农夫John发现了做出全威斯康辛州最甜的黄油的方法:糖。
把糖放在一片牧场上,他知道 N 只奶牛会过来舔它,这样就能做出能卖好价钱的超甜黄油。
当然,他将付出额外的费用在奶牛上。
农夫John很狡猾,就像以前的巴甫洛夫,他知道他可以训练这些奶牛,让它们在听到铃声时去一个特定的牧场。
他打算将糖放在那里然后下午发出铃声,以至他可以在晚上挤奶。
农夫John知道每只奶牛都在各自喜欢的牧场(一个牧场不一定只有一头牛)。
给出各头牛在的牧场和牧场间的路线,找出使所有牛到达的路程和最短的牧场(他将把糖放在那)。
数据保证至少存在一个牧场和所有牛所在的牧场连通。
输入格式
第一行: 三个数:奶牛数 N,牧场数 P,牧场间道路数 C。
第二行到第 N+1 行: 1 到 N 头奶牛所在的牧场号。
第 N+2 行到第 N+C+1 行:每行有三个数:相连的牧场A、B,两牧场间距 D,当然,连接是双向的。
输出格式
共一行,输出奶牛必须行走的最小的距离和。
数据范围
1≤N≤500,
2≤P≤800,
1≤C≤1450,
1≤D≤255
输入样例:
3 4 5
2
3
4
1 2 1
1 3 5
2 3 7
2 4 3
3 4 5输出样例:
8代码如下
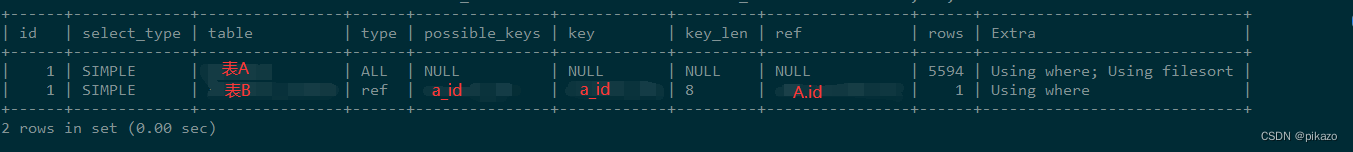
dijkstra和spfa两个代码AC时间

第一个是spfa,第二个是dijkstra,但是我还是更喜欢dijkstra(heihei)
spfa
#include<cstring>
#include<iostream>
#include<algorithm>
#include<queue>
using namespace std;
typedef pair<int, int> PII;
const int N = 810, M = 3000, INF = 0x3f3f3f3f;
int n, p, m;//n是奶牛数量,p是牧场数量,m是道路数量
int h[N], w[M], e[M], ne[M], idx;
int dist[N], cnt[N];//cnt记录编号
bool st[N];
void add(int a, int b, int c)
{
e[idx] = b, w[idx] = c, ne[idx] = h[a], h[a] = idx ++;
}
int spfa(int u)
{
memset(dist, 0x3f, sizeof dist);
//memset(st, 0, sizeof st);//这里不需要每次清空st数组
queue<int> q;
dist[u] = 0;
q.push(u);
st[u] = true;
while(q.size())
{
auto t = q.front();
q.pop();
st[t] = false;
for(int i = h[t]; ~i; i = ne[i])
{
int j = e[i];
if(dist[j] > dist[t] + w[i])
{
dist[j] = dist[t] + w[i];
if(!st[j])
{
st[j] = true;
q.push(j);
}
}
}
}
int res = 0;
for(int i = 0; i < n; i ++)
{
int j = cnt[i];
if(dist[j] == INF) return INF;
res += dist[j];把每次求的结果相加起来
}
return res;
}
int main()
{
cin >> n >> p >> m;
memset(h, -1, sizeof h);
for(int i = 0; i < n; i ++) cin >> cnt[i];
while(m --)
{
int a, b, c;
scanf("%d%d%d", &a, &b, &c);
add(a, b, c), add(b, a, c);
}
int t = INF;
for(int i = 1; i <= p; i ++)
{
t = min(t, spfa(i));//求最小距离
}
cout << t << endl;
return 0;
}1、注意输入,总是输入出错误,哭死,因为每片牧场不只有一头牛,所以cnt数组记录牛的编号
然后注意道路是m,因为是求到牧场之间的距离和,所以是1到p
2、每次跑完最短路之后把每次的距离和相加起来
3、剩下的就是模板
dijkstra
#include<cstring>
#include<iostream>
#include<algorithm>
#include<queue>
using namespace std;
typedef pair<int, int> PII;
const int N = 810, M = 3000, INF = 0x3f3f3f3f;
int n, p, m;
int h[N], w[M], e[M], ne[M], idx;
int dist[N], cnt[N];
bool st[N];
void add(int a, int b, int c)
{
e[idx] = b, w[idx] = c, ne[idx] = h[a], h[a] = idx ++;
}
int dijkstra(int u)
{
memset(st, 0, sizeof st);
memset(dist, 0x3f, sizeof dist);
priority_queue<PII, vector<PII>, greater<PII>> heap;
heap.push({0, u});
dist[u] = 0;
while(heap.size())
{
auto t = heap.top();
heap.pop();
int ver = t.second, distance = t.first;
if(st[ver]) continue;
st[ver] = true;
for(int i = h[ver]; i != -1; i = ne[i])
{
int j = e[i];
if(dist[j] > dist[ver] + w[i])
{
dist[j] = dist[ver] + w[i];
heap.push({dist[j], j});
}
}
}
int res = 0;
for(int i = 0; i < n; i ++)
{
int j = cnt[i];
if(dist[j] == INF) return INF;
res += dist[j];
}
return res;
}
int main()
{
cin >> n >> p >> m;
memset(h, -1, sizeof h);
for(int i = 0; i < n; i ++) cin >> cnt[i];
while(m --)
{
int a, b, c;
scanf("%d%d%d", &a, &b, &c);
add(a, b, c), add(b, a, c);
}
int t = INF;
for(int i = 1; i <= p; i ++)
{
t = min(t, dijkstra(i));
}
cout << t << endl;
return 0;
}1、其实代码都相差不多,就是注意dijkstra每次都要清空st数组
2、希望小伙伴两种算法都能熟练地背下来,一个处理正权,一个处理友负权边的问题