本文是基于 OpenCV4.80 进行的,关于环境的配置可能之后会单独说,先提一嘴 vcpkg 真好用
1 大致流程
从多张图片逐步生成稀疏点云,这个过程通常包括以下步骤:
-
初始重建:
初始两张图片的选择十分重要,这是整个流程的基础,后续的增图都是在这两张图片的基础上进行的
- 对于输入图像,首先需要提取特征点(例如,SIFT、SURF或ORB特征点)。然后,通过匹配不同图像中的特征点,建立它们之间的对应关系
- 通过两张图像之间的本质矩阵
E估计相机的外参矩阵(旋转矩阵R和平移向量T),然后使用三角测量法计算出一些初始的三维点
具体操作可以查看我前面的博客
-
增量式重建:
从这开始,逐步增加图像,逐渐扩展三维点云
- 添加新的图像:将新的图像加载到重建流程中
- 特征提取和匹配:对新的图像提取特征点并与先前图像匹配以获得新的匹配关系
- 位姿估计:估计新图像相对于先前图像的相机位姿,通常使用
PnP(Perspective-n-Point)—— 在已知相机内参数K的前提下,用该角度下的三维点(object_points)与它们对应的图像点(image_points)坐标,估算出此时拍摄位置的信息 - 三维点三角测量:使用新的匹配对和估计的位姿(
R,T)来三角测量,生成新的三维点。 - 点云合并:将新生成的三维点与先前的点云进行合并,构建一个更大的稀疏点云
-
全局点云优化:在稀疏点云已经生成后,可以使用全局点云优化技术,例如Bundle Adjustment,来提高点云的准确性
2 准备代码
之前文章中,我们讲所有代码都挤到了main函数中,十分不美观,现在我们进行一下代码的优化
由于才学C++,比较菜请见谅
2.1 Include.h
这里包含了所有用到的头文件和宏,方便之后使用
由于之后要用 Bundle Adjustment,所以引入了 ceres,具体环境配置之后可能会说(真的比较麻烦,强烈推荐 vcpkg ),其中大量的 #define 和 #pragma warning(disable: 4996) 都是关于 ceres 的报错的
#ifndef INCLUDES_H
#define INCLUDES_H
#define GLOG_NO_ABBREVIATED_SEVERITIES
#define _CRT_NONSTDC_NO_DEPRECATE
#define NOMINMAX
#define _CRT_NONSTDC_NO_WARNINGS
#pragma warning(disable: 4996)
#include <opencv2/opencv.hpp>
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <fstream>
#include <ceres/ceres.h>
#include <ceres/rotation.h>
using namespace cv;
using namespace std;
#endif // !INCLUDES_H
#pragma once
2.2 Constructor
Constructor 类,其中包含了三维重建的几个关键步骤的函数:
findCamera:初始构建使用的求取 E 矩阵和R,T(其中包括了RANSAC)maskoutPoints:通过内点标记mask,来对点进行筛选pointsReconstruct:通过 R,T 匹配点来进行三角化生成三维点云
Constructor.h:
#ifndef CONSTRUCTOR_H
#define CONSTRUCTOR_H
#include "Includes.h"
#include "Images.h"
class Constructor
{
public:
// 输入K,图1的匹配点,图2的匹配点;输出R,T;点经过筛选
static void findCamera(Mat K, vector<Point2f>& point1, vector<Point2f>& point2, Mat& output_R, Mat& output_T, vector<uchar>& mask);
// 输入图匹配点,内点标记mask;返回mask后的vector<Point2f>匹配点
static void maskoutPoints(vector<Point2f>& input_points, vector<uchar>& input_mask);
// 输入图一的R,T,匹配点,图二的R,T,匹配点;返回vector<Point3f>三维点
static vector<Point3d>& pointsReconstruct(const Mat& K, Mat& R1, Mat& T1, Mat& R2, Mat& T2, vector<Point2f>& points1, vector<Point2f>& points2);
};
#endif // !CONSTRUCTOR_H
#pragma once
Constructor.cpp:
#include "Constructor.h"
void Constructor::findCamera(Mat K, vector<Point2f>& point1, vector<Point2f>& point2, Mat& output_R, Mat& output_T, vector<uchar>& mask)
{
vector<uchar> inliers;
Mat F;
F = findFundamentalMat(point1, point2, inliers, FM_RANSAC, 1, 0.5);
Mat E = K.t() * F * K;
//Mat E = findEssentialMat(point1, point2, K, RANSAC, 0.6, 1.0, inliners);
mask = inliers;
// 根据内点筛选出新的匹配点
Constructor::maskoutPoints(point1, inliers);
Constructor::maskoutPoints(point2, inliers);
// 分解E矩阵,获取R,T矩阵
int pass_count = recoverPose(E, point1, point2, K, output_R, output_T);
}
void Constructor::maskoutPoints(vector<Point2f>& input_points, vector<uchar>& input_mask)
{
vector<Point2f> temp_points(input_points);
input_points.clear();
for (int i = 0; i < temp_points.size(); ++i)
{
if (input_mask[i])
{
input_points.push_back(temp_points[i]);
}
}
}
vector<Point3d>& Constructor::pointsReconstruct(const Mat& K, Mat& R1, Mat& T1, Mat& R2, Mat& T2, vector<Point2f>& points1, vector<Point2f>& points2)
{
// 构造投影矩阵
Mat proj1(3, 4, CV_32FC1);
Mat proj2(3, 4, CV_32FC1);
// 将旋转矩阵和平移向量合并为投影矩阵
R1.convertTo(proj1(Range(0, 3), Range(0, 3)), CV_32FC1);
T1.convertTo(proj1.col(3), CV_32FC1);
R2.convertTo(proj2(Range(0, 3), Range(0, 3)), CV_32FC1);
T2.convertTo(proj2.col(3), CV_32FC1);
// 将内参矩阵与投影矩阵相乘,得到最终的投影矩阵
Mat fK;
K.convertTo(fK, CV_32FC1);
proj1 = fK * proj1;
proj2 = fK * proj2;
// 三角化,得到齐次坐标
Mat point4D_homogeneous(4, points1.size(), CV_64F);
triangulatePoints(proj1, proj2, points1, points2, point4D_homogeneous);
// 将齐次坐标转换为三维坐标
vector<Point3d> point3D;
point3D.clear();
point3D.reserve(point4D_homogeneous.cols);
for (int i = 0; i < point4D_homogeneous.cols; ++i)
{
Mat<float> col = point4D_homogeneous.col(i);
col /= col(3);
point3D.push_back(Point3d(col(0), col(1), col(2)));
}
// 将三维坐标存储在Point3d向量中并返回
return point3D;
}
2.3 Image
为了增图,我们需要存储图像中每个特征点在空间中的对应点—— correspond_struct_idx
Image 类,其中有成员变量:
Mat image—— 存储图像vector<KeyPoint> keyPoints—— 存储特征点Mat descriptor—— 存储特征描述符vector<int> correspond_struct_idx—— 匹配点所对应的空间点在点云中的索引vector<Point2f> matchedPoints—— 存储匹配点vector<Vec3b> colors—— 存储匹配点的颜色信息Mat R, T—— 存储相机的旋转矩阵和平移向量
同时还有几个关于图像处理的重要函数:
Images:构造函数,读取图像时就进行了特征点的提取matchFeatures:匹配特征点findColor:提取颜色信息getObjPointsAndImgPoints:找出当前匹配中已经在点云中的点,获取 object_points,以及 image_points —— 为 PnP 做准备
Image.h:
#ifndef IMAGES_H
#define IMAGES_H
#include "Includes.h"
class Images
{
public:
Mat image; // 存储图像
vector<KeyPoint> keyPoints; // 存储特征点
Mat descriptor; // 存储特征描述符
vector<int> correspond_struct_idx; // 匹配点所对应的空间点在点云中的索引
vector<Point2f> matchedPoints; // 存储匹配点
vector<Vec3b> colors; // 存储匹配点的颜色信息
Mat R, T; // 存储相机的旋转矩阵和平移向量
vector<Point3f> object_points; // 前一张图中匹配点对应的三维点
vector<Point2f> image_points; // 在现图像中对应的像素点
// 构造函数,从指定路径读取图像,并提取SIFT特征点和描述符
Images(string const image_paths);
// 特征匹配函数,将当前图像与另一个图像进行特征匹配
void matchFeatures(Images& otherImage, vector<DMatch>& outputMatches);
// 从匹配点中提取颜色信息
void findColor();
// 遍历当前匹配,找出当前匹配中已经在点云中的点,获取object_points,以及image_points
void getObjPointsAndImgPoints(vector<DMatch>& matches, vector<Point3d>& all_reconstructed_points, Images& preImage);
};
#endif // !IMAGES_H
#pragma once
Image.cpp:
#include "Images.h"
Images::Images(string const image_path)
{
// 读取图像
this->image = imread(image_path);
if (this->image.empty())
{
cout << "Could not read image: " << image_path << endl;
}
// 提取SIFT特征点和描述符
Ptr<SIFT> sift = SIFT::create(0, 17, 0.0000000001, 16);
sift->detectAndCompute(this->image, noArray(), this->keyPoints, this->descriptor);
for (int i = 0; i < keyPoints.size(); i++)
{
correspond_struct_idx.push_back(-1);
}
}
void Images::findColor()
{
// 遍历所有匹配点
for (Point2f& Points : this->matchedPoints)
{
// 获取像素点的颜色
Vec3b color = this->image.at<Vec3b>(Points.y, Points.x);
// 将颜色存储在颜色向量中
this->colors.push_back(color);
}
}
void Images::matchFeatures(Images& otherImage, vector<DMatch>& outputMatches)
{
// 清空匹配点
otherImage.matchedPoints.clear();
this->matchedPoints.clear();
vector<vector<DMatch>> matches;
FlannBasedMatcher matcher;
// 使用FlannBasedMatcher进行特征匹配
matcher.knnMatch(this->descriptor, otherImage.descriptor, matches, 2);
// 计算最小距离
float min_dist = FLT_MAX;
for (int r = 0; r < matches.size(); ++r)
{
// 如果最近邻距离大于次近邻距离的2.5倍,则跳过该匹配点
if (matches[r][0].distance < 2.5 * matches[r][1].distance)
{
// 计算最小距离
float dist = matches[r][0].distance;
if (dist < min_dist)
{
min_dist = dist;
}
}
}
// 筛选出好的匹配点
for (int i = 0; i < matches.size(); i++)
{
if (matches[i][0].distance < 0.76 * matches[i][1].distance && matches[i][0].distance < 8 * max(min_dist, 10.0f))
{
outputMatches.push_back(matches[i][0]);
}
}
// 将匹配点存储在matchedPoints向量中
for (int i = 0; i < outputMatches.size(); ++i)
{
this->matchedPoints.push_back(this->keyPoints[outputMatches[i].queryIdx].pt);
otherImage.matchedPoints.push_back(otherImage.keyPoints[outputMatches[i].trainIdx].pt);
}
}
// 从匹配点中获取三维空间点和图像点
void Images::getObjPointsAndImgPoints(vector<DMatch>& matches, vector<Point3d>& all_reconstructed_points, Images& preImage)
{
// 清空object_points和image_points
this->object_points.clear();
this->image_points.clear();
// 遍历所有匹配点
for (int i = 0; i < matches.size(); i++)
{
// 获取匹配点在前一张图像中对应的三维空间点的索引
int matched_world_point_indices = preImage.correspond_struct_idx[matches[i].queryIdx];
// 如果匹配点在前一张图像中对应的三维空间点存在
if (matched_world_point_indices > 0)
{
// 将其(前一张图像中的三维点)添加到object_points中
this->object_points.push_back(all_reconstructed_points[matched_world_point_indices]);
// 将匹配点(该新图像的二维点)添加到image_points中
this->image_points.push_back(this->keyPoints[matches[i].trainIdx].pt);
}
}
}
3 具体实现
在先前的两张图片的初始三维点云的构建的基础上,我们来实现多张图的增量构建
3.1 初始构建
在前面几篇博客中已经详细讲述过了:匹配,用计算 E 矩阵的方式求得相机外参 R,T,进行三角化构建点云
特别:为了后面的增图重建,我们需要记录初始两张图各个点和点云的关系
void initConstruction(vector<Images>& initImages, vector<Point3d>& all_reconstructed_points, vector<Vec3b>& all_points_colors)
{
initImages.push_back(*(new Images(INIT_IMG_PATH1)));
initImages.push_back(*(new Images(INIT_IMG_PATH2)));
vector<DMatch> matches;
initImages[0].matchFeatures(initImages[1], matches);
vector<uchar> mask;
Constructor::findCamera(K, initImages[0].matchedPoints, initImages[1].matchedPoints, initImages[1].R, initImages[1].T, mask);
initImages[0].R = Mat::eye(3, 3, CV_64FC1);
initImages[0].T = Mat::zeros(3, 1, CV_64FC1);
all_reconstructed_points = Constructor::pointsReconstruct(K, initImages[0].R, initImages[0].T, initImages[1].R, initImages[1].T, initImages[0].matchedPoints, initImages[1].matchedPoints);
initImages[1].findColor();
for (int i = 0; i < initImages[1].colors.size(); i++)
{
all_points_colors.push_back(initImages[1].colors[i]);
}
// 根据mask来记录初始两张图各个点和点云的关系
int idx = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < matches.size(); i++)
{
if (mask[i])
{
initImages[0].correspond_struct_idx[matches[i].queryIdx] = idx;
initImages[1].correspond_struct_idx[matches[i].trainIdx] = idx;
idx++;
}
}
}
3.2 增量构建
-
创建
subImageBag,然后将initImages[1]添加到容器中,即表示initImages中的第二张图像(数组索引为1)将与后续进行比较(否则下一张图添加进来跟谁进行匹配呢) -
循环,遍历
sub_image_paths容器中的图像文件路径 -
在循环中,为每个图像文件路径创建一个新的
Images,并将其添加到subImageBag容器中。这样,容器subImageBag中就包含了多张图像,其中第一张图像是初始图像对的第二张,其余图像是逐步添加的 -
调用
addImageConstruction函数,将subImageBag作为参数传递,以及用于存储稀疏点云的all_reconstructed_points和点云颜色的all_points_colors-
循环遍历
subImageBag容器中的每个图像,从索引1开始(因为第一个图像是初始图像用于了初始构建,跳过) -
对于每对相邻的图像,执行以下操作:
-
使用
matchFeatures方法,找到两个相邻图像之间的特征点匹配关系,并将匹配结果存储在matches容器中 -
使用
getObjPointsAndImgPoints方法,获取匹配的特征点对应的三维点和图像点 —— 为 PnP 做准备 -
通过RANSAC筛选,使用
findCamera方法筛选匹配点并生成一个mask,用于标记有效的匹配点(只是为了筛选罢了) -
使用
solvePnPRansac方法,估计新图像的相机位姿,获得R,T -
转换旋转向量为旋转矩阵(
solvePnPRansac得到的是 r 向量) -
使用
pointsReconstruct方法,重建新图像与前图像之间的三维点,并将结果存储在new_restructure_points中 -
使用
findColor方法,获取新图像中点的颜色信息 -
记录初始两张图各个点和点云的关系:
遍历
matches,根据mask中的标记,将新生成的点与初始两张图像的各个点和点云的关系进行记录,维护点与点云之间的对应关系 -
最后,将新生成的三维点
new_restructure_points以及它们的颜色信息添加到all_reconstructed_points和all_points_colors中,不断扩展点云
-
-
void addImageConstruction(vector<Images>& subImageBag, vector<Point3d>& all_reconstructed_points, vector<Vec3b>& all_points_colors)
{
for (int i = 1; i < subImageBag.size(); i++)
{
cout << i << endl;
vector<DMatch> matches;
subImageBag[i - 1].matchFeatures(subImageBag[i], matches);
subImageBag[i].getObjPointsAndImgPoints(matches, all_reconstructed_points, subImageBag[i - 1]);
// 只是为了进行RANSAC筛选匹配点和获取mask
vector<uchar> mask;
Mat discardR, discardT;
Constructor::findCamera(K, subImageBag[i - 1].matchedPoints, subImageBag[i].matchedPoints, discardR, discardT, mask);
solvePnPRansac(subImageBag[i].object_points, subImageBag[i].image_points, K, noArray(), subImageBag[i].R, subImageBag[i].T);
Rodrigues(subImageBag[i].R, subImageBag[i].R);
vector<Point3d> new_restructure_points;
new_restructure_points = Constructor::pointsReconstruct(K, subImageBag[i - 1].R, subImageBag[i - 1].T, subImageBag[i].R, subImageBag[i].T, subImageBag[i - 1].matchedPoints, subImageBag[i].matchedPoints);
subImageBag[i].findColor();
// 记录初始两张图各个点和点云的关系
int idx = 0;
for (int k = 0; k < matches.size(); k++)
{
if (mask[k])
{
subImageBag[i - 1].correspond_struct_idx[matches[k].queryIdx] = all_reconstructed_points.size() + idx;
subImageBag[i].correspond_struct_idx[matches[k].trainIdx] = all_reconstructed_points.size() + idx;
idx++;
}
}
for (int k = 0; k < new_restructure_points.size(); k++)
{
all_reconstructed_points.push_back(new_restructure_points[k]);
all_points_colors.push_back(subImageBag[i].colors[k]);
}
}
}
3.3 完整main.cpp
// 定义图像文件路径和保存结果的路径
//#define INIT_IMG_PATH1 "test_img\\images\\100_7103.jpg"
//#define INIT_IMG_PATH2 "test_img\\images\\100_7104.jpg"
#define INIT_IMG_PATH1 "test_img\\First stage\\B25.jpg"
#define INIT_IMG_PATH2 "test_img\\First stage\\B24.jpg"
#define PLY_SAVE_PATH "test_img\\results\\output.ply"
#include "Includes.h"
#include "Images.h"
#include "Constructor.h"
//const Mat K = (Mat_<double>(3, 3) << 2905.88, 0, 1416, 0, 2905.88, 1064, 0, 0, 1);
const Mat K = (Mat_<double>(3, 3) << 719.5459, 0, 0, 0, 719.5459, 0, 0, 0, 1);
//const vector<string> sub_image_paths = { /*"test_img\\images\\100_7100.jpg", "test_img\\images\\100_7101.jpg", "test_img\\images\\100_7102.jpg",*/ /*"test_img\\images\\100_7103.jpg", "test_img\\images\\100_7104.jpg",*/ "test_img\\images\\100_7105.jpg", "test_img\\images\\100_7106.jpg", "test_img\\images\\100_7107.jpg", "test_img\\images\\100_7108.jpg", "test_img\\images\\100_7109.jpg"/*, "test_img\\images\\100_7110.jpg"*/ };
const vector<string> sub_image_paths = { "test_img\\First stage\\B23.jpg", "test_img\\First stage\\B22.jpg", "test_img\\First stage\\B21.jpg" };
void initConstruction(vector<Images>& initImages, vector<Point3d>& all_reconstructed_points, vector<Vec3b>& all_points_colors)
{
initImages.push_back(*(new Images(INIT_IMG_PATH1)));
initImages.push_back(*(new Images(INIT_IMG_PATH2)));
vector<DMatch> matches;
initImages[0].matchFeatures(initImages[1], matches);
vector<uchar> mask;
Constructor::findCamera(K, initImages[0].matchedPoints, initImages[1].matchedPoints, initImages[1].R, initImages[1].T, mask);
initImages[0].R = Mat::eye(3, 3, CV_64FC1);
initImages[0].T = Mat::zeros(3, 1, CV_64FC1);
all_reconstructed_points = Constructor::pointsReconstruct(K, initImages[0].R, initImages[0].T, initImages[1].R, initImages[1].T, initImages[0].matchedPoints, initImages[1].matchedPoints);
initImages[1].findColor();
for (int i = 0; i < initImages[1].colors.size(); i++)
{
all_points_colors.push_back(initImages[1].colors[i]);
}
// 根据mask来记录初始两张图各个点和点云的关系
int idx = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < matches.size(); i++)
{
if (mask[i])
{
initImages[0].correspond_struct_idx[matches[i].queryIdx] = idx;
initImages[1].correspond_struct_idx[matches[i].trainIdx] = idx;
idx++;
}
}
}
void addImageConstruction(vector<Images>& subImageBag, vector<Point3d>& all_reconstructed_points, vector<Vec3b>& all_points_colors)
{
for (int i = 1; i < subImageBag.size(); i++)
{
cout << i << endl;
vector<DMatch> matches;
subImageBag[i - 1].matchFeatures(subImageBag[i], matches);
subImageBag[i].getObjPointsAndImgPoints(matches, all_reconstructed_points, subImageBag[i - 1]);
// 只是为了进行RANSAC筛选匹配点和获取mask
vector<uchar> mask;
Mat discardR, discardT;
Constructor::findCamera(K, subImageBag[i - 1].matchedPoints, subImageBag[i].matchedPoints, discardR, discardT, mask);
solvePnPRansac(subImageBag[i].object_points, subImageBag[i].image_points, K, noArray(), subImageBag[i].R, subImageBag[i].T);
Rodrigues(subImageBag[i].R, subImageBag[i].R);
vector<Point3d> new_restructure_points;
new_restructure_points = Constructor::pointsReconstruct(K, subImageBag[i - 1].R, subImageBag[i - 1].T, subImageBag[i].R, subImageBag[i].T, subImageBag[i - 1].matchedPoints, subImageBag[i].matchedPoints);
subImageBag[i].findColor();
// 记录初始两张图各个点和点云的关系
int idx = 0;
for (int k = 0; k < matches.size(); k++)
{
if (mask[k])
{
subImageBag[i - 1].correspond_struct_idx[matches[k].queryIdx] = all_reconstructed_points.size() + idx;
subImageBag[i].correspond_struct_idx[matches[k].trainIdx] = all_reconstructed_points.size() + idx;
idx++;
}
}
for (int k = 0; k < new_restructure_points.size(); k++)
{
all_reconstructed_points.push_back(new_restructure_points[k]);
all_points_colors.push_back(subImageBag[i].colors[k]);
}
}
}
int main()
{
try
{
vector<Images> initImages;
vector<Point3d> all_reconstructed_points;
vector<Vec3b> all_points_colors;
initConstruction(initImages, all_reconstructed_points, all_points_colors);
vector<Images> subImageBag;
subImageBag.push_back(initImages[1]);
for (auto& image_path : sub_image_paths)
{
subImageBag.push_back(Images(image_path));
}
addImageConstruction(subImageBag, all_reconstructed_points, all_points_colors);
// 手动输出点云ply文件
std::ofstream plyFile(PLY_SAVE_PATH);
// ply的头部信息
plyFile << "ply\n";
plyFile << "format ascii 1.0\n";
plyFile << "element vertex " << all_reconstructed_points.size() << "\n";
plyFile << "property float x\n";
plyFile << "property float y\n";
plyFile << "property float z\n";
plyFile << "property uchar blue\n";
plyFile << "property uchar green\n";
plyFile << "property uchar red\n";
plyFile << "end_header\n";
// 写入点云数据
for (int i = 0; i < all_reconstructed_points.size(); ++i)
{
cv::Vec3b color = all_points_colors[i];
cv::Point3f point = all_reconstructed_points[i];
plyFile << point.x << " " << point.y << " " << point.z << " "
<< static_cast<int>(color[0]) << " "
<< static_cast<int>(color[1]) << " "
<< static_cast<int>(color[2]) << std::endl;
}
plyFile.close();
return 0;
}
catch (Exception e)
{
cout << e.msg << endl;
}
}
4 总结注意
源码 即上面给出的 Include.h,Constructor.h,Constructor.cpp,Image.h,Image.cpp,main.cpp
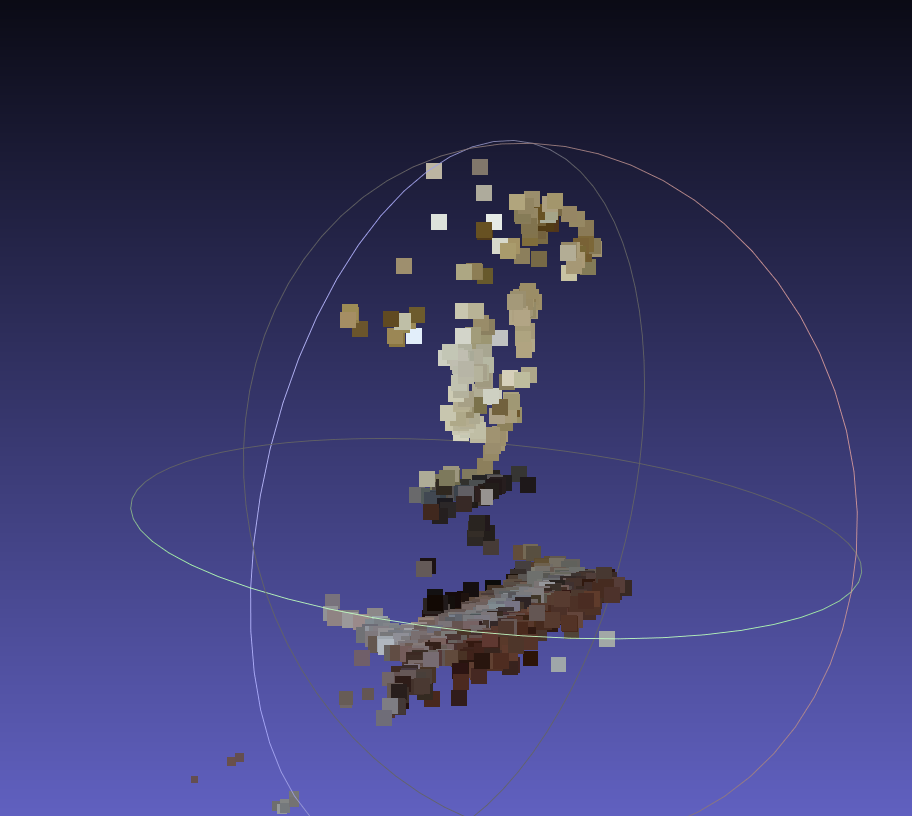
增量加图前(两张初始图的构建):
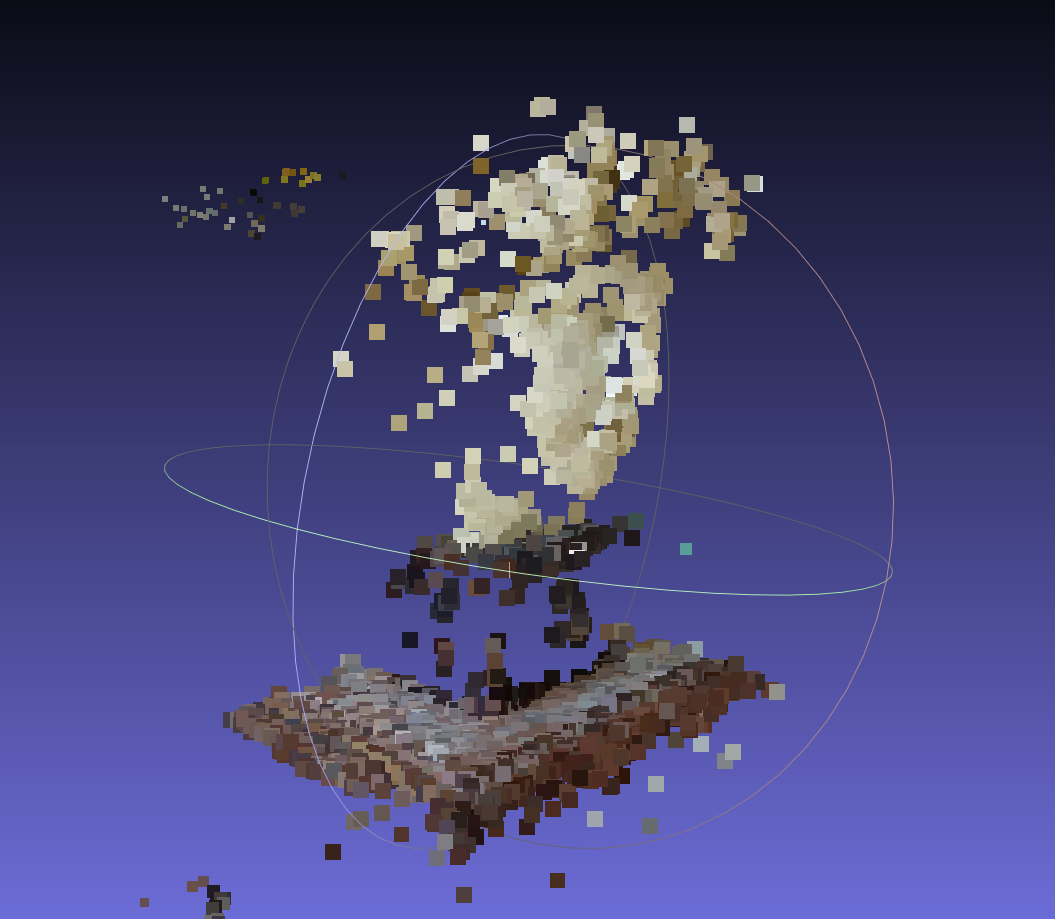
增量加图构造后:
注意:
目前只是完成了基本流程,有很多地方都需要优化,比如
- SIFT 的参数设置
- RANSAC 的参数设置
- 初始图片的选择(很重要)
matchFeatures中的 ratio test 的设置- 还可以增加其他优化措施来剔除离谱点
- 最重要的 BA 还没有加入!
- ·······
目前,出来的效果不好,革命尚未成功,同志还需努力!😭😭😭