目录
一、容器适配器
(一)什么是适配器
(二)stack和queue的底层结构
二、Stack
三、queue
四、deque双端队列
(一)优点
(二)缺陷
五、优先级队列
(一)介绍
(二)仿函数
(三)模拟实现一
(四)模拟实现(带compare)
一、容器适配器
(一)什么是适配器
适配器是一种设计模式(设计模式是一套被反复使用的、多数人知晓的、经过分类编目的、代码设计经验的总结),该种模式是将一个类的接口转换成客户希望的另外一个接口。
(二)stack和queue的底层结构
- stack和queue没有迭代器

Container 也是一个模板参数,它用于指定在 stack 内部使用的容器类型。默认情况下,它使用了一个 deque(双端队列)作为内部容器,但你也可以自定义一个不同类型的容器来替代它 。
二、Stack
- 模拟实现stack,stack是先进后出
#pragma once
#include<iostream>
#include<deque>
using namespace std;
namespace Imitate_stack
{
template <class T, class Container = deque<T> >
class stack
{
public:
void push(const T& x)//插入数据
{
_con.push_back(x);
}
void pop()//删除数据
{
_con.pop_back();//用于移除并返回双端队列的最右端(尾部)元素
}
const T& top()
{
return _con.back();//用于返回双端队列的最右端(尾部)元素,但不会从队列中删除该元素
}
bool empty()
{
return _con.empty();
}
size_t size()
{
return _con.size();
}
private:
Container _con;
};
}
三、queue
- queue是先进先出
#pragma once
#include<iostream>
#include<deque>
using namespace std;
namespace Imitate_stack
{
template <class T, class Container = deque<T> >
class queue
{
public:
void push(const T& x)//尾插
{
_con.push_back(x);
}
void pop()//头删
{
_con.pop_front();
}
const T& back()//得到尾部数据
{
return _con.back();
}
const T& front()//得到头部数据
{
return _con.front();
}
bool empty()
{
return _con.empty();
}
size_t size()
{
return _con.size();
}
private:
Container _con;
};
}四、deque双端队列
(一)优点
是一种双开口的"连续"空间的数据结构,双开口的含义是:可以在头尾两端进行插入和删除操作,且时间复杂度为O(1)
- 与vector比较,头插效率高,不需要搬移元素
- 与list比较,空间利用率比较高
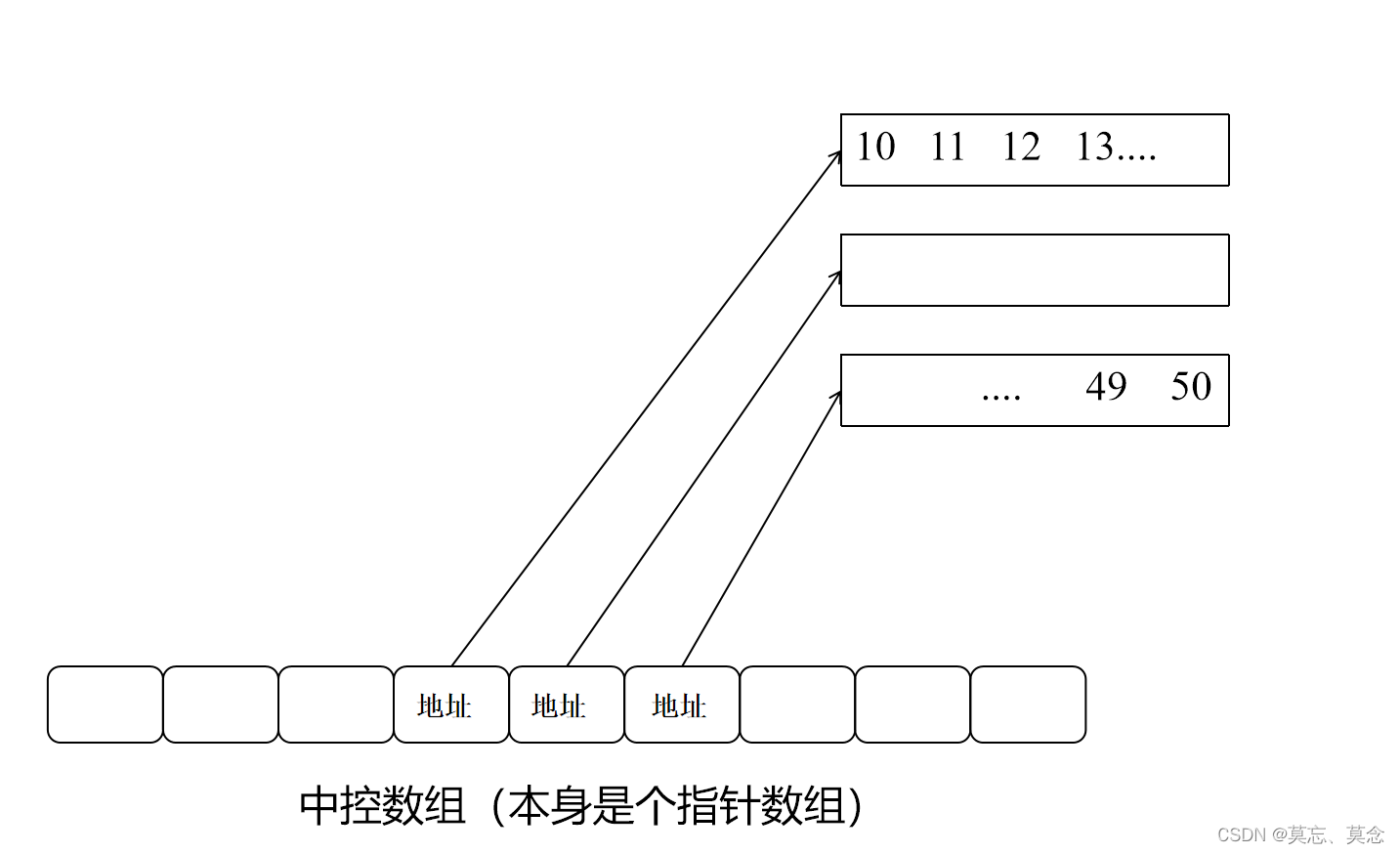
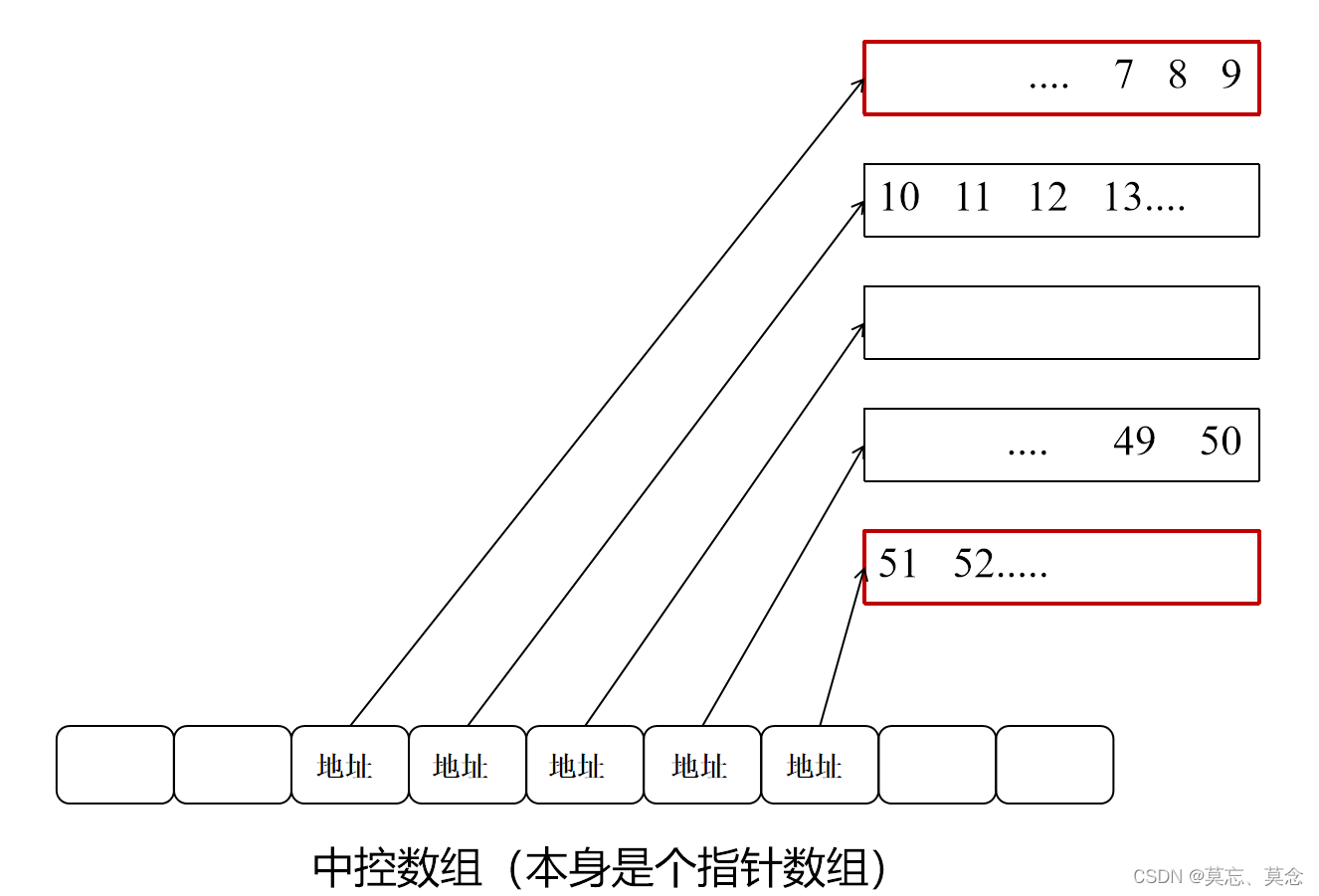
(二)缺陷
- 下标的随机访问不如vector
- 中间插入、删除速度不如list
- 不适合遍历,因为在遍历时,deque的迭代器要频繁的去检测其是否移动到
某段小空间的边界,导致效率低下
五、优先级队列
(一)介绍

priority_queue<int> first;//建立大根堆
priority_queue<int> first(data.begin(), data.end());//建立大根堆
priority_queue<int, vector<int>, greater<int>> second;//建立小根堆#include<iostream>
#include<queue>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
priority_queue<int> first;//建立大根堆
first.push(56);
first.push(12);
first.push(67);
first.push(1);
first.push(78);
first.push(6);
while (!first.empty())//78 67 56 12 6 1
{
cout << first.top() << " ";
first.pop();
}
return 0;
}#include<iostream>
#include<vector>
#include<queue>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
vector<int>data = {56,12,67,1,78,6};
priority_queue<int> first(data.begin(), data.end());//建立大根堆
while (!first.empty())//78 67 56 12 6 1
{
cout << first.top() << " ";
first.pop();
}
return 0;
}#include<iostream>
#include<queue>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
priority_queue<int, vector<int>, greater<int>> second;//建立小根堆
second.push(56);
second.push(12);
second.push(67);
second.push(1);
second.push(78);
second.push(6);
while (!second.empty())//1 6 12 56 67 78
{
cout << second.top() << " ";
second.pop();
}
return 0;
}(二)仿函数
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
template<class T>
class Less
{
public:
bool operator()(const T& x, const T& y)
{
return x < y;
}
};
template<class T>
class greater
{
public:
bool operator()(const T& x, const T& y)
{
return x > y;
}
};
int main()
{
Less<int> less1;//函数对象
cout << less1(1, 3) << endl;
Less<double> less2;
cout << less1(4.5, 3.5) << endl;
return 0;
}(三)模拟实现一
PriorityQueue.h
#pragma once
#include<iostream>
#include<vector>
using namespace std;
namespace Imitate_priorityQueue
{
template<class T, class Container = vector<T>>
class priority_queue
{
public:
void adjust_up(int child)//向上调整
{
int parent = (child - 1) / 2;
while (child >0 )
{
if (_con[child] > _con[parent])//建立大根堆
{
swap(_con[child], _con[parent]);
child = parent;
parent = (child - 1) / 2;
}
else
{
break;
}
}
}
void adjust_down(int parent)//向下调整
{
int child = parent * 2 + 1;
while (child < _con.size())
{
if (child + 1 < _con.size() && _con[child] < _con[child + 1])//开始默认右孩子大
{
++child;
}
if (_con[child] > _con[parent])
{
swap(_con[child], _con[parent]);
parent=child;
child = parent * 2 + 1;
}
else
{
break;
}
}
}
void push(const T& x)
{
_con.push_back(x);
adjust_up(_con.size() - 1);
}
void pop()
{
swap(_con[0], _con[_con.size() - 1]);
_con.pop_back();
adjust_down(0);
}
const T& top()const
{
return _con.front();
}
bool empty()const
{
return _con.empty();
}
private:
Container _con;
};
}
test.h
#include"PriorityQueue.h"
int main()
{
Imitate_priorityQueue::priority_queue<int, vector<int>> q;
q.push(89);
q.push(1);
q.push(45);
q.push(14);
q.push(11);
q.push(19);
while (!q.empty())//89 45 19 14 11 1
{
cout << q.top() << " ";
q.pop();
}
return 0;
}(四)模拟实现(带compare)
PriorityQueue.h
#pragma once
#include<iostream>
#include<vector>
using namespace std;
namespace Imitate_priorityQueue
{
比较方式
template<class T>
struct less
{
bool operator()(const T& x, const T& y)
{
return x < y;
}
};
//比较方式
template<class T>
struct greater
{
bool operator()(const T& x, const T& y)
{
return x > y;
}
};
template<class T, class Container = vector<T>, class Compare = less<T>>
class priority_queue
{
public:
void adjust_up(int child)//向上调整
{
int parent = (child - 1) / 2;
while (child >0 )
{
if (_com(_con[parent],_con[child]))
{
swap(_con[child], _con[parent]);
child = parent;
parent = (child - 1) / 2;
}
else
{
break;
}
}
}
void adjust_down(int parent)//向下调整
{
int child = parent * 2 + 1;
while (child < _con.size())
{
if (child + 1 < _con.size() && _com(_con[child] , _con[child + 1]))//开始默认右孩子大
{
++child;
}
if (_com(_con[parent], _con[child]))
{
swap(_con[child], _con[parent]);
parent=child;
child = parent * 2 + 1;
}
else
{
break;
}
}
}
void push(const T& x)
{
_con.push_back(x);
adjust_up(_con.size() - 1);
}
void pop()
{
swap(_con[0], _con[_con.size() - 1]);
_con.pop_back();
adjust_down(0);
}
const T& top()const
{
return _con.front();
}
bool empty()const
{
return _con.empty();
}
private:
Container _con;
Compare _com;
};
}
#include"PriorityQueue.h"
int main()
{
Imitate_priorityQueue::priority_queue<int, vector<int>, greater<int>> q;
q.push(89);
q.push(1);
q.push(45);
q.push(14);
q.push(11);
q.push(19);
while (!q.empty())
{
cout << q.top() << " ";
q.pop();
}
return 0;
}

![[架构之路-230]:计算机硬件与体系结构 - 可靠性、可用性、稳定性;MTTF、MTTR、MTBF](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/7f3a36c73b134a8f9f8763ee01450773.png)