模型实战一之YOLOv7实例分割、模型训练自己数据集
1.环境准备
- 下载yolov7实例分割模型:
git clone https://github.com/WongKinYiu/yolov7.git -b mask yolov7-mask
cd yolov7-mask
- 安装环境
#查看已安装环境
conda info --envs
#查看安装了哪些包
conda list
#创建环境
conda create -n yolov7 python=3.8
#激活
conda activate yolov7
# 安装 torch 1.8.2+cu11.1
pip install torch==1.8.2 torchvision==0.9.2 torchaudio===0.8.2 --extra-index-url https://download.pytorch.org/whl/lts/1.8/cu111
#其他版本:torch+cuda10.2
pip install torch==1.8.1+cu102 torchvision==0.9.1+cu102 torchaudio===0.8.1 -f https://download.pytorch.org/whl/torch_stable.html
# 修改requirements.txt,将其中的torch和torchvision注释掉
pip install -r requirements.txt
- 安装detectron2
detectron是facebook发布的开源机器视觉库,安装教程参考:https://blog.csdn.net/qq_45770232/article/details/126471738
# 安装detectron2
#先安装ninja
pip install ninja
git clone https://github.com/facebookresearch/detectron2
cd detectron2
python setup.py install
cd ..
2.测试实例分割demo
- 测试:
下载权重放在detect.py路径下:yolov7.pt ... yolov7-mask.pt
测试yolov7目标检测:
python detect.py --weights yolov7.pt --conf 0.25 --img-size 640 --source inference/images/horses.jpg
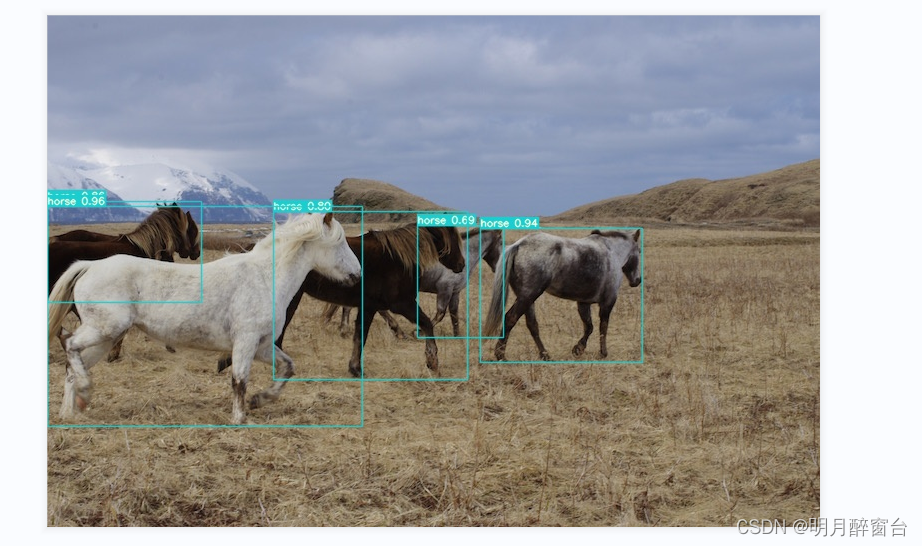
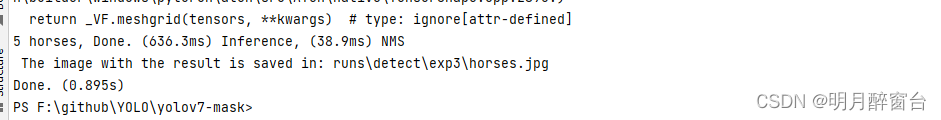

- 测试实例分割 - python
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import torch
import cv2
import yaml
from torchvision import transforms
import numpy as np
from utils.datasets import letterbox
from utils.general import non_max_suppression_mask_conf
from detectron2.modeling.poolers import ROIPooler
from detectron2.structures import Boxes
from detectron2.utils.memory import retry_if_cuda_oom
from detectron2.layers import paste_masks_in_image
device = torch.device("cuda:0" if torch.cuda.is_available() else "cpu")
with open('data/hyp.scratch.mask.yaml') as f:
hyp = yaml.load(f, Loader=yaml.FullLoader)
weigths = torch.load('./weights/yolov7-mask.pt')
model = weigths['model']
model = model.half().to(device)
_ = model.eval()
image = cv2.imread('inference/images/horses.jpg') # 504x378 image
image = letterbox(image, 640, stride=64, auto=True)[0]
image_ = image.copy()
image = transforms.ToTensor()(image)
image = torch.tensor(np.array([image.numpy()]))
image = image.to(device)
image = image.half()
output = model(image)
inf_out, train_out, attn, mask_iou, bases, sem_output = output['test'], output['bbox_and_cls'], output['attn'], output['mask_iou'], output['bases'], output['sem']
bases = torch.cat([bases, sem_output], dim=1)
nb, _, height, width = image.shape
names = model.names
pooler_scale = model.pooler_scale
pooler = ROIPooler(output_size=hyp['mask_resolution'], scales=(pooler_scale,), sampling_ratio=1, pooler_type='ROIAlignV2', canonical_level=2)
output, output_mask, output_mask_score, output_ac, output_ab = non_max_suppression_mask_conf(inf_out, attn, bases, pooler, hyp, conf_thres=0.25, iou_thres=0.65, merge=False, mask_iou=None)
pred, pred_masks = output[0], output_mask[0]
base = bases[0]
bboxes = Boxes(pred[:, :4])
original_pred_masks = pred_masks.view(-1, hyp['mask_resolution'], hyp['mask_resolution'])
pred_masks = retry_if_cuda_oom(paste_masks_in_image)( original_pred_masks, bboxes, (height, width), threshold=0.5)
pred_masks_np = pred_masks.detach().cpu().numpy()
pred_cls = pred[:, 5].detach().cpu().numpy()
pred_conf = pred[:, 4].detach().cpu().numpy()
nimg = image[0].permute(1, 2, 0) * 255
nimg = nimg.cpu().numpy().astype(np.uint8)
nimg = cv2.cvtColor(nimg, cv2.COLOR_RGB2BGR)
nbboxes = bboxes.tensor.detach().cpu().numpy().astype(np.int32)
pnimg = nimg.copy()
for one_mask, bbox, cls, conf in zip(pred_masks_np, nbboxes, pred_cls, pred_conf):
if conf < 0.25:
continue
color = [np.random.randint(255), np.random.randint(255), np.random.randint(255)]
pnimg[one_mask] = pnimg[one_mask] * 0.5 + np.array(color, dtype=np.uint8) * 0.5
pnimg = cv2.rectangle(pnimg, (bbox[0], bbox[1]), (bbox[2], bbox[3]), color, 2)
#label = '%s %.3f' % (names[int(cls)], conf)
#t_size = cv2.getTextSize(label, 0, fontScale=0.5, thickness=1)[0]
#c2 = bbox[0] + t_size[0], bbox[1] - t_size[1] - 3
#pnimg = cv2.rectangle(pnimg, (bbox[0], bbox[1]), c2, color, -1, cv2.LINE_AA) # filled
#pnimg = cv2.putText(pnimg, label, (bbox[0], bbox[1] - 2), 0, 0.5, [255, 255, 255], thickness=1, lineType=cv2.LINE_AA)
# coco example
# %matplotlib inline
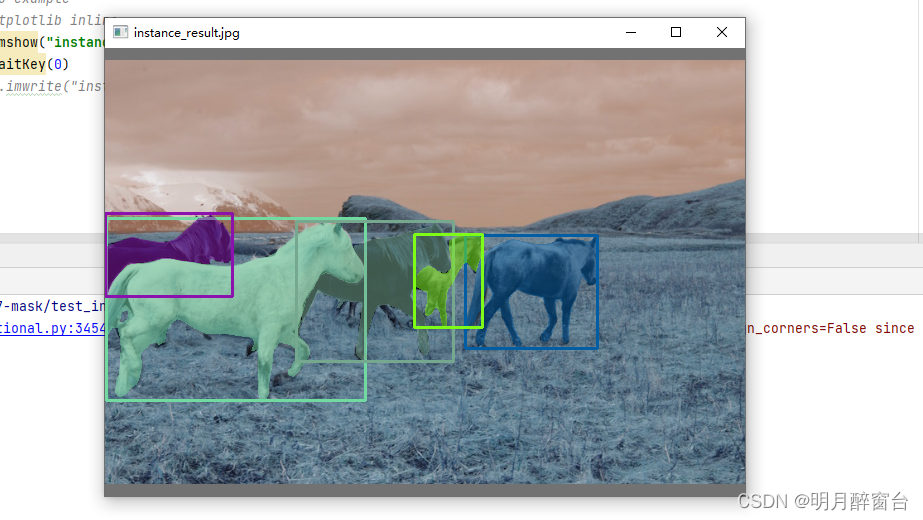
cv2.imshow("instance_result.jpg", pnimg)
cv2.waitKey(0)
# cv2.imwrite("instance_result.jpg", pnimg)
3.训练自己的数据集
- 实例分割时
目标检测与语义分割的结合,所以其标注文件初始为通过labelme标注的json格式,要用yolo模型进行训练,需要将其转换为yolo所需要的txt格式:
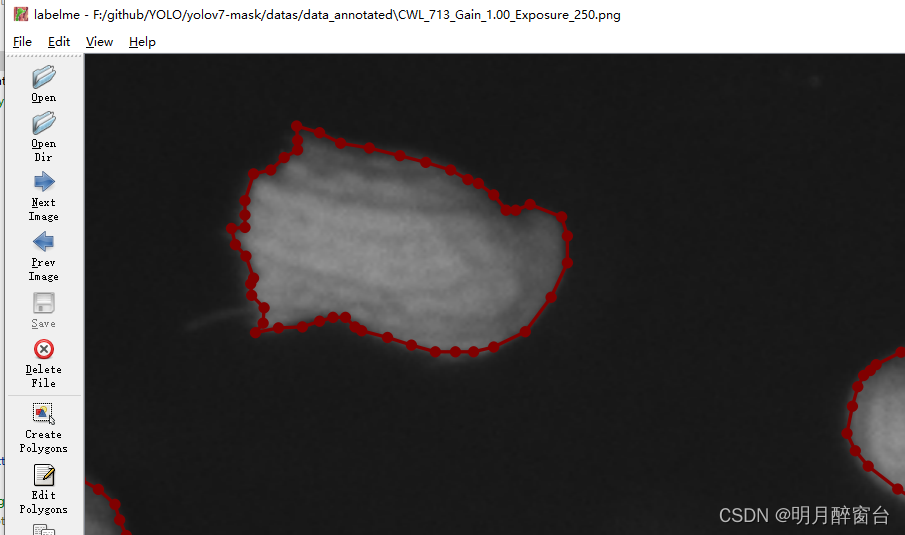
- 转换
demo如下:
参考:https://blog.csdn.net/qq_57329395/article/details/128079776
# 处理labelme多边形矩阵的标注 json转化txt
import json
import os
name2id = {'peanuthull': 0, 'kernel': 1}
def convert(img_size, box):
dw = 1. / (img_size[0])
dh = 1. / (img_size[1])
x = (box[0] + box[2]) / 2.0
y = (box[1] + box[3]) / 2.0
w = abs(box[2] - box[0])
h = abs(box[3] - box[1])
x = x * dw
w = w * dw
y = y * dh
h = h * dh
return (x, y, w, h)
def decode_json(json_floder_path, txt_outer_path, json_name):
# json_floder_path='E:\\Python_package\\itesjson\\'
# json_name='V1125.json'
txt_name = txt_outer_path + json_name[:-5] + '.txt'
with open(txt_name, 'w') as f:
json_path = os.path.join(json_floder_path, json_name) # os路径融合
data = json.load(open(json_path, 'r', encoding='gb2312', errors='ignore'))
img_w = data['imageWidth'] # 图片的高
img_h = data['imageHeight'] # 图片的宽
isshape_type = data['shapes'][0]['shape_type']
print(isshape_type)
# print(isshape_type)
# print('下方判断根据这里的值可以设置为你自己的类型,我这里是polygon'多边形)
# len(data['shapes'])
for i in data['shapes']:
label_name = i['label'] # 得到json中你标记的类名
if (i['shape_type'] == 'polygon'): # 数据类型为多边形 需要转化为矩形
x_max = 0
y_max = 0
x_min = 100000
y_min = 100000
for lk in range(len(i['points'])):
x1 = float(i['points'][lk][0])
y1 = float(i['points'][lk][1])
# print(x1)
if x_max < x1:
x_max = x1
if y_max < y1:
y_max = y1
if y_min > y1:
y_min = y1
if x_min > x1:
x_min = x1
bb = (x_min, y_max, x_max, y_min)
if (i['shape_type'] == 'rectangle'): # 为矩形不需要转换
x1 = float(i['points'][0][0])
y1 = float(i['points'][0][1])
x2 = float(i['points'][1][0])
y2 = float(i['points'][1][1])
bb = (x1, y1, x2, y2)
bbox = convert((img_w, img_h), bb)
try:
f.write(str(name2id[label_name]) + " " + " ".join([str(a) for a in bbox]) + '\n')
except:
pass
if __name__ == "__main__":
json_floder_path = 'data_\\jsons\\' # 存放json的文件夹的绝对路径
txt_outer_path = 'data_\\txts\\' # 存放txt的文件夹绝对路径
json_names = os.listdir(json_floder_path)
print("共有:{}个文件待转化".format(len(json_names)))
flagcount = 0
for json_name in json_names:
decode_json(json_floder_path, txt_outer_path, json_name)
flagcount += 1
print("还剩下{}个文件未转化".format(len(json_names) - flagcount))
# break
print('转化全部完毕')
-
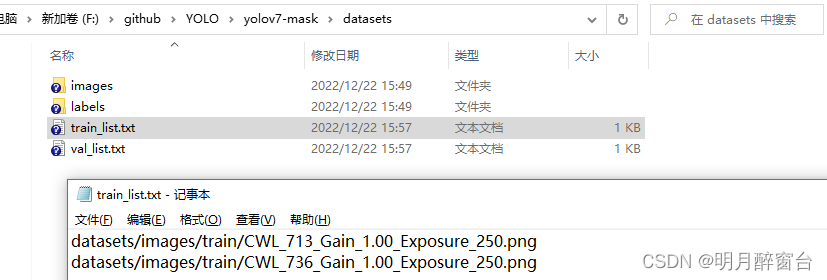
数据集存放格式:
-
datasets:
-
images:
- train:
.jpg - val:
.jpg
- train:
-
labels:
- train:
.txt - val:
.txt
- train:
-
train_list.txt
-
val_list.txt
-
-
train_list及val_list存放绝对路径,如下:

参考:https://blog.csdn.net/matt45m/article/details/127416919?spm=1001.2014.3001.5502






![[Java实战]Squaretest单元测试生成利器...一天生成所有简单单元测试...[新手开箱可用]](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/63768885cc8343d18794a954a6c61892.png)