数值极限
提供查询所有基础数值类型的性质的接口
定义于头文件 <limits>
template< class T > class numeric_limits;numeric_limits 类模板提供查询各种算术类型属性的标准化方式(例如 int 类型的最大可能值是 std::numeric_limits<int>::max() )。
辅助类
指示浮点舍入模式
std::float_round_styleenum float_round_style {
round_indeterminate = -1,
round_toward_zero = 0,
round_to_nearest = 1,
round_toward_infinity = 2,
round_toward_neg_infinity = 3
};std::float_round_style 类型的枚举常量指示浮点算术在凡将表达式结果存储于浮点类型对象时所用的舍入模式。值为:
枚举常量
| 名称 | 定义 |
| std::round_indeterminate | 无法确定舍入风格 |
| std::round_toward_zero | 向零舍入 |
| std::round_to_nearest | 向最近可表示值舍入 |
| std::round_toward_infinity | 向正无穷大舍入 |
| std::round_toward_neg_infinity | 向负无穷大舍入 |
调用示例
#include <iostream>
#include <cmath>
#include <limits>
#include <cfenv>
int main()
{
double number = 2.5;
std::cout << "std::numeric_limits<double>::round_style: "
<< std::numeric_limits<double>::round_style << std::endl;
std::fesetround(FE_TONEAREST); // 设置舍入规则为最接近的整数
std::cout << "Round to nearest: " << std::round(number) << std::endl;
std::fesetround(FE_DOWNWARD); // 设置舍入规则为向零舍入
std::cout << "Round toward zero: " << std::round(number) << std::endl;
std::fesetround(FE_UPWARD); // 设置舍入规则为向正无穷大舍入
std::cout << "Round toward infinity: " << std::round(number) << std::endl;
std::cout << "std::numeric_limits<double>::round_style: "
<< std::numeric_limits<double>::round_style << std::endl;
return 0;
}指示浮点非规格化模式
std::float_denorm_styleenum float_denorm_style {
denorm_indeterminate = -1,
denorm_absent = 0,
denorm_present = 1
};枚举常量
| 名称 | 定义 |
| std::denorm_indeterminate | 无法确定是否支持非正规值 |
| std::denorm_absent | 类型不支持非正规值 |
| std::denorm_present | 类型允许非正规值 |
调用示例
#include <iostream>
#include <cmath>
#include <limits>
int main()
{
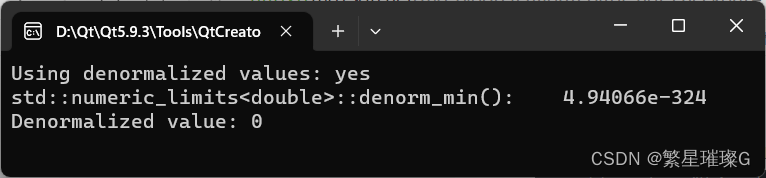
std::cout << "Using denormalized values: ";
if (std::numeric_limits<float>::has_denorm == std::denorm_present)
{
std::cout << "yes" << std::endl;
std::cout << "std::numeric_limits<double>::denorm_min(): "
<< std::numeric_limits<double>::denorm_min() << std::endl;
float a = std::numeric_limits<float>::denorm_min();
float b = std::numeric_limits<float>::denorm_min();
float c = a * b;
std::cout << "Denormalized value: " << c << std::endl;
}
else
{
std::cout << "no" << std::endl;
}
return 0;
}在这个例子中,首先检查std::numeric_limits<float>::has_denorm来判断系统是否支持denormalized值。如果支持,就将浮点数的denormalized值处理方式设置为std::denorm_present。然后,通过std::numeric_limits<float>::denorm_min()获取最小的denormalized值,并计算它们的乘积。最后,输出计算结果。
输出



![相同的树[简单]](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/837ec5c97d7448538ac26558947e20c7.png)