文章目录
- 1. Apollo参考线介绍
- 1.1 参考线的作用
- 1.2 导航规划的路线
- 1.3 为什么需要重新生成参考线
- 1.4 ReferenceLine数据结构
- 1.5 ReferencePoint数据结构
- 1.6 参考线处理流程
- 1.7 参考线生成
- 2. 参考线平滑算法
- 2.1 参考线平滑算法总览
- 2.2 参考线平滑算法流程
- 2.2.1 设置中间点anchor points
- 2.2.2 Smooth函数
- 2.2.3FemPosSmooth
- 2.2.4 Solve函数
- 2.3 优化问题构造和求解
- 2.4 平滑代价
- 2.5 约束条件
- 2.5.1 位置约束
- 2.5.2 曲率约束
- 3. U型道路仿真演示
1. Apollo参考线介绍
1.1 参考线的作用
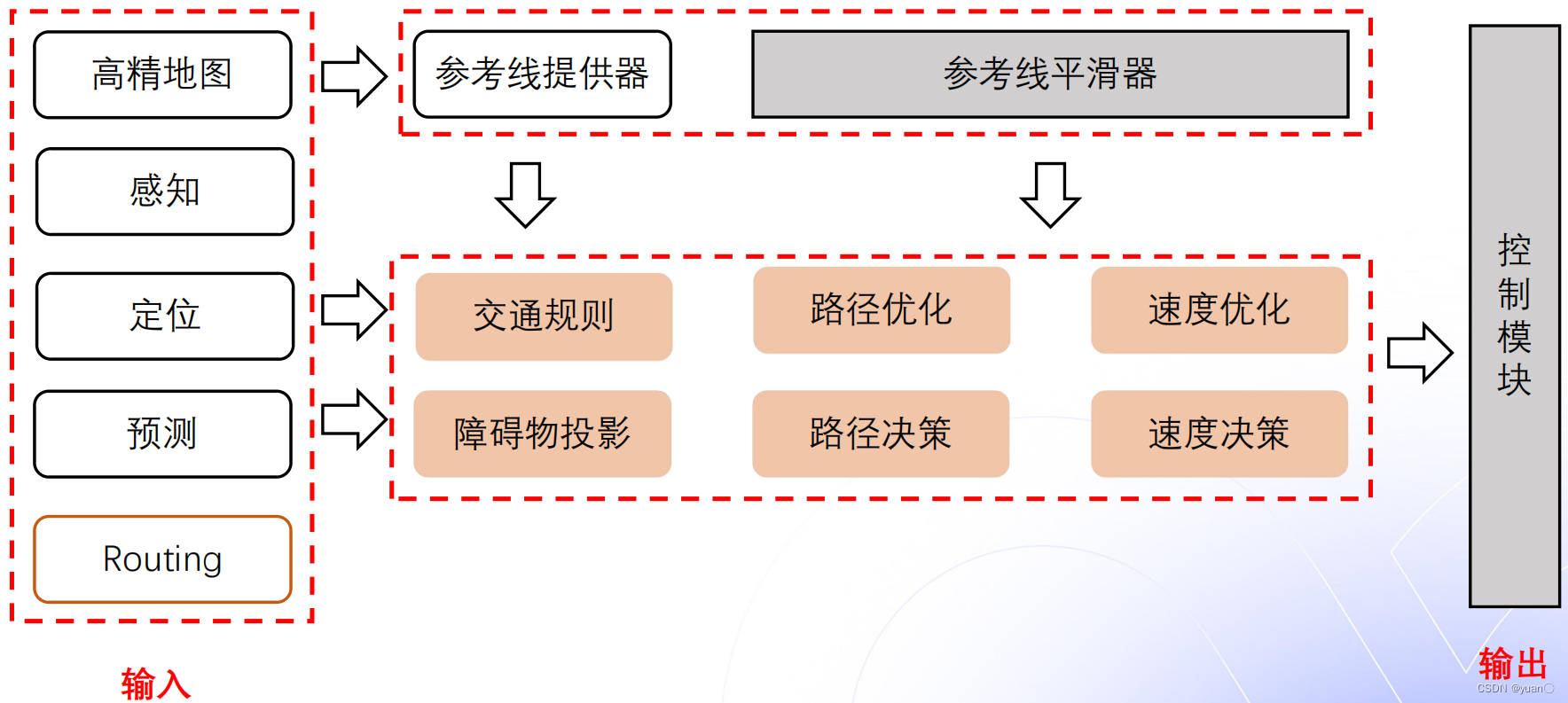
1.2 导航规划的路线
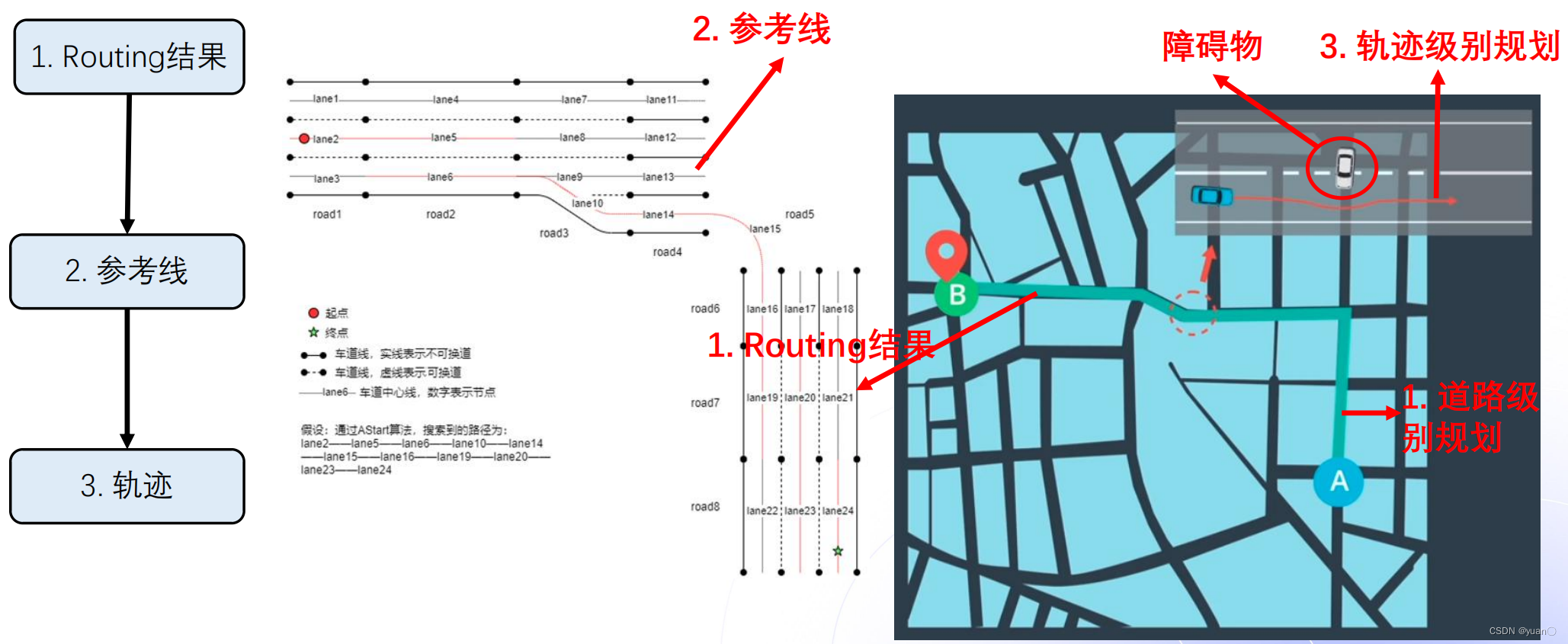 导航规划的路线一般由三个部分组成:Routing、参考线以及轨迹。
导航规划的路线一般由三个部分组成:Routing、参考线以及轨迹。
Routing: 全局路径规划的结果,一般规划出来的长度为几十公里甚至上百公里,若没有障碍物,车辆将会沿着这条路径一直行驶。若有障碍物,则会由Planning模块发布回Routing模块进行重新规划。
参考线: 决策规划模块根据车辆的实时位置进行计算。参考线的计算依赖于Routing的结果,但同时需要车辆周围的动态信息(障碍物、交通规则)。参考线相当于Routing结果里局部数据(车辆当前位置的一段Routing),距离通常只有几百米。参考线可能会有多条。
轨迹: 是规划决策模块的最终输出结果。轨迹的输入是参考线。轨迹不仅包含车辆的路径信息,也包括车辆的动态信息(速度、加速度等)。
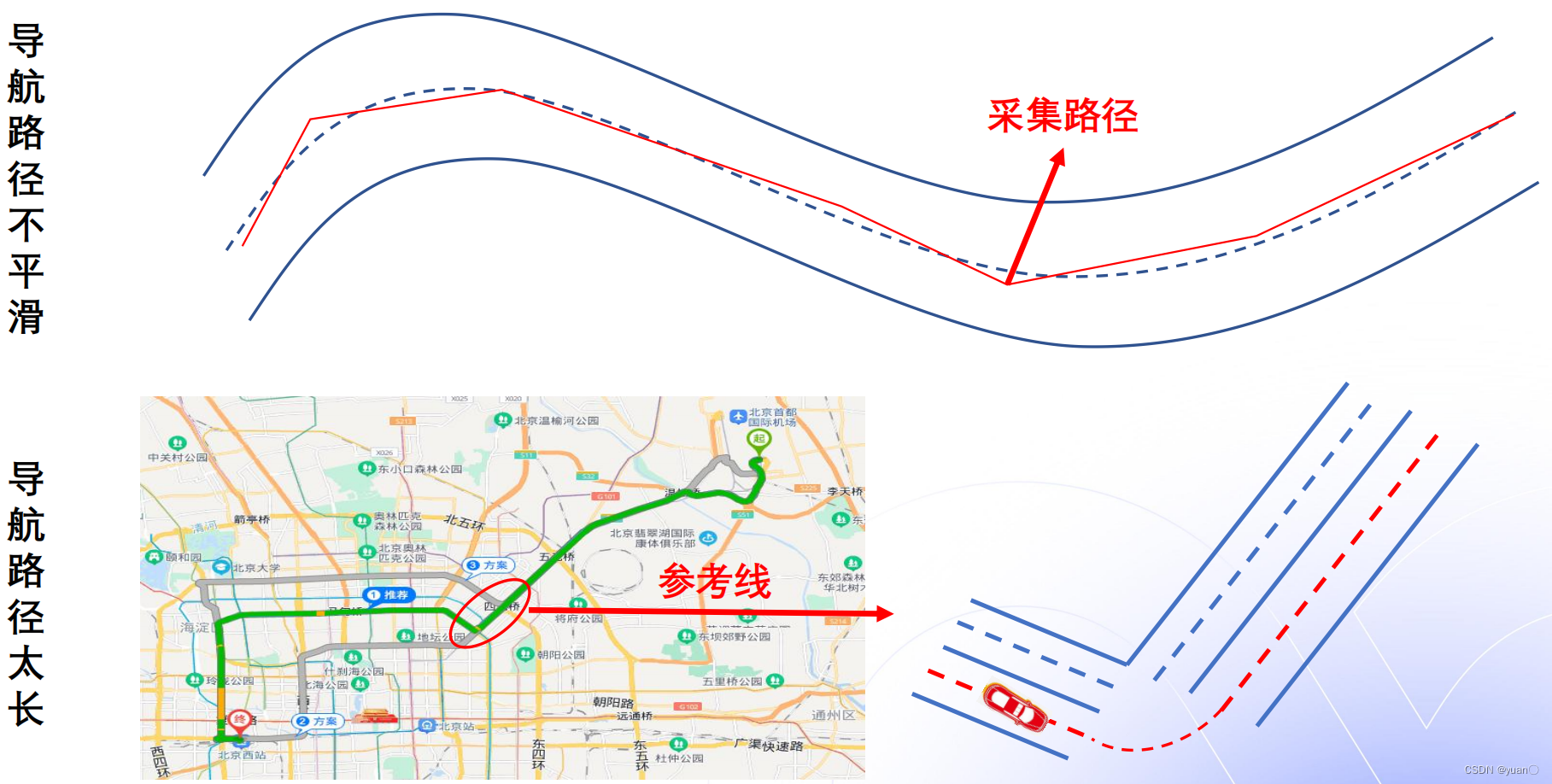
1.3 为什么需要重新生成参考线
1.4 ReferenceLine数据结构
 优先级:当有多条参考线时,具有优先级。
优先级:当有多条参考线时,具有优先级。
SpeedLimit:车辆在一段参考线里的速度限制。起始点的速度限制/终点的限制
speed_limit_:是一个数组,分段限速。
reference_points_:参考点,同样是数组。
map_path_:地图中的参考线,与planning中的参考线具有一一映射关系,参考点的数目是相同的。
1.5 ReferencePoint数据结构
 ReferencePoint继承自MapPathPoint,MapPathPoint继承自Vec2d。
ReferencePoint继承自MapPathPoint,MapPathPoint继承自Vec2d。
Vec2d:包含了点的二维数据。
MapPathPoint:包含了点的朝向以及地图上的点对应道路上的点。
ReferencePoint:包含了曲线的曲率与曲率的导数。
1.6 参考线处理流程
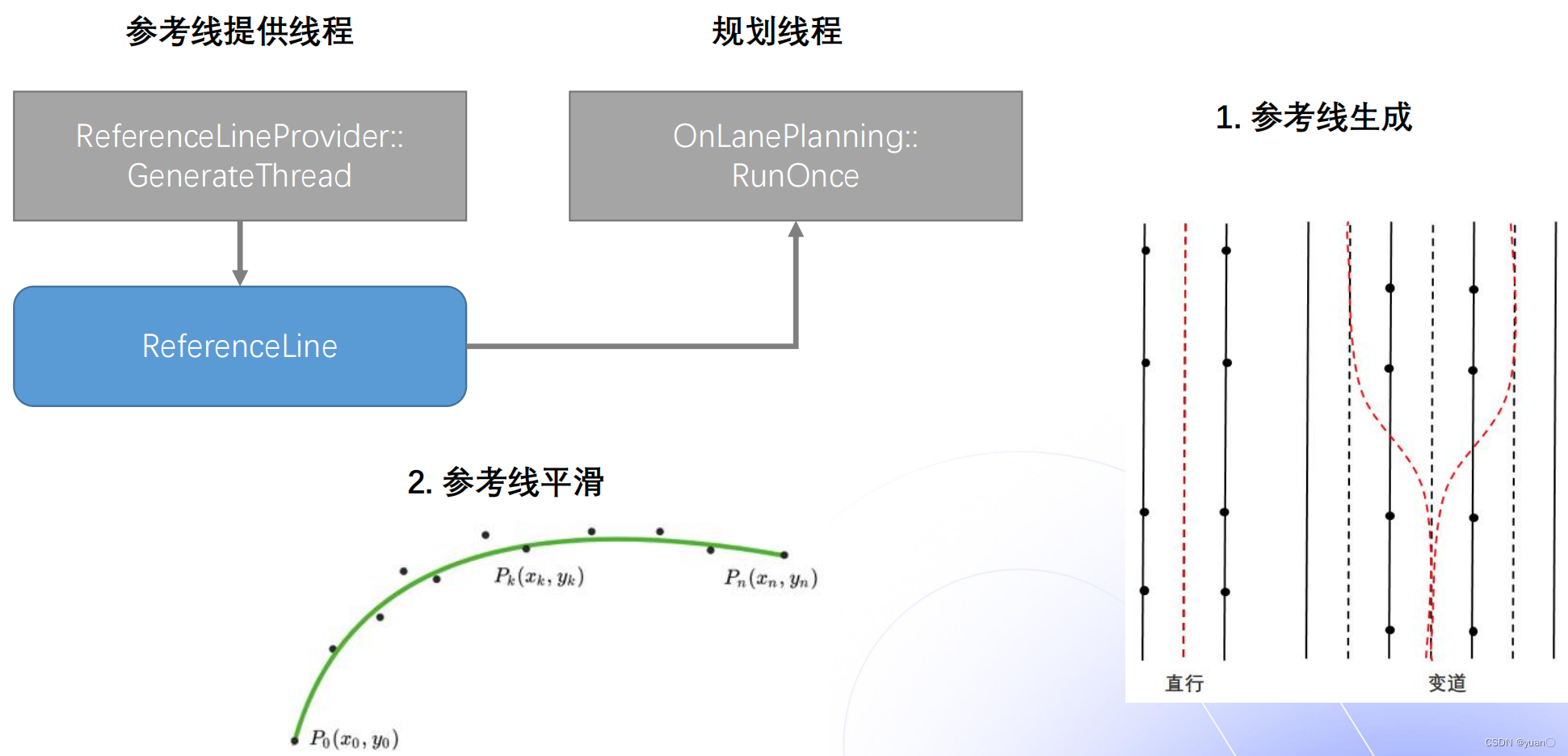 参考线的处理主要涉及两个线程:一个是参考线提供线程,另一个是规划线程。参考线提供线程提供参考线给规划线程去规划出一条轨迹。参考线的处理有两个步骤:首先是参考线的生成,直行时生成一条参考线,当有变道发生时,生成多条参考线。接下来是参考线的平滑,常见的参考线平滑方式有:离散点的平滑(Apollo采用)、螺旋线的平滑以及样条曲线的平滑。
参考线的处理主要涉及两个线程:一个是参考线提供线程,另一个是规划线程。参考线提供线程提供参考线给规划线程去规划出一条轨迹。参考线的处理有两个步骤:首先是参考线的生成,直行时生成一条参考线,当有变道发生时,生成多条参考线。接下来是参考线的平滑,常见的参考线平滑方式有:离散点的平滑(Apollo采用)、螺旋线的平滑以及样条曲线的平滑。
1.7 参考线生成
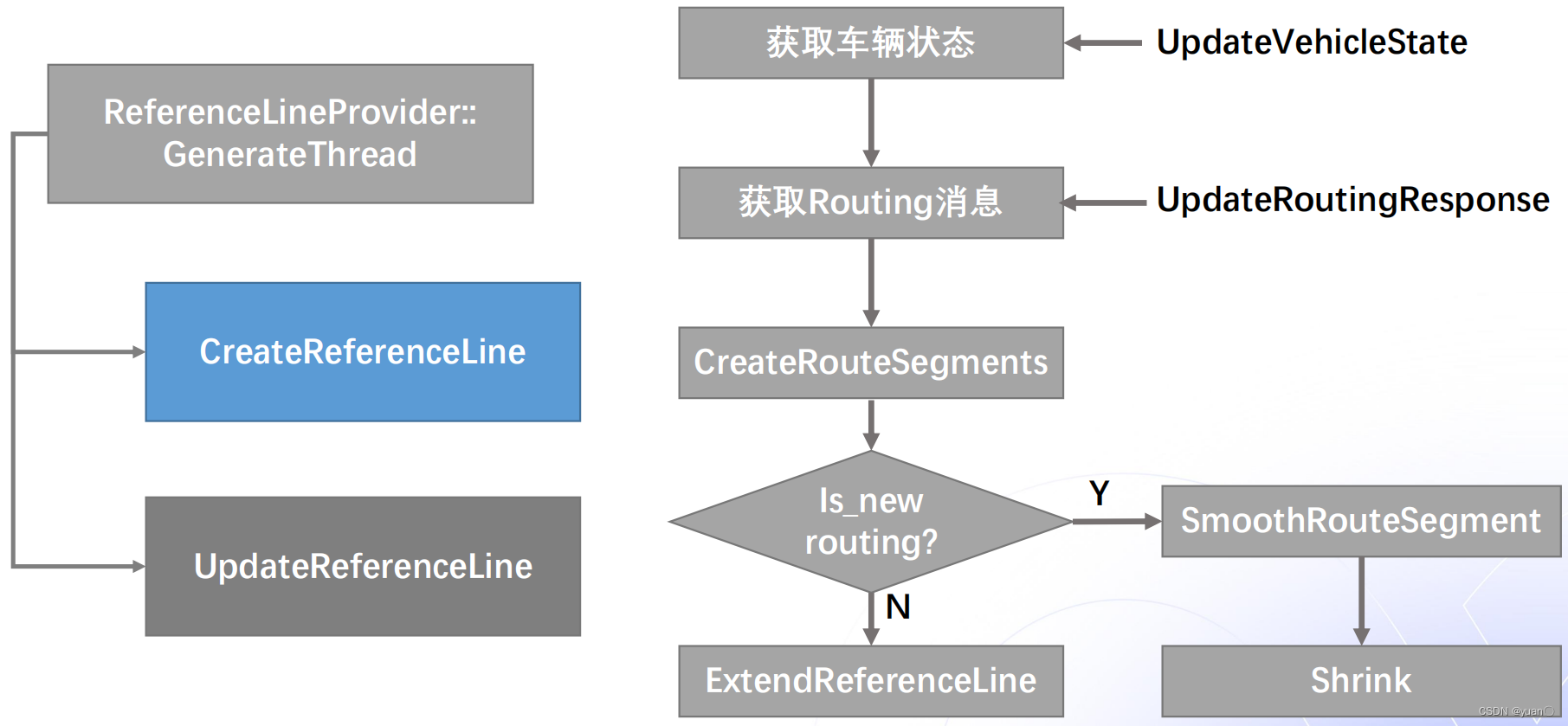 参考线生成是由CreateReferenceLine函数实现的。首先由UpdateVehicleState函数获取车辆的状态,再由UpdateRoutingResponse函数获取Routing的结果,生成RouteSegment。若routing是新生成的,则对其进行平滑与分割;若不是,则沿用上一个周期的参考线,并对其进行扩展与延伸。
参考线生成是由CreateReferenceLine函数实现的。首先由UpdateVehicleState函数获取车辆的状态,再由UpdateRoutingResponse函数获取Routing的结果,生成RouteSegment。若routing是新生成的,则对其进行平滑与分割;若不是,则沿用上一个周期的参考线,并对其进行扩展与延伸。
2. 参考线平滑算法
2.1 参考线平滑算法总览
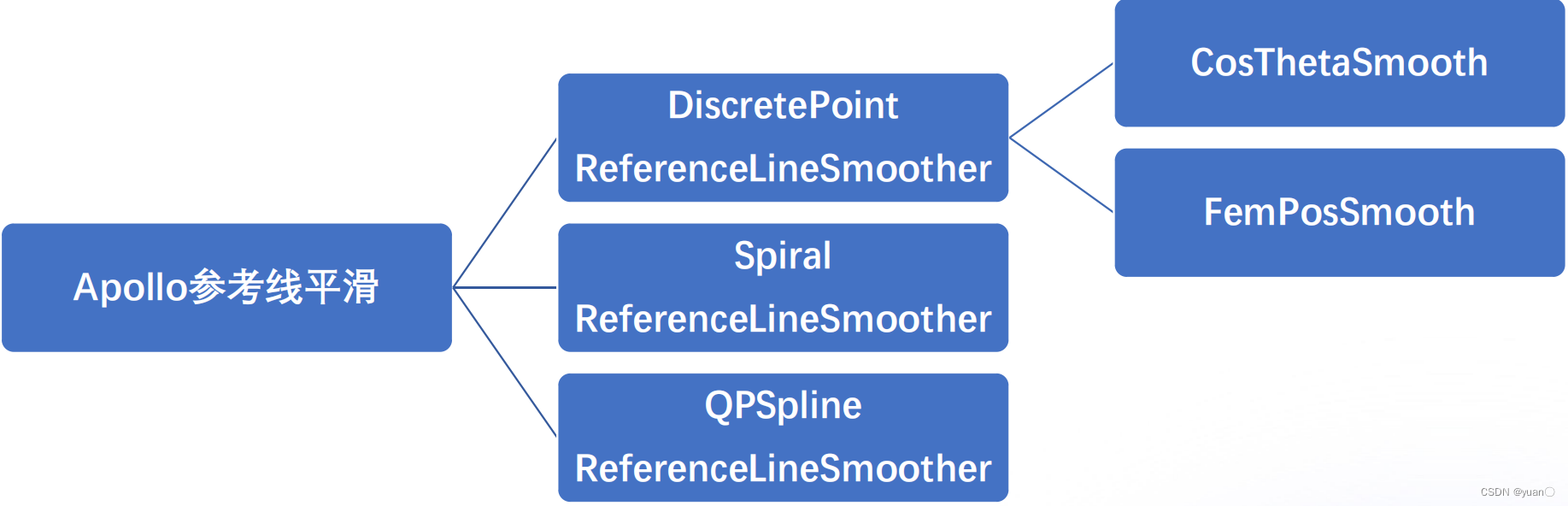 常见的参考线平滑方式有:离散点的平滑(Apollo采用)、螺旋线的平滑以及样条曲线的平滑。
常见的参考线平滑方式有:离散点的平滑(Apollo采用)、螺旋线的平滑以及样条曲线的平滑。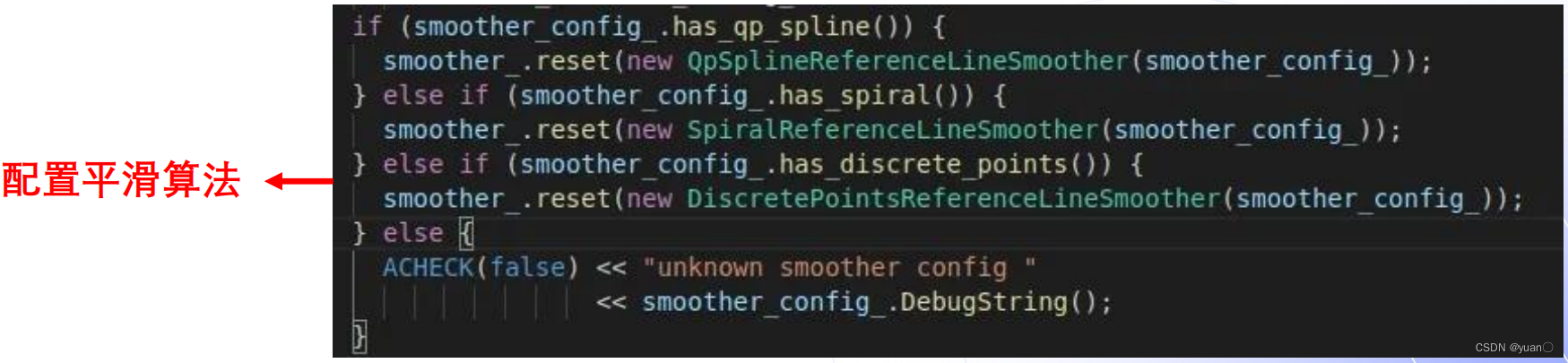
// /home/yuan/apollo-edu/modules/planning/reference_line/reference_line_provider.cc
if (smoother_config_.has_qp_spline()) {
smoother_.reset(new QpSplineReferenceLineSmoother(smoother_config_));
} else if (smoother_config_.has_spiral()) {
smoother_.reset(new SpiralReferenceLineSmoother(smoother_config_));
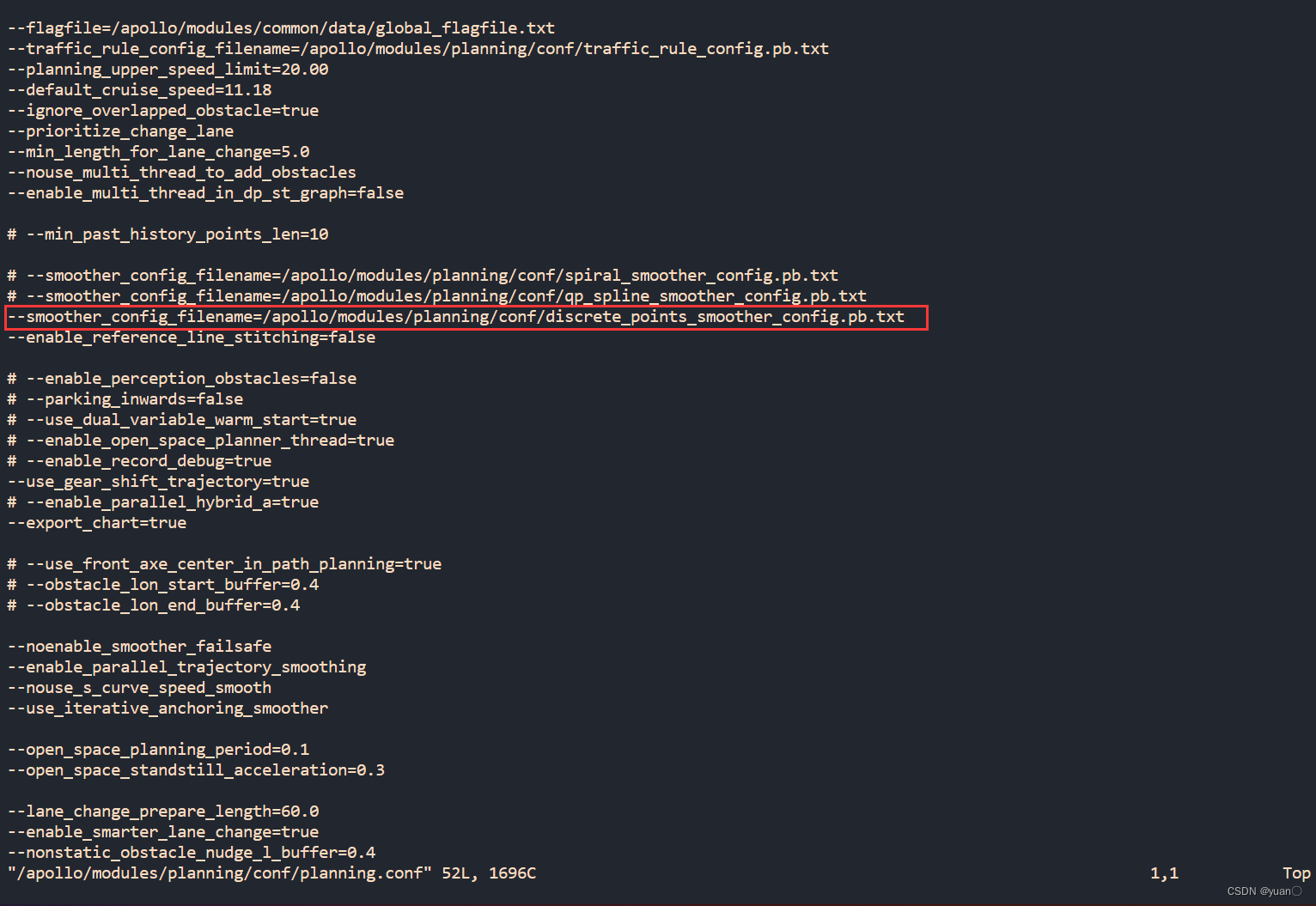
} else if (smoother_config_.has_discrete_points()) {
smoother_.reset(new DiscretePointsReferenceLineSmoother(smoother_config_));
} else {
ACHECK(false) << "unknown smoother config "
<< smoother_config_.DebugString();
}
2.2 参考线平滑算法流程
// /home/yuan/apollo-edu/modules/planning/reference_line/reference_line_provider.cc
bool ReferenceLineProvider::SmoothReferenceLine(
const ReferenceLine &raw_reference_line, ReferenceLine *reference_line) {
if (!FLAGS_enable_smooth_reference_line) {
*reference_line = raw_reference_line;
return true;
}
// generate anchor points:
std::vector<AnchorPoint> anchor_points;
GetAnchorPoints(raw_reference_line, &anchor_points);
smoother_->SetAnchorPoints(anchor_points);
if (!smoother_->Smooth(raw_reference_line, reference_line)) {
AERROR << "Failed to smooth reference line with anchor points";
return false;
}
if (!IsReferenceLineSmoothValid(raw_reference_line, *reference_line)) {
AERROR << "The smoothed reference line error is too large";
return false;
}
return true;
}

GetAnchorPoints(raw_reference_line, &anchor_points);用于设置设置中间点
if (!smoother_->Smooth(raw_reference_line, reference_line)) {为平滑算法
2.2.1 设置中间点anchor points
// /home/yuan/apollo-edu/modules/planning/reference_line/reference_line_smoother.h
struct AnchorPoint {
common::PathPoint path_point;
double lateral_bound = 0.0;
double longitudinal_bound = 0.0;
// enforce smoother to strictly follow this reference point
bool enforced = false;
};
根据ReferenceLine选取中间点。根据ReferenceLine s(纵向距离上的投影)的值,进行均匀采样,采样的间隔约为0.25m。采样之后得到一系列的AnchorPoint,每个AnchorPoint包含PathPoint、横纵向的裕度以及是否为强约束的判断(若是,则必须为满足横纵向裕度,一条参考线只有首尾的点是强约束)。
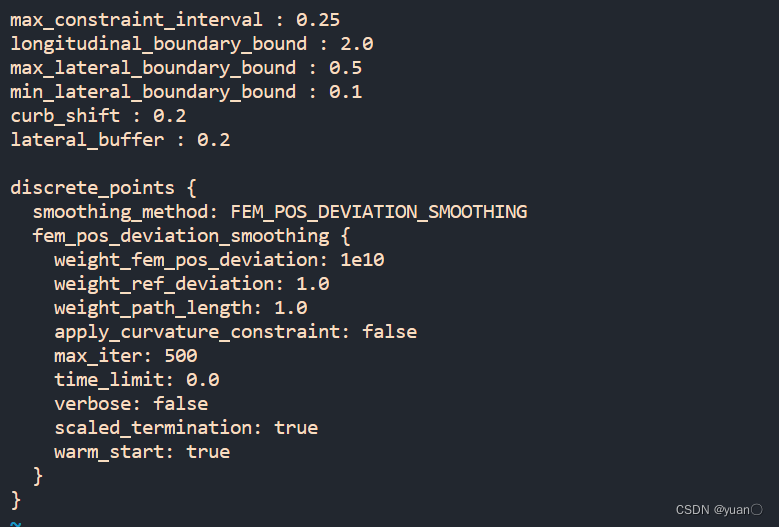
// /home/yuan/apollo-edu/modules/planning/conf/discrete_points_smoother_config.pb.txt
max_constraint_interval : 0.25
longitudinal_boundary_bound : 2.0
max_lateral_boundary_bound : 0.5
min_lateral_boundary_bound : 0.1
curb_shift : 0.2
lateral_buffer : 0.2
discrete_points {
smoothing_method: FEM_POS_DEVIATION_SMOOTHING
fem_pos_deviation_smoothing {
weight_fem_pos_deviation: 1e10
weight_ref_deviation: 1.0
weight_path_length: 1.0
apply_curvature_constraint: false
max_iter: 500
time_limit: 0.0
verbose: false
scaled_termination: true
warm_start: true
}
}
主要参数
max_constraint_interval采样间隔
longitudinal_boundary_bound纵向边界
max_lateral_boundary_bound最大横向边界
min_lateral_boundary_bound最小横向边界
curb_shift与道路边缘的缓冲,若为实线,再增加一个buffer缓冲
lateral_buffer与道路边缘的缓冲
smoothing_method: FEM_POS_DEVIATION_SMOOTHING采用FemPosSmooth平滑算法
weight_fem_pos_deviation平滑度的代价权值
c
o
s
t
s
m
o
o
t
h
{cost_{smooth}}
costsmooth
weight_ref_deviation相对原始点偏移量的代价权值
c
o
s
t
e
r
r
{cost_{err}}
costerr
weight_path_length参考线长度的代价权值
c
o
s
t
l
e
n
g
t
h
{cost_{length}}
costlength
实验时主要考虑平滑,所以将平滑度的权值设得非常大,而其他权值忽略不计。
2.2.2 Smooth函数
/home/yuan/apollo-edu/modules/planning/reference_line/discrete_points_reference_line_smoother.cc
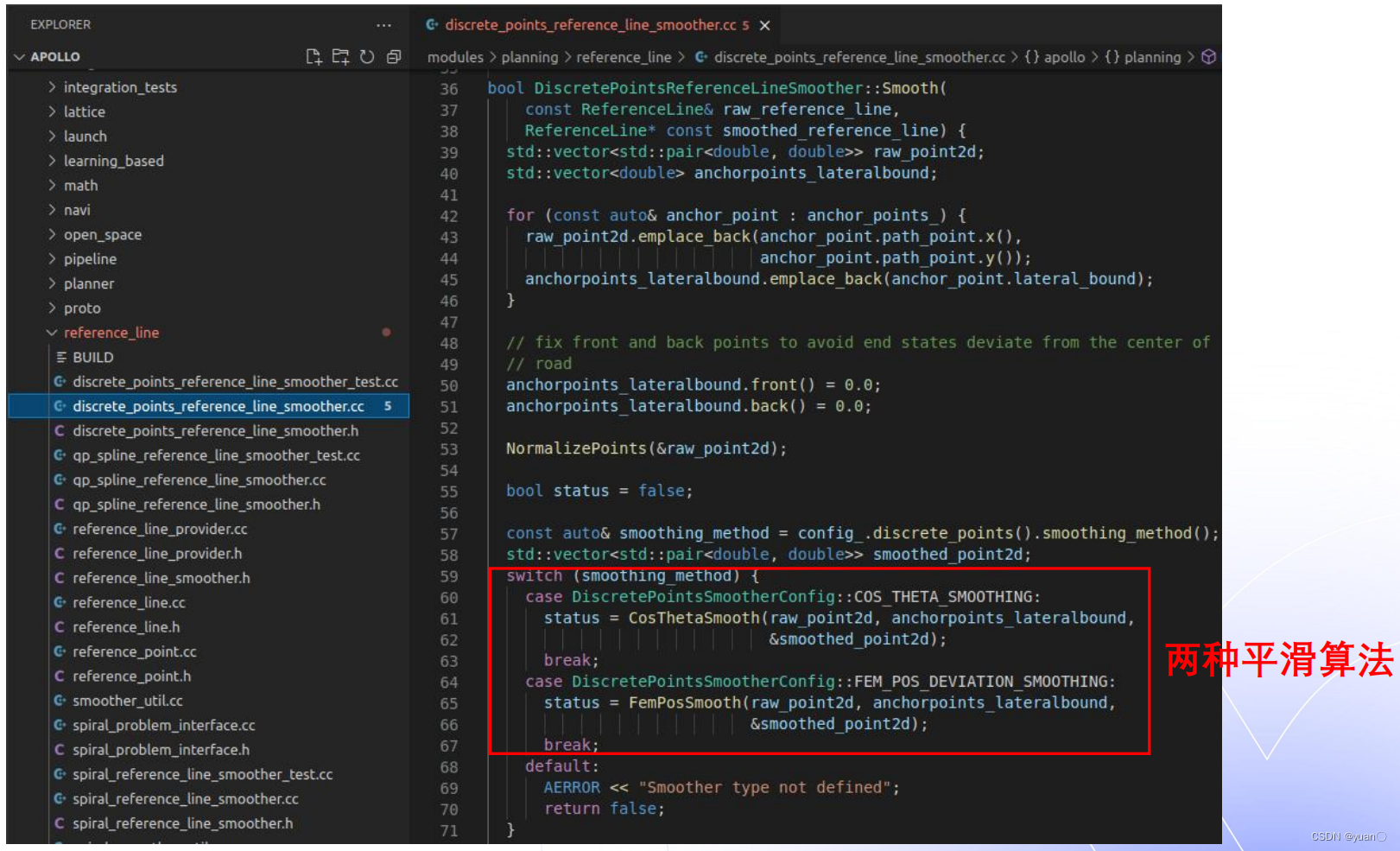 两种平滑算法通过配置文件去选择。
两种平滑算法通过配置文件去选择。
2.2.3FemPosSmooth
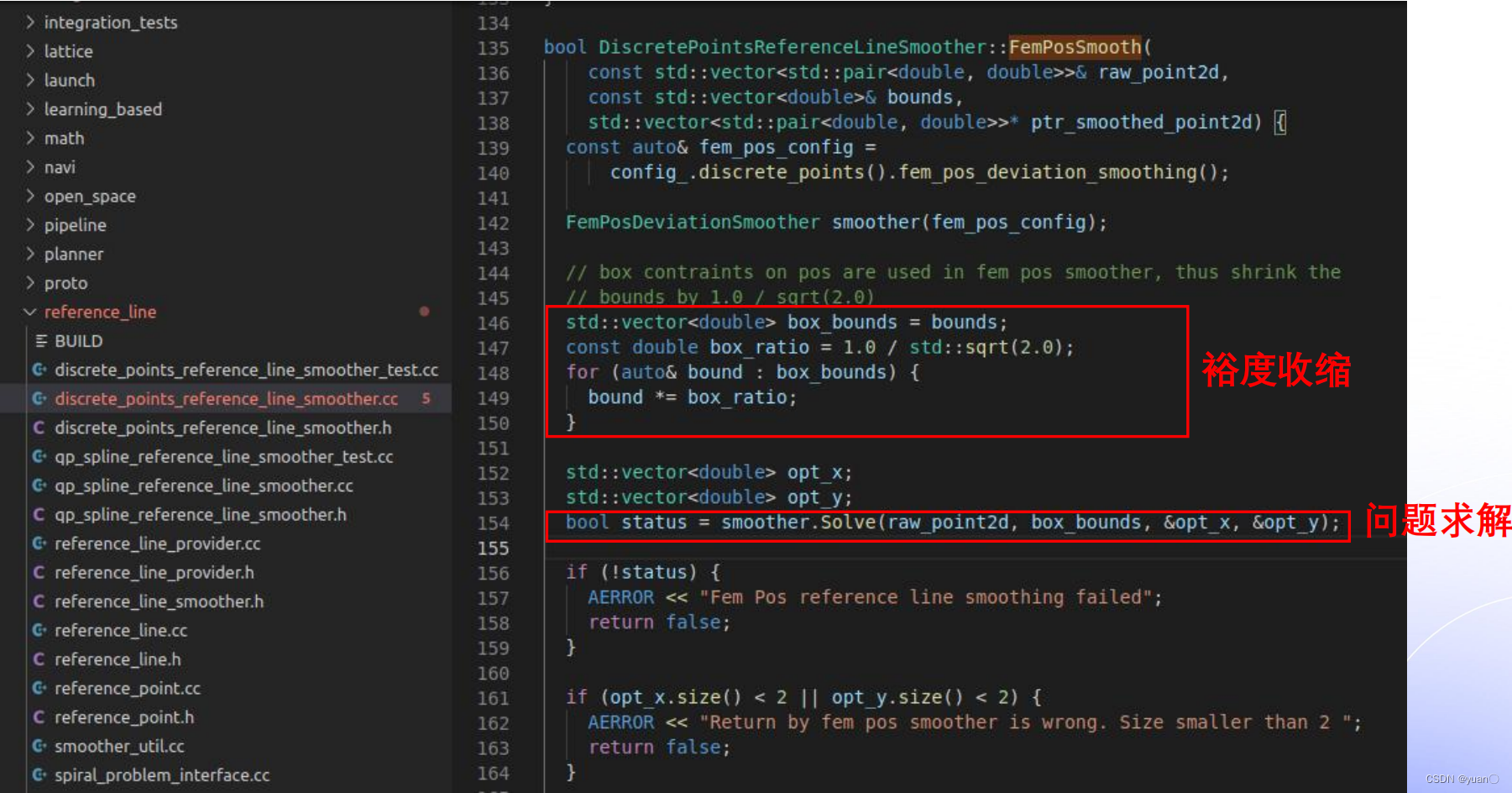
2.2.4 Solve函数
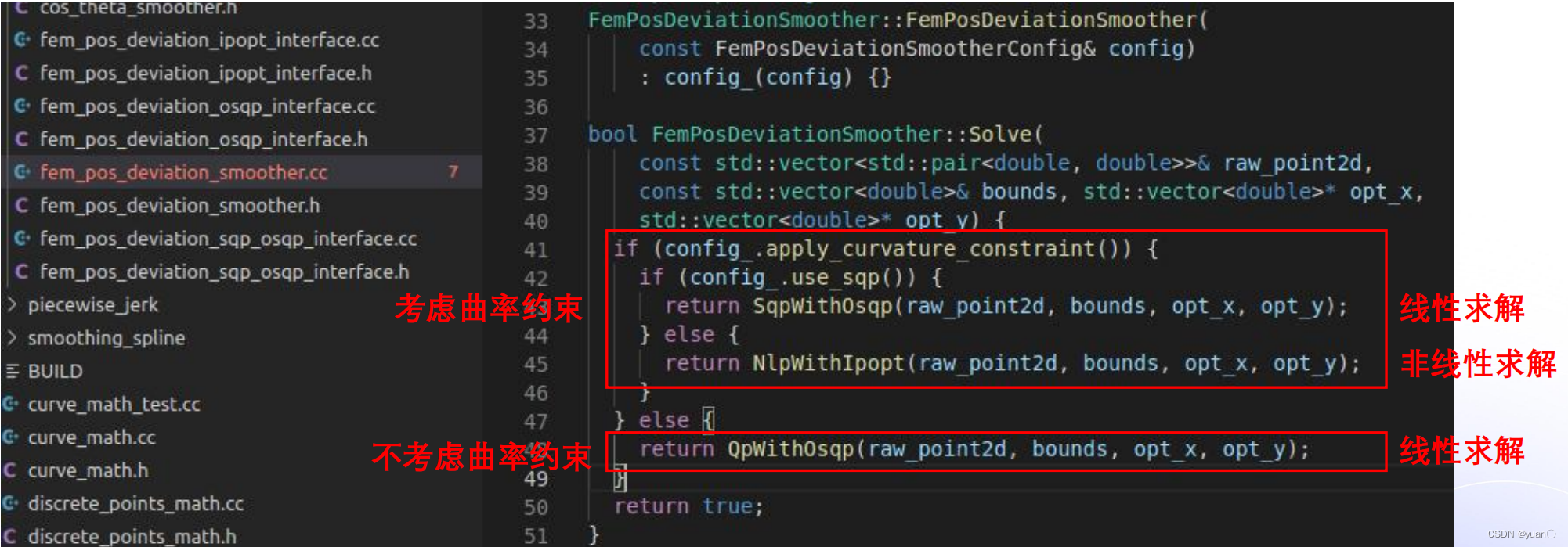
Apollo默认不考虑曲率的约束
2.3 优化问题构造和求解
 Apollo主要是对离散点进行求解,通过构造二次规划问题,利用OSQP求解器进行求解。
Apollo主要是对离散点进行求解,通过构造二次规划问题,利用OSQP求解器进行求解。
优化变量:离散点 P k ( x k , y k ) {P_k(x_k,y_k)} Pk(xk,yk)
优化目标: 平滑度、长度 、相对原始点偏移量
优化函数: c o s t = c o s t s m o o t h + c o s t l e n g t h + c o s t e r r {cost=cost_{smooth}+cost_{length}+cost_{err}} cost=costsmooth+costlength+costerr
c o s t s m o o t h {cost_{smooth}} costsmooth——平滑度的代价
c o s t l e n g t h {cost_{length}} costlength——参考线长度的代价 c o s t l e n g t h = ∑ i = 0 n − 1 ( x i − x i − 1 ) 2 + ( y i − y i − 1 ) 2 cos{t_{length}} = \sum\limits_{i = 0}^{n - 1} {{{({x_i} - {x_{i - 1}})}^2}} + {({y_i} - {y_{i - 1}})^2} costlength=i=0∑n−1(xi−xi−1)2+(yi−yi−1)2 c o s t e r r {cost_{err}} costerr——相对原始点偏移量的代价 c o s t e r r = ∑ i = 0 n − 1 ( x i − x i _ r e f ) 2 + ( y i − y i _ r e f ) 2 cos{t_{err}} = \sum\limits_{i = 0}^{n - 1} {{{({x_i} - {x_{i\_ref}})}^2}} + {({y_i} - {y_{i\_ref}})^2} costerr=i=0∑n−1(xi−xi_ref)2+(yi−yi_ref)2
2.4 平滑代价
c
o
s
t
s
m
o
o
t
h
{cost_{smooth}}
costsmooth有两种计算方式:FemPosSmooth与CosThetaSmooth。
FemPosSmooth:


构造方式:一个参考点 P 1 ( x 1 , y 1 ) {P_1(x_1,y_1)} P1(x1,y1)以及其前后两个相邻点 P 0 ( x 0 , y 0 ) {P_0(x_0,y_0)} P0(x0,y0)、 P 2 ( x 2 , y 2 ) {P_2(x_2,y_2)} P2(x2,y2)构成的向量 P 1 P 0 → \overrightarrow {{P_{\rm{1}}}{P_{\rm{0}}}} P1P0、 P 1 P 2 → \overrightarrow {{P_{\rm{1}}}{P_{\rm{2}}}} P1P2的合向量 P 1 P s → \overrightarrow {{P_{\rm{1}}}{P_{\rm{s}}}} P1Ps,求其模的平方。
CosThetaSmooth:

 构造方式:利用相邻两个向量
P
0
P
1
→
\overrightarrow {{P_{\rm{0}}}{P_{\rm{1}}}}
P0P1、
P
1
P
2
→
\overrightarrow {{P_{\rm{1}}}{P_{\rm{2}}}}
P1P2的夹角
θ
\theta
θ的余弦值进行构造。
构造方式:利用相邻两个向量
P
0
P
1
→
\overrightarrow {{P_{\rm{0}}}{P_{\rm{1}}}}
P0P1、
P
1
P
2
→
\overrightarrow {{P_{\rm{1}}}{P_{\rm{2}}}}
P1P2的夹角
θ
\theta
θ的余弦值进行构造。
2.5 约束条件
2.5.1 位置约束
 约束方程:
约束方程:
 保证点在boundingbox之内。
保证点在boundingbox之内。
2.5.2 曲率约束

曲率约束首先有以下三个假设:

通过三个假设,构造出约束方程:

∆
s
∆s
∆s是采样平均长度,
c
u
r
c
s
t
r
{cur_{cstr}}
curcstr是最大曲率约束.
3. U型道路仿真演示
云平台地址——Apollo规划之U型路口仿真调试
启动DreamView
bash scripts/apollo_neo.sh bootstrap
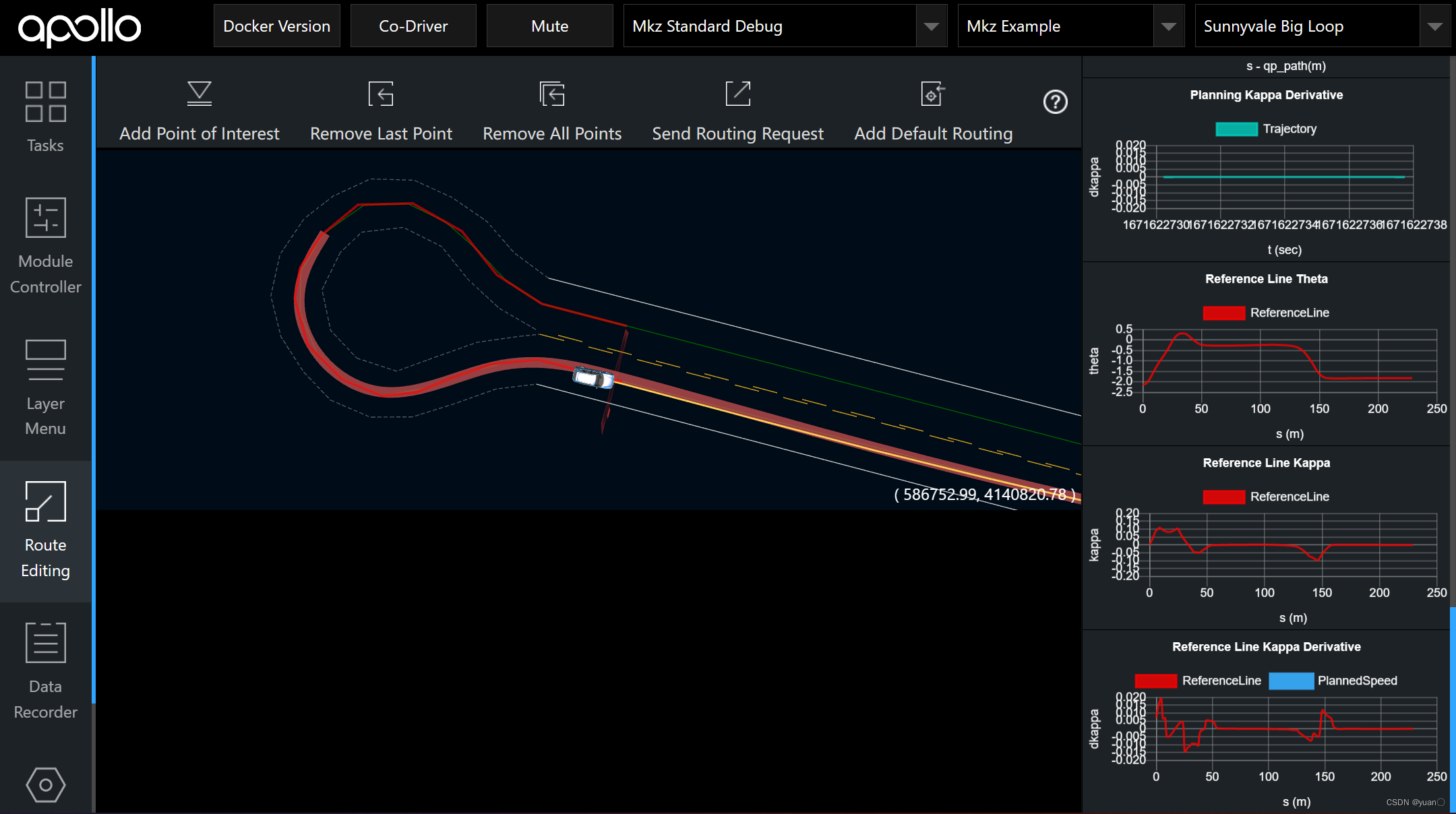
如图所示选好
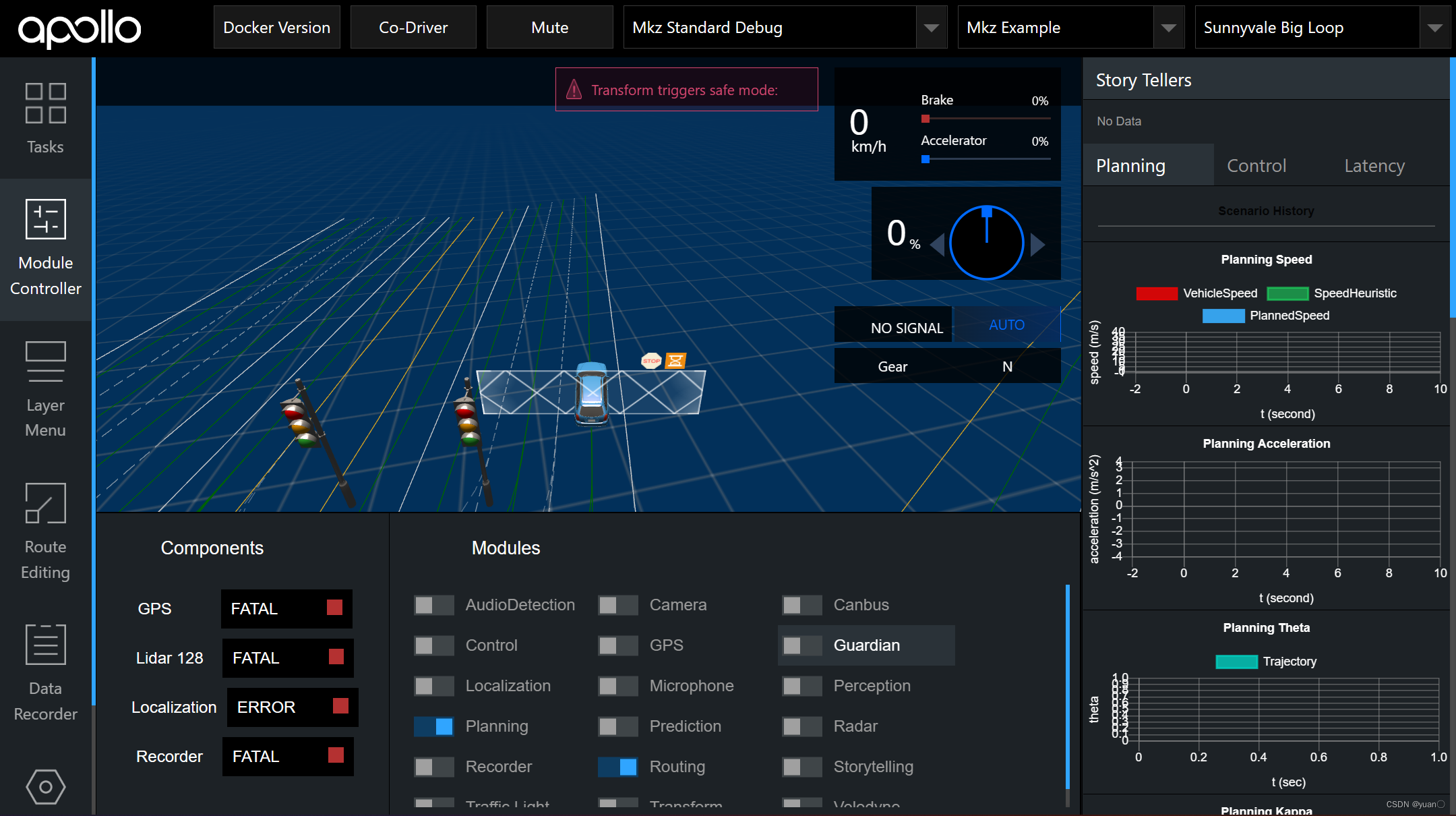
曲率较大的U型弯
打开 jupyter notebook,绘制脚本在/modules/tools 下
jupyter notebook
脚本代码
import json
import sys
import argparse
import sys
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import math
from cyber.python.cyber_py3.record import RecordReader
from modules.common_msgs.planning_msgs import planning_pb2
class RefLineInfo():
def __init__(self, x, y, s, theta, kappa, dkappa):
self.x = x
self.y = y
self.s = s
self.theta = theta
self.kappa = kappa
self.dkappa = dkappa
def trim_path_by_distance(adc_trajectory, s):
path_coords = []
path_points = adc_trajectory.trajectory_point
for point in path_points:
if point.path_point.s <= s:
path_coords.append([point.path_point.x, point.path_point.y])
return path_coords
def project(point, ref_line):
start_point = ref_line[0]
end_point = start_point
for line_point in ref_line:
if line_point.s - ref_line[0].s < 0.2:
continue
point_dir = [start_point.x - point.x, start_point.y - point.y]
line_dir = [line_point.x - start_point.x, line_point.y - start_point.y]
dot = point_dir[0] * line_dir[0] + point_dir[1] * line_dir[1]
if dot > 0.0:
start_point = line_point
continue
s = dot / math.sqrt(line_dir[0] * line_dir[0] + line_dir[1] * line_dir[1])
return start_point.s - s
def align_reference_lines(ref_line1, ref_line2):
if len(ref_line1) < 2 or len(ref_line2) < 2:
return [0.0, 0.0]
if ref_line1[-1].s < 0.5 or ref_line2[-1].s < 0.5:
return [0.0, 0.0]
s_ref_line1 = [ref_line1[0].x, ref_line1[0].y]
cur_index = 1
e_ref_line1 = [ref_line1[cur_index].x, ref_line1[cur_index].y]
while ref_line1[cur_index].s < 0.5:
cur_index = cur_index + 1
e_ref_line1 = [ref_line1[cur_index].x, ref_line1[cur_index].y]
start_point2 = ref_line2[0]
line_dir = [e_ref_line1[0] - s_ref_line1[0], e_ref_line1[1] - s_ref_line1[1]]
start_dir = [s_ref_line1[0] - start_point2.x, s_ref_line1[1] - start_point2.y]
dot = line_dir[0] * start_dir[0] + line_dir[1] * start_dir[1]
if dot > 0.0:
return [0.0, project(ref_line1[0], ref_line2)]
return [project(start_point2, ref_line1), 0.0]
def get_ref_line(record_path, ref_line_index=0):
reader = RecordReader(record_path)
current_ref_line_index = 0
for msg in reader.read_messages():
if msg.topic == "/apollo/planning":
if current_ref_line_index != ref_line_index:
current_ref_line_index = current_ref_line_index + 1
continue
adc_trajectory = planning_pb2.ADCTrajectory()
adc_trajectory.ParseFromString(msg.message)
for path in adc_trajectory.debug.planning_data.path:
if path.name != 'planning_reference_line':
continue
path_coords = trim_path_by_distance(adc_trajectory, 5.0)
ref_line = []
last_theta = path.path_point[0].theta
for point in path.path_point:
if point.theta - last_theta > math.pi:
point.theta = point.theta - 2.0 * math.pi
elif last_theta - point.theta > math.pi:
point.theta = point.theta + 2.0 * math.pi
ref_line.append(RefLineInfo(point.x, point.y, point.s, point.theta, point.kappa, point.dkappa))
return ref_line
def plot_ref_line(start_s, ref_line, use_dot):
x = []
y = []
s = []
theta = []
kappa = []
dkappa = []
scale_factor = 10.0
for point in ref_line:
if point.s < start_s:
continue
x.append(point.x)
y.append(point.y)
s.append(point.s)
theta.append(point.theta)
kappa.append(point.kappa * scale_factor)
dkappa.append(point.dkappa * scale_factor)
if use_dot:
plt.plot(s, theta, 'b--', alpha=0.5, label='theta')
plt.plot(s, kappa, 'r--', alpha=0.5, label='kappa')
plt.plot(s, dkappa, 'g--', alpha=0.5, label='dkappa')
else:
plt.plot(s, theta, 'b', alpha=0.5, label='theta')
plt.plot(s, kappa, 'r', alpha=0.5, label='kappa')
plt.plot(s, dkappa, 'g', alpha=0.5, label='dkappa')
def plot_ref_path(record_file1, record_file2):
ref_line1 = get_ref_line(record_file1)
ref_line2 = get_ref_line(record_file2)
[s1, s2] = align_reference_lines(ref_line1, ref_line2)
plot_ref_line(s1, ref_line1, True)
plot_ref_line(s2, ref_line2, False)
record_file1 = './20221221113737.record.00000'
record_file2 = './20221221120201.record.00000'
plot_ref_path(record_file1, record_file2)
plt.legend()
plt.show()
cyber_recorder record -a记录数据
cyber_recorder record -a
我们所需要记录并绘制的数据 将记录好的数据移动到
将记录好的数据移动到./modules/tools/下
到/apollo/modules/planning/conf/planning.conf 下查看所用的是哪个平滑算法
vim /apollo/modules/planning/conf/planning.conf
进入平滑算法的配置文件
vim /apollo/modules/planning/conf/discrete_points_smoother_config.pb.txt
修改参数,并重启DreamView,防止数据残留。
bash scripts/bootstrap_neo.sh restart
按照之前的步骤得到第二份数据。

max_lateral_boundary_bound : 0.2 其他不变
虚线为未更改的参考线数据,实现为更改后的参考线数据
可以看到,调整横向的参数对整体平滑具有较大的影响。
按照之前的步骤得到第三份数据。

虚线为未更改的参考线数据,实现为更改后的参考线数据
可以看到,调整纵向的参数对于参考线的平滑影响不大。