链表(重点):
链表是物理存储结构上面非连续的存储结构,数据元素的逻辑顺序是通过链表中的引用链接次序实现的
1)在顺序表中,我们不光引入了一段连续的内存,还引入了一块连续的内存空间,叫做usedsize,来表示对应数组中元素的个数,在我们增加和删除元素的时候,都会涉及到一定范围内下标的移动;
2)在我进行扩容的时候,例如说我原来想要进行扩容,以数组的二倍形式来进行扩容,但是我进行而被扩容之后只放了一个元素,扩容的效率就会大大降低,我们想要一种数据结构,再进行插入元素和删除元素的时候,都不要涉及到原来元素的插入和删除,时间复杂度可以达到O(1),节省空间
下面我们主要介绍的是单向,不带头非循环的和双向,不带头,非循环的链表
1)带头:也是有一个head(是一个傀儡节点),head里面的数据是任意的,真正的有效数据放到head.next的下一个节点之后,当我们使用傀儡节点的时候是用头插法,只能插入到傀儡节点和头结点的中间,head的指向是不会发生变化的,这样就可以不用修改头指针了,所以说带头的链表每一次都不用修改头指针,否则不带头的话,头结点会一直发生改变
但是如果不是用带头的傀儡节点,每一次使用头插法的时候,head头节点都会发生变化
2)循环:尾巴节点的next域指向head节点,如果next指向了head.next或者其他节点,就是带有环的链表
3)双向:每一个节点即存放下一个结点的地址,也保存前一个结点地址,还保存数据;
单向带头循环的链表:链表的最后一个节点的next域指向傀儡节点的下一个节点
单向不带头循环的链表:链表的最后一个节点的next域指向第一个节点,也就是head节点
节点:有数据域(主要是进行存放数据)和指针域(存放下一个结点的地址),本质上是一个类;
下面我们来实现一个链表:
1)用一个类来进行描述一个节点,因为链表就是一个一个的节点构成的
2)实现一个链表的类
我们链表的头部节点和尾部节点都是属于链表中的一部分,所以说我们定义的head和tail都是linkedlist中的一个属性
下面的方法:一定要记住,以后做链表的题的时候,一定要先绑定后面
1)头插法
if(this.head==null){ this.head=node; }else{ node.next=this.head; this.head=node; }2)尾插法:有两种写法,是按照存储的顺序来进行存储的
所以说使用尾插法进行插入元素,一定要判断head是否为空 if(head==null){ Node node=new Node(data); head=node; tail=node; return; }else{ Node node=new Node(data); tail.next=node; tail=node; }2.1)尾差的顺序就是按照存储的位置进行存放的
我们进行寻找尾节点的方式,让current指向头结点,不断遍历如果current.next为空,
说明current指向的节点是尾巴结点,我们此时就可以新创建结点进行插入
2.2)如果说此时current为一开始指向的头结点就是空,链表里面一个元素也没有,循环进不去current一直为空,如果说此时你让current.next=node,此时就会发生空指针异常3)求单链表的长度
4)查看某一个关键字key是否在单链表里面
package OperateNode; public class MyLinkedList { public Node head; public Node tail; //遍历整个链表 public void Display(Node head){ Node current=this.head; while(current!=null){ //这里面的条件不能写成current.next!=null,因为这会少打印一个节点.因为current.next为空了 那么就满足循环退出条件,所以说此时就不会进入到循环,因此也就少打印出了一个节点 System.out.println(current.data); current=current.next; } } //查看单链表的长度 public int Size(){ int count=0; Node current=this.head; while(current!=null){ current=current.next; count++; } return count; } //查找是否包含某个关键字Key是否在单链表里面 public boolean contains(int key){ Node current=this.head; while(current!=null){ if(current.data==key){ return true; } current=current.next; } return false; } //继续进行头插法 public void addFrist(int data){ //如果说一个节点也没有,那么就说明head为空 //但是下面的代码已经囊盖了这种情况就不需要进行额外考虑 //head为空的情况了 Node node=new Node(data); node.next=head; head=node; } //继续进行尾插法 public void addLast(int data){//我们在这里面是寻找最后一个节点的位置 Node node=new Node(data); if(head==null){ head=node; }else{ Node current=head; while(current.next!=null){ current=current.next; } //此时的current的next为空,我们在这里面就可以进行设置 current.next=node; } } public static void main(String[] args) { MyLinkedList list=new MyLinkedList(); list.addLast(1); list.addLast(23); list.addLast(98); list.addLast(100); list.addLast(101); list.show(list.head); } }
链表的指定位置插入:给定固定数据和要进行插入的位置进行插入操作,两种写法
1)咱们的这种思想就是说比如说插入到了2号位置,那么就新建一个节点保存要插入的数据,将原有的2号位置的元素以及2号位置之后的元素向后移动
2)所以比如说我们要往4号位置插入,那么就应该先让指针走到1号位置
public void Insert(int pos,int data){//从0好位置元素开始记起 if(pos<0||pos>Size()){ throw new RuntimeException("当前您插入的位置下标不合法"); } Node PreNode=this.head; for(int i=0;i<pos-1;i++){ PreNode=PreNode.next; }//先让他走index-1步,让他找到index节点的前一个节点 Node node=new Node(data); if(head==PreNode){//判断是否是头结点,要进行特殊处理 node.next=head; head=node; }else {//不是头结点 node.next = PreNode.next; PreNode.next = node; } }public void Insert(int pos,int data){//从0好位置元素开始记起 if(pos<0||pos>Size()){ throw new RuntimeException("当前您插入的位置下标不合法"); } //判断是不是在头结点进行插入 if(pos==0) { addFrist(data); return;//在这里面要进行返回操作,不要再让程序进行向下执行 } //判断是否在为节点进行插入 if(pos==Size()){ addLast(data); return; } //代码走到这里面说明已经我们想要进行插入的节点是中间的节点,设置的节点既不是头结点也不是尾结点 Node current=this.head; for(int i=0;i<pos-1;i++){ //这段代码的意思是也就是说这个条件是当current走到了pos-1的位置的时候会进行退出 current=current.next; } Node node=new Node(data); node.next=current.next; current.next=node; }删除第一次出现的指定节点:
public void remove(int key){ if(head==null)//先判断链表里面是否有元素 { throw new RuntimeException("当前您的链表里面没有元素"); } if(head.data==key){ head=head.next;//头结点进行特殊处理 return; } Node PreNode=null; Node current=this.head; while(current!=null){ if(current.data==key){ break; } PreNode=current; current=current.next; } if(current==null){//如果说当前链表没有这个结点,抛出异常 throw new RuntimeException("当前链表里面没有你指定的节点"); } PreNode.next=current.next; }1)先进行判断整个链表是否为空,在进行判断当前删除的元素是否是头结点
2)如果是头结点,删除头结点,否则就进行查找要删除节点的前一个节点
第二种方法:遍历链表一遍,删除所有值为key的结点
public void remove(int key){ if(this.head==null){//先进行判断当前链表中是否有元素 throw new RuntimeException("此处的链表中的元素是空,不能进行删除操作"); } if(head.data==key){//观察头结点是否是删除的节点 head=head.next; return; } Node current=this.head;//我们想要最后删除的节点的前一个结点是current //开始找要被删除节点的前一个节点 while(current.next!=null){//意思是说如果current在循环退出指向的是最后一个节点,那么说明key根本就在链表中不存在 if(current.next.data==key){ break; } current=current.next; } if(current.next==null){ throw new RuntimeException("当前您想要删除的key根本就不在链表里面"); } Node Pre=current; Node Del=current.next; Pre.next=Del.next; }删除一个链表中所有指定为Key的结点:
public void removeAll(int key){ if(head==null){ throw new RuntimeException("当前整个链表里面没有元素"); } Node current=this.head; Node prev=null; while(current!=null){ if(current.data==key){ //首先判断是否是头结点 if(head.data==key){ head=head.next; current=head; }else{ prev.next=current.next; current=prev.next; } }else{ prev=current; current=current.next; } }public void removeAll(int key){ if(head==null){ throw new RuntimeException("当前整个链表里面没有元素"); } Node current=this.head.next; Node prev=this.head; while(current!=null){ if(current.data==key){ prev.next=current.next; current=prev.next; }else{ prev=current; current=current.next; } } if(head.data==key){ this.head=this.head.next; } }清空链表:
1)直接置为空
2)逐步将每一个结点的next置为空
public void clear(){ Node current=null; while(head!=null){ current=head.next; head.next=null; head=current; } head=null; }
1)进行反转单链表
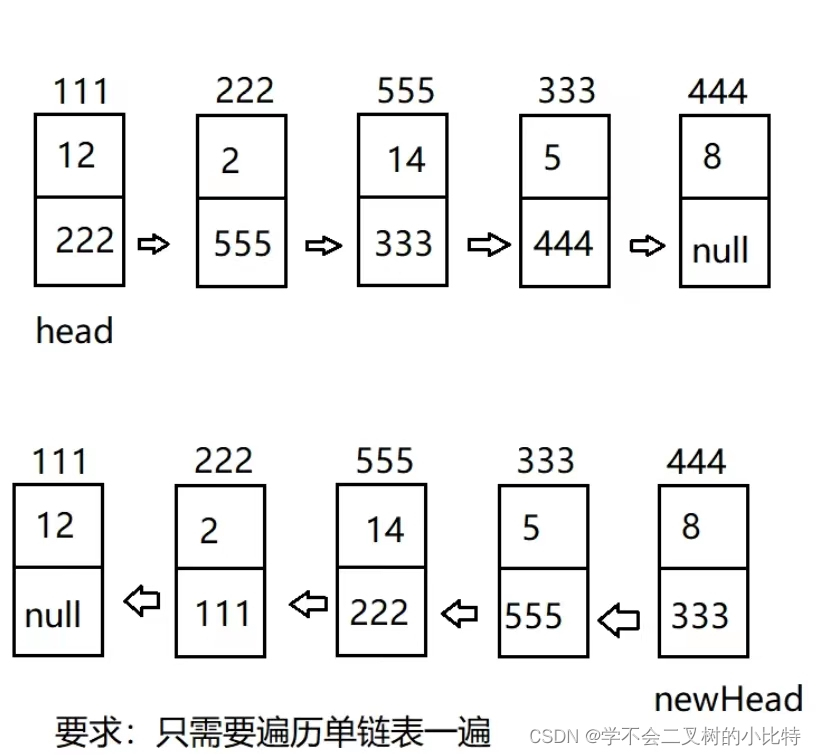
输入:1,2,3,4,5;
输出:5,4,3,2,1;
1)我们先写两个变量,front=head,current=front.next;我们设想一下只用这两个变量是否可以进行反转单链表的操作呢;
我让current.next=front,再让front=current;这是我们就发现current已经无法走到下一个节点了,因为此时current.next已经被修改了,所以我们可以让curNext来进行保存每一次反转操作的current.next的值(这个操作再循环中的第一条语句)
2)循环条件为current.next!=null;
public Node resverse() { if(head==null) { throw new RuntimeException("链表长度为空"); } Node front=null; Node current=head; Node currentNext=head.next; while(current!=null) { currentNext=current.next; current.next=front; front=current; current=currentNext; } return front; }2.只遍历单链表一遍,找出链表的中间节点,如果有两个中间节点,那么返回第二个中间节点
输入:1,2,3,4,5; 返回:3
输入:1,2,3,4,5,6;返回:4;如果一个链表有两个中间节点,那么我们返回第二个节点
思路:进行快慢指针,我们可以定义一个快慢指针,一开始让fast节点和slow节点都指向head,然后我们指向循环,让fast一次走两步,让slow一次走一步;
最终slow就是中间节点
我们可以自己画图演示一下,链表长度为奇数或者链表长度是偶数的截至条件是不一样的
public ListNode middleNode(ListNode head) {
ListNode fast=head;
ListNode slow=head;
while(fast!=null&&fast.next!=null)
{
fast=fast.next.next;
slow=slow.next;
}
return slow;
3.找出链表中的倒数第K个节点,能不能遍历单链表一遍
要找到倒数第K个,要从前向后走len-k步(至少要遍历两遍,因为首先要知道链表的长度);
1)我们进行定义两个快慢指针,fast为快指针,slow是慢指针,我们先让fast走k-1步,然后再让fast和slow同时走;等到fast.next为空的时候(或者说fast走到最后一个节点),并返回slow节点,这时的slow才为倒数第K个节点;
2)更简单的方法是先求出链表的长度,让current走len-k步
class Solution { public ListNode getKthFromEnd(ListNode head, int k) { if(k<=0||k>size()){//必须加上,否则下面的循环会出现空指针异常 return null; } int count=0; ListNode current=head; while(current!=null){ count++; current=current.next; } current=head; for(int i=0;i<count-k;i++){ current=current.next; } return current; } }
public Node returnLastK(int index) { if(index<0) { throw new UnsupportedOperationException("此时的链表的倒数第K个节点位置不正确"); } if(head==null) { throw new UnsupportedOperationException("此时链表长度是空"); } Node fast=head; Node slow=head; for(int i=0;i<index-1;i++) { fast=fast.next; if(fast==null) { throw new UnsupportedOperationException("当前你输入的index的值已经超过了链表的长度"); } } while(fast.next!=null) { fast=fast.next; slow=slow.next; } return slow; }
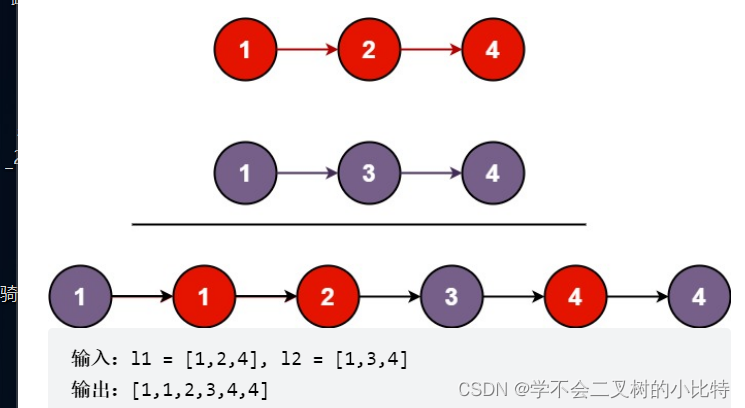
4.合并两个有序链表
思路:
1)我们首先定义一个虚拟节点是newHead作为要合并在一起的总链表的新节点,注意它是一个虚拟节点,里面的值是任意的
2)我们再合并headA和headB这两个链表的时候,保存两个链表的右节点是没有什么用处的,如果发现headA.data>headB.data,我们就把HeadA指向的这个头结点放到先开辟的链表后面,同时让headA进行向后移动
if(headA.data>headB.data)
{
}else if(HeadA.data<HeadB.data){
}else{
}
3)再进行合并的过程中,两个链表所走的过程中都不可以是空的,所以循环条件是HeadA!=null&&HeadB!=null
4)在循环出来之后,会出现一种情况,HeadA过长或者HeadB过长,此时我们还要进行特殊处理
public ListNode mergeTwoLists(ListNode list1, ListNode list2) {
ListNode HeadA=list1;
ListNode HeadB=list2;
ListNode newHead=new ListNode(-1);
ListNode temp=newHead;
while(HeadA!=null&&HeadB!=null)
{
if(HeadA.val<HeadB.val)
{
temp.next=HeadA;
HeadA=HeadA.next;
temp=temp.next;
}else
{
temp.next=HeadB;
HeadB=HeadB.next;
temp=temp.next;
}
}
if(HeadA!=null)
{
temp.next=HeadA;
}
if(HeadB!=null)
{
temp.next=HeadB;
}
return newHead.next;class Solution {
public ListNode mergeTwoLists(ListNode list1, ListNode list2) {
ListNode head1=list1;
ListNode head2=list2;
ListNode NewHead=new ListNode(17);
ListNode current=NewHead;
while(head1!=null&&head2!=null){
if(head1.val>=head2.val){
ListNode node=new ListNode(head2.val);
current.next=node;
head2=head2.next;
current=current.next;
}else{
ListNode node=new ListNode(head1.val);
current.next=node;
head1=head1.next;
current=current.next;
}
}
while(head1!=null){
ListNode node=new ListNode(head1.val);
current.next=node;
head1=head1.next;
current=current.next;
}
while(head2!=null){
ListNode node=new ListNode(head2.val);
current.next=node;
head2=head2.next;
current=current.next;
}
return NewHead.next;
}
}