Spring:
图片出处:b站黑马 ssm学习截图
是一个大家族 ,是一套完整的开发生态圈。可以利用这个spring全家桶快速构建企业级开发环境。
Spring Freamwork 是其他框架的基础
Springbot 使用了注解开发
SpringCloud 分布式 云服务
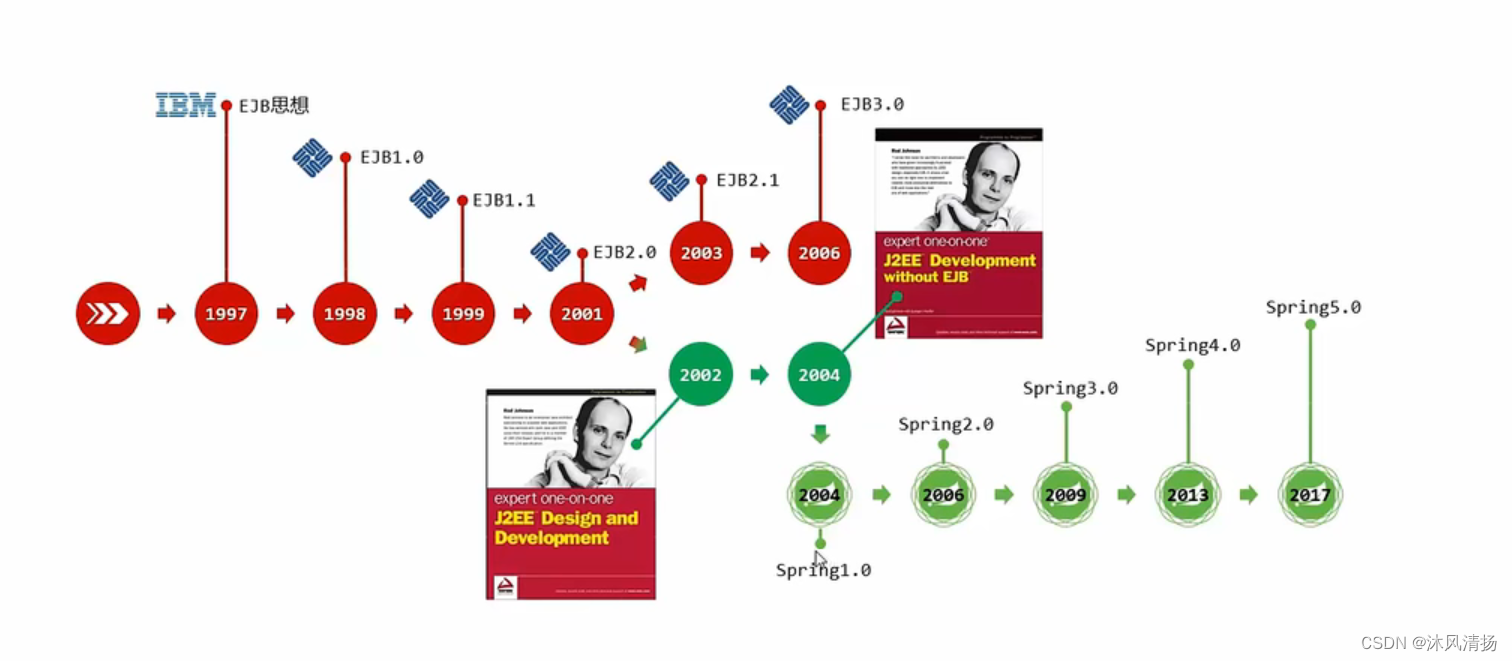
Spring 4架构图
容器:
用来管理Java对象

AOP:
面向切面编程
Aspets:
Aop的实现
Data Access :
数据访问

Spring核心概念:
为什么出现这些框架?
以前的 开发 代码耦合度太高 ,牵一发而动全身,耗费成本太高。

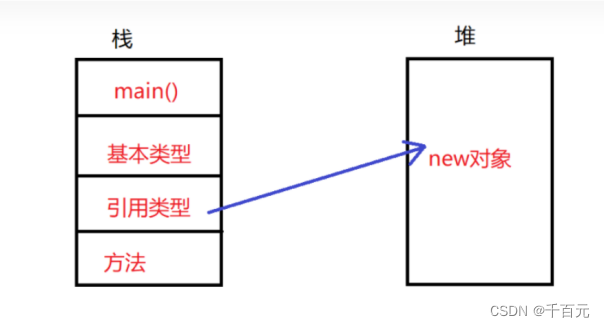
控制反转:IOC
对象的创建控制权发生了转移,Spring提供了容器,实现了对象的创建,由主动创建对象 到ioc创建对象并且初始化,这里创建的对象统一称为bean。
依赖注入:Di
例如service和dao的bean就可以使用依赖注入

IOC DI入门:
我们先
导入依赖
这里导入org.sprinngframework的包 导入成功后
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 http://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd">
<modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion>
<groupId>org.example</groupId>
<artifactId>springtext</artifactId>
<version>1.0-SNAPSHOT</version>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-context</artifactId>
<version>6.0.1</version>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
<properties>
<maven.compiler.source>8</maven.compiler.source>
<maven.compiler.target>8</maven.compiler.target>
</properties>
</project>建包
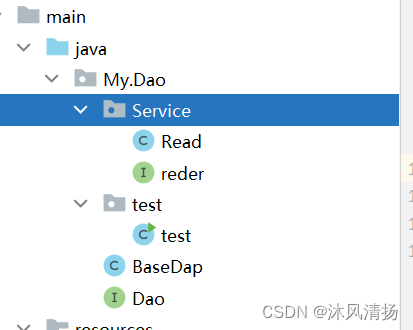
这里我只分了业务层和dao层 随便写的接口和实现类
这个具有内容自己写就行 随便写两个方法 去实现 只要能帮助你理解就行
上面提到 我们用bean容器 来管理 和创建对象 实现解耦的作用
所以导入依赖之后
先来配置bean
在resource下新建xml 导入依赖成功的话 选springconfig就行

这里我们命名为
applicationContext.xml
在文件里创建<bean>即可 class指向他所在的包,也就是你要管理的对象
这里我们新建DAO和service的
id就是它们的标识
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd">
<!--
导入包后 开始配置bean
-->
<bean class="My.Dao.Service.Read" id="Read">
<property name="Read" ref="read1"></property>
</bean>
<bean class="My.Dao.Service.Read" id="read1"></bean>
</beans>建个测试类测试一下:
可以看到 无需用new来创建对象 而是将控制权移交给了ioc容器
package My.Dao.test;
import My.Dao.Service.Read;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext;
public class test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ApplicationContext cs=new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("appliactionContext.xml");
//拿到bean对象
Read R= (Read) cs.getBean("read");
//调用方法
R.reading();
}
}
完成控制权的转移之后 我们为了实现充分解耦 就需要使用
依赖注入
将 bean相关的依赖对应起来
这里对业务层 所需要的dao进行依赖注入
按照传统的方式 这里的业务层是依托于Dao层 以前都是new对象来创建dao的实例
那么这里利用依赖注入只需要封装dao层 给它设置一个set方法即可
package My.Dao.Service;
import My.Dao.BaseDap;
public class Read implements reder{
public void setBs(BaseDap bs) {
this.bs = bs;
}
private BaseDap bs;
@Override
public void reading() {
System.out.println("正在阅读");
}
}
在applicationContext.xml里进行如下操作
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd">
<!--
导入包后 开始配置bean
-->
<bean class="My.Dao.Service.Read" id="Read">
<!-- //这里是业务的bean对象 class指向它所在的包-->
<property name="Read" ref="baseDap">
<!-- //利用property属性 对bean相关的进行设置-->
</property>
</bean>
<!-- //property 的name 是业务层的封装的dao 可以利用set方法给它传值 这里的ref 指向的就是下面这个bean-->
<bean class="My.Dao.BaseDap" id="baseDap">
</bean>
</beans>注入之后就完成了解耦 这时候再去跑一下
测试代码
package My.Dao.test;
import My.Dao.Service.Read;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext;
public class test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ApplicationContext cs=new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("appliactionContext.xml");
Read R= (Read) cs.getBean("read");
R.reading();
}
}
这里就完成了初步的入门
Bean配置:
基础配置已经在上面给出
下面是别名配置:
即 在配置文中对bean 的name 设置多个参数 就可以通过别名调用
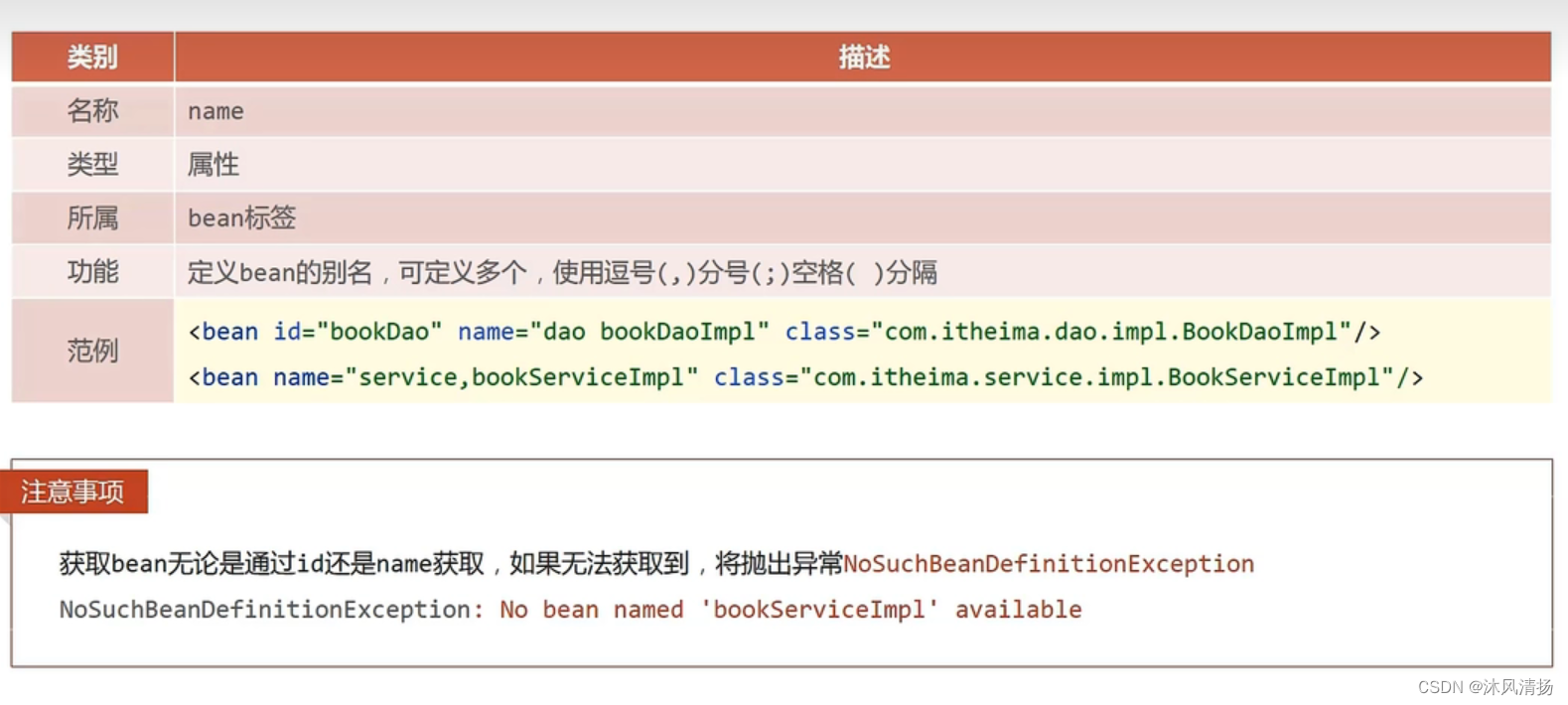
bean的作用范围
这里的作用范围默认的单例


Bean的实例化
创建bean的三种方式:
构造方法

静态工厂创建bean

实例工厂造对象:

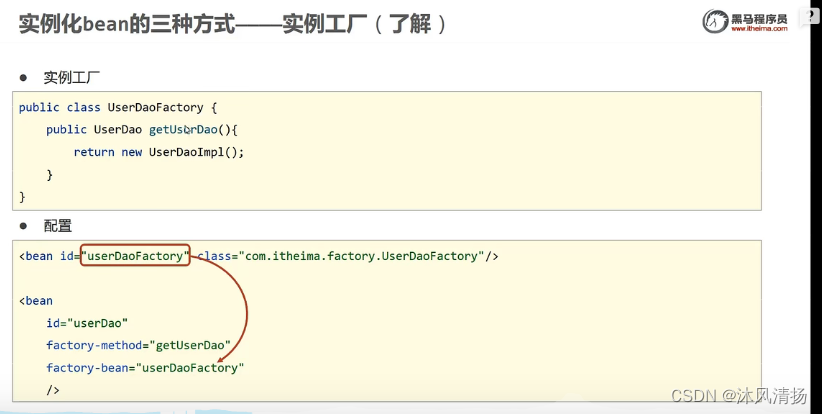
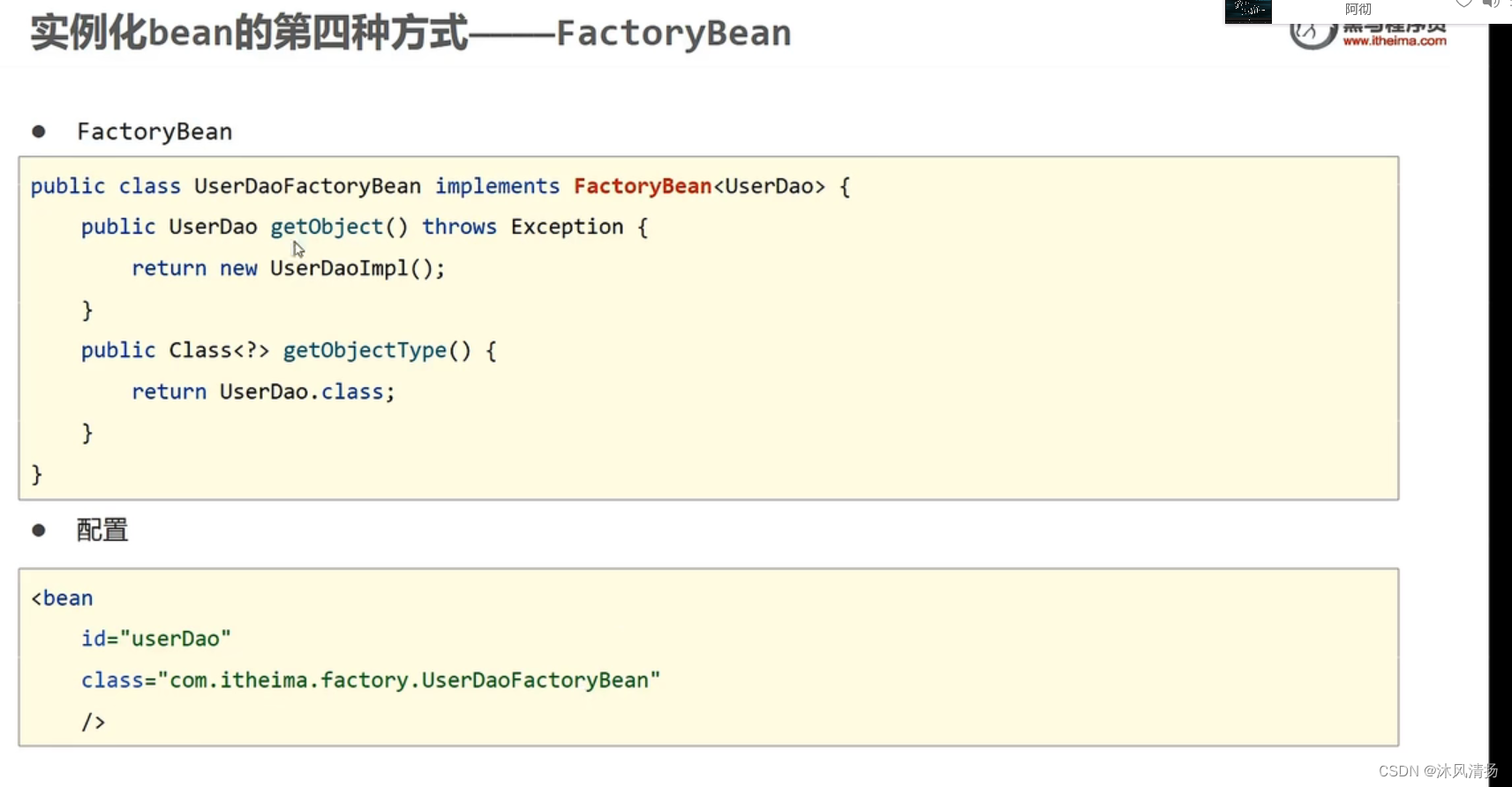
factoryBean构造对象