1.什么是jsoup
jsoup:Java HTML解析器,专为HTML编辑,清理,抓取和XSS安全而构建

2.依赖
<dependency>
<!-- jsoup HTML parser library @ https://jsoup.org/ -->
<groupId>org.jsoup</groupId>
<artifactId>jsoup</artifactId>
<version>1.15.3</version>
</dependency>
//方便处理数据 ,你可以用Google 的JSON 或者其他的JSON都行
<!--json-->
<dependency>
<groupId>com.alibaba</groupId>
<artifactId>fastjson</artifactId>
<version>1.2.47</version>
</dependency>3.使用
1.发送请求
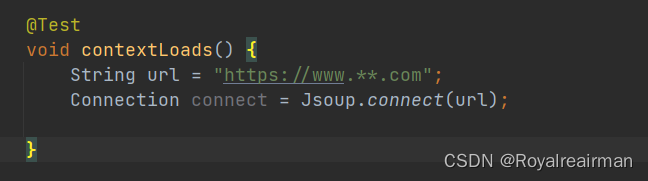
2.设置请求方式
第一种:

第二种:
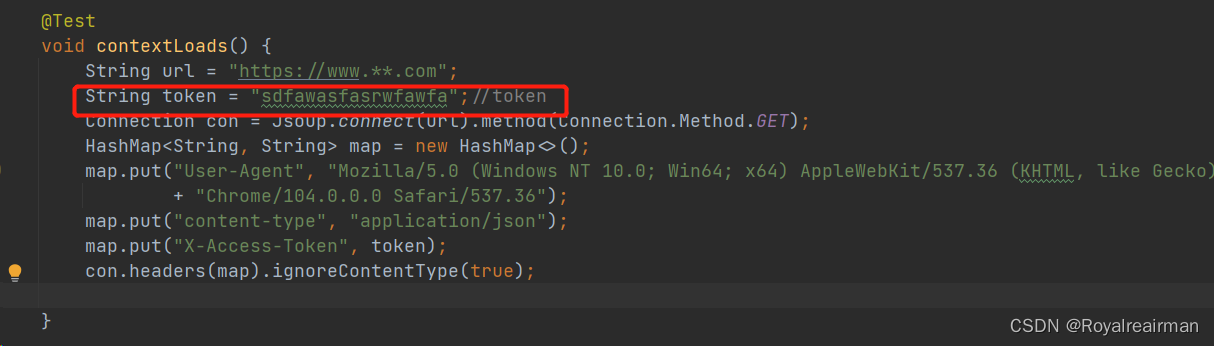
3.设置请求头
token也是放在请求头中,请求头内容设置也有可能是存在多条
4.传参
@RequestBody 和@RequestParam,
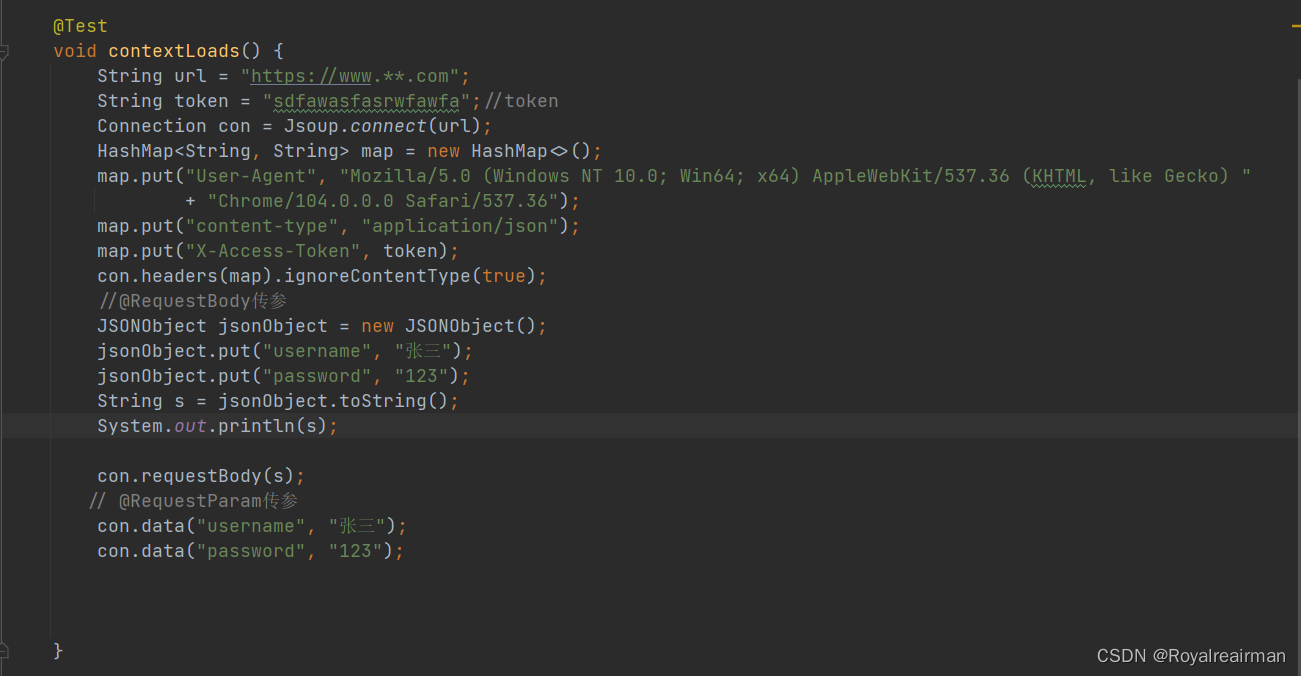
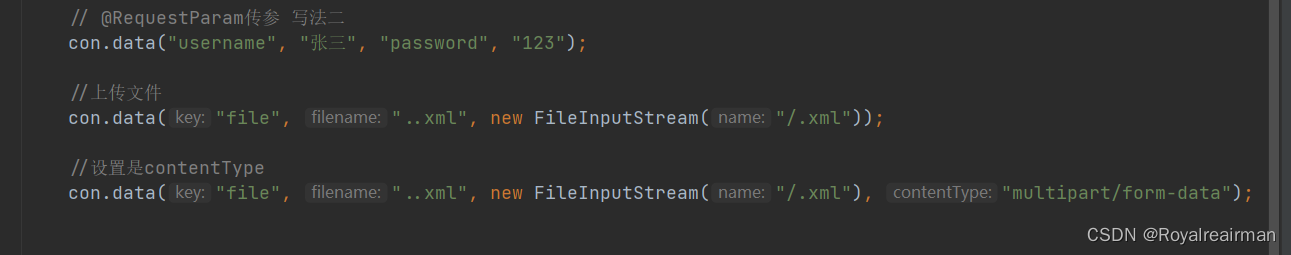
上传文件
5.响应
处理响应一般分为对JSON的处理 和对流的处理,JSON这么处理 我这里就不说了,主要说下下载文件,jsoup下载文件 默认是1 M ,
写法一:
@Test
void contextLoads() throws Exception {
String url = "https://search.**.com" ;
Connection con = Jsoup.connect(url);
Connection.Response response =
con.maxBodySize(999999999).method(Connection.Method.GET).ignoreContentType(true).execute();
byte[] bufferedInputStream = response.bodyAsBytes();
saveFile(bufferedInputStream,"/.");
}
/**
* saveFile 保存文件操作
*
* @param in 字节数组
* @param savePath 存储路径
* @throws IOException 异常处理
*/
static void saveFile(byte[] in, String savePath) throws IOException {
//byte[] buffer = new byte[1024];
//int len = 0;
// 创建缓冲流
FileOutputStream fileOutStream = new FileOutputStream(new File(savePath));
BufferedOutputStream bufferedOut = new BufferedOutputStream(fileOutStream);
// 图片写入
bufferedOut.write(in, 0, in.length);
// 缓冲流释放与关闭
bufferedOut.flush();
bufferedOut.close();
}
写法二:
@Test
void contextLoads() throws Exception {
String url = "https://search.**.com" ;
Connection con = Jsoup.connect(url);
Connection.Response response =
con.maxBodySize(999999999).method(Connection.Method.GET).ignoreContentType(true).execute();
BufferedInputStream bufferedInputStream = response.bodyStream();
System.out.println(response.contentType());
saveFile(bufferedInputStream,"C:\\Users\\19167\\Desktop\\1.jpg");//保存文件的地址
}
/**
* 保存文件到本地
* @param bufferedInputStream
* @param savePath
*/
public static void saveFile(BufferedInputStream bufferedInputStream,String savePath) throws IOException {
//一次最多读取1k
byte[] buffer = new byte[1024];
//实际读取的长度
int readLenghth;
//根据文件保存地址,创建文件输出流
FileOutputStream fileOutputStream = new FileOutputStream(new File(savePath));
//创建的一个写出的缓冲流
BufferedOutputStream bufferedOutputStream = new BufferedOutputStream(fileOutputStream);
//文件逐步写入本地
while ((readLenghth = bufferedInputStream.read(buffer,0,1024)) != -1){//先读出来,保存在buffer数组中
System.out.println(readLenghth);
bufferedOutputStream.write(buffer,0,readLenghth);//再从buffer中取出来保存到本地
}
//关闭缓冲流
bufferedOutputStream.close();
fileOutputStream.close();
bufferedInputStream.close();
}
如果你只是为了完成上面的操作,你可以不用jsoup,如果只是简单的调接口,选择hutool ,httpclient 等。我个人喜欢用hutool,主要是比较全,大部分要的功能都有
6.HTML解析
jsoup的也支持html文件的解析
@Test
void contextLoads() throws Exception {
String url = "https://**.jd.com/Search?keyword=%E7%AC%94%E8%AE%B0%E6%9C%AC&enc=utf-8&wq=%E7%AC%94%E8%AE%B0%E6%9C%AC&pvid=7df949471db54d0f8da255705846b05c" ;
Document document = Jsoup.parse(new URL(url), 30000);
System.out.println(document+"测试时候后");
}
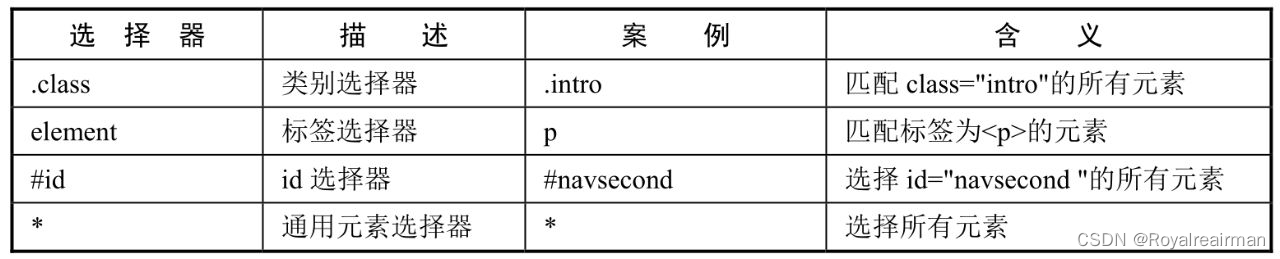
1.属性值
@Test
void contextLoads() throws Exception {
String url = "https://**.jd.com/Search?keyword=%E7%AC%94%E8%AE%B0%E6%9C%AC&enc=utf-8&wq=%E7%AC%94%E8%AE%B0%E6%9C%AC&pvid=7df949471db54d0f8da255705846b05c";
Document document = Jsoup.parse(new URL(url), 30000);
//类别选择器 .class
document.getElementsByClass("dd").text();
// 标签选择器
document.getElementsByTag("title").text();
//id选择器
document.getElementById("J_accessibility").text();
//根据属性获取元素 target="_blank"
final Element target = document.getElementsByAttribute("target").first();
System.out.println(target.text());
//根据 属性 的key和值 获取值
Element first = document.getElementsByAttributeValue("target", "_blank").first();
System.out.println(first.text());
}2.从元素中获取
@Test
void contextLoads() throws Exception {
String url = "https://**.jd.com/Search?keyword=%E7%AC%94%E8%AE%B0%E6%9C%AC&enc=utf-8&wq=%E7%AC%94%E8%AE%B0%E6%9C%AC&pvid=7df949471db54d0f8da255705846b05c";
Document doc = Jsoup.parse(new URL(url), 30000);
Element element = doc.getElementById("J_accessibility");
//获取元素中的 id
String id = element.id();
//获取元素中的 class
String name = element.className();
//从元素中获取属性的值 attr
final String id1 = element.attr("id");
//从元素中获取所有属性
final Attributes attributes = element.attributes();
//从元素中获取文本text
element.text();
}
· 3.通过选择器
//通过标签
Elements div = doc.select("div");
for (Element element : div) {
System.out.println(element.text());
}
//通过 id查找 #id 写法为: #+(id标签值)
Elements ids = doc.select("#dd");
for (Element id : ids) {
System.out.println(id.text());
}
//通过 .class查找元素 写法为 .+(class标签的值)
final Elements select = doc.select(".ss");
//利用属性值查找元素
Elements select1 = doc.select("[adc]");
// [attr=value]: 利用属性值来查找元素,比如:[width=500]
doc.select("[class=vlli]").first().text();
4.组合使用
String str = "";
// 组合选择器
// el#id: 元素+ID,比如: div#logo
str = doc.select("li#auto-header-fenzhan").first().text();
// el.class: 元素+class,比如: div.masthead
str = doc.select("a.greylink").first().text();
// el[attr]: 元素+属性,比如: a[href]
str = doc.select("a[href]").first().attr("href");
// 任意组合,比如:a[href].highlight
str = doc.select("a[href].greylink").first().attr("href");
// ancestor child: 查找某个元素下子元素,比如:可以用.body p 查找"body"下的所有 p
str = doc.select("div.mini-left a").text();
// parent > child: 查找某个父元素下的直接子元素,比如:div.content > p 查找 p
str = doc.select("div.mini-left ul > li").text();
// parent > * 查找某个父元素下所有直接子元素
Elements elements = doc.select("div.mini-left > *");
for (Element ele : elements) {
System.out.println(ele.tagName());
}
- el#id: 元素+ID,比如: div#logo
- el.class: 元素+class,比如: div.masthead
- el[attr]: 元素+属性名,比如: a[href]
- 任意组合,比如:a[href].highlight
- ancestor child: 查找某个元素下子元素,比如:.body p 查找"body"下的所有 p
- parent > child: 查找某个父元素下的直接子元素,比如:div.content > p 查找 p
- parent > * 查找某个父元素下所有直接子元素
- siblingA + siblingB: 查找在A元素之前第一个同级元素B,比如:div.head + div
- siblingA ~ siblingX: 查找A元素之前的同级X元素,比如:h1 ~ p
- :lt(n): 查找哪些元素的同级索引值(它的位置在DOM树中是相对于它的父节点)小于n,比如:td:lt(3) 表示小于三列的元素
- :gt(n):查找哪些元素的同级索引值大于n,比如: div p:gt(2)表示哪些div中有包含2个以上的p元素
- :eq(n): 查找哪些元素的同级索引值与n相等,比如:form input:eq(1)表示包含一个input标签的Form元素
- :has(seletor): 查找匹配选择器包含元素的元素,比如:div:has(p)表示哪些div包含了p元素
- :not(selector): 查找与选择器不匹配的元素,比如: div:not(.logo) 表示不包含 class=logo 元素的所有 div 列表
- :contains(text): 查找包含给定文本的元素,搜索不区分大不写,比如: p:contains(jsoup)
- :containsOwn(text): 查找直接包含给定文本的元素
- :matches(regex): 查找哪些元素的文本匹配指定的正则表达式,比如:div:matches((?i)login)
- :matchesOwn(regex): 查找自身包含文本匹配指定正则表达式的元素
- 注意:上述伪选择器索引是从0开始的,也就是说第一个元素索引值为0,第二个元素index为1等