# include <stdio.h> # include <stdlib.h> typedef int DataType;
struct Node
{
DataType data;
struct Node * next;
} ;
typedef struct Node * PNode;
typedef struct Node * LinkList;
LinkList SetNullList_Link ( )
{
LinkList head = ( LinkList) malloc ( sizeof ( struct Node ) ) ;
if ( head != NULL ) head-> next = NULL ;
else printf ( "alloc failure" ) ;
return head;
}
void CreateList_Tail ( struct Node * head)
{
PNode p = NULL ;
PNode q = head;
DataType data;
scanf ( "%d" , & data) ;
while ( data != - 1 )
{
p = ( struct Node * ) malloc ( sizeof ( struct Node ) ) ;
p-> data = data;
p-> next = NULL ;
q-> next = p;
q = p;
scanf ( "%d" , & data) ;
}
}
int Inserch_num ( LinkList head, int x)
{
LinkList p;
int i= 0 ;
p= head-> next;
while ( p)
{
if ( i== 0 && p-> data== x)
{
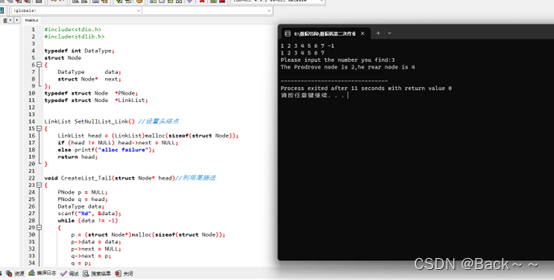
printf ( "The Prodrove node is head,the position of the rear node is at position 2 of the linked list\n" ) ;
return 0 ;
}
if ( p-> data== x&& p-> next== NULL )
{
printf ( "The Prodrove node is %d,there is no rear node\n " , i) ;
return 0 ;
}
if ( p-> data== x)
{
printf ( "The Prodrove node is %d,he rear node is %d\n" , i, i+ 2 ) ;
return 0 ;
}
i++ ;
p = p-> next;
}
return 0 ;
}
void print ( LinkList head)
{
PNode p = head-> next;
while ( p)
{
printf ( "%d " , p-> data) ;
p = p-> next;
}
}
void DestoryList_Link ( LinkList head)
{
PNode pre = head;
PNode p = pre-> next;
while ( p)
{
free ( pre) ;
pre = p;
p = pre-> next;
}
free ( pre) ;
}
int main ( )
{
LinkList head = NULL ;
int x= 0 , a= 0 ;
head = SetNullList_Link ( ) ;
CreateList_Tail ( head) ;
print ( head) ;
printf ( "\n" ) ;
printf ( "Please input the number you find:" ) ;
scanf ( "%d" , & x) ;
a= x;
Inserch_num ( head, a) ;
DestoryList_Link ( head) ;
return 0 ;
}
# include <stdio.h> # include <stdlib.h> typedef int DataType;
struct Node {
DataType data;
struct Node * next;
} ;
typedef struct Node * PNode;
typedef struct Node * LinkList;
LinkList CreateList_Tail_loop ( )
{
LinkList head = ( LinkList) malloc ( sizeof ( struct Node ) ) ;
PNode cur = NULL ;
PNode tail = head;
DataType data;
scanf ( "%d" , & data) ;
while ( data != - 1 )
{
cur = ( struct Node * ) malloc ( sizeof ( struct Node ) ) ;
cur-> data = data;
tail-> next = cur;
tail = cur;
scanf ( "%d" , & data) ;
}
tail-> next = head;
return tail;
}
PNode Move_Odd_Even ( LinkList tail)
{
PNode head= tail-> next, pre= head-> next, q= pre-> next;
PNode pre1, head1= ( PNode) malloc ( sizeof ( struct Node ) ) ;
PNode pre2, head2= ( PNode) malloc ( sizeof ( struct Node ) ) ;
pre1= head1;
pre2= head2;
while ( q!= head-> next)
{
if ( pre-> data% 2 == 0 )
{
pre-> next= pre1-> next;
pre1-> next= pre;
pre1= pre;
}
else
{
pre-> next= pre2;
pre2-> next= pre;
pre2= pre;
}
pre= q;
q= q-> next;
}
head1= head1-> next;
pre2-> next= head1;
pre1-> next= head2;
return pre1;
}
void print ( LinkList tail)
{
PNode head = tail-> next;
PNode p = head-> next;
while ( p != head)
{
printf ( "%d " , p-> data) ;
p = p-> next;
}
}
void DestoryList_Link ( LinkList tail)
{
PNode pre = tail-> next;
PNode p = pre-> next;
while ( p != tail)
{
free ( pre) ;
pre = p;
p = pre-> next;
}
free ( pre) ;
free ( tail) ;
}
int main ( )
{
LinkList tail = NULL ;
LinkList p = NULL ;
tail = CreateList_Tail_loop ( ) ;
p = Move_Odd_Even ( tail) ;
print ( p) ;
DestoryList_Link ( tail) ;
return 0 ;
}
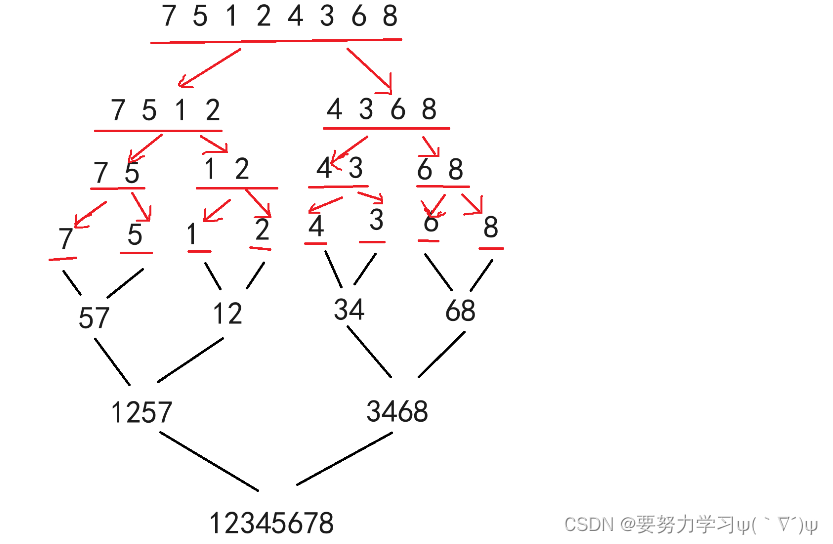
# include <stdio.h> # include <stdlib.h> # define MAX_SIZE 100 void mergeAndRemoveDuplicates ( int list1[ ] , int list2[ ] , int n1, int n2, int list3[ ] ) {
int i = 0 , j = 0 , k = 0 ;
while ( i < n1 && j < n2) {
if ( list1[ i] < list2[ j] ) {
list3[ k] = list1[ i] ;
i++ ;
k++ ;
} else if ( list1[ i] > list2[ j] ) {
list3[ k] = list2[ j] ;
j++ ;
k++ ;
} else {
list3[ k] = list1[ i] ;
i++ ;
j++ ;
k++ ;
}
}
while ( i < n1) {
list3[ k] = list1[ i] ;
i++ ;
k++ ;
}
while ( j < n2) {
list3[ k] = list2[ j] ;
j++ ;
k++ ;
}
}
void removeDuplicates ( int list[ ] , int size) {
int i, j, k;
for ( i = 0 ; i < size; i++ ) {
for ( j = i + 1 ; j < size; ) {
if ( list[ j] == list[ i] ) {
for ( k = j; k < size - 1 ; k++ ) {
list[ k] = list[ k + 1 ] ;
}
size-- ;
} else {
j++ ;
}
}
}
}
int main ( ) {
int i = 0 ;
int list1[ ] = { 1 , 2 , 3 , 5 , 7 } ;
int list2[ ] = { 3 , 4 , 5 , 6 , 8 } ;
int n1 = sizeof ( list1) / sizeof ( list1[ 0 ] ) ;
int n2 = sizeof ( list2) / sizeof ( list2[ 0 ] ) ;
int list3[ MAX_SIZE] ;
mergeAndRemoveDuplicates ( list1, list2, n1, n2, list3) ;
removeDuplicates ( list3, n1 + n2) ;
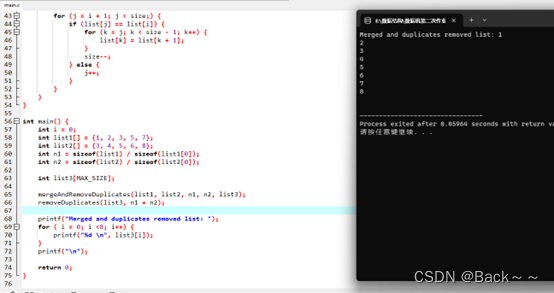
printf ( "Merged and duplicates removed list: " ) ;
for ( i = 0 ; i < 8 ; i++ ) {
printf ( "%d \n" , list3[ i] ) ;
}
printf ( "\n" ) ;
return 0 ;
}
# include <stdio.h> # include <stdlib.h> struct ListNode {
int val;
struct ListNode * next;
} ;
struct ListNode * createNode ( int val) {
struct ListNode * newNode = ( struct ListNode * ) malloc ( sizeof ( struct ListNode ) ) ;
newNode-> val = val;
newNode-> next = NULL ;
return newNode;
}
struct ListNode * mergeAndRemoveDuplicates ( struct ListNode * list1, struct ListNode * list2) {
struct ListNode * p = list1;
struct ListNode * q = list2;
struct ListNode * list3 = NULL ;
struct ListNode * tail = NULL ;
while ( p && q) {
if ( p-> val < q-> val) {
if ( list3 == NULL ) {
list3 = tail = createNode ( p-> val) ;
} else {
tail-> next = createNode ( p-> val) ;
tail = tail-> next;
}
p = p-> next;
} else if ( p-> val > q-> val) {
if ( list3 == NULL ) {
list3 = tail = createNode ( q-> val) ;
} else {
tail-> next = createNode ( q-> val) ;
tail = tail-> next;
}
q = q-> next;
} else {
if ( list3 == NULL ) {
list3 = tail = createNode ( p-> val) ;
} else {
tail-> next = createNode ( p-> val) ;
tail = tail-> next;
}
p = p-> next;
q = q-> next;
}
}
while ( p) {
tail-> next = createNode ( p-> val) ;
tail = tail-> next;
p = p-> next;
}
while ( q) {
tail-> next = createNode ( q-> val) ;
tail = tail-> next;
q = q-> next;
}
struct ListNode * cur = list3;
while ( cur && cur-> next) {
if ( cur-> val == cur-> next-> val) {
struct ListNode * temp = cur-> next;
cur-> next = cur-> next-> next;
free ( temp) ;
} else {
cur = cur-> next;
}
}
return list3;
}
void printList ( struct ListNode * head) {
struct ListNode * cur = head;
while ( cur != NULL ) {
printf ( "%d " , cur-> val) ;
cur = cur-> next;
}
printf ( "\n" ) ;
}
int main ( ) {
struct ListNode * list1 = createNode ( 1 ) ;
list1-> next = createNode ( 2 ) ;
list1-> next-> next = createNode ( 3 ) ;
list1-> next-> next-> next = createNode ( 5 ) ;
list1-> next-> next-> next-> next = createNode ( 7 ) ;
struct ListNode * list2 = createNode ( 3 ) ;
list2-> next = createNode ( 4 ) ;
list2-> next-> next = createNode ( 5 ) ;
list2-> next-> next-> next = createNode ( 6 ) ;
list2-> next-> next-> next-> next = createNode ( 8 ) ;
struct ListNode * list3 = mergeAndRemoveDuplicates ( list1, list2) ;
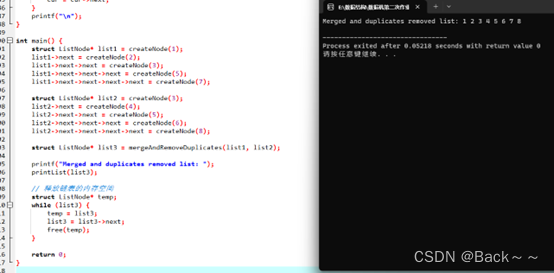
printf ( "Merged and duplicates removed list: " ) ;
printList ( list3) ;
struct ListNode * temp;
while ( list3) {
temp = list3;
list3 = list3-> next;
free ( temp) ;
}
return 0 ;
}
# include <stdio.h> # include <stdlib.h> struct DoubleListNode {
int data;
int freq;
struct DoubleListNode * llink;
struct DoubleListNode * rlink;
} ;
struct DoubleListNode * createNode ( int data) {
struct DoubleListNode * newNode = ( struct DoubleListNode * ) malloc ( sizeof ( struct DoubleListNode ) ) ;
if ( newNode == NULL ) {
printf ( "Memory allocation failed.\n" ) ;
exit ( 1 ) ;
}
newNode-> data = data;
newNode-> freq = 0 ;
newNode-> llink = NULL ;
newNode-> rlink = NULL ;
return newNode;
}
void insertNode ( struct DoubleListNode * * head, int data) {
struct DoubleListNode * newNode = createNode ( data) ;
if ( * head == NULL ) {
* head = newNode;
return ;
}
newNode-> rlink = * head;
( * head) -> llink = newNode;
* head = newNode;
}
void increaseFreq ( struct DoubleListNode * * head, int data) {
if ( * head == NULL ) {
return ;
}
struct DoubleListNode * cur = * head;
while ( cur != NULL ) {
if ( cur-> data == data) {
cur-> freq++ ;
struct DoubleListNode * prev = cur-> llink;
while ( prev != NULL && prev-> freq < cur-> freq) {
struct DoubleListNode * next = cur-> rlink;
if ( prev-> llink) {
prev-> llink-> rlink = cur;
}
cur-> llink = prev-> llink;
cur-> rlink = prev;
prev-> llink = cur;
if ( next) {
next-> llink = prev;
}
prev-> rlink = next;
prev = cur-> llink;
}
break ;
}
cur = cur-> rlink;
}
}
void printList ( struct DoubleListNode * head) {
struct DoubleListNode * cur = head;
while ( cur != NULL ) {
printf ( "(%d,%d) " , cur-> data, cur-> freq) ;
cur = cur-> rlink;
}
printf ( "\n" ) ;
}
void freeList ( struct DoubleListNode * head) {
struct DoubleListNode * cur = head;
while ( cur != NULL ) {
struct DoubleListNode * temp = cur;
cur = cur-> rlink;
free ( temp) ;
}
}
int main ( ) {
struct DoubleListNode * head = NULL ;
insertNode ( & head, 3 ) ;
insertNode ( & head, 5 ) ;
insertNode ( & head, 2 ) ;
insertNode ( & head, 8 ) ;
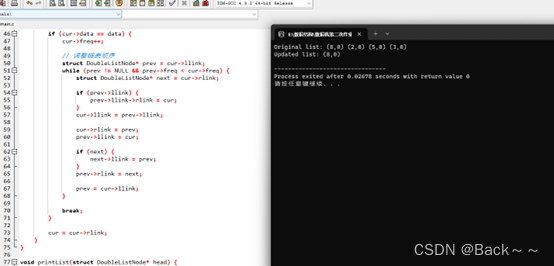
printf ( "Original list: " ) ;
printList ( head) ;
increaseFreq ( & head, 2 ) ;
increaseFreq ( & head, 5 ) ;
increaseFreq ( & head, 3 ) ;
printf ( "Updated list: " ) ;
printList ( head) ;
freeList ( head) ;
return 0 ;
}