| 作用 | 函数 |
|---|---|
| 不变大小改变shape | view / reshape |
| 删减与增加维度 | squeeze / unsqueeze |
| 维度扩展 | expand / repeat |
| 矩阵转置,单次和多次交换操作 | t / transpose / permute |
1、 view reshape
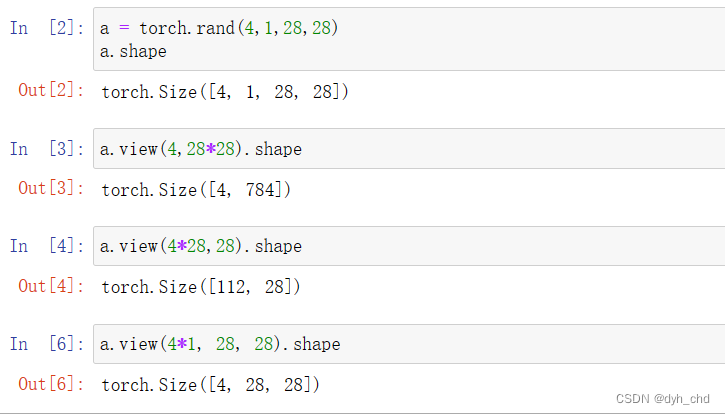
view与reshape效果一致,且可以通用。直接以view为例:
a = torch.rand(4,1,28,28)
a.view(4,28*28)
2、squeeze unsqueeze
① unsqueeze
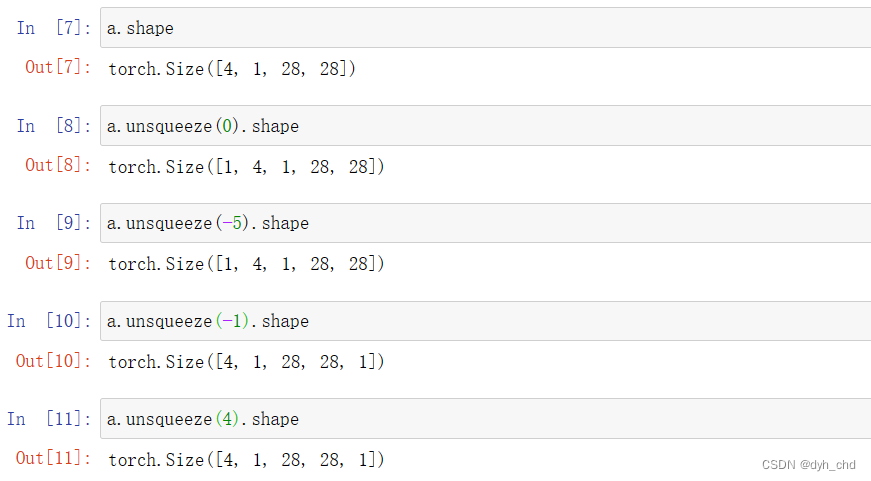
新插入一个维度,这个维度的插入不会改变数据本身。
在a中插入维度指定索引:[-a.dim()-1, a.dim()+1)
a.shape
a.unsqueeze(0).shape
a.unsqueeze(-5).shape
a.unsqueeze(-1).shape
a.unsqueeze(4).shape
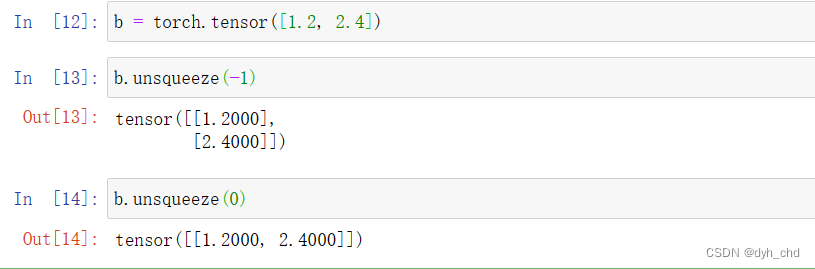
通过简单的数据例子理解增加维度的效果:
b = torch.tensor([1.2, 2.4])
#shape为(1,2)
b.unsqueeze(-1)
#将所有最小维度单位的元素再放入一个小盒子中,并不改变数据本身
b.unsqueeze(0)
#将所有维度数据整体放入一个大袋子中
②squeeze
与unsqueeze相反,挤压掉指定维度
b.squeeze(idx)
b = torch.rand(1, 32, 1, 1)
b.squeeze().shape #将其他维度都是1的给挤压掉
b.squeeze(0).shape
b.squeeze(-1).shape

3、expand repeat

expand与repeat之间,推荐使用expand。
expand改变了我们对数据的理解方式,但没有增加数据,repeat实实在在增加了数据,两种方法最终的效果是等效的,区别在于expand不会主动复制数据,只会在有需要的时候复制。
a = torch.rand(4, 32, 14, 14)
b.shape #(1, 32, 1, 1)
b.expand(4, 32, 14, 14).shape
#只有原维度是1在expand的时候不会报错,这里32不需要expand
b.expand(-1, 32, -1, -1).shape
#-1表示保持原维度大小不变,这里只改变第二维度,从32变为32,相当于没变

# repeat函数中输入的参数不是要变换得到的维度大小,而是copy的次数
b.repeat(4,1,14,14)
第一维度复制4次,三四维度复制14次
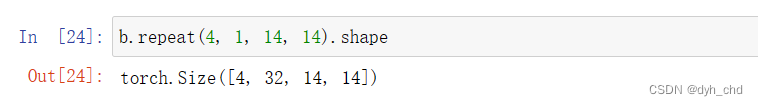
4、t transpose permute
① .t
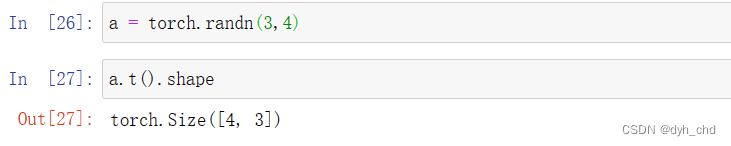
该方法只能适用于2D的tensor,即只能适用于矩阵
a = torch.randn(3, 4)
a.t().shape
② transpose
要人为跟踪好维度顺序
原为 [b, c, h, w] -> 索引1、3维度交换顺序后为 [b, w, h, c]
!要变回原shape,一定要保证w和h的顺序不乱!
a.shape # [4, 3, 32, 32]
a1 = a.transpose(1, 3).contiguous().view(4, 3*32*32).view(4, 3, 32, 32)
# 加入contiguous函数避免数据顺序问题报错
#a1中的 3*32*32,是c*w*h,顺序不对
a2 = a.transpose(1, 3).contiguous.view(4, 3*32*32).view(4,32*32*3).transpose(1,3)
#a2中的32*32*3是w*h*c,此时在1、3交换,就变回原来的a
# 验证a1和a2与a的数据一致性关系
torch.all(torch.eq(a, a1))
torch.all(torch.eq(a, a2))

③ permute
permute使用相对简单且易理解
以dim=4的张量b为例
b = torch.rand(4, 3, 28, 32)
b.permute(0, 2,3, 1)
# [b, c, w, h],只想让c的维度移到后面,图片信息w和h的顺序不变,直接指定索引变换,c对应的维度索引为1,移动到最后。
transpose等效操作:
b.transpose(1,3).transpose(1,2)







![[WUSTCTF2020]颜值成绩查询 布尔注入二分法](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/0592b587c5eb42c2b81108986f6cb789.png)