}
public boolean hasEdge(int v, int w){
validateVertex(v);
validateVertex(w);
return adj[v].contains(w);
}
public Iterable<Integer> adj(int v){ // 可以是TreeSet,但是数组、链表、红黑树都是实现了Iterable的接口,因此可以统一写成这样
validateVertex(v);
return adj[v];
}
public int degree(int v){
validateVertex(v);
return adj[v].size(); // Iterable没有size()方法
}
@Override
public String toString(){
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
sb.append(String.format("V = %d, E = %d\n", V, E));
for (int i = 0; i < V; i++) {
sb.append(String.format("%d:",i));
for (int w: adj[i]) {
sb.append(String.format("%d ",w));
}
sb.append('\n');
}
return sb.toString();
}
public static void main(String[] args){
AdjSet adjSet = new AdjSet("g1.txt"); //新建邻接矩阵,并从文件内容初始化
System.out.println(adjSet);
}
}
5.3 邻接矩阵-LinkedList
package Chapt01_Adjacency;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class AdjMatrix {
private int V;
private int E;
private int[][] adj;
// 构造函数,从文件内容初始化邻接矩阵
public AdjMatrix(String filename){
File file = new File(filename);
try(Scanner scanner = new Scanner(file)){
V = scanner.nextInt(); //读取第一行第一个数,代表图中的顶点数
if(V < 0) throw new IllegalArgumentException("V must be non-negative");
adj = new int[V][V]; //构造邻接矩阵
E = scanner.nextInt(); //读取第一行第二个数,代表图中边的数量
if(E < 0) throw new IllegalArgumentException("E must be non-negative");
// E是边的数量,在g.txt中表示为第二行开始的E行
for (int i = 0; i < E; i++) {
int a = scanner.nextInt(); //读取边的一个顶点
validateVertex(a);
int b = scanner.nextInt(); //读取边的另一个顶点
validateVertex(b);
if(a == b) throw new IllegalArgumentException("Self Loop is Detected"); //判断是够存在自环边
if(adj[a][b] == 1) throw new IllegalArgumentException("Parallel Edges are Detected"); //判断是否存在平行l边
adj[a][b] = 1; //存在边则设置为1
adj[b][a] = 1;
}
}
catch (IOException e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
private void validateVertex(int v){
if(v < 0 || v >= V)
throw new IllegalArgumentException("vertex" + v + "is invalid");
}
public int V(){
return V;
}
public int E(){
return E;
}
public boolean hasEdge(int v, int w){
validateVertex(v);
validateVertex(w);
return adj[v][w] == 1;
}
public ArrayList<Integer> adj(int v){
validateVertex(v);
ArrayList<Integer> res = new ArrayList<>();
for (int i = 0; i < V; i++) {
if(adj[v][i] == 1) res.add(i);
}
return res;
}
public int degree(int v){
return adj(v).size(); //adj(v)是上方的adj方法,size()是ArrayList的接口
}
// 用于在控制台打印该临接矩阵
@Override
public String toString(){
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
sb.append(String.format("V = %d, E = %d\n", V, E)); //打印顶点数和边的数量
for (int i = 0; i < V; i++) { //行
for (int j = 0; j < V; j++) { //列
sb.append(String.format("%d",adj[i][j])); //读取矩阵的值
}
sb.append('\n'); //行尾换行
}
return sb.toString(); //返回该邻接矩阵
}
public static void main(String[] args){
AdjMatrix adjMatrix = new AdjMatrix("g1.txt"); //新建邻接矩阵,并从文件内容初始化
System.out.println(adjMatrix);
}
}
5.4 输入文件
7 9
0 1
0 3
1 2
1 6
2 3
2 5
3 4
4 5
5 6