文章目录
- 前言
- 代码仓库
- 内容
- 代码(有详细注释)
- 编译和运行命令
- 结果
- 总结
- 参考资料
- 作者的话
前言
C++代码示例:排列数简单生成工具。
代码仓库
- yezhening/Programming-examples: 编程实例 (github.com)
- Programming-examples: 编程实例 (gitee.com)
内容
- 简单地生成排列数
- 有详细的步骤解析
代码(有详细注释)
cpermutation.cpp
#include <vector>
#include <iostream>
#include <unordered_set>
using std::cout;
using std::endl;
using std::unordered_set;
using std::vector;
class CPermutation
{
public:
CPermutation(const int &n, const int &m) : n(n), m(m), flags(0), curPerm(0), permCount(0) {}
bool next()
{
// 第一次进入初始化当前排列,如m=3,this->curPerm为012,从012开始遍历
if (this->curPerm.empty() == true)
{
for (int i = 0; i < this->m; ++i)
{
this->curPerm.push_back(i);
this->flags.insert(i); // 记录哈希
}
++this->permCount;
return true;
}
// 1. 首先,确定某个位置是否已经达到了当前意义下的“最大值”—“当前” 的意义:前面的位置数值固定之后
// 求当前位置应当的最大值
// 注意理解:如014,索引2位置可取23,最大值为3;索引1位置可取234,最大值为4;索引0位置可取1234,最大值为4,左边位置的取值范围要包括右边的位置
// 从后往前大到小遍历,如果这个数不在哈希表中就是应该的最大值
// 2. 然后,从后向前寻找第一个不是当前最大值的位置
// 修正:小于当前应当最大值的位置
// 如014,则求得的位置是索引1
int curPos = this->m - 1;
int curMax = 0;
while (curPos >= 0)
{
// 1.
for (int i = this->n - 1; i >= 0; --i)
{
if (flags.find(i) == flags.end())
{
curMax = i;
break; // 找到就退出for
}
}
// 2.
if (this->curPerm.at(curPos) >= curMax) // 未找到位置移动
{
flags.erase(this->curPerm.at(curPos)); // 哈希表减少
--curPos;
}
else // 找到位置退出while
{
break;
}
}
if (curPos < 0) // 没找到位置搜完排列
{
return false;
}
// 3.这个位置上的数值最小限度地增加—“最小限度”,前面的数值排除之后,取剩余的、大于该值的最小值
// 从前往后小到大遍历,如果这个数不在哈希表中就是应该变换的值
// 注意:此时可能处理左边的位置,哈希表还是删减状态以让左边位置可以取到右边的值
// 如014,遍历012到2最小且不在哈希表,将索引1位置元素1换成2,该位置后续可以取到右边的值4,右边的值相应的会减小不再是4保证不重复
for (int i = this->curPerm.at(curPos); i < this->n; ++i)
{
if (flags.find(i) == flags.end())
{
this->flags.erase(this->curPerm.at(curPos)); // 哈希删除
this->curPerm.at(curPos) = i;
this->flags.insert(i); // 哈希插入
break;
}
}
// 归位哈希表。因为右边的数要填充了
// 如034,位置1可以取到4,但此时哈希表是没有4的,将3变为4后,需要加入哈希表,右边的值填充时不能再是4,不是044而是041
for (const int p : this->curPerm)
{
flags.insert(p);
}
// 4. 该位置确定后,后面的位置依次取剩余数值的最小几个
// 对右边的所有位置
// 从前往后小到大遍历,如果这个数不在哈希表中就是应该变换的值
// 如024,遍历01到1最小且不在哈希表,
for (int i = curPos + 1; i < this->m; ++i)
{
for (int j = 0; j < this->n; ++j)
{
if (flags.find(j) == flags.end())
{
this->flags.erase(this->curPerm.at(i)); // 哈希删除
this->curPerm.at(i) = j;
this->flags.insert(j); // 哈希插入
break;
}
}
}
++this->permCount;
return true;
}
inline void printCurPerm()
{
for (const int p : this->curPerm)
{
cout << p << " ";
}
cout << endl;
}
inline void printPermCount()
{
cout << this->permCount << endl;
}
private:
const int n; // 从n个取m个
const int m;
vector<int> curPerm; // 当前排列,存储排列的索引
unordered_set<int> flags; // 哈希标志,标记已在排列中的索引
int permCount; // 排列数的数量
};
int main()
{
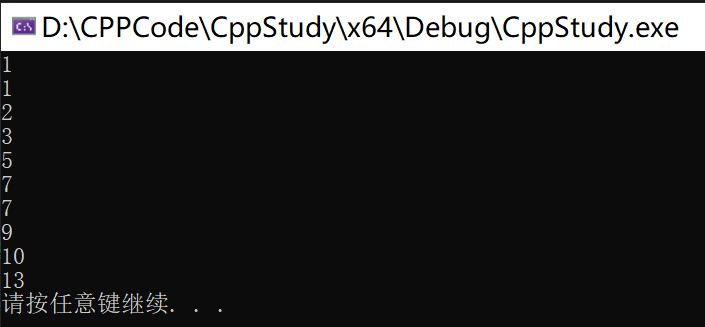
const int n = 5;
const int m = 3;
CPermutation perm(n, m);
while (perm.next())
{
perm.printCurPerm();
}
perm.printPermCount();
return 0;
}
编译和运行命令
g++ -o cpermutation cpermutation.cpp
./cpermutation.exe
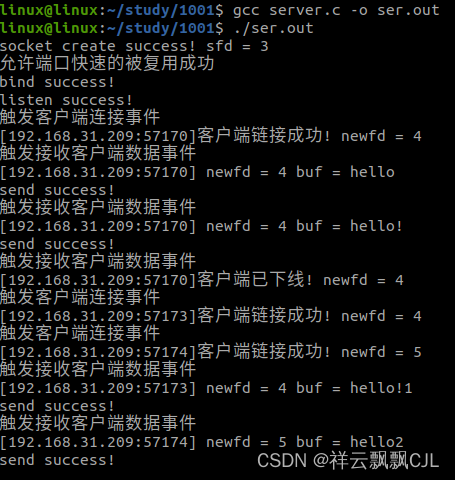
结果

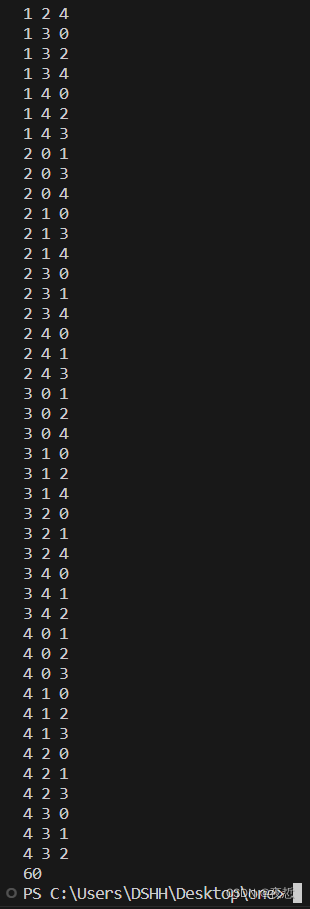
总结
C++代码示例:排列数简单生成工具。
参考资料
- 学校《高级算法设计与分析》课程课件的算法思路
作者的话
- 感谢参考资料的作者/博主
- 作者:夜悊
- 版权所有,转载请注明出处,谢谢~
- 如果文章对你有帮助,请点个赞或加个粉丝吧,你的支持就是作者的动力~
- 文章在描述时有疑惑的地方,请留言,定会一一耐心讨论、解答
- 文章在认识上有错误的地方, 敬请批评指正
- 望读者们都能有所收获





![[管理与领导-108]:IT人看清职场中的隐性规则 - 5 - 你会在不经意间被归属在不同的分类中,一旦分类定型,你就会被打上了某种标签(职场分类方法大全)](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/1c3e04878a8e4576a2bb515607f6fdb9.png)