给你一个下标从 0 开始的二维整数数组 flowers ,其中 flowers[i] = [starti, endi] 表示第 i 朵花的 花期 从 starti 到 endi (都 包含)。同时给你一个下标从 0 开始大小为 n 的整数数组 people ,people[i] 是第 i 个人来看花的时间。
请你返回一个大小为 n 的整数数组 answer ,其中 answer[i]是第 i 个人到达时在花期内花的 数目 。
示例 1:
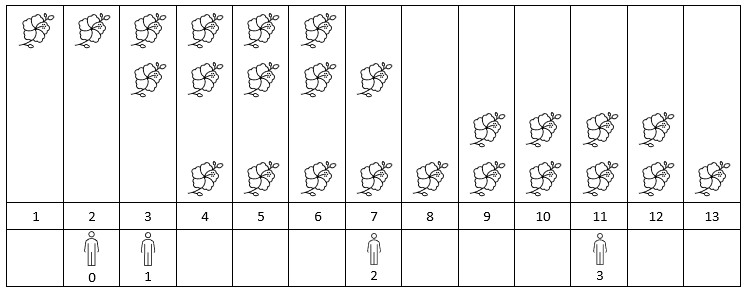
输入:flowers = [[1,6],[3,7],[9,12],[4,13]], people = [2,3,7,11] 输出:[1,2,2,2] 解释:上图展示了每朵花的花期时间,和每个人的到达时间。 对每个人,我们返回他们到达时在花期内花的数目。
示例 2:
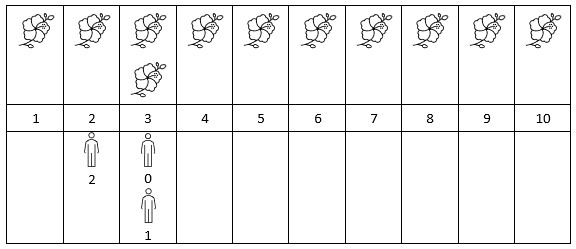
输入:flowers = [[1,10],[3,3]], people = [3,3,2] 输出:[2,2,1] 解释:上图展示了每朵花的花期时间,和每个人的到达时间。 对每个人,我们返回他们到达时在花期内花的数目。
提示:
1 <= flowers.length <= 5 * 104flowers[i].length == 21 <= starti <= endi <= 1091 <= people.length <= 5 * 1041 <= people[i] <= 109
答:
import java.util.Arrays;
public class Solution {
public int[] numFlowersInBloom(int[][] flowers, int[] people) {
Arrays.sort(flowers, (a, b) -> Integer.compare(a[1], b[1])); // 按结束时间排序
int n = people.length;
int[] answer = new int[n];
int ptr = 0; // 指向当前未被看的花期
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
int arriveTime = people[i];
// 找到所有结束时间小于等于arriveTime的花期,并统计花的数量
while (ptr < flowers.length && flowers[ptr][1] <= arriveTime) {
if (flowers[ptr][0] <= arriveTime) { // 花期的开始时间小于等于arriveTime
answer[i]++;
}
ptr++;
}
}
return answer;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Solution solution = new Solution();
int[][] flowers = {{1,6},{3,7},{9,12},{4,13}};
int[] people = {2,3,7,11};
int[] result = solution.numFlowersInBloom(flowers, people);
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(result)); // 输出:[1, 2, 2, 2]
}
}